Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Structure
Uploaded by
erincole0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesA root anchors a vascular plant, absorbs minerals and water, and stores organic nutrients. A stem is an organ consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes nodes are the points at which leaves are attached internodes are the stem segments between nodes leaves have veins, which is vascular tissue of the leaves.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA root anchors a vascular plant, absorbs minerals and water, and stores organic nutrients. A stem is an organ consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes nodes are the points at which leaves are attached internodes are the stem segments between nodes leaves have veins, which is vascular tissue of the leaves.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesPlant Structure
Uploaded by
erincoleA root anchors a vascular plant, absorbs minerals and water, and stores organic nutrients. A stem is an organ consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes nodes are the points at which leaves are attached internodes are the stem segments between nodes leaves have veins, which is vascular tissue of the leaves.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Plant Structure
Period 6
The Basics
The is a hierarchy in a plant body goes like this.
Cells Tissues Organs
There are three basic plant organs Roots Stems Leaves
Plants must absorb water and minerals below ground and sunlight and CO2 from above ground
In order to do this, plants have a root and shoot system
Get back to your Roots!
A root is an organ that anchors a vascular plant, absorbs minerals and water, and stores organic nutrients There are three types of roots in plants Taproot system- it consists of one main vertical which branches out into lateral roots Vascular plants Example- Carrots and dandelions Fibrous root system- a mat of smaller/thin roots that spread out below the soil; there is no main root Seedless vascular plants Example- Grasses Adventitious root system- roots arising from the stem Seedless vascular plant Example- Palms and bamboo
Stems
A stem is an organ
consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes
Nodes are the points at
which leaves are attached
Internodes are the stem
segments between the nodes
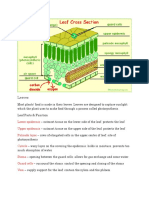
Leaves
The leafs main job is photosynthesis in vascular plants Leaves generally consist of a flattened blade and a stalk, the petiole The petiole joins the leaf to a node on the stem Leaves have veins, which is the vascular tissue of the leaves Some plants have leaves that have adapted different functions, such as support, protection, storage, or reproduction
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Behavior Management Plan High School Biology: Statement of PurposeDocument3 pagesBehavior Management Plan High School Biology: Statement of PurposeerincoleNo ratings yet
- Crop 1Document6 pagesCrop 1Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Plant and Animal ClassificationDocument11 pagesDr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Plant and Animal ClassificationHarshaWakodkar100% (1)
- BoooplDocument2 pagesBoooplChristian Josh DinoyNo ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Plant OrgansDocument76 pagesChapter Four Plant OrgansASHFAQ AHMADNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant Parts ExplainedDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant Parts ExplainedAndrea ValiaoNo ratings yet
- First Look Background InformationDocument6 pagesFirst Look Background Informationahuddle1No ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- LEAVESDocument9 pagesLEAVESAbdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagesPlant Structure and FunctionVonetta GrantNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Plants and Animal CellDocument3 pagesParts and Function of Plants and Animal CellPrince AbraganNo ratings yet
- Parts of Plant and Their FunctionsDocument23 pagesParts of Plant and Their Functionssarahbaharudin85No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Document66 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Magy Tabisaura GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Body Structure: Roots and ShootsDocument2 pagesPlant Body Structure: Roots and ShootsdenzelsantosNo ratings yet
- PLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesPLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionNis DancelNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7 - Learn CBSEDocument1 pageGetting To Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7 - Learn CBSEAaditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledDocument44 pagesAn Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- Network Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafDocument5 pagesNetwork Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafMarwana SuaibNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Plant and Their FunctionsDocument15 pagesParts of The Plant and Their FunctionsDiane MaryNo ratings yet
- LeafanatomyDocument18 pagesLeafanatomyTeach FrezNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesLesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203Document76 pagesChapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203chelseapujeda4No ratings yet
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomDocument4 pages1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Structure and FunctionsahiNo ratings yet
- Sporophyte Seed Germination Radicle Hypocotyl Cotyledons Flowering Plants Monocotyledons Dicotyledons Gymnosperms Pine AcotyledonsDocument2 pagesSporophyte Seed Germination Radicle Hypocotyl Cotyledons Flowering Plants Monocotyledons Dicotyledons Gymnosperms Pine AcotyledonsRonaldoNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument21 pagesPlant PhysiologyPANSARILI KONo ratings yet
- PLANTS: KEY ANATOMY AND REPRODUCTIONDocument20 pagesPLANTS: KEY ANATOMY AND REPRODUCTIONMarie Angelie AcapNo ratings yet
- Plant Structures: Leaves: CMG Gardennotes #134Document7 pagesPlant Structures: Leaves: CMG Gardennotes #134Megan GordonNo ratings yet
- Botany LeavesDocument27 pagesBotany Leavesartadiel28No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and MorphologyDocument85 pagesPlant Anatomy and MorphologyHarinder Kaur100% (1)
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument6 pagesGetting To Know Plantsamp1279No ratings yet
- Roots-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesRoots-WPS OfficeAlmaNo ratings yet
- LeafDocument50 pagesLeafJawher AliNo ratings yet
- Tissues System of The Plant BodyDocument47 pagesTissues System of The Plant BodyJana Natassia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function ExplainedDocument10 pagesPlant Structure and Function ExplainedsehvastianNo ratings yet
- Section B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesSection B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II NotesDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY II NotesDarwin SawalNo ratings yet
- CL 6 CH 7 Science NotesDocument5 pagesCL 6 CH 7 Science NotesSantosh Kumar VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Structure of PlantsDocument17 pagesStructure of PlantsJillian Lao100% (5)
- How Plants Adapt to Life on LandDocument6 pagesHow Plants Adapt to Life on LandLuis Ureña HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Functions: By: Alisa Kowalski Jessi Spry Alyson WilsonDocument26 pagesPlant Parts and Functions: By: Alisa Kowalski Jessi Spry Alyson WilsonAlfie BurbosNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy: Plant Body Organization Short Note.: by @tamiyaDocument25 pagesPlant Anatomy: Plant Body Organization Short Note.: by @tamiyaTeamireab DestaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheDocument3 pagesLeaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheANo ratings yet
- Biology - Leaf ChapterDocument4 pagesBiology - Leaf ChapterWriddhi MononNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs - 14 WeekDocument22 pagesPlant Organs - 14 WeekKUTAY ÖZELNo ratings yet
- Plant Task 1 &2 FADocument8 pagesPlant Task 1 &2 FACornelius Olsa OlberntNo ratings yet
- Primary Plant Body Brainiac ?Document6 pagesPrimary Plant Body Brainiac ?davidoluwadimu28No ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Their FunctionsDocument8 pagesPlant Parts and Their FunctionsReanna Mae A. BaganiNo ratings yet
- Botany-Plant Morphology-Anatomy-PhysiologyDocument89 pagesBotany-Plant Morphology-Anatomy-PhysiologyNehaNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- Roots & StemsDocument12 pagesRoots & StemserincoleNo ratings yet
- Modified Plant OrgansDocument7 pagesModified Plant OrgansEllaine Kate RoquenNo ratings yet
- Basic BotanyDocument47 pagesBasic Botanyartadiel28No ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- Main Function of LeavesDocument3 pagesMain Function of LeavesAndrea AnoverNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Plant ScienceDocument8 pagesBiology Notes - Plant Sciencesarah_beck100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsYashiNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just Something Santa Leaves in Your StockingDocument9 pagesIt's Not Just Something Santa Leaves in Your StockingerincoleNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument10 pagesGeothermal EnergyerincoleNo ratings yet
- Intro To Alternative EnergyDocument6 pagesIntro To Alternative EnergyerincoleNo ratings yet
- Diversity StatementDocument1 pageDiversity StatementerincoleNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeerincoleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Botany: Exploratory Science-Period 6Document6 pagesIntroduction To Botany: Exploratory Science-Period 6erincoleNo ratings yet
- Roots & StemsDocument12 pagesRoots & StemserincoleNo ratings yet
- HW Handout1Document3 pagesHW Handout1erincoleNo ratings yet
- Philosophy StatementDocument1 pagePhilosophy StatementerincoleNo ratings yet
- Candy UnitDocument2 pagesCandy UniterincoleNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere of Different WorldsDocument2 pagesAtmosphere of Different WorldserincoleNo ratings yet
- Life Around Rain ShadowDocument6 pagesLife Around Rain ShadowerincoleNo ratings yet
- Life ProjectDocument1 pageLife ProjecterincoleNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life Debate PrepDocument6 pagesOrigin of Life Debate PrepmarisakendallNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life-Reading GuideDocument4 pagesOrigin of Life-Reading GuidemarisakendallNo ratings yet
- Semester ProjectDocument3 pagesSemester ProjecterincoleNo ratings yet
- Semester ProjectDocument3 pagesSemester ProjecterincoleNo ratings yet