Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NDE Volumetric Vs Planar Defects Ratio
Uploaded by
lram70Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NDE Volumetric Vs Planar Defects Ratio
Uploaded by
lram70Copyright:
Available Formats
Some basic information about Planar Vs Volumetric defects in NDE
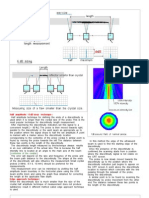
Defect shape is usually classified in two types: volumetric, for which the ratio between height and width is next to unity, and planar, whose width is, indeed, very small with respect to the height. What are planar defect? Give example Planar flaws are thin in one dimension but larger in the other two dimensions. Defect Height to Width Ratio above 6 is called as Planar defects. Planar defect example (e.g. cracks, lack of fusion and incomplete penetration) Comparing based on ratio of Height to Width
Planar defects (Height to Width ratio)
For Sl no 4: Defect Height in mm 4 4 Defect Width in mm 0.5 0.3 Ratio H/W Defect type 8 Planar
For Sl no 5:
13.33 Planar
For Planar defects, the width may be very small, with respect to the height.
Generally, When the Ratio of H /W= 6 and above, these type of defects are characterised as planar defects. What are volumetric defects and Defect Height to Width ratio? Volumetric flaws can be described by three dimensions or a volume. Volumetric defect height to width ratio is between 1 to 3.8 (refer graph)
Volumetric defects such as slag entrapment and porosity are all easily detected.
UT is used for 1. It is very good for the detection of planar defects and cracks. RT is used for 1. Good for finding volumetric defects such as slag and porosity. 2. There are problems in detecting planar defects and fine cracks if these are normal to the beam. Various defects Height to Width ratio (H/ W Ratio) shapes
Volumetric defect Heigth to width ratio 1.0 to 3.8 ,Transition 3.8 to6, Planar 6 and above
Sl no 1 to5 Sl no 1: Sl no 2 :
Volumetric Vs Planar defects ( Height to Width ratio) Widt Height h Ratio 3 4 3 1.5 1 2.66
Defect type Volumetric defect Volumetric defect Partially Volumetric (or) Planar Planar defect Planar defect
Sl no : 3 Sl no 4: Sl no: 5
4 4 4
1 0.5 0.3
4 8 13.33
Reference: http://www.oegfzp.at/fileadmin/papers/28_wcndtfinal00028.pdf
Schematic diagram showing the Volumetric defect Vs Planar Defect ratios
Volumetric flaw classification and NDE detection methods
Volumetric flaws Porosity,Inclusions,Slag,Tungsten &Other, Shrinkage,Holes and voids,Corrosion thinning,Corrosion pitting NDE Detection methods Visual (surface),Replica (surface),Liquid penetrant (surface),Magnetic particle (surface and subsurface),Eddy current,Microwave,Ultrasonic,Radiography
Table 2 lists some of the various types of planar flaws, along with appropriate NDE detection methods.
Planar flaw classification and NDE detection methods
Planar flaws Seams,Lamination,Lack of bonding,Forging or rolling lap,Casting cold shut, Heat treatment cracks,Grinding cracks,Plating cracks,Fatigue cracks,Stress-corrosion cracks,Welding cracks,Lack of fusion,Incomplete penetration Brazing debond NDE detection methods Visual,Replication microscopy,MT,Magnetic field, ECT,Microwave,Electric current perturbation,Magabsorption,UT,Acoustic emission,Thermography
Reference: http://www.oegfzp.at/fileadmin/papers/28_wcndtfinal00028.pdf
Compiled By LRamachandran
You might also like
- Magnetic Particle Examination of WeldsDocument4 pagesMagnetic Particle Examination of WeldsshruthiNo ratings yet
- VT For NDT - 2017Document29 pagesVT For NDT - 2017Selvakpm06No ratings yet
- NDT4 - L2 Final Review (EOC) 020219Document13 pagesNDT4 - L2 Final Review (EOC) 020219Ibnu Hamdun100% (1)
- Penetrant Testing (PT)Document11 pagesPenetrant Testing (PT)Maria Cristina DijmarescuNo ratings yet
- How to Prepare for the ASNT NDT Level-III Visual and Optical Testing ExaminationDocument23 pagesHow to Prepare for the ASNT NDT Level-III Visual and Optical Testing ExaminationIke Duaka100% (2)
- PCN NDT Training Facility in ChennaiDocument17 pagesPCN NDT Training Facility in ChennaiAMITNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Inspection QuizDocument30 pagesMagnetic Particle Inspection QuizMohammad Saif100% (2)
- PT Quiz & Ans 2Document6 pagesPT Quiz & Ans 2Goutam Kumar Deb100% (1)
- 25 MM Nozzle Paut Scan PlanDocument4 pages25 MM Nozzle Paut Scan PlanRupam BaruahNo ratings yet
- Visual Testing Level I and II Course OutlineDocument1 pageVisual Testing Level I and II Course OutlineMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing ManualDocument88 pagesUltrasonic Testing ManualphillipskincaidNo ratings yet
- PT Level 3 Preparation 1 PDFDocument25 pagesPT Level 3 Preparation 1 PDFtariqNo ratings yet
- MT - GenDocument8 pagesMT - GenkanchanabalajiNo ratings yet
- Astm Reference Block For MetalDocument10 pagesAstm Reference Block For MetalrupamNo ratings yet
- 11 Ut ProcedureDocument11 pages11 Ut ProcedureSajeesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- UT ProcedureDocument6 pagesUT ProcedureMurali YNo ratings yet
- Dac CurveDocument24 pagesDac Curvesantu_23No ratings yet
- 01-M115 Iss 2 (BS en 1290 - Electromagnet, (Fluorescent) )Document3 pages01-M115 Iss 2 (BS en 1290 - Electromagnet, (Fluorescent) )DeepakNo ratings yet
- PRR CalculationDocument4 pagesPRR CalculationnavitaNo ratings yet
- Visual Testing - L-3 - QBDocument16 pagesVisual Testing - L-3 - QBManoj SivalingamNo ratings yet
- ASNT RECER RT QB (Aligned) MAIN FOILDERDocument26 pagesASNT RECER RT QB (Aligned) MAIN FOILDERkingston100% (1)
- Ut Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBDocument25 pagesUt Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBkingstonNo ratings yet
- RT IQI SelectionDocument1 pageRT IQI SelectionVipin Peter100% (1)
- 8.4.4 - Radiographic Training ProgramDocument31 pages8.4.4 - Radiographic Training ProgramMaduabuchi Serge Enemuo100% (1)
- PAUT for Heavy Wall Austenitic SS WeldsDocument10 pagesPAUT for Heavy Wall Austenitic SS WeldsrupamNo ratings yet
- Technology Multiple Choice Exam 1Document8 pagesTechnology Multiple Choice Exam 1saifullah629No ratings yet
- MT Work InstructionDocument3 pagesMT Work Instructionpandab bkNo ratings yet
- Demo 6 Indication CompareDocument23 pagesDemo 6 Indication CompareRudolph RednoseNo ratings yet
- Iqi'sDocument6 pagesIqi's24inspector100% (1)
- Example Report TOFD 2 INT-GP1186!09!70Document1 pageExample Report TOFD 2 INT-GP1186!09!70EMTC EMTC100% (1)
- UT TEST PROCEDURE LAMINATIONSDocument8 pagesUT TEST PROCEDURE LAMINATIONSperogami100% (1)
- Angle DACDocument1 pageAngle DACJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Visual Examination Procedure: 1. PurposeDocument4 pagesVisual Examination Procedure: 1. PurposeElvin MenlibaiNo ratings yet
- UltrasonicDocument26 pagesUltrasonicJayesh88% (8)
- Demo SUMDocument27 pagesDemo SUMRudolph RednoseNo ratings yet
- Tutorial IIIDocument21 pagesTutorial IIIravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- VT General QuestionsDocument6 pagesVT General Questionsgopakumar72100% (1)
- Radiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Document7 pagesRadiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Mohammed Aljawhar100% (1)
- Level III Preparations Study Plan Basic RT and MTDocument2 pagesLevel III Preparations Study Plan Basic RT and MTjasminnee50% (2)
- RT Specific ExamDocument3 pagesRT Specific ExamGoutam Kumar Deb100% (1)
- C.V Utekar Assistant Manager ASNT Level IIIDocument4 pagesC.V Utekar Assistant Manager ASNT Level IIIShrikant UtekarNo ratings yet
- OK-UT-04 - Ultrasonic Technique SheetDocument1 pageOK-UT-04 - Ultrasonic Technique SheetMike Boyes100% (1)
- PAUT - Phased Array and ToFD - V - Radiography PDFDocument14 pagesPAUT - Phased Array and ToFD - V - Radiography PDFdarouichNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing: Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument48 pagesRadiographic Testing: Basic Principles and TechniquesArjun LalitNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Lab: Shear Wave Calibration and Reference Block MeasurementsDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Testing Lab: Shear Wave Calibration and Reference Block MeasurementsdarouichNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Ultrasonic ScanningDocument7 pagesHigh Temperature Ultrasonic ScanningscribdmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Inspection-Test BlocksDocument0 pagesUltrasonic Inspection-Test BlocksSreeji ChittamveeduNo ratings yet
- UT Level 1 Trial QuestionsDocument6 pagesUT Level 1 Trial QuestionsKhepa BabaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing: Weld Inspection Using AWS D1.1Document65 pagesUltrasonic Testing: Weld Inspection Using AWS D1.1CLIFFORDPANo ratings yet
- AWS D1.1 Weld Technique SketchDocument6 pagesAWS D1.1 Weld Technique SketchnathgsurendraNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing Theory and InterpretationDocument44 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing Theory and InterpretationCRISTIAN SILVIU IANUCNo ratings yet
- AutoCad Assigment 2Document4 pagesAutoCad Assigment 2Abdullrahman ElkhatebNo ratings yet
- How To Characterize Warp PDFDocument2 pagesHow To Characterize Warp PDFBruno MauroNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Tolerances & Fits GuideDocument33 pagesGeometrical Tolerances & Fits GuideSUMEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Tofd PDFDocument11 pagesTofd PDFsubhaNo ratings yet
- Limits Fits and Tolerances (Dfc-Jo7237-03l's Conflicted Copy 2018-03-01)Document56 pagesLimits Fits and Tolerances (Dfc-Jo7237-03l's Conflicted Copy 2018-03-01)Itemogeng Bernatt BabeNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument6 pagesSurface RoughnessIltefatNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument9 pagesSurface RoughnessKarthick DuraiNo ratings yet
- Basic Principle of Ultrasonic Testing Is ReflectionDocument13 pagesBasic Principle of Ultrasonic Testing Is ReflectionJayaram MVNo ratings yet
- SS Iron Contamination Acid RemovalDocument1 pageSS Iron Contamination Acid Removallram70No ratings yet
- Sleeping PosturesDocument2 pagesSleeping Postureslram70No ratings yet
- PAUTDocument7 pagesPAUTDeepakNo ratings yet
- Mentorship Junior Employees BasicsDocument4 pagesMentorship Junior Employees Basicslram70No ratings yet
- Why Welding Edge Preparation by Grinding Wheel of Aluminium Oxide To Be Cleaned in Sodium Based Nuclear ReactorDocument1 pageWhy Welding Edge Preparation by Grinding Wheel of Aluminium Oxide To Be Cleaned in Sodium Based Nuclear Reactorlram70No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Degreaser and CleanerDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Degreaser and Cleanerlram70No ratings yet
- Why Nitrogen Is Not Used For SS Welding Torch Shield or Purging GasDocument1 pageWhy Nitrogen Is Not Used For SS Welding Torch Shield or Purging Gaslram70No ratings yet
- Why SS Surface To Be Removed of Free Iron ContaminationDocument1 pageWhy SS Surface To Be Removed of Free Iron Contaminationlram70No ratings yet
- NItric Acid + Iron Contamination Removal Acid in SSDocument1 pageNItric Acid + Iron Contamination Removal Acid in SSlram70No ratings yet
- Determination of Iron .R. A. Koenig and C. R. JohnsonDocument3 pagesDetermination of Iron .R. A. Koenig and C. R. Johnsonlram70No ratings yet
- KTA 3201.4 New Addition Details German CodeDocument6 pagesKTA 3201.4 New Addition Details German Codelram70No ratings yet
- Organic Acids For Ss Acid CleaningDocument1 pageOrganic Acids For Ss Acid Cleaninglram70No ratings yet
- Class 3 Iron Free Components InspectionDocument1 pageClass 3 Iron Free Components Inspectionlram70No ratings yet
- Can Phosphoric Acid Be Used To Remove CorrosionDocument1 pageCan Phosphoric Acid Be Used To Remove Corrosionlram70No ratings yet
- Can Sulfamic Acid Used To Remove Rust From SS SurfaceDocument1 pageCan Sulfamic Acid Used To Remove Rust From SS Surfacelram70No ratings yet
- How To Identify and Reduce ElectrosmogDocument2 pagesHow To Identify and Reduce Electrosmoglram70No ratings yet
- Can Oxalic Acid Be Used To Remove Rust Corrosion in SS ProductDocument1 pageCan Oxalic Acid Be Used To Remove Rust Corrosion in SS Productlram70No ratings yet
- EMF and Radiation Measurement QuestionDocument3 pagesEMF and Radiation Measurement Questionlram70No ratings yet
- Difference Between Dissertation Vs ThesisDocument2 pagesDifference Between Dissertation Vs Thesislram70No ratings yet
- WRI Tiruchy India and Welding TrainingDocument3 pagesWRI Tiruchy India and Welding Traininglram70No ratings yet
- Welded Connection Weld DesignDocument12 pagesWelded Connection Weld Designlram70No ratings yet
- RF Color Charts PDFDocument11 pagesRF Color Charts PDFTorrey PinesNo ratings yet
- Constant Current vs. Constant Voltage Output - Lincoln ElectricDocument5 pagesConstant Current vs. Constant Voltage Output - Lincoln ElectricgobiNo ratings yet
- Berilliyum Neutron Capture Therapy For Cancer-Projects Worldwide - Kiyanagi2019Document10 pagesBerilliyum Neutron Capture Therapy For Cancer-Projects Worldwide - Kiyanagi2019lram70No ratings yet
- Gnyusov EA 395 9 Weld 2011 PDFDocument7 pagesGnyusov EA 395 9 Weld 2011 PDFlram70No ratings yet
- Clinical Practice in BNCT To The Brain-Japan 32030440Document10 pagesClinical Practice in BNCT To The Brain-Japan 32030440lram70No ratings yet
- Why PPM Is Ambiguous? - Mass Voulme or AtomicDocument3 pagesWhy PPM Is Ambiguous? - Mass Voulme or Atomiclram70No ratings yet
- Cigweld-Deposited Rates PDFDocument7 pagesCigweld-Deposited Rates PDFNam_HitechNo ratings yet
- KOBE Steel SS Weld Filler Tables and Comparison SMAW GTAW SAW FCAW KWT - SUS - 3edDocument22 pagesKOBE Steel SS Weld Filler Tables and Comparison SMAW GTAW SAW FCAW KWT - SUS - 3edlram70No ratings yet
- Weber 2016Document6 pagesWeber 2016charon lastNo ratings yet
- Jig Ohba SikiDocument1 pageJig Ohba SikiAgungNo ratings yet
- Bengalac Red Oxide PrimerDocument3 pagesBengalac Red Oxide PrimerNagendra BurabattulaNo ratings yet
- Smaw 9 Summative Test Q1Document2 pagesSmaw 9 Summative Test Q1Jose Intraboy Arais Tabugoc Jr.No ratings yet
- Questions CswipDocument63 pagesQuestions CswipMohamed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Gas 2019 Part 1 - 2 PDFDocument71 pagesSynthesis Gas 2019 Part 1 - 2 PDFcap n3moNo ratings yet
- Basic Welding TheoryDocument15 pagesBasic Welding TheoryCarina MostralesNo ratings yet
- Duratomic TP Brochure GT15-214 PDFDocument24 pagesDuratomic TP Brochure GT15-214 PDFDeysi CardenasNo ratings yet
- Alim Knit (BD) LTD.: Coagulation Tank With AgitatorDocument1 pageAlim Knit (BD) LTD.: Coagulation Tank With AgitatorKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Specification FormDocument5 pagesSpecification Formpowdertech100% (2)
- TDS Nitoproof Damp Protect India2Document2 pagesTDS Nitoproof Damp Protect India2hitesh315No ratings yet
- CHS - Steel Circular Hollow Sections, Polsteel London Structural Steel SupplierDocument4 pagesCHS - Steel Circular Hollow Sections, Polsteel London Structural Steel Supplierchigbo13No ratings yet
- Ball Check Valves FlangedDocument1 pageBall Check Valves FlangedeliiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Interplus 356 PDFDocument4 pagesInterplus 356 PDFDamen JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lab#7: Complex Part Using G03 Ijk Input: DescriptionDocument3 pagesLab#7: Complex Part Using G03 Ijk Input: DescriptionAbdul MunimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Manufacturing Systems Design and Analysis: Spring 2019 Isye 415Document24 pagesIntroduction To Manufacturing Systems Design and Analysis: Spring 2019 Isye 415VaikunthtendulkarNo ratings yet
- WhizCut 2022Document88 pagesWhizCut 2022Mann Sales & MarketingNo ratings yet
- Lathe Machine TDocument10 pagesLathe Machine TAdebisi IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Axle Costing Sheet Format 1Document6 pagesAxle Costing Sheet Format 1Brain TeaserNo ratings yet
- Piping Comp-Din, Satm PDFDocument178 pagesPiping Comp-Din, Satm PDFVinit Dhande100% (2)
- Determining The Short Term Tensile Weld Strength of Chemical-Resistant ThermoplasticsDocument4 pagesDetermining The Short Term Tensile Weld Strength of Chemical-Resistant ThermoplasticsFernando Da RosNo ratings yet
- Catálogo 37FSDocument6 pagesCatálogo 37FSMarcos Marcandali de JesusNo ratings yet
- 高强度输送带用钢丝绳 High strength steel wire ropes for conveyor beltsDocument4 pages高强度输送带用钢丝绳 High strength steel wire ropes for conveyor beltsNorberto A. GhiggiNo ratings yet
- Guardrail Installation ProcedureDocument5 pagesGuardrail Installation ProcedureThandabantu Magengelele50% (2)
- 1 TextbookDocument42 pages1 TextbookMoataz MandorNo ratings yet
- Hempadur Avantguard 750 Product Data SheetDocument4 pagesHempadur Avantguard 750 Product Data SheetfaisalfaiNo ratings yet
- AWS N-9 Stud Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) FormDocument1 pageAWS N-9 Stud Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) FormNatalia StarkNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 Hot-Dip Zinc Coatings On Steel and Cast Iron ProductsDocument2 pagesAmendment No. 1 Hot-Dip Zinc Coatings On Steel and Cast Iron ProductsGMSNo ratings yet
- Nitoproof 600: Liquid Applied, Elastomeric, One Coat Waterproofing MembraneDocument3 pagesNitoproof 600: Liquid Applied, Elastomeric, One Coat Waterproofing MembraneFarah HaseenahNo ratings yet
- Wooden Mallet Plans - WoodArchivistDocument4 pagesWooden Mallet Plans - WoodArchivistErics100% (1)