Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cable Fault
Uploaded by
Yasin YusoffCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cable Fault
Uploaded by
Yasin YusoffCopyright:
Available Formats
3/7/2011
CABLE FAULTS
INTRODUCTION
Cable fault is referring to something that occurs current cant flow smoothly. It is because open circuit or short circuit that means the current flow is high value. Most faults are caused by dampness in the paper insulation of the cable due to porous or otherwise damaged lead sheath. The causes of damage to the lead sheath are: crystallization of the lead through vibration; chemical action on the lead when buried in the earth and insufficiently protected; and mechanical damage.
Main equipment to determine cable fault is ohmmeter. Beside that, a few test can be done to determine cable faults such as: 1. Continuity Test 2. Insulation Resistance Test
3/7/2011
TYPES OF CABLE FAULTS The faults which are most likely to occur in the cables are:1. Ground or Earth Faults (Break-down of cable insulation) When the insulation of the cable gets damaged, the current starts flowing from core to earth or to cable sheath. Short Circuit Faults When the insulation between two cables or between two cores of a multicore cable gets damaged, the current starts flowing from one cable to another cable or from one core to another core of a multi-core cable directly (without passing through load) Open Circuit Faults When the conductor of a cable is broken or joint is pulled out there is no current in the cable.
2.
3.
PROCEDURE TO FIND CABLE FAULT To find the cable faults, it has four steps, that is:1. Testing a. Continuity Test open circuit faults b. Insulation Test short circuit faults 2. Locating cable fault test from terminal cables To find length of faults from testing station 3. Confirmation fault point test To find actual location faults 4. Repair the fault
3/7/2011
CABLE FAULTS TEST Continuity Test Continuity test is to checking open circuit of cable faults. Usually, this test uses a bell and battery or multimeter. This test is dividing to two types, that is: 1. Short alignment 2. Long alignment
Short Alignment Using a bell and battery. This test is used for conduit types. For testing CC 1 cables, a connection is jointed between C and C1 through a bell and battery. If a bell ringing, the cable in continues condition, and the cable is marked with C1, if the bell not ringing, the cable is not in continues condition. For A and B cable, the same method is used to test cable condition.
Figure 7.1: Short alignment for Continuity Test
3/7/2011
Long Alignment
Figure 7.2: Long alignment for Continuity Test
Figure 7.2, the method is suitable to use for long cable. For cable A, B and C, choose a pair of cable, for example cable A and B will be connected with tester while the end of the same cable with short circuit. If the test shows an open circuit, the end of the cable will change with another pair and the circuit will test again. If a low reading is detected, so the cables are label with A1 or B1. Then, connect one of the cables with another cable for example cable A and B, and test with the same method. If reading is low, so cable A and C will detect and right. Thus, the cable will label clearly. The same method can be done for another cable in the same alignment.
3/7/2011
Insulation Resistance Test Insulation resistance is resistance that measured in ohm units between live part of equipment and earth for installation. Resistance will measured through insulation that covered conductor. Insulation Resistance Test Used to test short circuit and thickness of insulator. One of the equipment to short circuit test is insulator resistance tester. In this test, a few tests on installation must be made before connect to supply.
Voltage test Need to test the voltage that used for Insulation resistance test. If the used voltage is DC voltage, it must less than two times normally DC voltage and if the used voltage is AC voltage, it must less than two times normal Vrms; but not more than 500v for medium voltage circuit. Earth Installation test The test is made with all fuses stay at their place. The main switch must be switch off. Switch off all lamps and test it by separately. Insulation that measured to the earth must less than 1M and range for the equipment made in difference must less than 0.5M to the earth and 0.5M between polar and phase.
3/7/2011
Figure 7.3 shown connections for insulation resistance to earth testing 2 wires installation that finish with other lamp and feel off other equipment. Both of the cable to main switch twist together and connected to line terminal at ohmmeter. Earth terminal for ohmmeter connect to user earthing. Figure 7.3: Insulation resistance test for finish installation The terminals for two way switches must be connected together for a few times.
Heating equipment shall be tested separately, and Figure 4 shows an example of tests made on the electric kettle.
Figure 4: Insulation Resistance Testing of Electric Kettle
3/7/2011
Testing between two conductor. Connect to pole or phase supply and between conductors to other pole or phase supply. Insulation resistance must be less than 1M. Figure 7.5 is an example of insulation resistance test between conductors.
Figure 7.5: Testing between conductors for 2 cables of single installation
LOCALIZATION CABLE FAULT TEST Murray loop test, Varley loop test and Pulse Echo test are simple and basic method to localize cable fault testing. This method used basic equipment that obtained easily. These tests are performed for the location of either an earth fault or short circuit fault in underground cable. In these tests the resistance of fault does not affect the results obtained except when the resistance of fault is very high. There are two loop tests usually used and are known as Murray Loop and Varley Loop Test. These tests emply the principle of Wheatstone bridge.
3/7/2011
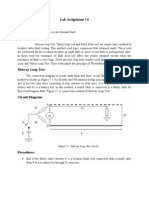
Murray Loop Test The connection diagrams to locate earth fault and short circuit fault by Murray loop test method are shown in Figure 7.6 respectively. As already said Wheatstone bridge principle is used in these tests. P and Q are two ratio arms consisting of step resistors or slide wire, G is a galvanometer, E is a battery and S1 is a battery key. In this method, a sound cable is connected to a faulty cable for find actual happen fault. Figure 7.6 is connection method of Murray Loop Test.
Figure 7.6: Murray Loop Test Circuit.
3/7/2011
Procedures:
End of the faulty cable (assume F is a location fault) was connected with a sound cable from F to b location test through D connector. At location test, end of cable a connected to b through a galvanometer and S1 switch. Bridge is balanced by adjusting the resistances of ratio arms P and Q until the galvanometer indicates zero. Assume the sound and faulty cable have same cross-section and lenght, thereby r /m is same.
In balanced condition of bridge:
If L be known, so Lx can be calculate, that is distance of cable fault from test station.
3/7/2011
If L and r of sound and faulty cable is not same, so the formula above will be change. Assume r = resistance/lenght unit of sound cable L = length of sound cable
Example: Murray loop is a variation of the Wheatstone bridge is used to determine the location of the shorted two wires between them. (i) Refer to the diagram below, show the following equation when equilibrium.
(ii) Calculate the distance of fault from a test station where the balance is found when L1 = 50km, L2 = 100km, R1 = 3.3 / m, R2 = 10 /m, A/B = 8/1
10
3/7/2011
Varley Loop Test In this test also a sound cable is required in addtion to the existing cable. The circuit diagrams to determine the location of ground fault and short circuit fault by method of Varley loop tests are shown Figure below,
11
3/7/2011
When the switch is in position (a), S is adjusted so that the bridge resistors in a balanced situation. Suppose that in a balanced situation is found S = S1.
When the switch is in position (b), S is adjusted so that the bridge resistors in a balanced situation. Suppose that in a balanced situation is found S = S2
Solve equation (1) and (2)
Example: For cable fault test using Varley loop, when the switch is placed in position 1, the variable resistance, S is adjusted to a value of 50 to achieve a balance bridge. When the switch is placed at 2, equilibrium occurs when S is 35. Find the distance fault location from the source if the cable is 25km long, given fault cable resistance is 15/km, P = Q = 150 and 200 .
12
3/7/2011
PULSE ECHO TEST
Cable line in underground has a coating act as absorption or moisture blocker into insulator cable or main cable conductor. This moisture or underground water will make problem because the water usually acided and grounded cable will be fault. Pulse Echo Test is to find fault cable in grounded coating cable with identified the location that directly detect with ground.
Procedure: Connect a battery at end to end faulty cable. (The current will flow along conductor to location fault, from location fault to earth and then from earth to other terminals battery. Current can be imaging like it flowing out from location fault to surround ways.) Put voltmeter probe at two points such as in Figure 7.10. Positive or negative value will be obtained, it depend on flowing current in ground that fault happen.
13
3/7/2011
Move the voltmeter along the cable until the value of current change ways. the point that the current changes the way shown actual location faulty happen.
14
You might also like
- Project: Introduction To Faults in CablesDocument8 pagesProject: Introduction To Faults in CablesNadish FatimaNo ratings yet
- How To Locate Faults in CablesDocument9 pagesHow To Locate Faults in CablesAkhilesh HarishmaNo ratings yet
- Cesc HTDocument4 pagesCesc HTAbhijit Guha RoyNo ratings yet
- Working: The Faulty Core Is Looped With Sound Core of The Same Cross Sectional AreaDocument3 pagesWorking: The Faulty Core Is Looped With Sound Core of The Same Cross Sectional AreaHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission 4Document7 pagesElectrical Power Transmission 4FaisalSoNo ratings yet
- LESSON NOTES HeszronDocument7 pagesLESSON NOTES HeszronHezron gibronNo ratings yet
- Cable FaultsDocument7 pagesCable FaultsNh Chuminda YapaNo ratings yet
- Murray Loop Test To Locate Ground FaultDocument2 pagesMurray Loop Test To Locate Ground FaultMohammed Nauman83% (6)
- Electrical Installation Earthing GuideDocument5 pagesElectrical Installation Earthing GuidedestawNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault Location in Power Cables: Fault Classification: Insulation and Resistance MeasurementDocument5 pagesCable Fault Location in Power Cables: Fault Classification: Insulation and Resistance Measurementmherold2No ratings yet
- Loop Tests For Locating Faults in Underground CablesDocument5 pagesLoop Tests For Locating Faults in Underground CablesAbdullah Al AsikNo ratings yet
- Testing Cables for Electrical SafetyDocument8 pagesTesting Cables for Electrical SafetyDiwakar DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault DetectionDocument8 pagesCable Fault DetectionSpring SuperbNo ratings yet
- Underground CablesDocument84 pagesUnderground Cableshaidarkukum5686100% (1)
- Electrical Installation Testing ProceduresDocument10 pagesElectrical Installation Testing ProcedurestemamNo ratings yet
- 4-Procedure Pipe To SoilDocument7 pages4-Procedure Pipe To SoilKhanh DTNo ratings yet
- Testing earth electrodesDocument11 pagesTesting earth electrodesAlliver SapitulaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cable Testing. How Is Cable Testing DoneDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cable Testing. How Is Cable Testing DoneAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- L 4 EEE251 RCL Measurements DMAKDocument37 pagesL 4 EEE251 RCL Measurements DMAKSojolNo ratings yet
- RKlala Doc SubmissionDocument2 pagesRKlala Doc SubmissionAnonymous wfXxOnQddNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1.1. Types of Faults in Cables 1.1.1. Open Circuit FaultDocument23 pagesChapter - 1: 1.1. Types of Faults in Cables 1.1.1. Open Circuit Faultl.maheshNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and SchematicsDocument42 pagesElectrical Symbols and Schematicsapi-384232693% (14)
- Measurement of Insulation Resistance IR Part 1Document5 pagesMeasurement of Insulation Resistance IR Part 1hafizg100% (1)
- What Is Cable Testing. How Is Cable Testing DoneDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cable Testing. How Is Cable Testing DoneNaveed IrshadNo ratings yet
- Quality Wireline - Field Leakage TestDocument3 pagesQuality Wireline - Field Leakage TestADebeliusNo ratings yet
- Cable Testing PDFDocument18 pagesCable Testing PDFusmanNo ratings yet
- XXL, Oct 2011Document5 pagesXXL, Oct 2011emediageNo ratings yet
- Fault Localization in LV CablesDocument6 pagesFault Localization in LV Cableswindreader1No ratings yet
- Blavier Test Board PDU Lab ProjectDocument6 pagesBlavier Test Board PDU Lab ProjectHassan ZiaNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticCompatibilityMethodsAnalysisCircuitsandMeasurementThirdEdition 1 PDFDocument1,151 pagesElectromagneticCompatibilityMethodsAnalysisCircuitsandMeasurementThirdEdition 1 PDFjotaruiz30No ratings yet
- 6/14/02 Chapter 14: Use of Electrical Test Equipment 1/20Document20 pages6/14/02 Chapter 14: Use of Electrical Test Equipment 1/20asfaw getuNo ratings yet
- 6/14/02 Chapter 14: Use of Electrical Test Equipment 1/20Document20 pages6/14/02 Chapter 14: Use of Electrical Test Equipment 1/20LeonardNo ratings yet
- Tran95-Sub Field TestDocument9 pagesTran95-Sub Field Testnellai_guna2008No ratings yet
- S1S2 Eee WSDocument37 pagesS1S2 Eee WShafizrahimmitNo ratings yet
- Shunt Calibration PDFDocument9 pagesShunt Calibration PDFMaxNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Measurement in HV JointsDocument4 pagesPartial Discharge Measurement in HV Jointsจีรศักดิ์ คงบุรีNo ratings yet
- Fluke - How Cables and Connectors Impact Measurement UncertaintyDocument4 pagesFluke - How Cables and Connectors Impact Measurement UncertaintyMatias RamosNo ratings yet
- Describe Methods and Equipment Used For The Various Electrical Test 223.59Document28 pagesDescribe Methods and Equipment Used For The Various Electrical Test 223.59velisbarNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults Incables: Open Circuit FaultDocument4 pagesTypes of Faults Incables: Open Circuit FaultRajNo ratings yet
- Iagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureDocument4 pagesIagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureShredder WardatNo ratings yet
- Cable Engineering in Substation and Power PlantDocument7 pagesCable Engineering in Substation and Power PlantVasudev AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Ieee UcfdDocument5 pagesIeee UcfdPrajwlaNo ratings yet
- Ee Construction MethoologyDocument5 pagesEe Construction MethoologyFennelyn JusayanNo ratings yet
- Tan Delta FAQDocument6 pagesTan Delta FAQDev SwainNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab ManualDocument122 pagesBEEE Lab ManualVikram Kamboj75% (4)
- Lab Answers p1Document10 pagesLab Answers p1api-343575651No ratings yet
- Xlpe Cable Commissioning Test Procedure Following Iec StandardDocument5 pagesXlpe Cable Commissioning Test Procedure Following Iec StandardAkd Deshmukh100% (2)
- Underground Cable Fault DetectionDocument4 pagesUnderground Cable Fault DetectionAnonymous HyOfbJ6100% (1)
- MeggerDocument10 pagesMeggershahanbashaNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Water Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorFrom EverandWater Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Electric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusFrom EverandElectric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Pfeiffer - Vacuum PumpsDocument160 pagesPfeiffer - Vacuum PumpsTrAm@nOis100% (1)
- Electrical Measuring & Test InstrumentsDocument42 pagesElectrical Measuring & Test InstrumentsMichael Parohinog GregasNo ratings yet
- MaintenanceDocument1 pageMaintenanceYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Measurement AccuracyDocument29 pagesChapter 4 - Measurement AccuracyYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Your SwitchgearDocument4 pagesMaintaining Your SwitchgearYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- PSD..UNIT 3..motor DrivesDocument38 pagesPSD..UNIT 3..motor Drivessatish reddyNo ratings yet
- Earhting Definition JiwinnieDocument48 pagesEarhting Definition JiwinnieYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Eee PC User ManualDocument62 pagesEee PC User ManualAli BoerhannoeddinNo ratings yet
- CalibrationDocument64 pagesCalibrationYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Unit 1aDocument20 pagesUnit 1aYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Accessories & ToolsDocument9 pagesAccessories & ToolsYasin YusoffNo ratings yet
- Sporty 7-Seater CrossoverDocument6 pagesSporty 7-Seater CrossoverYasin YusoffNo ratings yet