Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3
Uploaded by
aikubingOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3
Uploaded by
aikubingCopyright:
Available Formats
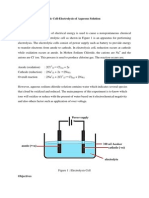
Set 3 8. Write the formula of all ions present in the electrolyte.
Write the formula of ion/ions which is/are attracted to anode and cathode. Which is selectively discharged? Give a reason. Write the half equation to represent the discharge. What will you observe at the electrode? Name the product. State the test to identify the product.
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
Anode Na+ , H+ , NO3- , OHNO3- , OHNa+ , H+
Cathode
OHIts lower than in electrochemical series 4OH- 2H2O + O2 + 4 e Colourless gas evolved / produced / liberated Oxygen gas -Place a glowing splinter inside the test tube filled with collected gas. -The glowing splinter will be rekindle.
H+ Its lower than Na+ in electrochemical series 2H+ + 2e H2 Colourless gas evolved / produced / liberated Hydrogen gas -Place a lighted splinter near the mouth of the test tube filled with collected gas. -A pop sound is heard.
9. Write the formula of all ions present in the electrolyte. Write the formula of ion/ions which is/are attracted to anode and cathode. Which is selectively discharged? Give a reason. Write the half equation to represent the discharge. What will you observe at the electrode? Name the product. 10. Write the formula of all ions present in the electrolyte. Write the formula of ion/ions which is/are attracted to anode and cathode. Which is selectively discharged? Give a reason. Write the half equation to represent the discharge. Anode Cu2+ , H+ , NO3- , OHNO3- , OHCu2+ , H+ Cu2+, Its lower than H+ in electrochemical series. Cu2+ + 2e Cu Cathode Anode K+, H+, OH- , ClOH- , ClClThe concentration of chloride ion, Cl- higher than OH-. 2Cl- Cl2 + 2e Greenish yellow gas produced. Chlorine gas K+, H+ H+ Its lower than Na+ in electrochemical series 2H+ + 2e H2 Colourless gas evolved / produced / liberated Hydrogen gas Cathode
No ions were being discharged, copper metal being ionized. (factor type of electrode) Cu Cu2+ + 2e
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
21
Set 3
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
What will you observe at the electrodes? Name the product. What will you observe to the electrolyte? Explain why?
Copper electrode becomes thinner/ mass decreases. Copper (II) ions
Brown solid formed / mass increases / becomes thicker Copper metal
Blue solution remains. The concentration of Cu2+ in the solution remains, because the rate of formation of Cu2+ at anode same as the rate of discharged of Cu2+ at cathode.
11. Negative terminal Cu2+ , H+, SO42- , OHZinc electrode, zinc is more electropositive than copper / zinc is higher than copper in electrochemical series. Zn Zn2+ + 2e Positive terminal
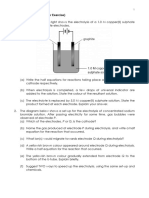
State all ions present in the electrolyte. Identify positive terminal and negative terminal. Explain why? Write half equation at negative terminal. Write the formula of ions which are moved to positive terminal. Which is selectively discharged? Give a reason. Half equation at positive terminal What will you observe at negative and positive terminal? What will you observe to the electrolyte? Explain why? Overall / Full ionic equation 14. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Copper electrode, copper is less electropositive than zinc /copper is lower than zinc in electrochemical series. Cu2+ , H+ Cu2+, Its lower than H+ in electrochemical series. Cu2+ + 2e Cu Brown solid formed / mass increases / becomes thicker The intensity of blue solution decreases / blue turns colourless/ blue becomes paler
Zinc electrode becomes thinner / mass decreases.
Zn + Cu2+ Zn2+ + Cu
Ag Ag+ + e + Ag + e Ag Becomes thinner / mass decreases iron covered by grey and silvery layer / becomes thicker - lower electric current is used - the surface area of the object to be electroplated is cleaned / polished.
PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE 1. (a) X : Cathode, Y : Anode (b) Na+, Cl-, H+, OH(c) (i) Hydrogen (ii) Place a lighted wooden splinter near the mouth of the test tube filled with collected gas. A pop sound is heard. (iii) 2H+ + 2e H2
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
22
Set 3 (d) (i) (ii)
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
(e)
Oxygen Place a glowing wooden splinter inside the test tube filled with collected gas. The glowing splinter will be rekindle. (iii) 4OH- 2H2 O + O2 + 4e The product produced at the anode will be chlorine gas. Because concentration of chloride ion, Cl- is high. Cu2+, SO42-,H+, OH(i) Oxygen (ii) 4OH- 2H2 O + O2 + 4e (i) Copper(II) ion (ii) Cu Cu2+ + 2e (i) (ii) (i) (ii) Decreases Copper(II) ion discharged at the cathode to form copper metal. Thus, concentration of ion decreases. Remains constant The copper(II) ion produce by copper anode is same as the copper(II) ion been discharged at the cathode to form copper metal. Thus, concentration of ion remains constant.
2. (a) (b) (c)
(d)
(e)
3. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
Dilute hydrochloride acid/ Aqueous sodium chloride. Electrode X to electrode Y. Z Z2+ + 2e The further the distance between two metals in the Electrochemical Series, the higher the voltage of the cell. W, Z, X, Y, V (i) Z (ii) Voltage = (1.05 + 0.70 + 0.50)V = 2.25 V (i) W and V (ii) Voltage = (1.55 + 0.70 + 0.50)V = 2.75 V
PAPER 2 : ESSAY 4. (a) (b) Hydrogen gas, 2H+ + 2e H2 Differences Type of electrode Cell Y Positive electrode/anode : Copper Negative electrode/cathode : Copper Electrical energy chemical energy Copper plate dissolves Brown solids deposited Cu Cu2+ + 2e Cu2+ + 2e Cu
Cell X Positive electrode/cathode : Copper Negative electrode/anode : Zinc Chemical energy electrical energy Brown solid deposited Zinc plate dissolves Cu2+ + 2e Cu Zn Zn 2+ + 2e
Change of energy Observation at the positive electrode Observation at the negative electrode Half-equation at the positive electrode Half-equation at the negative electrode
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
23
Set 3 (c)
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
Material : Impure copper plate, pure copper plate, copper(II0 sulphate solution Apparatus : Battery, connecting wires, ammeter, beaker Diagram:
impure copper plate
Pure copper plate copper(II) sulphate solution
Procedure: a. Impure copper plate is used as anode. b. Pure copper late is used as cathode. c. Copper(II) sulphate solution is used as electrolyte. d. The circuit is completed by allowing the electric current to flow through the electrolyte. Observation : Anode : Impure copper plate dissolved/becomes thinner. Cathode : Pure copper plate becomes thicker/ Brown solid deposited. Chemical equations : Anode : Cu Cu2+ + 2e Cathode : Cu2+ + 2e Cu
PAPER 3 : STRUCTURE 5. (a) Metal plate Zinc Iron (b) Type of variables (i) Metal pairs (ii) Voltmeter reading (iii) Zinc electrode Action to be taken use different pairs of metal voltmeter readings which varies use the same zinc electrode Observation Zinc dissolves Brown solid deposited Inference Zinc loses electron to form zinc ion Copper(II) ion receives electrons to form copper metal.
(c) (d) 6. (a) (b)
The further the distance between two metals in the Electrochemical Series, the higher the voltmeter reading. Between 0.4 1.1 V When the concentration of chloride ions is higher, chloride ions will be selectively discharged at the anode. (i) Concentration of hydrochloride acid (ii) Ions discharged at the anode (iii) Type of electrodes, duration of electrolysis
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
24
Set 3 (c)
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
Set 1 ( 0.001 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid ) Anode Cathode Bubbles of colourless gas are released. The gas lighted up a glowing wooden splinter. Bubbles of colourless gas are released. The gas produces pop sound with lighted wooden splinter.
Set 2 ( 1.0 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid ) Greenish-yellow gas is released. It turns blue litmus paper red and then white. Bubbles of colourless gas are released. The gas produces pop sound with lighted wooden splinter.
(d)
Set 1 : 4OH- 2H2O + O2 + 4e Set 2 : 2 Cl- Cl2 + 2e
(e)
Anode
: Bubbles of colourless gas are released. The gas lighted up a glowing wooden splinter. Cathode : Bubbles of colourless gas are released. The gas produces pop sound with a lighted wooden splinter.
PAPER 3 : ESSAY 7. (a) (b) (c) Does concentration of ions affect the product of electrolysis at the anode? The higher the concentration of ions at the anode, the higher its tendency to be discharge. Manipulated variables : concentration of sodium chloride solution Responding variables : product formed at anode Controlled variables : quantity of current, carbon electrodes Materials : 0.0001 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution, 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution. Apparatus : carbon electrode, electrolytic cell, test tubes, dry cell, blue litmus paper, wooden splinter, Bunsen burner. Procedure : 1. Electrolytic cell is filled with 0.0001 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution. 2. The carbon electrodes are connected to the power supply and ammeter. 3. Current is passed through into 0.0001 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution for half hour. 4. The gas collected at the anode is tested with a glowing wooden splinter and a damp blue litmus paper. 5. Experiment is repeated by replacing 0.0001 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution with 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution. Tabulation of data: Solution 0.0001 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution Observation Product formed at anode
(d)
(e)
(f)
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
25
Set 3
Marking Scheme : Electrochemistry
2010
8. Question Number (a) Rubric [ Able to give the aim of the experiment correctly ] Example : To construct the electrochemical series based on the potential differences between metals [ Able to state All variables correctly ] Example : Manipulated variable : Pairs of different metals//Different types of metals Responding variable : Potential differences Constant variable : Concentration of Copper(II) sulphate, positive terminal [ Able to give the hypothesis correctly] Example : The distance between two metals increase/decrease, the potential difference will increase/ decrease [ Able to give the list of the apparatus and materials correctly and completely] Example : List of apparatus and materials Copper strip, lead strip, iron strip, zinc strip, aluminium strip, magnesium strip, copper (II) sulphate solution, sand paper, voltmeter, beaker, connecting wires with crocodile clip [ Able to state all procedures correctly ] Example : 1. Clean the metals with sand paper 2. Fill a beaker with copper(II)sulphate solution 3. Dip/ place/ immerse the magnesium strip and copper strip into the copper(II)sulphate solution 4. Connect the electrodes to voltmeter using connecting wire with crocodile clip. 5.. Complete the circuit//switch-on the circuit 6. Record the potential difference between the metals 7. Determine and record which metal strip is the negative terminal 8. Repeat steps 1 to 6 using other metals to replace magnesium strip [ Able to exhibit the tabulation of data correctly ] Tabulation of data has the following element : 1. 3 columns and 6 rows Example : Pair of metals Potential difference (V) Mg and Cu Al and Cu Zn and Cu Pb and Cu Fe and Cu Score
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
3 Negative terminal
(f)
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 3
26
You might also like
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument10 pagesExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionimizzNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis reactions and observationsDocument35 pagesElectrolysis reactions and observationsBOOKwormNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Ions, Cells and ReactionsDocument62 pagesElectrochemistry: Ions, Cells and Reactionshanifzainol100% (1)
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument8 pagesExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionNad Sng90% (21)
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - 555Document9 pagesLab 2 - 555Nurzawanah AkmarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Electrolytic Cell Nurul Husna Binti IbrahimDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 Electrolytic Cell Nurul Husna Binti IbrahimNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis HLDocument34 pagesElectrolysis HLRyan BoukaaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesDocument20 pagesElectricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis key-H.w(4)-Ionic compoundsDocument4 pagesElectrolysis key-H.w(4)-Ionic compoundsbedo lucyNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi ElektrolisisDocument35 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi ElektrolisisAmir Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (34)
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- Peka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesPeka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryWong Wai Lun75% (8)
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6Elynn TanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistrysinghkhoosbu6No ratings yet
- H.W (4) - Electrolysis of Aqueous Solution of Ionic Compounds-G9 PDFDocument4 pagesH.W (4) - Electrolysis of Aqueous Solution of Ionic Compounds-G9 PDFbedo lucyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Lab Results SummaryDocument4 pagesElectrolysis Lab Results SummaryCornelius PaunNo ratings yet
- Problems Solved in 25 MinutesDocument11 pagesProblems Solved in 25 MinutesorlandompsilvaNo ratings yet
- Electrol Yte Ion Present Anod e Catho de Not E: Easy To Discharge (More Electronegativity) Easy To DischargeDocument4 pagesElectrol Yte Ion Present Anod e Catho de Not E: Easy To Discharge (More Electronegativity) Easy To DischargeMohamad Fazdir SallehNo ratings yet
- FORM 4 Chemistry Lesson 23 ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesFORM 4 Chemistry Lesson 23 ElectrochemistrySiang DanielNo ratings yet
- Presentation KPTDocument79 pagesPresentation KPTNor Fatihah Ab Malek100% (1)
- ELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN SALTDocument33 pagesELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN SALTTom TommmaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesElectrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- NEW ELECTROLYSIS 1Document18 pagesNEW ELECTROLYSIS 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron ArrangementDocument3 pagesHydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron Arrangementcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesElectrochemistryShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis WorksheetDocument5 pagesElectrolysis WorksheetnataliihamadeeNo ratings yet
- Mypchem Ch10answersDocument3 pagesMypchem Ch10answersPikunoShuousNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 NotesDocument18 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesElectrolysisMahmudul Hassan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991No ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellsDocument32 pagesElectrolytic CellsHendi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document11 pagesChapter 4J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Text 2didididDocument3 pagesText 2didididhussainshakeel.mzNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: How Electrical Energy Converts to Chemical EnergyDocument2 pagesElectrolysis: How Electrical Energy Converts to Chemical EnergySunnyNo ratings yet
- 4.2 ElectrolysisDocument5 pages4.2 Electrolysis211273wNo ratings yet
- IB CHEM HL Oxidation and Reduction Note CardsDocument9 pagesIB CHEM HL Oxidation and Reduction Note Cards陳定均No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Redox ReactionsDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Redox Reactionsapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Electroplating: M6 Section-6 Group-ADocument25 pagesElectroplating: M6 Section-6 Group-AMunib KhanNo ratings yet
- CHEM SS2 NoteDocument6 pagesCHEM SS2 NoteEli yunanaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAyush RorNo ratings yet
- Revision -2- on ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesRevision -2- on ElectrochemistryKiro RemonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of molten lead bromideDocument38 pagesElectrolysis of molten lead bromidehemanth PNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument10 pagesElectrochemistrySsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 ElctrochemistryDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 6 ElctrochemistryMohd Nazri Mat JaridNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Scientific Comment: July 20, 1992 Accepted in Revised Form March 11, 1993)Document6 pagesScientific Comment: July 20, 1992 Accepted in Revised Form March 11, 1993)Mismel Ruiz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ial WCH05 01 Nov19 PDFDocument28 pagesIal WCH05 01 Nov19 PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Standard Classification Materials DimensionsDocument3 pagesStandard Classification Materials DimensionsamoldholeNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Test Ethene Gas from EthanolDocument6 pagesPrepare and Test Ethene Gas from EthanolanockNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Treatment of Melts With Charge Weights Up To 30 Tons: Vacuum Induction Degassing VID 400 - VID 3000Document8 pagesVacuum Treatment of Melts With Charge Weights Up To 30 Tons: Vacuum Induction Degassing VID 400 - VID 3000sureshkumar908No ratings yet
- Sample Paper T-2, XI-Chem, 2021-22Document3 pagesSample Paper T-2, XI-Chem, 2021-22SushantNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Phenol Over Mixed (Al-Cu)-Pillared ClaysDocument6 pagesCatalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Phenol Over Mixed (Al-Cu)-Pillared ClayssquivviaNo ratings yet
- Vanadium Lab Report (TeoZhiYuan)Document7 pagesVanadium Lab Report (TeoZhiYuan)Nor Ashikin Ismail50% (6)
- SALT ANALYSIS - Chemistry Practical XII PDFDocument12 pagesSALT ANALYSIS - Chemistry Practical XII PDFDr. Md. Tanweer Alam80% (5)
- ZGCE O-Level Chemistry Exam SyllabusDocument34 pagesZGCE O-Level Chemistry Exam SyllabusCollins JimNo ratings yet
- ALS Environmental Australia Sample Collection Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesALS Environmental Australia Sample Collection Pocket GuideSagar A ShahNo ratings yet
- 1001ch PDocument41 pages1001ch P50calpotatoNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Properties, Examples and UsesDocument16 pagesAcids and Bases: Properties, Examples and UsesAbc Abc100% (1)
- AISECT TUTORIALS: CHEMISTRY OF METALLURGICAL OPERATIONSDocument38 pagesAISECT TUTORIALS: CHEMISTRY OF METALLURGICAL OPERATIONSALI HADIRNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations S ChandDocument2 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations S ChandNishtha poptani100% (1)
- Welding RodDocument368 pagesWelding Rodjrod91586% (29)
- Ionisation Energies and Electronic StructureDocument6 pagesIonisation Energies and Electronic StructureApar100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsSachi Srivastava ; 51 ; 5724No ratings yet
- Electrochemical Reduction/Oxidation in The Treatment of Heavy Metal WastewaterDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Reduction/Oxidation in The Treatment of Heavy Metal WastewaterSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- Ebay Gold RecoveryDocument11 pagesEbay Gold RecoveryAFLAC ............90% (10)
- Potassium Hydroxide - Wikipedia PDFDocument42 pagesPotassium Hydroxide - Wikipedia PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS) As A Concrete AdditiveDocument135 pagesGround Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS) As A Concrete AdditiveE Hammam El Missiry100% (1)
- Jeff Prager - 911 Dust (2011)Document26 pagesJeff Prager - 911 Dust (2011)messiahgov4824100% (3)
- Exam VedaDocument13 pagesExam VedaLoganathan NNo ratings yet
- Cocaine SynthDocument4 pagesCocaine Synthjoepoker3785100% (2)
- Summative Test Q2 Si 9 10 ItemsDocument3 pagesSummative Test Q2 Si 9 10 ItemsorculloNo ratings yet
- Bleach Storage Guidelines For End UsersDocument2 pagesBleach Storage Guidelines For End UsersNilson BispoNo ratings yet
- SL Topic 2: Atomic Structure: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDocument8 pagesSL Topic 2: Atomic Structure: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingCarlos Moreno BorralloNo ratings yet
- Ford f150 2015 Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocument22 pagesFord f150 2015 Electrical Wiring Diagramsshaunthomas011196cbg100% (69)
- Harit Sanjivani - Training PresentationDocument25 pagesHarit Sanjivani - Training PresentationSamir K Mishra100% (4)