Professional Documents
Culture Documents
About Leopard
Uploaded by
Riswan Hanafyah HarahapCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
About Leopard
Uploaded by
Riswan Hanafyah HarahapCopyright:
Available Formats
EX T
NE T
CLICK
HERE
General Description Physical characteristics Biology and Behavior
Food
Hunting
Credits
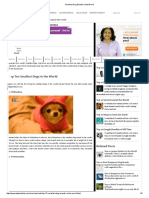
The leopard (Panthera pardus, is a member of the Felidae Familyand the smallest of the four bigs cat" in the genus Panthera, the other three being the tiger, lion and jaguar. Once distributed across eastern and southern Asia and Africa, from Siberia to South Africa, the leopard's range of distribution has decreased radically because of hunting and loss of habitat
The leopard is an agile and stealthy predator. Although smaller than other members of the Panthera genus, the leopard is still able to take large prey given its massive skull that facilitates powerful jaw muscles.Its body is comparatively long for a cat and its legs are short.Head and body length is between 125 and 165 cm (49 and 65 in) and the tail reaches 60 to 110 cm (24 to 43 in). Shoulder height is 45 to 80 cm (18 to 31 in). The muscles attached to the scapula are exceptionally strong, which enhances the leopard's ability to climb trees.
The leopard is known for its ability in climbing, and it has been observed resting on tree branches during the day, dragging its kills up trees and hanging them there, and descending from trees headfirst.It is a powerful swimmer, although not as strong as some other big cats, such as the tiger. The leopard is also very agile, and can run at over 58 kilometres per hour (36 mph), leap over 6 metres (20 ft) horizontally and jump up to 3 metres (9.8 ft) vertically.Leopards produce a number of vocalizations, including grunts, roars, growls, meows and "sawing" sounds
Leopards are generally considered to be noctural. However, the animal has primarily been studied in open savannah habitats, which may have biased common descriptions. Activity level may vary depending on the habitat and the type of prey it hunts. For instance, radio-tracking and scat analysis in West Africa has found that rainforest leopards are more likely to be diural and crepuscular. Forest leopards are also more specialized in prey selection and exhibit seasonal differences in activity patterns.
Leopards eat small hoofstock such as gazelle, impala, deer and wildebeast. On occasion, they may also hunt monkeys, rodents and birds.
Leopards are versatile, opportunistic hunters. In the open savanna, they are most successful when hunting between sunset and sunrise, though they may hunt during the day, especially in forest areas when they have the advantage of being hidden by dense brush or cloudy skies.The leopard stalks its prey silently and at the last minute pounces on its prey and strangles its throat with a quick bite. Leopards often hide their kills in dense vegetation or take them up trees, and are capable of carrying animals up to three times their own weight this way.[The leopard is the only big cat known to carry its prey up into a tree.
You might also like
- Author Guidelines: Halu Oleo Legal Research (HOLRESCH) Is A Main Headings of ManuscriptsDocument2 pagesAuthor Guidelines: Halu Oleo Legal Research (HOLRESCH) Is A Main Headings of ManuscriptsRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About PinguinDocument12 pagesAbout PinguinRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- HKIDocument19 pagesHKIRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About ScorpionDocument29 pagesAbout ScorpionRiswan Hanafyah Harahap100% (1)
- English Exercise: Created By: Name: Dessi Andriani Class: XI - IA.2Document8 pagesEnglish Exercise: Created By: Name: Dessi Andriani Class: XI - IA.2Riswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About BatDocument16 pagesAbout BatRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About AnoaDocument8 pagesAbout AnoaRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- Camel: Created By: Miftahul Munir Rsbi Xi-Ia-2Document8 pagesCamel: Created By: Miftahul Munir Rsbi Xi-Ia-2Riswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About HyenaDocument24 pagesAbout HyenaRiswan Hanafyah Harahap0% (1)
- About Pink DolphinDocument12 pagesAbout Pink DolphinRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- About Flying LizardDocument11 pagesAbout Flying LizardRiswan Hanafyah HarahapNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Financial Returns To Industry From The Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Program - 2011Document96 pagesFinancial Returns To Industry From The Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Program - 2011shootingcouncilNo ratings yet
- English Mandinka DictionaryDocument9 pagesEnglish Mandinka DictionaryAlero ViteNo ratings yet
- 2009 FishingDocument68 pages2009 FishingAdnan GrebovićNo ratings yet
- Back To Basic: How To Train Like Primitive Man - StrongFirstDocument13 pagesBack To Basic: How To Train Like Primitive Man - StrongFirstManjeet ParasharNo ratings yet
- TOEFL ReadingDocument7 pagesTOEFL ReadingBla100% (1)
- My Shetland Sheepdog PuppyDocument4 pagesMy Shetland Sheepdog Puppyapi-213368444No ratings yet
- Mahabharata Story Arjuna ArcheryDocument3 pagesMahabharata Story Arjuna ArcherypriyamanidNo ratings yet
- 2009 Barska Binoculars, Riflescopes Optics CatalogDocument96 pages2009 Barska Binoculars, Riflescopes Optics Catalogjoernet100% (1)
- Easton ChartDocument1 pageEaston ChartAl Hadid DPMNo ratings yet
- .308 Winchester: 1 Cartridge Dimensions 2 Usage and PerformanceDocument4 pages.308 Winchester: 1 Cartridge Dimensions 2 Usage and PerformancevnfloreaNo ratings yet
- Reading - Fox Hunting in BritainDocument3 pagesReading - Fox Hunting in BritainViktor VasNo ratings yet
- Animal Facts For KidsDocument2 pagesAnimal Facts For Kidskamarb31No ratings yet
- When The Tiger Was King - Ruskin BondDocument63 pagesWhen The Tiger Was King - Ruskin BondUmang Aggarwal0% (1)
- Bow Construction 1999Document37 pagesBow Construction 1999arami7373100% (3)
- Native American Internet Scavenger HuntDocument26 pagesNative American Internet Scavenger Huntapi-299408675No ratings yet
- Sierra 7mm08 Reloading DataDocument9 pagesSierra 7mm08 Reloading DataBIBI1978No ratings yet
- EthengarDocument102 pagesEthengarbroodhunter2No ratings yet
- ExcerptDocument18 pagesExcerptGraciela AndreattaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Intermediate Achievement Test 3 (Units 7-9) : Listening GrammarDocument1 pagePre-Intermediate Achievement Test 3 (Units 7-9) : Listening GrammarAndrewKanischev100% (2)
- 2011 ASASportfishing in America Report January 2013 PDFDocument12 pages2011 ASASportfishing in America Report January 2013 PDFyeokeehuiNo ratings yet
- FishDocument5 pagesFishNirmala JosephineNo ratings yet
- Smallest Dog Breeds in The WorldDocument5 pagesSmallest Dog Breeds in The WorldtourisminfopediaNo ratings yet
- Factual Report LionDocument2 pagesFactual Report LionMuhammad Azhar HadiNo ratings yet
- How and Why Wonder Book of Extinct AnimalsDocument52 pagesHow and Why Wonder Book of Extinct Animalskett8233100% (5)
- Calvert Cliffs State Park BrochureDocument2 pagesCalvert Cliffs State Park BrochureMaryland State ParksNo ratings yet
- Feinwerkbau 2017Document27 pagesFeinwerkbau 2017Peter DavidsonNo ratings yet
- A To Z Team Building ActivitiesDocument6 pagesA To Z Team Building ActivitiesSvetlin RanguelovNo ratings yet
- Frank & Frank Decoy Auction Fall 2011Document68 pagesFrank & Frank Decoy Auction Fall 2011pirates96No ratings yet
- Wolf Cubs HandbookDocument0 pagesWolf Cubs Handbooka172678No ratings yet