Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Analysis of GSK Consumer Healthcare
Uploaded by
adnan424Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial Analysis of GSK Consumer Healthcare
Uploaded by
adnan424Copyright:
Available Formats
A REPORT ON RATIO ANALYSIS OF GLAXOSMITHKLINE
COURSE: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS FINANCE TEACHER: SIR MIRZA SIKANDER TAJ PREPARED BY: SYED ADNAN SHAH SALEEM REG # 53128
[GSK PHARMACEUTICALS]
Financial Management
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
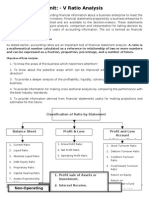
FINANCIAL RATIOS
LIQUIDITY RATIO:
Liquidity ratios are calculated to measure the short term financial soundness of the business. The ratios assess the capacity of the company to repay its short term liability. Banks and other money lenders for short period are interested in the current assets of the company i.e. short term financial position of the business. The important liquidity ratios are: current ratio, acid-test ratio and cash ratio.
1. CURRENT RATIO: This is a popular ratio which expresses the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. The current ratio is a popular ratio, and it can be expressed as Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities Current assets include cash, current investments, debtors, inventories, loans and advances and prepaid expenses. Current Liabilities represent liabilities that are expected to mature in the next twelve months. These comprise (1) loans, secured or unsecured, that are due in the next twelve months and (2) current liabilities and provisions.
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
2011
(In Cr.)
932.92 810.46
2010
(In Cr.)
771.90 682.68
2009
(In Cr.)
808.84 589.91
2008
(In Cr.)
864.78 610.84
2007
(In Cr.)
755.42 569.97
Total Current Assets (A) Total Current Liabilities (B) Current Ratio (A/B)
1.15
1.13
1.37
1.42
1.33
Analysis: The current ratio of the company is currently at 1.15 which is a good sign; it implies that for every one rupee of liabilities the firm has Rs. 1.15 assets. But the share of inventories is 18.8 % of the total current assets in 2010, lower than the previous year which was at 16.2 % and the cause for current ratio to drop from 1.37 (2009) to 1.13 (2010) is the increase in current liabilities.
2. QUICK RATIO: Quick ratio is also known as Acid Test Ratio Historically this ratio is regarded as a good indicator of liquidity. Quick Ratio refers to those current assets which can be converted into cash quickly. They include all Current assets except inventories or stock which are not sufficiently liquid. Quick ratio = Quick Assets/ Current Liabilities Or Quick ratio = Current assets (Inventory) / Current Liabilities
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
2011 Total Current Assets Inventories CA Inventories (A) Total Current Liabilities (B) Quick Ratio (A/B)
932.92 194.82
2010
771.90 145.57
2009
808.84 131.04
2008
864.78 85.17
2007
755.42 92.33
738.10
810.46
626.33
682.68
677.80
589.91
779.61
610.84
663.09
569.97
0.91
0.92
1.15
1.28
1.16
Analysis: The acid test ratio is ideally 1:1 or better i.e. the ratio should be greater than or equal to one. But since the current ratio industrial average is less than 1, therefore the industrial quick ratio average is estimated to be below 1. Hence a quick ratio of the company is quite good indicating a healthy liquidity position of the company.
TURNOVER RATIOS:
Turnover ratios are referred to as activity ratios or asset management ratios, measures how efficiently the assets are employed by a firm. These ratios are based on the relationship between the level of activity, represented by sales or cost of goods sold, and various levels of assets. The important turnover ratios are: inventory turnover, average collection period, receivables turnover, fixed assets turnover, and total assets turnover.
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
1. INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO: The inventory turnover, or stock turnover, measures how fast the inventory is moving through the firm and generating sales. It is defined as:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = COGS / Average Inventory
The inventory turnover reflects the efficiency of inventory management. The higher the ratio, the more efficient the management of inventories and vice versa. However, this may not always be true. A high inventory turnover may be caused by a low level of inventory which may result in frequent stock outs and loss of sales and customer goodwill. 2011 Net Sales Gross Profit COGS (A) Inventory Average Inventory (B) Inventory Turnover Ratio (A/B) 1273 520 753 194.8 170.2 4.42 2010 1109 473 636 145.6 138.32 4.59 2009 965 388 577 131.04 108.1 5.33 2008 861 350 512 85.17 88.8 5.76 2011 780 311 485 92.33 89.1 5.45
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Analysis: The Inventory Turnover Ratio has not improved from the previous year indicating that the company has increased its blocked inventory. The average inventories in 2011 have increased by 23.15% from 2010 and by 27.9% from the previous year but the Cost of Goods Sold has grown at 18.3% this year. This ratio has been steadily coming down over the past 5 years indicating a stable efficient management. A low ratio implies either low sales or an increase in inventory. For the company this ratio has decreased due to increase in inventory.
2. FIXED ASSET TURNOVER RATIO: Fixed Assets are used in the business for producing goods to be sold. The effective utilization of Fixed Assets will result in increased production and reduced cost. It also ensures whether the investment in the assets have been judicious or not. Higher ratio indicates better performance. The ratio is very significant for manufacturing enterprises, where fixed assets employed are more than working capital.
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio = Net Sales/ Fixed Assets
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
2011 Net Sales (A) Net Block (Fixed Assets) (B) Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio (A/B) 1273 226 5.63
2010 1109 251 4.41
2009 965 272.9 3.53
2008 861 300.1 2.86
2011 780 323.5 2.41
Analysis: An ideal Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio for any company is 5:1. GSK-CH has maintained this ratio well above the ideal value indicating that it generates Rs. 5.63 from every 1 Re of its fixed assets. It could be due to the depreciation charged on the gross block, due to which the net block is a lower value which in turn increases this ratio. This ratio shows an upward moving trend on analysis.
3. DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO: Debtor turnover ratio indicates the number of times the debtors are turned during the year. This ratio is calculated with the Net sales over the Average debtor. Debtor turnover ratio indicates the number of times the debts are collected in a year.
Debtor turnover Ratio = Net sales / Average Debtors
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
2011 Net Sales (A) Sundry Debtors Average Sundry Debtors (B) Debtors Turnover Ratio (A/B) 1273 27.3 27.7 45.9
2010 1109 28.1 26.1 42.5
2009 965 24.1 24.6 39.2
2008 861 25.2 21.75 39.5
2011 780 18.3 31.3 24.9
Analysis: The DTR ratio for GSK has increased from the previous years indicating that its ability to turn debtors to cash has increased and has maintained similar rates over the years. This ratio is very close to the industrial average.
4. AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD (ACP): The average collection period represents the number of days worth of credit sales that is locked in sundry debtors. Shorter the average collection period the better is the ratio and higher is the liquidity.
Average Collection Period = 365/Debtors Turnover Or Average Collection Period= Average Sundry Debtors / Average daily credit sales
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
2011 Average Collection Period 8
2010 9
2009 9
2008 9
2011 15
Analysis: Since GSK has a high DTR its Average Collection Period is lower i.e. it has reduced the time for which credit sales is outstanding. This ratio gives a positive indication about the company revenue collections. ACP decreased from 15days in 2011 to 9 days in 2008 and had been the same for some years and decreased further to 8.The Company is quite healthy.
5. TOTAL ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO (TATR): The ratio establishes the relationship between net sales and total assets of the firm. It shows in what proportion the total assets of the firm have contributed to the sales.
Total Assets Turnover Ratio = Net Sales / Average Total Assets
2011 Net Sales (A) Total Assets Average Total Assets (B) T.A.T.R (A/B) 1273 646.3 594.5 2.14
2010 1109 542.7 508.9 2.17
2009 965 475.1 502.2 1.92
2008 861 529.3 510.7 1.68
2011 780 492.1 487.6 1.59
Amrita School of Business
10
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Analysis: A TATR of 2.14 indicates that the company can generate net sales 2.14 times its total asset value, i.e. for every one rupee of total assets the company generates Rs.2.14. The company had shown a steady increase in the ratio for the last five years.
PROFITABILITY RATIO:
Profitability reflects the final results of business operations. Profitability ratios are the ratios which measure the profitability of a concern. In other words, they are the ratios which reveal the total effect of the business transactions on the profit position of an enterprise and indicate how far the enterprise has been successful in its aim and how far it has achieved its objectives. There are two types of profitability ratios: profit margin ratios and rate of return ratios. Profit margin ratios show the relationship between profit and sales. The most popular profit margin ratios are: Gross Profit Margin, Operating Profit Margin and Net Profit margin. Rate of return ratios reflect the relationships between profit and investment. The most popular rate of return measures are: Return on Assets, Earning Power, Return on Capital Employed and Return on Equity.
1. GROSS PROFIT MARGIN (GPM): It shows the relationship between the gross profit and sales. This ratio shows the margin of profits on sales. This ratio measures the efficiency of production and pricing. This ratio indicates the margin left after meeting manufacturing costs.
Amrita School of Business 11
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Net sales) * 100
2011 Gross Profit (A) Net Sales (B) G.P.M (A/B) 520 1273 40.84%
2010 473 1109 42.65%
2009 388 965 40.20%
2008 350 862 40.6%
2011 311 796 39.07%
Analysis: A GPM of 40.84% indicates that the company has 40.84% of sales remaining after meeting its operating costs. This ratio is showed a decline in the present year 07 from 42% in the previous year. The decline of GPM in FY07 can be attributed to the increase in cost of raw materials without an equally significant increase in net sales. However the company has worked hard to maintain its margin at around 40% for the last few years which is really good sign.
2. NET PROFIT MARGIN (NPM): The ratio establishes relationship between net profit and net sales. Net profit or the Net income is the gross profit less selling, distribution and financial expenses. This ratio indicates earnings left for preference and equity shareholders as a percentage of net sales. It measures the overall efficiency of production, administration, financing, pricing and tax management.
Amrita School of Business
12
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Net Sales) * 100
2011 Reported Net Profit (PAT) (A) Net Sales (B) N.P.M (A/B) 163 1273 12.80%
2010 127 1109 11.45%
2009 107 965 11.08%
2008 73 862 8.47%
2011 76 796 9.55%
Analysis: The NPM has increased from FY03 to FY07 except for the FY04. A NPM of 12.8% indicates that the company has 12.8% of its net sales revenue remaining for its owners. Higher the ratio indicates greater utilization of its resources and better returns to its owners.
3. RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED (ROCE): This is one of the most important ratios for the measure of overall profitability. It indicates the relationship of net profit with capital employed in the business. Here for calculating return on investment will mean the net profit before interest, tax and dividend.Net profit means net profit of the year excluding undivided profit and reserves. ROCE is post-tax version of earning power. It considers the effect of taxation, but not the capital structure. It is internally consistent. Its merit is that it is defined in such a way that it can be compared directly with the post-tax weighted average cost of capital of the firm.
Amrita School of Business
13
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
ROCE = (PBIT (1-T) / Average Total Assets) * 100
2011 Tax PBT (1) Interest (2) PBIT (1+2) PBIT(1-T) (A) Average Total Assets (B) ROCE (A/B) 84 245 5 250 165 595 27.73%
2010 62 191 4 195 129 509 25.34%
2009 55 162 4 166 110 502 21.91%
2008 39 116 5 121 80 511 15.66%
2011 31 100 5 105 69 488 14.13%
Analysis: The ROCE of the company increased to 27.73% from the previous years value of 25.34%. This ratio indicates that the company made a return of 27.73% with the capital it has employed. A higher value is a good indication for the company.
4. RETURN ON EQUITY (ROE): This ratio measures the profitability of the capital invested in the business by equity shareholders. As the business is conducted with a view to earn profit, return on equity capital measures the business success and managerial efficiency. This ratio is also called the return on net worth .It measures the productivity of risk capital.
Amrita School of Business 14
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Return on Equity = Equity Earnings / Average Net Worth
2011 Equity Earnings (PAT) (A) Total Shareholders Funds (B) Return on Equity (A/B) 162.68 646.35 27.3%
2010 126.93 542.72 23.38%
2009 107.15 475.11 22.55%
2008 73.16 529.35 13.82%
2011 76.35 492.11 15.51%
Analysis: This ratio indicates the company has made a profit of 25.16% from the equity earnings invested in the firm. The ROE fell by about 10.8% in FY04 due reduction in net profits and an increase in shareholders funds. The decrease during FY04 was followed by increase in ROE in the next three years. The increase in ROE was due to increased gross profits. Since the equity returns have increased it is good from the shareholders point of view.
5. Return on Investment (ROI): This ratio show the return on the investment made in the company. Every Investor would like to have a higher return on the investment made in the company. It is also called as earning power. Earning power is a measure of business performance which is not affected by interest charges and tax burden. It abstracts away the effect of capital structure and tax factor and
Amrita School of Business
15
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
focuses on operating performance. It is eminently suited for inter-firm comparison. It is internally consistent.
ROI = (PBIT / Average Total Assets) *100
2011 PBT (1) Interest (2) PBIT (1+2) (A) Average Total Assets (B) ROI (A/B) 245 5 250 594.5 42%
2010 191 4 195 508.9 38.3%
2009 162 4 166 502.2 33.1%
2008 116 5 121 510.7 23.7%
2011 100 5 105 487.6 21.5%
Analysis: This ratio indicates that the company has made a profit of 42% on the total investments. This ratio has not been stable over the past five years. This fluctuation was due the disparity in the changes of raw materials, sales and acquisition of assets. However the matter of paramount importance is that there is increase in ROI steadily.
6. Return on Assets (ROA): This ratio measures the efficiency of capital employed. Both the numerator and denominator are internally inconsistent.
Amrita School of Business
16
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Return on Assets=Net Profit after Tax/Average Total Assets
2011 PAT (A) Average Total Assets (B) Return on Assets (A/B) 162.68 594.5 27.3%
2010 126.93 508.9 24.9%
2009 107.15 502.2 21.3%
2008 73.16 510.7 14.3%
2011 76.35 487.6 15.6%
Analysis: This ratio indicates the company has made a net profit of 27.3% from the total assets it has employed. The higher the value of ROA the better, because the company is earning more money on its assets. The company is showing an increasing trend in ROA which is clearly evident from the table provided above. These are promising signs for the future.
LEVERAGE RATIOS:
Financial leverage refers to the use of debt finance. Leverage ratios help in assessing the risk arising from the use of debt capital. Two types of ratios are commonly used to analyze financial leverage: structural ratios and coverage ratios. Structural ratios are based on the proportions of debt and equity in the financial structure of the firm. The important structural ratios are: debtequity ratio and debt-assets ratio. Coverage ratios show the relationship between debt servicing commitments and the sources for meeting these
Amrita School of Business
17
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
burdens. The most important coverage ratios are: interest coverage ratio fixed charges coverage ratio and debt service coverage ratio. 1. DEBT EQUITY RATIO: This expresses the relationship between debt and equity of the firm. It shows the relative contribution of creditors and owners. The lower the Debt Equity Ratio greater the protection for creditors. This ratio does not reflect the market value of equity or the current value of asset. Debt Equity Ratio= Debt/ Equity
2011 Total Debt Share Capital Reserves Total (A) (a) (b) 0 42 604
2010 0 42 501
2009 0 42 433
2008 0 45.4 483
2011 0 45.4 447
Total Shareholders funds ( a + b ) (B) D/E (A/B) 646 0 543 0 475 0 528.4 0 492.4 0
Analysis: This ratio indicates that the total debt raised by the company is 0. The lower this ratio indicates higher degree of protection by the creditors. This value has remained the same for the previous years indicating a higher level of security for the outsiders of the company. The lower the ratio the better it is for the
Amrita School of Business 18
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
shareholders of the company, this is because a) A higher value would mean higher debt which implies increased interest payments resulting in lower returns and b) The investor would be the last person to receive any money in case the company is liquidated and the higher the debt the lower this amount would be.
2. INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO: It is also called the times interest earned, the ratio is expressed as Interest Coverage Ratio=PBIT/Interest A high interest coverage ratio means that the firm can easily meet its burden even if profit before interest and tax suffer a considerable decline. A low interest coverage ratio may result in financial embarrassment when
earnings before and taxes decline. This ratio is widely used by lenders to assess a firms debt capacity. It is a major determinant of bond rating. This ratio measures the margin of safety with reference to interest payment. 2011 Profit before Tax Interest PBIT (1+2) Interest ICR (B/A) (1) (2) (B) (A) 245 5 250 5 50 2010 191 4 195 4 48.75 2009 162 4 166 4 41.75 2008 116 5 121 5 24.2
19
2011 100 5 105 5 21
Amrita School of Business
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Analysis: The higher the Interest Coverage Ratio the better for the company since it measure the interest paying capacity of the company on its debt. This ratio has gone up for the company during the last five years due to lower or zero total debts (both secured and unsecured loans) and hence no interest payable.
3. Debt Asset Ratio: The ratio measures the extent to which borrowed funds support the firms assets. Lower this ratio lesser is the leverage and lesser is the risk. Debt Ratio= Debt/Assets
2011 Total Debts Total Assets Debt/asset ratio (A) (B) (A/B) 0 1159 0
2010 0 1023 0
2009 0 1082 0
2008 0 1165 0
2011 0 1079 0
Analysis: This ratio shows the relation between total debt and total assets. This ratio also shows the same trend. This is mainly due to no debt raised by the firm.
Amrita School of Business
20
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
VALUATION RATIOS:
Valuation ratios indicate how the equity stock of the company is assessed in the capital market. Since the market value of equity reflects the combined influence of risk and return, valuation ratios are the most comprehensive measures of a firms performance. The important valuation ratios are: priceearnings ratio, EV-EBITDA ratio, and market value to book ratio.
1. Earnings per Share: It helps to determine the market price of the company. A higher EPS indicates that the Market Value of Equity Shares will be higher. E P S = (Net Profit- Preference Dividend)/ Equity Share holders
2011 Reported Net Profit- PAT (A) No of equity shareholders (B) EPS (A/B) 162.68 4.2 38.73
2010 126.93 4.2 30.22
2009 107.15 4.2 25.51
2008 73.16 4.54 16.11
2011 76.35 4.54 16.82
Analysis: The EPS of GSK has gone up due to higher net profits .Net Profits improved by 28.16% in 2011, resulting in a 28.16% increase in EPS. The higher the EPS the better is the companys performance. It is to be noted that the increase in PAT
Amrita School of Business 21
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
and EPS in percentage terms is the same due to zero debt and zero preference dividend.
2. Price-earnings Ratio (P/E ratio): The price-earnings ratio is a summary measure which primarily reflects the following factors: growth prospects, risk characteristics, shareholder
orientation, corporate image and the degree of liquidity. It reflects price per rupee of earning. Higher the ratio higher are the expectation of growth rate, dividend payout etc. P/E Ratio =Market price per share/Earnings per share
2011 MPS EPS P/E Ratio (52 week Average) (B) (A/B) 651.7 38.73 16.83
2010 547 30.22 18.1
2009 445 25.51 17.44
2008 325.6 16.11 20.21
2011 292.83 16.82 17.4
Analysis: The P/E ratio indicates how many years it will take to get back the value invested in one share if the same EPS and MPS are maintained. The P/E ratio of GSK indicates that it will take 16.83 years to get back the money invested. The P/E ratio showed a decline from 2010 to 2011. The P/E has shown a mixed trend from 2011 to 2011 i.e. an intermittent increase and decrease. The P/E
Amrita School of Business 22
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
ratio is as indication of market expectations of the returns. A very high value would imply that the share value is overvalued and possess increased speculation. 3. Market Value to Book Value Ratio: This ratio reflects the contribution of a firm to the wealth of society. Market to Book Value Ratio=Market Value per Share/Book Value per Share
2011 MPS (52 week Average) (B) 651.7 153.67 4.24
2010 547 129.03 4.23
2009 445 112.96 3.94
2008 325.6 116.65 2.79
2011 292.83 108.44 2.7
Book Value
Market to book value (A/B)
Analysis: A Market Value to Book Value Ratio of greater than one indicates that the firm has contributed to the wealth of the society. A ratio of less than 1 indicates that the firm has detracted wealth from the society. GSK has contributed wealth to the society in the past four years. For FY07 this ratio is 4.24 which means that for every Rs. 1 invested by the society the firm has returned Rs 4.24. The MPS is the major influencing factor in determination of this ratio, i.e. the expectations of the market. This ratio indicates by what factor the market expectations exceed the book value of the company. A value of above 1 indicates higher market expectations.
Amrita School of Business 23
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
4. Dividend per Share: This ratio is a better indicator of company' s performance when compared to EPS as it shows what exactly owners are entitled to receive on a per share basis. Dividend per Share = Equity Dividend/ Total Equity Shares 2011 Dividend (A) 50.47 4.2 12.02 2010 42.06 4.2 10.01 2009 33.64 4.2 8.01 2008 31.77 4.54 6.99 2011 31.77 4.54 6.99
No of equity shareholders (B) DPS (A/B)
Analysis: The dividend per share for FY07 is 12.02, which is higher than the previous years value, it indicates that the company has given increased returns to its shareholders, higher the DPS value the better it is for the shareholders. The DPS remained the same in 2011-04 periods and then increased 14.5% to 8.01. Then it increased by 20.07% in the current year. 5. Dividend Yield: A financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. In the absence of any capital gains, the dividend yield is the return on investment for a stock. Dividend yield is a way to measure how much cash flow you are getting for each rupee invested in equity.
Amrita School of Business 24
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Dividend Yield = (DPS/ Price) * 100
2011 DPS MPS (52 week average) 12.02 651.7 1.84%
2010 10.01 547 1.83%
2009 8.01 445 1.8%
2008 6.99 325.6 2.1%
2011 6.99 292.83 2.4%
Dividend yield
Analysis: The Dividend Yield remained the same for the last 3 years at 1.8%. However it fell from 2.1% to 1.8% in 2009. This is due to an increase in the 52 week average market price of the company and buyback of shares by the firm. The company has a significant improvement in the payment of dividends. The investor should look into the dividend yield also for making the investment decisions, since it implies the annual returns from the company.
Amrita School of Business
25
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
KEY RATIOS
2011 Liquidity Ratios CR Quick Ratio Leverage Ratios Debt Equity Debt Asset Interest coverage Profitability Ratios Gross Profit Net profit Return on Assets Return on Capital Employed Return on Equity Return on Investment Turnover Ratios Inventory Turnover Fixed Asset Turnover Total Asset Turnover Debtors Turnover Average Collection Period MPS (52 week Avg) Valuation Ratios P/E Ratio (A/B) Market To Book Value (A/B) DPS Dividend Yield EPS
1.15 0.91
0 0 50
40.84 12.8 27.3 27.73 27.3 42
4.42 5.63 2.14 45.9 8 651.7
16.83 4.24 12.02 1.84 38.73
Amrita School of Business
26
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
INDUSTRIAL AVERAGE
Amrita School of Business
27
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
DU PONT ANALYSIS
Return on Equity 27.3
ROTA 27.3
* *
Net Sales 1273
Total assets/ Equity 1
Net Profit Margin 12.8
Total assets Turnover 2.14
Net Profit 163
Net Sales 1273
Total Assets 594.5
Net Sales 1273
Total Costs 1110
Fixed Assets 226
Current Assets 368.5
Amrita School of Business
28
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
BALANCE SHEET
Year SOURCES OF FUNDS : Share Capital + Reserves Total + Total Shareholders Funds Secured Loans + Unsecured Loans + Total Debt Total Liabilities APPLICATION OF FUNDS : Gross Block + Less : Accumulated Depreciation + Net Block + Lease Adjustment Capital Work in Progress+ Investments + Current Assets, Loans & Advances Inventories + Sundry Debtors + Cash and Bank+ Loans and Advances + Total Current Assets Less : Current Liabilities and Provisions Current Liabilities + Provisions + Total Current Liabilities Net Current Assets Miscellaneous Expenses not written off + Deferred Tax Assets Deferred Tax Liability Net Deferred Tax Total Assets Contingent Liabilities+
Dec 07 42.06 604.29 646.35 0 0 0 646.35 523.67 297.65 226.02 0 17.31 297.84 194.82 27.36 93.67 617.07 932.92 220.31 590.15 810.46 122.46 0 6.07 23.35 -17.28 646.35 0
Dec 06 42.06 500.66 542.72 0 0 0 542.72 521.69 270.32 251.37 0 6.52 219.68 145.57 28.09 47.92 550.32 771.9 188.23 494.45 682.68 89.22 0 4.58 28.65 -24.07 542.72 0
Dec 05 42.06 433.05 475.11 0 0 0 475.11 506.91 233.95 272.96 0 10.83 0 131.04 24.11 185.8 467.89 808.84 176.58 413.33 589.91 218.93 0 5.29 32.9 -27.61 475.11 27.51
Dec 04 45.38 483.97 529.35 0 0 0 529.35 497.33 197.24 300.09 0 7.3 0 85.17 25.22 264.47 489.92 864.78 169.69 441.15 610.84 253.94 0 6.57 38.55 -31.98 529.35 22.27
Dec 03 45.38 446.73 492.11 0 0 0 492.11 485.86 162.31 323.55 0 6.36 0 92.33 18.38 203.8 440.91 755.42 169.11 400.86 569.97 185.45 4.91 6.66 34.82 -28.16 492.11 20.57
Amrita School of Business
29
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
Year INCOME : Sales Turnover + Excise Duty Net Sales Other Income + Stock Adjustments + Total Income EXPENDITURE : Raw Materials + Power & Fuel Cost+ Employee Cost + Other Manufacturing Expenses + Selling and Administration Expenses + Miscellaneous Expenses + Less: Pre-operative Expenses Capitalised+ Total Expenditure Operating Profit Interest + Gross Profit Depreciation+ Profit Before Tax Tax+ Deferred Tax+ Reported Net Profit Extraordinary Items + Adjusted Net Profit Adjst. below Net Profit + P & L Balance brought forward Statutory Appropriations + Appropriations + P & L Balance carried down Dividend Preference Dividend Equity Dividend % Earnings Per Share-Unit Curr Book Value-Unit Curr Dec 07(12) Dec 06(12) Dec 05(12) Dec 04(12) 981.72 120.19 861.53 48.48 -5.81 904.2 224.26 24.85 103.64 129.18 229.63 30.25 0 741.81 162.39 5.25 157.14 41.46 115.68 38.7 3.82 73.16 -0.01 73.17 0 0 0 73.16 0 31.77 0 70 15.21 116.65 Dec 03(12) 908.95 113.07 795.88 51.53 4.77 852.18 205.27 23.52 97.16 125.91 217.34 32.83 0 702.03 150.15 4.99 145.16 45.58 99.58 30.7 -7.47 76.35 -0.06 76.41 0 0 0 76.35 0 31.77 0 70 15.93 108.44
1,395.51 1,210.19 1,089.02 122.09 101.34 124.43 1,273.42 1,108.85 964.59 68.86 58.16 49.12 27.34 1.44 38.1 1,369.62 1,168.45 1,051.81 347.66 30.44 149.99 189.7 322.78 35.83 0 1,076.40 293.22 4.61 288.61 43.49 245.12 84.48 -6.79 162.68 0.12 162.56 0 0 0 162.68 0 50.47 0 120 36.64 153.67 275.05 29.93 130.35 172.7 296.42 27.19 0 931.64 236.81 3.53 233.28 42.71 190.57 62.13 -3.53 126.93 -0.24 127.17 0 0 0 126.93 0 42.06 0 100 28.78 129.03 251.86 27.35 115.24 157.01 265.52 26.34 0 843.32 208.49 4.22 204.27 41.85 162.42 55.49 -4.38 107.15 -0.28 107.43 0 0 0 107.15 0 33.64 0 80 24.35 112.96
Amrita School of Business
30
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Common Base Year Financial Statements Balance Sheet
Year SOURCES OF FUNDS : Share Capital + Reserves Total + Total Shareholders Funds Secured Loans + Unsecured Loans + Total Debt Total Liabilities APPLICATION OF FUNDS : Gross Block + Less : Accumulated Depreciation + Net Block + Lease Adjustment Capital Work in Progress+ Investments + Current Assets, Loans & Advances Inventories + Sundry Debtors + Cash and Bank+ Loans and Advances + Total Current Assets Less : Current Liabilities and Provisions Current Liabilities + Provisions + Total Current Liabilities Net Current Assets Miscellaneous Expenses not written off + Deferred Tax Assets Deferred Tax Liability Net Deferred Tax Total Assets Contingent Liabilities+
2011 92.68 138.02 133.76 100 100 100 133.76 112.12 242.58 57.93 100 627.17 297.84 226.32 61.73 93.87 975.75 317.94 129.66 8018.34 457.16 105.43 0 121.4 57.47 48.49 133.75 0
2010 92.68 114.34 112.31 100 100 100 112.31 101.73 220.31 64.43 100 236.23 219.68 169.11 63.38 48.02 870.21 263.06 110.78 6718.07 385.08 76.81 0 91.6 70.51 67.56 112.31 0
2009 92.68 98.91 98.32 100 100 100 100 98.86 190.67 69.97 100 392.39 100 152.23 54.39 186.19 739.86 275.65 103.92 5615.89 332.76 188.49 0 105.8 80.97 77.49 98.32 5502
2002 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
Amrita School of Business
31
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Profit and Loss Account
particulars / year INCOME : Sales Turnover + Excise Duty Net Sales Other Income + Stock Adjustments + Total Income EXPENDITURE : Raw Materials + Power & Fuel Cost+ Employee Cost + Other Manufacturing Expenses + Selling and Administration Expenses + Miscellaneous Expenses + Less: Pre-operative Expenses Capitalised+ Total Expenditure Operating Profit Interest + Gross Profit Depreciation+ Profit Before Tax Tax+ Deferred Tax+ Reported Net Profit Extraordinary Items + Adjusted Net Profit
2011 60.21 3.4 69.12 36.41 403.5 69.32 88.98 53.58 52.22 74.69 63.19 12.92 0 68.41 72.75 -62.69 77.9 22.44 93.43 146.73 -210.01 91.35 300 91.36
2010 38.93 -14.17 47.26 15.21 -73.48 44.45 49.52 51.01 34.02 59.04 49.86 -14.31 0 45.76 39.51 -52.93 43.79 20.24 50.39 81.45 -59.95 49.31 -500 49.71
2009 25.02 5.39 28.1 -2.69 601.66 30.03 36.91 37.99 18.49 44.59 34.24 -16.99 0 31.94 22.83 -77.73 25.91 17.82 28.17 62.06 -158.63 26.04 -566.67 26.46
2002 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
Amrita School of Business
32
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Common Size Financial Statements Balance Sheet
Year SOURCES OF FUNDS : Share Capital + Reserves Total + Total Shareholders Funds Secured Loans + Unsecured Loans + Total Debt Total Liabilities APPLICATION OF FUNDS : Gross Block + Less : Accumulated Depreciation + Net Block + Lease Adjustment Capital Work in Progress+ Investments + Current Assets, Loans & Advances Inventories + Sundry Debtors + Cash and Bank+ Loans and Advances + Total Current Assets Less : Current Liabilities and Provisions Current Liabilities + Provisions + Total Current Liabilities Net Current Assets Miscellaneous Expenses not written off + Deferred Tax Assets Deferred Tax Liability Net Deferred Tax Total Assets Contingent Liabilities+
2011 6.51 93.49 100 0 0 0 100 81.02 46.05 34.97 0 2.68 46.08 30.14 4.23 14.49 95.47 144.34 34.09 91.31 125.39 18.95 0 0.94 3.61 -2.67 100 0
2010 7.75 92,25 100 0 0 0 100 96.13 49.81 46.32 0 1.2 40.48 26.82 5.18 8.83 101.4 142.23 34.68 91.11 125.79 16.44 0 0.84 5.28 -4.44 100 0
2009 8.85 91.15 100 0 0 0 100 106.69 49.24 57.45 0 2.28 0 27.58 5.07 39.11 98.48 170.24 37.17 87 124.16 46.08 0 1.11 6.92 -5.81 100 5.79
2008 8.57 91.43 100 0 0 0 100 93.95 37.26 56.69 0 1.38 0 16.09 4.76 49.96 92.55 163.37 32.06 83.34 115.39 47.97 0 1.24 7.28 -6.04 100 4.21
2011 9.22 90.78 100 0 0 0 100 98.73 32.98 65.75 0 1.29 0 18.76 3.73 41.41 89.6 153.51 34.36 81.46 115.82 37.68 1 1.35 7.08 -5.72 100 4.18
Amrita School of Business
33
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Profit and Loss Account
Year INCOME : Sales Turnover + Excise Duty Net Sales Other Income + Stock Adjustments + Total Income EXPENDITURE : Raw Materials + Power & Fuel Cost+ Employee Cost + Other Manufacturing Expenses + Selling and Administration Expenses + Miscellaneous Expenses + Less: Pre-operative Expenses Capitalised+ Total Expenditure Operating Profit Interest + Gross Profit Depreciation+ Profit Before Tax Tax+ Deferred Tax+ Reported Net Profit Extraordinary Items + Adjusted Net Profit
Dec 07(12)
Dec 06(12)
Dec 05(12)
106.70 109.14 112.90 6.7 9.139198 12.89978 100.00 100.00 100 5.4 5.245074 5.092319 -2.1 -0.12986 3.949865 103.30 105.37 109.04 27.30128 2.390413 11.77852 14.89689 25.34749 2.813683 0 84.53 23.02618 0.362017 22.66416 3.415213 19.24895 6.634103 -0.53321 12.77505 0.009423 12.76562 24.80498 2.699193 11.75542 15.57469 26.7322 2.45209 0 84.01858 21.35636 0.318348 21.03801 3.851738 17.18627 5.603102 -0.31835 11.44699 -0.02164 11.46864 26.11058 2.835402 11.94704 16.27738 27.52672 2.730694 0 87.42782 21.61436 0.437492 21.17687 4.338631 16.83824 5.752703 -0.45408 11.10835 -0.02903 11.13737
Amrita School of Business
34
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
Recommendation The current market scenario is a one with high market instability which is due to high volatility and global slowdown. The effect of slowdown on the consumer goods sector has been quite less compared to the other sectors. This is a positive sign for the companies in this sector. Based on current market performance of the company and the better performance expectation we recommend the current share holders to HOLD the shares and the prospective buyers to BUY the share. These recommendations are on the basis of following factors. 1. Global slowdown: The effect of global slowdown has been quite less in the consumer and healthcare sector as compared to other sectors. As a result the demand for the products of the company has been steady even now. Also Indian economy has been projected to be effected by a minimal scale. These reasons indicate a higher growth prospectus for the company. 2. Ratio Analysis: The key ratios of the company are the leading indicators about the companys overall performance. Ratio analysis of the company have indicated factors like healthy liquidity of the company , higher profitability, healthier leverage margins and higher payout ratios which are good signs for the company. 3. EPS and P/E Ratios: These ratios indicate the earnings for the share holders and the market expectation about the company. The company has provided good returns to its investors and the P/E ratio is also attractive one for a retail investor.
Amrita School of Business
35
2012
[GSK CONSUMER HEALTHCARE]
BIBLIOGRAPHY
www.gsk-ch.in www.moneycontrol.com www.myiris.com www.marketingpractice.blogspot.com www.economictimes.indiatimes.com www.bseindia.com www.capitaline.com
Amrita School of Business
36
You might also like
- Metropolis Healthcare Limited Annual Report 2018-19Document260 pagesMetropolis Healthcare Limited Annual Report 2018-19Tybcom Hons bNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Business Strategy V4Document15 pagesAssignment - Business Strategy V4supunNo ratings yet
- The Headaches of GlaxowellcomeDocument11 pagesThe Headaches of GlaxowellcomeRiffat Al ImamNo ratings yet
- # (Article) Benchmarking Forecasting Processes (2007)Document7 pages# (Article) Benchmarking Forecasting Processes (2007)M YazdkhastiNo ratings yet
- Project 2 Institutions Analysis Group PowerpointDocument16 pagesProject 2 Institutions Analysis Group Powerpointapi-454324937No ratings yet
- Final Paper - Final Draft - JDocument16 pagesFinal Paper - Final Draft - Japi-562187732No ratings yet
- Singapore's Political Factors and Economic SuccessDocument3 pagesSingapore's Political Factors and Economic SuccessIsabelle Laing-MeasonNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Firm Resources with the VRIO FrameworkDocument21 pagesAnalyzing Firm Resources with the VRIO Frameworksajeet sahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsDocument11 pagesLecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsAngelica SmithNo ratings yet
- India: Supply Demand Barriers To Entry Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Buyers CompetitionDocument2 pagesIndia: Supply Demand Barriers To Entry Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Buyers CompetitionminaxiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Analysis LeboldDocument12 pagesOrganizational Analysis Leboldapi-282606117No ratings yet
- SMEsinternationalizationDocument22 pagesSMEsinternationalizationRaihan RakibNo ratings yet
- Dividend Policy Analysis For Sun PharmaceuticalsDocument16 pagesDividend Policy Analysis For Sun PharmaceuticalsIshita SoodNo ratings yet
- OM 7011 Summer AssignmentDocument12 pagesOM 7011 Summer AssignmentrssarinNo ratings yet
- Dishman Pharma SWOT & PESTEL AnalysisDocument6 pagesDishman Pharma SWOT & PESTEL AnalysisshivangiNo ratings yet
- Final Capstone Report ArupDocument70 pagesFinal Capstone Report ArupChristopher Y. WangNo ratings yet
- About GojekDocument6 pagesAbout GojekDaffa IqbalNo ratings yet
- Strategic HRM at The Mayo Clinic: A Case Study: Sunil RamlallDocument23 pagesStrategic HRM at The Mayo Clinic: A Case Study: Sunil RamlallKarthik Reddy100% (1)
- Pestel AnalysisDocument4 pagesPestel AnalysisNimrah RaoNo ratings yet
- Management in Healthcare ReportDocument28 pagesManagement in Healthcare ReportJessica Margaux MercadoNo ratings yet
- Apollo Gleneagles Hospitals Next Steps for Growth (39Document23 pagesApollo Gleneagles Hospitals Next Steps for Growth (39sujal verma100% (1)
- Apple Financial ReportDocument3 pagesApple Financial ReportBig ManNo ratings yet
- Automated Guided VehicleDocument17 pagesAutomated Guided VehicleTedy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Ma PiyushDocument15 pagesResearch Paper Ma Piyushpiyushpurva2005No ratings yet
- Techniques For Analyzing Corporate Diversification StrategiesDocument7 pagesTechniques For Analyzing Corporate Diversification Strategiesapi-3738338100% (1)
- Best Selction Practice ToyotaDocument3 pagesBest Selction Practice ToyotaManpreet Singh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Digikala-Ramin Shabanpour (2016)Document19 pagesDigikala-Ramin Shabanpour (2016)Ramin ShabNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth, Rizki, Talita - IE 5Document34 pagesElizabeth, Rizki, Talita - IE 5bontjelNo ratings yet
- Google's Human Resource Management PracticesDocument9 pagesGoogle's Human Resource Management PracticesAKASH KCNo ratings yet
- ToolsCorp Corporation's Business PlanDocument7 pagesToolsCorp Corporation's Business PlanericNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary Abu Dhabi CateringDocument22 pagesExecutive Summary Abu Dhabi CateringGhadoor Mmsk50% (2)
- HOW TO BUILD RISK INTO YOUR BUSINESS MODEL AND STRENGTHEN VIRTUOUS CYCLESDocument23 pagesHOW TO BUILD RISK INTO YOUR BUSINESS MODEL AND STRENGTHEN VIRTUOUS CYCLESRaman Sharma100% (1)
- Role of risk and compensation committees in managing financial firm riskDocument17 pagesRole of risk and compensation committees in managing financial firm riskquangphungNo ratings yet
- GDNA Managers Guide v.1.4Document84 pagesGDNA Managers Guide v.1.4Sebastian FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Investment Detective CaseDocument1 pageInvestment Detective CaseJonathan ZhaoNo ratings yet
- M4 - Group Assignment Final DraftDocument23 pagesM4 - Group Assignment Final DraftEudeanJames0% (1)
- Work From Home A Curse or Boon Analyzing People's SentimentsDocument8 pagesWork From Home A Curse or Boon Analyzing People's SentimentsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument25 pagesBCG MatrixKhairul Haizam100% (1)
- GEHC White Papers Digital PathologyDocument13 pagesGEHC White Papers Digital PathologySoodn Kang SoodnNo ratings yet
- Definition of A ConstraintDocument9 pagesDefinition of A Constraintrajlaxmi_patilNo ratings yet
- Go JekDocument10 pagesGo JekSandro Fernando SethieawanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur Innovation (Tan Sri A.K. Nathan)Document12 pagesEntrepreneur Innovation (Tan Sri A.K. Nathan)Thava Selvy100% (1)
- Strategy AssignmentDocument12 pagesStrategy AssignmentGarry StephenNo ratings yet
- Open Innovation As A Competitive StrategyDocument20 pagesOpen Innovation As A Competitive Strategyajax980No ratings yet
- Virtualization Pharma BR 1638314 PDFDocument24 pagesVirtualization Pharma BR 1638314 PDFParth DesaiNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis For An It IndustryDocument7 pagesSwot Analysis For An It Industrymonika_ifimNo ratings yet
- Not ADocument4 pagesNot AKasia PilecwzNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management PreetDocument28 pagesInventory Management PreetKawalpreet Singh MakkarNo ratings yet
- Samsung Vs SonyDocument5 pagesSamsung Vs SonycustodiobNo ratings yet
- FM Assignment - EVA and DuPont Analysis For CompaniesDocument10 pagesFM Assignment - EVA and DuPont Analysis For Companiesamitbharadwaj7No ratings yet
- Corporate Financial Distress - Corporate Debt Restructuring Mechanism in IndiaDocument7 pagesCorporate Financial Distress - Corporate Debt Restructuring Mechanism in IndiaGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument13 pagesSwot AnalysisEr Paras ThakurNo ratings yet
- Vertical IntegrationDocument36 pagesVertical IntegrationYvan Cham0% (1)
- The Benefits and Challenges of E-Health Applications in Developing Nations: A ReviewDocument10 pagesThe Benefits and Challenges of E-Health Applications in Developing Nations: A ReviewbennyNo ratings yet
- What Motivates Ecopreneurs To Start Businesses?Document25 pagesWhat Motivates Ecopreneurs To Start Businesses?chandmagsi100% (1)
- Spotting Earning ManagementDocument14 pagesSpotting Earning ManagementTri SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Harvard-UWE Referencing GuideDocument30 pagesHarvard-UWE Referencing GuiderufftuffcookieNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Financial AccountingDocument15 pagesAssignment of Financial AccountingBhushan WadherNo ratings yet
- HeinekenDocument8 pagesHeinekenErick KinotiNo ratings yet
- Working Capital & Dividend PolicyDocument9 pagesWorking Capital & Dividend PolicyLipi Singal0% (1)
- VC Glossary Terms TLV PartnersDocument12 pagesVC Glossary Terms TLV PartnersAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Fs AnalysisDocument74 pagesRatio and Fs AnalysisRubie Corpuz SimanganNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Financial StatementDocument2 pagesRatio Analysis Financial Statementsatya100% (2)
- MODULE 1a - Partnership Nature and FormationDocument31 pagesMODULE 1a - Partnership Nature and FormationNichole Joy XielSera TanNo ratings yet
- BUS 485 Life InsuranceDocument27 pagesBUS 485 Life InsuranceF.T. BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- T4 Business Economics Q&ADocument14 pagesT4 Business Economics Q&ABiplob K. SannyasiNo ratings yet
- GCC Insurers 2023Document18 pagesGCC Insurers 2023Atlas MagazineNo ratings yet
- Finance - Cost of Capital TheoryDocument30 pagesFinance - Cost of Capital TheoryShafkat RezaNo ratings yet
- @icmaifamily CA CMA Final SFM Theory NotesDocument156 pages@icmaifamily CA CMA Final SFM Theory NotesOmkar Pednekar100% (1)
- Capital Structure Composition and Financial Performance of Firms in The Brewery Industry: Evidence From NigeriaDocument9 pagesCapital Structure Composition and Financial Performance of Firms in The Brewery Industry: Evidence From NigeriaToheeb AtandaNo ratings yet
- Equity Analysis With Reference To Automobile IndustryDocument79 pagesEquity Analysis With Reference To Automobile Industrysmartway projectsNo ratings yet
- How Debt Affects Risk and ReturnDocument61 pagesHow Debt Affects Risk and ReturnChincel G. ANINo ratings yet
- Financial Markets & Institutions: Chapter 1Document305 pagesFinancial Markets & Institutions: Chapter 1Ase Sharew100% (1)
- Similarity Report1Document38 pagesSimilarity Report1Sansar ParajuliNo ratings yet
- CSG Ar 2019 en PDFDocument442 pagesCSG Ar 2019 en PDFBelalHossainNo ratings yet
- International FinDocument454 pagesInternational FinPiyush KashyapNo ratings yet
- Fact Orders Tec Stored A To S 2022Document2,364 pagesFact Orders Tec Stored A To S 2022Mikel SUAREZ BARREIRONo ratings yet
- Company Financial Statements: Dr. Kavitha MenonDocument82 pagesCompany Financial Statements: Dr. Kavitha MenonAlex JayachandranNo ratings yet
- V Ratio Analysis InsightsDocument7 pagesV Ratio Analysis Insightsrupeshdahake8586No ratings yet
- Capital Structure Dessertation FinalDocument29 pagesCapital Structure Dessertation FinalBasavaraj MtNo ratings yet
- Final Project KusumgarDocument62 pagesFinal Project KusumgarAvinash SahuNo ratings yet
- Carrefour S, ADocument14 pagesCarrefour S, Aketut_widya67% (3)
- 2023 - Chapter 1 - Overview of FMIDocument27 pages2023 - Chapter 1 - Overview of FMITrần Anh TuấnNo ratings yet
- FM Assignment AnanduDocument23 pagesFM Assignment AnanduAmrutha P RNo ratings yet
- Question of Cost of CapitalDocument3 pagesQuestion of Cost of CapitalAngel Atia IbnatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document27 pagesChapter 6adNo ratings yet
- Gilkes Energy Brochure - Lo ResDocument8 pagesGilkes Energy Brochure - Lo RessercopetrolNo ratings yet
- Mba II Financial Management (14mba22) NotesDocument53 pagesMba II Financial Management (14mba22) NotesPriya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance For Managers - Course Material PDFDocument94 pagesAccounting and Finance For Managers - Course Material PDFbil gossayw100% (1)
- Indian Financial System An IntroductionDocument4 pagesIndian Financial System An IntroductionRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- How to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)From EverandHow to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Accounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsFrom EverandAccounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)From EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindFrom EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (231)
- LLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyFrom EverandLLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Profit First for Therapists: A Simple Framework for Financial FreedomFrom EverandProfit First for Therapists: A Simple Framework for Financial FreedomNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionFrom EverandFinancial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- The ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!From EverandThe ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Love Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantFrom EverandLove Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (146)
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetFrom EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineFrom EverandA Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Project Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessFrom EverandProject Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping: An Essential Guide to Bookkeeping for Beginners along with Basic Accounting PrinciplesFrom EverandBookkeeping: An Essential Guide to Bookkeeping for Beginners along with Basic Accounting PrinciplesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- The E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItFrom EverandThe E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (13)
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsFrom EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping: A Beginner’s Guide to Accounting and Bookkeeping for Small BusinessesFrom EverandBookkeeping: A Beginner’s Guide to Accounting and Bookkeeping for Small BusinessesNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting: Service Business Study GuideFrom EverandBasic Accounting: Service Business Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The CEO X factor: Secrets for Success from South Africa's Top Money MakersFrom EverandThe CEO X factor: Secrets for Success from South Africa's Top Money MakersNo ratings yet
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Mysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungFrom EverandMysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)