Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Translation
Uploaded by
Tiara HassanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Translation
Uploaded by
Tiara HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
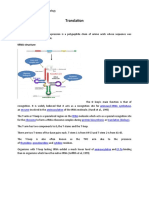
Initiation Prokaryote Three initiation factors (IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3) first bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit.
This step is followed by binding of the mRNA and the initiator N-formylmethionyl (fMet) tRNA, which is recognized by IF-2 bound to GTP. IF-3 is then released, and a 50S subunit binds to the complex, triggering the hydrolysis of bound GTP, followed by the release of IF-1 and IF-2 bound to GDP. Eukaryote Initiation factors eIF-3, eIF-1, and eIF-1A bind to the 40S ribosomal subunit. The initiator methionyl tRNA is brought to the ribosome by eIF-2 (complexed to GTP), and the mRNA by eIF-4E (which binds to the 5 cap), eIF-4G (which binds to both eIF-4E at the 5 cap and PABP at the 3 poly-A tail), eIF4A, and eIF-4B. The ribosome then scans down the mRNA to identify the first AUG initiation codon. Scanning requires energy and is accompanied by ATP hydrolysis. When the initiating AUG is identified, eIF-5 triggers the hydrolysis of GTP bound to eIF-2, followed by the release of eIF-2 (complexed to GDP) and other initiation factors. The 60S ribosomal subunit then joins the 40S complex.
Elongation Prokaryote Ribosome has three tRNA-binding sites, designated P (peptidyl), A (aminoacyl), and E (exit). initiating N-formylmethionyl tRNA is positioned in the P site, leaving an empty A site. Second aminoacyl tRNA (e.g., alanyl tRNA) is then brought to the A site by EF-Tu (complexed with GTP. Following GTP hydrolysis, EF-Tu (complexed with GDP) leaves the ribosome, with alanyl tRNA inserted into the A site. Peptide bond is then formed, resulting in the transfer of methionine to the aminoacyl tRNA at the A site.Ribosome then moves three nucleotides (1 codon) along the mRNAtranslocates the peptidyl (Met-Ala) tRNA to the P site and the uncharged tRNA to the E site, leaving an empty A site ready for addition of the next amino acid. Translocation is mediated by EF-G, coupled to GTP hydrolysis.Process similar in eukaryote expcept name of EF in sukaryote differ. Termination A termination codon (e.g., UAA) at the A site is recognized by a release factor rather than by a tRNA. The result is the release of the completed polypeptide chain, followed by the dissociation of tRNA and mRNA from the ribosome.
You might also like
- TRANSLATIONDocument16 pagesTRANSLATIONkhushboo bhardwajNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument1 pageTranslationGianne AbcedeNo ratings yet
- Translation in ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesTranslation in ProkaryotesAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Protien Synthesis Elongation & TerminationDocument14 pagesProtien Synthesis Elongation & TerminationvesascNo ratings yet
- Translation: The Synthesis of Polypeptides Using Mrna TemplatesDocument4 pagesTranslation: The Synthesis of Polypeptides Using Mrna TemplatesMudjaijah draNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Translation NotesDocument9 pagesCentral Dogma: Translation NotesRomel Greg TulangNo ratings yet
- translation1Document68 pagestranslation1Disha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Translation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020Document1 pageTranslation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020ADIKKI ANOOHYANo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument2 pagesTranslationYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- Translation 30th March 2009Document16 pagesTranslation 30th March 2009api-26794308No ratings yet
- Translation: The Last Stage of Central DogmaDocument10 pagesTranslation: The Last Stage of Central DogmaChandu Kishore KalloniNo ratings yet
- 2022-05-15 L8 - Protein SynthesisDocument64 pages2022-05-15 L8 - Protein SynthesisTamara ElyasNo ratings yet
- L5-6 Translation in ProkaryotesDocument17 pagesL5-6 Translation in ProkaryotesArchana BhartiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Translation MechanismDocument22 pagesProkaryotic Translation MechanismManoj JoshiNo ratings yet
- Translation New1Document43 pagesTranslation New1Vishal KalebarNo ratings yet
- TRANSLATIONDocument19 pagesTRANSLATIONUsha SuthersonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Chemistryprize2009 PDFDocument24 pagesAdvanced Chemistryprize2009 PDFJeremy GordonNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 6 TranslationDocument31 pagesMB Chapter 6 TranslationMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- SYMC Biochemistry Translation of mRNA into ProteinDocument46 pagesSYMC Biochemistry Translation of mRNA into ProteinPascal TurksonNo ratings yet
- Translation - IDocument35 pagesTranslation - ISahil RanaNo ratings yet
- Ekspresi Gen PDFDocument36 pagesEkspresi Gen PDFainulavidaNo ratings yet
- Lec. 6Document10 pagesLec. 6Dr. Mohamed ShamsNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 12 TranslationDocument17 pagesLECTURE 12 TranslationAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationDocument4 pages10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationWidya NingsiNo ratings yet
- The Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesThe Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document63 pagesLesson 5charith chiranthaNo ratings yet
- ActiveDocs - Biochemistry Review Block IIDocument145 pagesActiveDocs - Biochemistry Review Block IIjavierNo ratings yet
- Translation: Presented By: Mrs. Priyanka Tyagi PGT (Biology) Kendriya Vidyalaya (Dogra Lines) Meerut CanttDocument17 pagesTranslation: Presented By: Mrs. Priyanka Tyagi PGT (Biology) Kendriya Vidyalaya (Dogra Lines) Meerut CanttKumar Munendra PrfNo ratings yet
- How Protien Is Being SynthesizedDocument5 pagesHow Protien Is Being SynthesizedMG Untalan BauzonNo ratings yet
- Translation Project OverviewDocument12 pagesTranslation Project OverviewNEET STUDIESNo ratings yet
- Presentation of BiochemistryDocument19 pagesPresentation of BiochemistryAnant kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Translation: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocument28 pagesTranslation: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarmskikiNo ratings yet
- MBII - L23 - Translation 2Document9 pagesMBII - L23 - Translation 2Miles NsgNo ratings yet
- 13 Miller Chap 4b LectureDocument21 pages13 Miller Chap 4b LectureGerone Tolentino AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Translation) - Mechanism and Control in Pro - and Eukaryotes.-3Document9 pagesProtein Synthesis (Translation) - Mechanism and Control in Pro - and Eukaryotes.-3carlottabovi28No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Synthetases, Protein Factors Involved in Initiation Elongation and TerminationDocument41 pagesProtein Synthesis: Synthetases, Protein Factors Involved in Initiation Elongation and TerminationAdith SaiNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Sharma XII - A Biology Investigatory Project - TranslationDocument24 pagesUtkarsh Sharma XII - A Biology Investigatory Project - TranslationUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument7 pagesTranslationFathimaNo ratings yet
- Transcription &translation: Mol. Biology Lec-4 TranscriptionDocument12 pagesTranscription &translation: Mol. Biology Lec-4 TranscriptionAhmed Ali AssafNo ratings yet
- Transcriptiontranslation 170210171328Document34 pagesTranscriptiontranslation 170210171328Farah B. BtoushNo ratings yet
- The Translation: Translation Is A Process by Which The Genetic Code Contained Within An mRNADocument5 pagesThe Translation: Translation Is A Process by Which The Genetic Code Contained Within An mRNAShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Genetic Codon: 3 NucleotidesDocument25 pagesGenetic Codon: 3 Nucleotidesmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument3 pagesTranslationmeryjuvelhNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument90 pagesTranslationspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Bio Short Notes FinalDocument5 pagesBio Short Notes FinalMUHAMMAD HAFIZ FAZRISHAH BIN JEFFRY KIMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 GeneticsDocument12 pagesChapter 6 GeneticsAmer ToutonjiNo ratings yet
- Translation: The Process of Protein SynthesisDocument12 pagesTranslation: The Process of Protein SynthesisHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Biology - Protein SynthesisDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Biology - Protein SynthesisShubham MauryaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein SynthesisabdullaNo ratings yet
- Translation AnoverviewDocument32 pagesTranslation AnoverviewshitalchandrasitNo ratings yet
- METAB TranslationDocument23 pagesMETAB TranslationCHIBUIKE DANIELNo ratings yet
- Post-Transcriptional Modification: An Overview of mRNA ProcessingDocument20 pagesPost-Transcriptional Modification: An Overview of mRNA ProcessingZain YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocument20 pagesPost Transcriptional ModificationZain YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Translation and Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument51 pagesTranslation and Regulation of Gene ExpressionP. Jacksen Sam PaulNo ratings yet
- Translation of mRNA: 3 Steps of Initiation, Elongation and TerminationDocument1 pageTranslation of mRNA: 3 Steps of Initiation, Elongation and TerminationJana OgnjanovskaNo ratings yet
- Translation in Prokaryotes: The Molecular StepsDocument48 pagesTranslation in Prokaryotes: The Molecular StepsFisyaNo ratings yet
- From Dna To ProteinDocument6 pagesFrom Dna To ProteinMadona BadoevNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument2 pagesTranslationneha agarwalNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code Translation ExplainedDocument17 pagesGenetic Code Translation Explainedahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument9 pagesStem CellsTiara HassanNo ratings yet
- Human CloningDocument6 pagesHuman CloningTiara HassanNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Cancer StatisticsDocument136 pagesMalaysia Cancer Statisticsdigital896100% (1)
- The Birth of Dolly The Sheep Was A Major Milestone in ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Birth of Dolly The Sheep Was A Major Milestone in ScienceTiara HassanNo ratings yet