Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA 2 EIGRP Skills Based Assessment Exam Answered
Uploaded by
Izza PachecoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA 2 EIGRP Skills Based Assessment Exam Answered
Uploaded by
Izza PachecoCopyright:
Available Formats
Exploration Routing: EIGRP Skills Based Assessment -Answered
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Subnet an address space with given requirements Assign appropriate addresses to interfaces and document them in the address table below Cable the network according to the diagram Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state. Configure EIGRP routing on all routers. Configure and propagate a default static route. Verify EIGRP operation. Test and verify full connectivity. Reflect upon and document the network implementation.
Scenario
In this lab, you will be given a summarized address which you will use to create an efficient addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. A combination of EIGRP and a static default route will be
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 4
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts
Exploration Routing: EIGRP Skills Based Assessment
required so that hosts on networks not directly connected can communicate. You have completed this lab when each host can ping the each other.
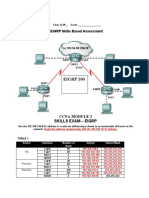
Task 1: Create an Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Use the 192.168.156.0/22 address to create an addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. Begin the address assignments with the 192.168.157.0 address. Document all subnet addresses in Table 1. Table 1 Device HQ Interface Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/1 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/0 Number of Hosts 90 /25 60 /26 2 /30 2 /30 30 /30 60 /26 2 /30 128 /24 60 /26 2 /30 Subnet Subnet Mask
Remote1
Remote2
192.168.158.0 192.168.158.12 8 192.168.159.96 192.168.159.10 0 192.168.159.64 192.168.158.19 2 192.168.159.96 192.168.157.0 192.168.159.0 192.168.159.10 0
255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252
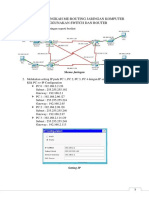
Step 2: Document router interface and PC addresses in Table 2. Assign the last usable IP address of each subnet to each PC. Table 2 Device HQ Interface Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/1 S0/0/0 Lo0 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0/0 Ethernet Ethernet Ethernet Ethernet Ethernet IP Address 192.168.158.1 192.168.158.129 192.168.159.97 192.168.159.101 189.54.69.254 192.168.159.65 192.168.158.193 192.168.159.98 192.168.157.1 192.168.159.1 192.168.159.102 192.168.158.126 192.168.158.190 192.168.159.94 192.168.158.254 192.168.159.62 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.192 Default Gateway 0.0.0.127 0.0.0.63 0.0.0.3 0.0.0.3 0.0.0.3 0.0.0.31 0.0.0.63 0.0.0.3 0.0.0.255 0.0.0.63 0.0.0.3 192.168.158.1 192.168.158.129 192.168.159.65 192.168.158.193 192.168.159.1
Page 2 of 4
Remote1
Remote2 PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts
Exploration Routing: EIGRP Skills Based Assessment
PC6
Ethernet
192.168.157.254
255.255.255.0
192.168.157.1
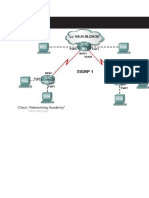
Step 3: Cable and configure the network based on the diagram and the addressing scheme you created in the previous step. Assign the last usable host address of each subnet to each PC. Instructors Initial ______
Task 2: Configure EIGRP with Process ID 1 using Wildcard Masks.
Step 1: Configure EIGRP on the HQ router and advertise all directly connected networks except the loopback interface. Advertise the network along with a wildcard mask for the appropriate subnet. Step 2: Configure EIGRP on the Remote1 router and advertise all directly connected networks. Advertise the network along with a wildcard mask for the appropriate subnet. Step 3: Configure EIGRP on the Remote2. Advertise the network along with a wildcard mask for the appropriate subnet.
HQ(config)#router eigrp 1 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.158.1 0.0.0.127 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.158.129 0.0.0.63 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.97 0.0.0.3 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.101 0.0.0.3 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.102 0.0.0.3 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.98 0.0.0.3 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.65 0.0.0.31 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.158.193 0.0.0.63 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.157.1 0.0.0.255 HQ(config-router)#network 192.168.159.1 0.0.0.63 HQ(config-router)#end interface loopback0 ip address 189. so shut end
Instructors Initial ______
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 4
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts
Exploration Routing: EIGRP Skills Based Assessment
Task 3: Discontiguous Networks.
Step 1: Configure each router so that subnet mask information about each network is propagated within the EIGRP updates. Step 2: Verify that each router has a path to each network in the autonomous system. router eigrp 1 no auto-summary
Instructors Initial ______
Task 4: Static Default Route
Step 1: Configure a static default route on the HQ router to the loopback interface. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 loopback0 Step 2: Propagate the static default route in the HQ routing update. router eigrp 1 redistribute static Step 3: Verify that the static default route is received by the Remote1 and Remote2 routers. show ip route Step 4: Ping the loop back interface on the ISP router from each host. Was PC1 successful? ___________ Was PC2 successful? ___________ Was PC3 successful? ___________ Was PC4 successful? ___________ Was PC5 successful? ___________ Was PC6 successful? ___________ If you are not successful, troubleshoot configurations using the appropriate show and debug commands.
Instructors Initial ______
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- EIGRP Skills AssessmentDocument2 pagesEIGRP Skills AssessmentquestionsremainthesameNo ratings yet
- Final Term Exam Data Communications LABDocument5 pagesFinal Term Exam Data Communications LABWOLFSNo ratings yet
- TRS2251 Routing and Switching: Name: ID No: Date: Lab 3: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design (3 %)Document5 pagesTRS2251 Routing and Switching: Name: ID No: Date: Lab 3: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design (3 %)Kavilan RrNo ratings yet
- CCNA ExplorationDocument9 pagesCCNA ExplorationCesc FabregabNo ratings yet
- 12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Use Documentation To Solve IssuesDocument3 pages12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Use Documentation To Solve Issuesalexismoto1230% (1)
- Packet Tracer Exercise 7.1 | Configuring NAT and PATDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer Exercise 7.1 | Configuring NAT and PATbrian sebastianNo ratings yet
- Solution For Lab 4.6.1Document5 pagesSolution For Lab 4.6.1Mouhamad BazziNo ratings yet
- 12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The NetworkDocument5 pages12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The NetworkHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Subnetting ActivityDocument5 pagesSubnetting ActivityaldreymartirezggNo ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Document16 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Deux AmisNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.6.2 Challenge Security ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 4.6.2 Challenge Security ConfigurationConfucius WillsonNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDocument5 pagesSubnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramJermyn G EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 9 6 2 InstructorDocument8 pagesE2 Lab 9 6 2 Instructordiverron100% (1)
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument10 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorOkta WijayaNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1 PT Curso 2Document5 pagesActividad 1 PT Curso 2jacastillo68No ratings yet
- Ccna2 Chap6 Lab 6.4.1Document3 pagesCcna2 Chap6 Lab 6.4.1jhe04No ratings yet
- Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayDocument9 pagesLab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayMartin O'grady0% (1)
- Enrutamiento DinamicoDocument6 pagesEnrutamiento DinamicoQuest Play (COREFRE277)No ratings yet
- FINAL EXAmDocument11 pagesFINAL EXAmAriel CalapitNo ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMDocument22 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMlokuras de la vidaNo ratings yet
- 22 Egi Wiratama Packet TracerDocument7 pages22 Egi Wiratama Packet TracerEgik SamsiahNo ratings yet
- E4 PTAct 4 7 1Document2 pagesE4 PTAct 4 7 1jeroberts01No ratings yet
- Tutorial Routing 4 RouterDocument5 pagesTutorial Routing 4 RouterIlhamNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Komputer: SEPTEMBER 1, 2017Document11 pagesJaringan Komputer: SEPTEMBER 1, 2017Aulia Ahlam MardhotillahNo ratings yet
- 12.6.2 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Use Documentation To Solve IssuesDocument6 pages12.6.2 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Use Documentation To Solve IssuesErika ProañoNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot LAN Connectivity IssuesDocument5 pagesTroubleshoot LAN Connectivity IssuesCao Bằng Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- 12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The NetworkDocument12 pages12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The Networkafq. abdlyNo ratings yet
- RIP RouteDocument2 pagesRIP RoutesampodesuyooNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.5.3: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 3: Topology DiagramDocument11 pagesLab 8.5.3: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 3: Topology DiagrambusmaniakNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementFrom EverandEthernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Broadband Wireless Mobile: 3G and BeyondFrom EverandBroadband Wireless Mobile: 3G and BeyondWillie W. LuNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: From the Physical Layer to Communication, Computing, Sensing and ControlFrom EverandWireless Networks: From the Physical Layer to Communication, Computing, Sensing and ControlNo ratings yet
- Profile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997From EverandProfile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997No ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- Network Infrastructure and Architecture: Designing High-Availability NetworksFrom EverandNetwork Infrastructure and Architecture: Designing High-Availability NetworksNo ratings yet
- IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks: Systems, Architectures, and ProtocolsFrom EverandIP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks: Systems, Architectures, and ProtocolsNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Virtual Private Networking: A Construction, Operation and Utilization GuideFrom EverandVirtual Private Networking: A Construction, Operation and Utilization GuideNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer Local Networks ReportFrom EverandPersonal Computer Local Networks ReportNo ratings yet
- Token Ring Technology ReportFrom EverandToken Ring Technology ReportNo ratings yet
- Multicast Communication: Protocols, Programming, & ApplicationsFrom EverandMulticast Communication: Protocols, Programming, & ApplicationsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamFrom EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Practical Industrial Data Networks: Design, Installation and TroubleshootingFrom EverandPractical Industrial Data Networks: Design, Installation and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet