Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The Lungs
Uploaded by
Sarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The Lungs
Uploaded by
Sarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanCopyright:
Available Formats
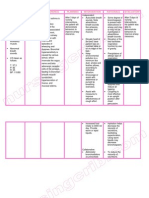
Assessment Subjective Cues: Objective Cues: Presence of Body Weakness GCS= 11 NGT ET Tube RR= 15bpm Crackles Left
s Left base of the lungs Symmetrical Chest Expansion PNSS 1L x KVO Right Arm 1314gtts Ongoing Blood Transfusion at Left arm For RECHECKING of Hourly monitoring of O2 Saturation ABG to be followed Chest X-ray Result of
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective airway clearance related to the accumulation of secretions as evidence by decrease in respiratory rate and NGT and ET tube attached and crackles at the left base of the lungs
Inference Irritant during inhalation due to microbial agents Inflammatory Responses Tissue Injury Vascular Responses Increase production of secretions Airway constriction Dyspnea
Planning After 8 hours of nursing interventions the patient secretions shall be mobilized and airway shall be maintained to be free of secretions as evidence by decrease secretions and clear lung sounds during auscultation
Nursing Interventions Independent: 1. Assess patient in semi fowlers position 2. Turn Patient side to side Q2 3. Perform Chest Physiotherapy(CPT) 4. Assess rate of respirations and chest movement
Rationale 1. Promoting chest expansion 2. It helps to liquefy the secretions by mobilizing 3. Is used to mobilize or loose secretions in the lungs 4. symmetrical chest movement are frequently present because of discomfort of moving chest wall or fluid in the lungs 5. Decrease airflow occurs in areas consolidated of fluid. Crackles can also occur in consolidated areas that can be heard during inspiration/expiration in response in fluid accumulation or thick secretions 1. To treat or prevent
Evaluation After 8 hours of nursing interventions the patient secretions shall be mobilized and airway shall be maintained to be free of secretions as evidence by decrease secretions and clear lung sounds during auscultation
5. Auscultate lung fields To note the areas of decrease airflow and adventitious sounds (Crackles)
Dependent: 1. Administer Salbutamol
Pneumonial Right Lung Smear shows presence of Gram + Cocci in 3 singly and in pairs with abundant leukocytes and fibrins
+ Ipratropium nebulizer Q6 PRN for DOB
bronchospasms and facilitate expectoration of mucus and airway clearance. Mechanism of Action: Salbutamol Inhibits the release of bronchoconstricting agents from mast cells, inhibits microvascular leakage, and enhances mucociliary clearance. Ipratropium It blocks muscarinic cholinergic receptors, Most likely due to actions of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) on intracellular calcium, this result in decreased contractility of smooth muscle. Used to reduce colonization or prophylactic treatment for localized infection process. Mechanism of Action: Azithromycin binds to the 50S subunit of the 70S bacterial ribosomes, and therefore inhibits
2. Administer Meropenem 1gm TIV Q12 and c 500g TIV + Azithromycin 100cc PNSS Q6 via soluset
RNA-dependent protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Meropenem readily penetrates the cell wall of most Grampositive and Gramnegative bacteria to reach penicillin-bindingprotein (PBP) targets. The bactericidal activity of meropenem results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. 3. Suction Secretions PRN Collaborative: 1. Check for Chest CT Scan 2. Take a Specimen for Sputum AFB and Gram Staining Result 3. To facilitate airway clearance 1. To find the cause of lung problem such as DOB and Chest pain. 2. To distinguish presence of infection, identify specific pathogens and influence of the choice of treatment
You might also like
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- Bank NIFTY Components and WeightageDocument2 pagesBank NIFTY Components and WeightageUptrend0% (2)
- Tracking Progress On Child and Maternal Nutrition: A Survival and Development PriorityDocument124 pagesTracking Progress On Child and Maternal Nutrition: A Survival and Development PriorityUNICEF100% (2)
- Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)Document6 pagesInterpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)afalfitraNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaNiel MinatozakiNo ratings yet
- Gas Dehydration (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)Document23 pagesGas Dehydration (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)Tu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsDocument157 pagesLecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsBảo Châu VươngNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215No ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Document182 pagesPhilippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Carl100% (1)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ExampleDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ExampleBrittanyNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- DLP in Health 4Document15 pagesDLP in Health 4Nina Claire Bustamante100% (1)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911No ratings yet
- NCP InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- NCP For StokeDocument5 pagesNCP For StokeMemedNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Multiodular non toxic goiter nursing care planDocument1 pageMultiodular non toxic goiter nursing care plankzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificDocument4 pagesWorksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificCj MayoyoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Document2 pagesRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesAssessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's Diseaseria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Tracheostomy and Intubation Related DysphagiaDocument25 pagesTracheostomy and Intubation Related DysphagiaVikashNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Malignant Pleural Effusion Secondary To Breast CancerDocument4 pagesA Case Study On Malignant Pleural Effusion Secondary To Breast Cancerpauline_almoNo ratings yet
- Methylxanthines and Short-Acting β-Adrenergic Receptor AgonistsDocument11 pagesMethylxanthines and Short-Acting β-Adrenergic Receptor AgonistsMukhammad FakhriNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal: MPT (Cardio Respiratory Disorders)Document14 pagesResearch Proposal: MPT (Cardio Respiratory Disorders)permanaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document6 pagesNCP 1Maedine Urbano-BrionesNo ratings yet
- Anti in Ammatory Effects of Statin in COPD: Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and TuberculosisDocument5 pagesAnti in Ammatory Effects of Statin in COPD: Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and TuberculosiszzakieNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Central Responsibilities of The Nurse ManagerDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Central Responsibilities of The Nurse ManagerSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Ten Good Reasons To Pass The RH Bill NowDocument7 pagesTen Good Reasons To Pass The RH Bill NowSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues NMLDocument22 pagesEthical Issues NMLSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium + CitilDocument4 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium + CitilSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis and Clinical FeaturesDocument30 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis and Clinical FeaturesOrion JohnNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudySarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- E-Cart Meds.Document46 pagesE-Cart Meds.Sarah Ann Jamilla Faciolan100% (1)
- CYSTOCLYSISDocument2 pagesCYSTOCLYSISSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Case Management For LTCS For Non-Reassure Fetal StatutsDocument3 pagesCase Management For LTCS For Non-Reassure Fetal StatutsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Practical Guidelines Blood TransfusionDocument64 pagesPractical Guidelines Blood TransfusionMazen MohamedNo ratings yet
- Aspects of HealthDocument33 pagesAspects of HealthSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- 18 Organizational TheoriesDocument16 pages18 Organizational TheoriesSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- All he has to do is fall for meDocument125 pagesAll he has to do is fall for meLissa MaeNo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCOPD Case PresentationSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Umibilical Cord ProlapseDocument58 pagesUmibilical Cord Prolapsekhadzx100% (3)
- Per Cutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomyDocument25 pagesPer Cutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomySarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Mitigating COVID-19 at Work: Policy Brief 19 May 2021Document21 pagesPreventing and Mitigating COVID-19 at Work: Policy Brief 19 May 2021Desy Fitriani SarahNo ratings yet
- PESO Online Explosives-Returns SystemDocument1 pagePESO Online Explosives-Returns Systemgirinandini0% (1)
- (23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) A Study of The Preload Force in Metal-Elastomer Torsion SpringsDocument6 pages(23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) A Study of The Preload Force in Metal-Elastomer Torsion Springsstefan.vince536No ratings yet
- SQL Guide AdvancedDocument26 pagesSQL Guide AdvancedRustik2020No ratings yet
- PointerDocument26 pagesPointerpravin2mNo ratings yet
- MODULE+4+ +Continuous+Probability+Distributions+2022+Document41 pagesMODULE+4+ +Continuous+Probability+Distributions+2022+Hemis ResdNo ratings yet
- Controle de Abastecimento e ManutençãoDocument409 pagesControle de Abastecimento e ManutençãoHAROLDO LAGE VIEIRANo ratings yet
- 5511Document29 pages5511Ckaal74No ratings yet
- #### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0Document9 pages#### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0MARCONo ratings yet
- Column Array Loudspeaker: Product HighlightsDocument2 pagesColumn Array Loudspeaker: Product HighlightsTricolor GameplayNo ratings yet
- Web Api PDFDocument164 pagesWeb Api PDFnazishNo ratings yet
- DIN Flange Dimensions PDFDocument1 pageDIN Flange Dimensions PDFrasel.sheikh5000158No ratings yet
- Riddles For KidsDocument15 pagesRiddles For KidsAmin Reza100% (8)
- Cushman Wakefield - PDS India Capability Profile.Document37 pagesCushman Wakefield - PDS India Capability Profile.nafis haiderNo ratings yet
- Impact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianDocument15 pagesImpact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianshantashriNo ratings yet
- En dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFDocument24 pagesEn dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFsaroniNo ratings yet
- Book Networks An Introduction by Mark NewmanDocument394 pagesBook Networks An Introduction by Mark NewmanKhondokar Al MominNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Advanced Family PDFDocument39 pagesThe Ultimate Advanced Family PDFWandersonNo ratings yet
- Ir35 For Freelancers by YunojunoDocument17 pagesIr35 For Freelancers by YunojunoOlaf RazzoliNo ratings yet
- Archlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Document16 pagesArchlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Goh Ka WeeNo ratings yet
- Experiences from OJT ImmersionDocument3 pagesExperiences from OJT ImmersionTrisha Camille OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Pom Final On Rice MillDocument21 pagesPom Final On Rice MillKashif AliNo ratings yet
- Surgery Lecture - 01 Asepsis, Antisepsis & OperationDocument60 pagesSurgery Lecture - 01 Asepsis, Antisepsis & OperationChris QueiklinNo ratings yet
- CIT 3150 Computer Systems ArchitectureDocument3 pagesCIT 3150 Computer Systems ArchitectureMatheen TabidNo ratings yet