Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fisiologi Bunyi Jantung
Uploaded by
Keyla Kehara PutriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fisiologi Bunyi Jantung
Uploaded by
Keyla Kehara PutriCopyright:
Available Formats
dr. Ikhlas M.
Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
Fisiologi Bunyi Jantung
aSSaLAMuAikum Hi guysDo u still remember me??OF course u doI knew it!! (pede bgt!!) HeY..pada kuliah ini ga??hayoouwpasti kuliah dOnKZ!!Hm..jujur aja ni, daku susah mendengar kan dengan jelas perkataan dari d. Ikhlas ini..tapi Ill try to elaborate it for u guysso, mohon maaf lahir bathin ya kalo ada kata2 yang ga sempurnaLOH???SO, ComONlet say BASMALAH together!!! Bismillahirrahmaanirrahiim
CONTENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Function of valves in circulation Cardiac cycle Cardiac sounds Physical diagnosis Additional cardiac sounds
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fungsi katup dalam sirkulasi Siklus jantung Bunyi jantung Diagnostik fisik Penambahan bunyi jantung
1. 2. 3. 4.
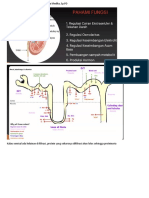
FACTORS NEEDED FOR PROPER CIRCULATION \ 1. Detak jantung yang ritmis untuk menyempurnakan A rhythmically beating heart to tekanan yang dibutuhkan generate the necessary pressure. 2. Kondisi yang baik pada pembuluh darah A proper condition of the blood vessels. 3. Jumlah yang adekuat dalam sirkulasi darah An adequate amount of circulating 4. Suatu mekanisme yang memastikan aliran secara blood. tidak langsung (katup) A mechanism for ensuring unidirectional flow (valves) SIKLUS KERJA JANTUNG (CARDIAC CYCLE)
Cardiac cycle is the period of single contraction (systole) with the ensuing relaxation of the heart (diastole). Siklus jantung merupakan waktu yang diperlukan untuk satu kali kontraksi pada jantung (sistole) dan satu
kali relaksasi pada jantung (diastole).
1. 2. 3. 4.
Inflow phase Isovolumetric contraction Outflow phase Isovolumetric relaxation
1. 2. 3. 4.
Fase inflow (fase dimana darah berbondong2 menuju jantung) Kontraksi isovolumetrik Fase outflow (fase dimana darah mulai kembali lagi ke seluruh tubuh) Relaksasi isovolumetrik
VENTRICLE WALL (DINDING VENTRIKEL)
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 47
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23 Ini gambar dari dinding ventrikel secara anatomis
Cardiac cycle/Siklus jantung
The systole of the ventricle Isovolumetric contraction Rapid ejection Reduced ejection Total The diastole of the ventricle Protodiastole Isovolumetric relaxation First rapid filling phase Diastasis (reduced filling phase) Last rapid filling phase ( atrial systole ) Total
Duration
0.05 seconds 0.10 seconds 0.15 seconds 0.30 seconds 0.04 seconds 0.06 seconds 0.10 seconds 0.20 seconds
0.10 seconds
0.50 seconds
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 48
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
CARDIAC SOUNDS Bunyi jantung 1. Two separate sounds are auscultated in each normal cardiac cycle, as lub dub. These sounds are known as cardiac sounds. 2. Investigation of the cardiac sounds is enormous practical importance since a number of disorders of the cardiac function leads to changes in those sound phenomena 3. First, we hear a longer sound of a low tone; this is the 1st cardiac sound (S1) 4. After a brief pause, it is followed by a higher-pitched but a shorter sound, the 2nd sound (S2) 5. After this comes a longer pause than the one between the two sounds. 6. With a new cardiac cycle, the two-tact rhythm of cardiac sounds is repeated.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Terdapat dua bunyi jantung yang bisa kita dengar pada siklus jantung normal, yaitu lub dub. Suara ini yang kita tahu sebagai bunyi jantung. Investigasi dari bunyi jantung merupakan hal penting sejak fungsi utama jantungnya mengalami gangguan. Pertama, kita dengar bunyi yang lama dengan nada rendah, inilah bunyi jantung pertama (S1). Setelah berhenti beberapa saat, akan terdengar bunyi nada tinggi namun singkat, inilah yang disebut dengan bunyi jantung kedua (s2). Setelah itu, berhenti agak lama dari sebelumnya, di antara dua bunyi yang tadi. Dengan siklus jantung yang baru, kedua bunyi jantung akan terdengar lagi.
S1 Bunyi jantung pertama The first heart sound develops with the onset of the ventricular systole 1. the period of tension 2. the beginning of the period when the blood is forced out of the heart The systolic sound S1 lasts approximately 0.12 second (0.09 0.16 second) Factors responsible for S1 1. The vibration of the AV valves & the chordae tendineae 2. The contraction of the ventricular muscle
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005 Page 49
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
Two components of S1 1. Mitral (M1) 2. Tricuspid (T1)
Bunyi jantung pertama terjadi pada saat sistole ventrikular 1. Masa dari tekanan 2. Awal dari masa itu, ketika darah dipaksa keluar dari jantung Bunyi sistolik Bunyi jantung pertama (S1) terjadi kira-kira 0.12 detik (0.09 0.16 detik) Faktor-faktor yang berperan pada S1: 1. Getaran dari katup AV (atrioventrikuler) dan corda tendinea 2. Kontraksi dari otot ventrikular Komponen dari S1 1. Mitral (M1) 2. Trikuspidalis (T1)
AV valve Katup Atrioventrikuler
ABNORMALITY IN S1 S1 yang abnormal A. Louder S1 mengerasnya bunyi jantung pertama 1. Too powerful left ventricel contraction Kerasnya kontraksi ventrikel kiri Pregnancy Hypertiroid Exercise Fever Anemia Hypertention Inotropik agent 2. Stenosis mitralis reumatik B. Softer S1 melemahnya bunyi jantung kedua 1. Weaker left ventricle contraction melemahnya kontraksi ventrikel kiri Hypotiroid Myocardial infarct Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Shock 2. Abnormal isovolumetric contraction kontraksi isovolumetrik yang abnormal Aortic regurgitation Mitral regurgitation 3. Calcification or destruction of the mitral valve Kalsifikasi/destruksi katup mitral S2 2005 Bunyi jantung kedua Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC
Page 50
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
The second heart sound occurs after the systole, as it produced at the moment the semilunar valves close at the end of the protodiastole. Diastolic sound It lasts about 0.08 seconds. Factors responsible for S2: 1. The closing of the semilunar valves. 2. The vibration of their elastic vessel walls. AORTIC AND PULMONAL VALVE Two components of S2 1. Aorta (A2) 2. Pulmonal (P2) S2 splitting 1. Physiologic 2. Persisten/ fixed 3. Paradoxical
Bahasa indonesianya Bunyi jantung kedua terjadi setelah sistole, pada saat katup semilunar menutup, setelah berakhirnya fase protodiastole. (bunyi diastole) Itu terjadi sekitar 0.08 detik. Faktor-faktor yang berperan pada S2 1. Menutupnya katup semilunar 2. Getaran dari dinding pembuluh elastisnya Dua komponen S2 1. Aorta (A2) 2. Pulmonal (P2) Bagian S2 1. Fisiologis 2. Persisten/campuran
3.
Paradoxical
HEART SOUNDS
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005 Page 51
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
Sound 1. Mitral component (M1) Tricuspid component (T1) 2. Aortic component (A2) Pulmonary component (P2) 3. Physiologic Pathologic 4. Pathologic
Origin Mitral valve closure Tricuspid valve closure Aortic valve closure Pulmonary valve closure Rapid LV filling Ventricular wall vibrations Enhanced atrial systole
SUMATION GALLOP
Bunyi jantung S1-4 yang terdengar membentuk irama kuadripel. Jika baik S3 ataupun S4 ada dan denyut jantung bertambah cepat, mereka S3 dan S4 terdengar sebagai Galoop Sumasi (SS) (Stein & Delman, 1985), biasanya terjadi pada gagal jantung.
PHYSICAL DIAGNOSIS
Gambar di atas ini adalah anatomi superfisial dan lokasi auskultasi katup jantung (Bykov, 1952)
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 52
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
ADDITIONAL CARDIAC SOUNDS OPENING SNAP Opening Snap merupakan bunyi gemeretak yang terjadi selama pembukaan katup mitral pada permulaan diastole. Biasanya diakibatkan oleh rheumatic heart fever. MURMUR Murmur terjadi apabila aliran darah pada bilik-bilik jantung menghasilkan aliran turbulen (Turbulent flow). TURBULENT FLOW ALIRAN TURBULEN When the velocity of circulation becomes very high (as after exercise, in thyrotoxicosis) When viscosity of blood is very low, such as in severe anemia Korotkovs sound, the sound produced when we do blood pressure measurement. narrowing of the artery causes rise the velocity of the blood In valvular diseases, such as in mitral stenosis.
The
Ketika kecepatan sirkulasi bertambah cepat (seperti setelah olahraga, pada thyrotoxicosis) Ketika kekentalan darah sangat rendah, seperti pada anemia yang sudah parah Korotkovs sound, yaitu bunyi yang terjadi pada saat pengukuran tekanan darah akibat adanya penyempitan arteri dan meningkatnya tekanan aliran darah. Pada penyakit valvular, misalnya pada stenosis mitral. Pada stenosis mitral terdapat penyempitan pada pembukaan katup mitral karena gangguan pada pembukaan katup mitral sehingga menyebabkan obstruksi pada aliran darah, sehingga menyebabkan aliran turbulen yang dapat menghasilkan murmur. Bil kecepatan aliran meningkat, maka murmur akan terdengar lebih keras. Peningkatan volume darah dapat juga menyebabkan lubang katup jantung seolah-olah menyempit.
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 53
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
STENOSIS AND REGURGITATION Stenosis Lubang katup mengecil atau gagal membuka seluruhnya dikatakan katup mengalami stenosis Regurgitasi/ insufisiensi Katup jantung tidak menutup sempurna dan masih terdapat lubang di mana sebagian darah dapat kembali
HEART MURMURS
Valve Aortic/ Pulmonary
Abnormality Stenosis Insufficiency
Timing of murmur Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic
Mitral/ Tricuspid
Stenosis Insufficiency
EJECTION CLICK High frequency sound that followed M1 of the S1 It occurs in the beginning of ventricle ejection
Bunyi frekuensi yang tinggi yang disertai M1 dari S1 Hal tersebut terjadi di awal ejeksi ventrikel
MID-SYSTOLIC CLICK High frequency sound that in the middle or in the end of systolic It is caused by a sudden pressure from chorda tendinae resulted from regurgitation of the mitral valve
Bunyi frekuensi tinggi yang ada di tengah-tengah atau di akhir sistolik Ini disebabkan oleh adanya tekanan tiba-tiba dari chorda tendinae yang dihasilkan dari regurgitasi katup mitral
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 54
dr. Ikhlas M. Jenie 10 Maret 2008 Edited by : BapaO_23
BISING DAN BUNYI TAMBAHAN Ejeksi sistolik Pansistolik Systolic Click Late Systolic
Innocent/Physiologic Aortic/Pulmonic Stenosis Early Diastolic
Mitral/Tricusp Regurgitation Mild Diastolic
Mitral Valve Prolapse Opening Snap Diastolic Rumble
Aortic Regurgitation Ejection Sound
Mitral/Tricusp Stenosis S3
Mitral Stenosis S4
Aortic Valve Disease
Normal in Children Heart Failure
Physiologic Various Diseases
Cardiovascular & Respiratory System MISC 2005
Page 55
You might also like
- Kolesistitis Dan KolelitiasisDocument40 pagesKolesistitis Dan KolelitiasisKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Contoh Surat PenawaranDocument1 pageContoh Surat PenawaranAgus MujionoNo ratings yet
- Contusio SerebriDocument17 pagesContusio SerebriHenny Marcellina WauNo ratings yet
- ENSEFALITISDocument25 pagesENSEFALITISnisaNo ratings yet
- Kor Pulmonale Chronic (CPCDocument4 pagesKor Pulmonale Chronic (CPCHaris NovirwanNo ratings yet
- Surat Serah Terima BarangDocument2 pagesSurat Serah Terima BarangFarinLimandaMuliaNo ratings yet
- Surat JalanDocument1 pageSurat JalanAbdul MujibNo ratings yet
- Surat Serah TerimaDocument1 pageSurat Serah TerimaZhieFaizaNo ratings yet
- PulmonologiDocument14 pagesPulmonologiavionikamNo ratings yet
- FilariasisDocument18 pagesFilariasisKadek AryatiNo ratings yet
- IPD - INGENIO - SOAL PREDIKSI BATCH 2 2019 - Unlocked PDFDocument238 pagesIPD - INGENIO - SOAL PREDIKSI BATCH 2 2019 - Unlocked PDFlinawatialimNo ratings yet
- Sasaran Keselamatan PasienDocument15 pagesSasaran Keselamatan PasienKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Kardiomegali Edem PulmoDocument30 pagesKardiomegali Edem PulmoDovi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Kejang Epilepsi Jenis dan PenanganannyaDocument4 pagesKejang Epilepsi Jenis dan PenanganannyaLucky Kurniawan100% (1)
- THT - SoalDocument11 pagesTHT - SoalCitra Aulia ShabariaNo ratings yet
- (INGENIO) Soal Prediksi IPD Batch 4 2018Document353 pages(INGENIO) Soal Prediksi IPD Batch 4 2018sarahcalah1104No ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik IpdDocument5 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Ipd1810147 Trinita Yosephine LamriaNo ratings yet
- TB ExtraparuDocument28 pagesTB ExtraparuSince Ivanna RumbiakNo ratings yet
- PSIKIATRIDocument101 pagesPSIKIATRIdr. Riri PutriaNo ratings yet
- ACLS REVIEWDocument73 pagesACLS REVIEWFitria NengsihNo ratings yet
- KEJANGDEMAMDocument25 pagesKEJANGDEMAMRohmah dini nur kusumaNo ratings yet
- Kelon Persiapan Koass - Radiologi - DR - ValdiDocument115 pagesKelon Persiapan Koass - Radiologi - DR - ValdiSundari Eka Putri100% (1)
- Hemlich ManeuverDocument9 pagesHemlich ManeuverRichy UdilNo ratings yet
- Referat Diabetes MelitusDocument38 pagesReferat Diabetes Melitusafdhalul mahfudNo ratings yet
- KATARAK OPTIMALDocument71 pagesKATARAK OPTIMALRino SetiadyNo ratings yet
- Referat Uveitis AnteriorDocument31 pagesReferat Uveitis AnteriorAgnes NugraheniNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystrophyDocument13 pagesMuscular DystrophyZarah Alifani DzulhijjahNo ratings yet
- Bimpus AnakDocument59 pagesBimpus AnakNafisah Putri WyangsariNo ratings yet
- Polip hidung grade 3 cocok dengan keluhan dan pemeriksaan fisik pasienDocument118 pagesPolip hidung grade 3 cocok dengan keluhan dan pemeriksaan fisik pasiennaily nrNo ratings yet
- Nefrologi UKMPPD FKUSU 2019Document79 pagesNefrologi UKMPPD FKUSU 2019Miranda NasutionNo ratings yet
- Responsi Tonsilofaringitis Akut Fixed FixedddDocument19 pagesResponsi Tonsilofaringitis Akut Fixed FixedddRaraniluh ParameswariNo ratings yet
- Makalah Referat Uveitis AnteriorDocument27 pagesMakalah Referat Uveitis AnteriorDavinPannaaustenNo ratings yet
- Free Class Medsense Emergency in Kidney DiseasaeDocument15 pagesFree Class Medsense Emergency in Kidney DiseasaeJames BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Specific Fractures and Joint Injuries in ChildrenDocument24 pagesSpecific Fractures and Joint Injuries in ChildrenBayu Wendy AryNo ratings yet
- Kata Kunci Sesak NafasDocument2 pagesKata Kunci Sesak NafasyunifatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus EncefalitisDocument25 pagesLaporan Kasus EncefalitisSholihinNo ratings yet
- KATARAK TRAUMATIKADocument26 pagesKATARAK TRAUMATIKAClara KumororiniNo ratings yet
- Referat Uveitis FaldiDocument26 pagesReferat Uveitis FaldiAnnisa Hyunnie ElfNo ratings yet
- Apley Bab 14Document23 pagesApley Bab 14oktorina dyah primayantiNo ratings yet
- Case PJR IlhamDocument70 pagesCase PJR IlhamRina NovitrianiNo ratings yet
- Fraktur Terbuka ApleyDocument4 pagesFraktur Terbuka ApleymorrisonmojoNo ratings yet
- BAHAS IKA - SOAL FASE CEPAT - BATCH I 2022 - Unlocked - 2022-01-08 - 20-15-42Document28 pagesBAHAS IKA - SOAL FASE CEPAT - BATCH I 2022 - Unlocked - 2022-01-08 - 20-15-42Marcelita DuwiriNo ratings yet
- Case - TonsilofaringitisDocument21 pagesCase - TonsilofaringitisWolfy D HaroldNo ratings yet
- Tugas Refarat AmbliopiaDocument16 pagesTugas Refarat AmbliopiaMariamargaretha ErroNo ratings yet
- ThorakkkkDocument48 pagesThorakkkkLivianty HukubunNo ratings yet
- Denyut JantungDocument5 pagesDenyut JantungNabela FikriyyaNo ratings yet
- Pengurusan EmosiDocument17 pagesPengurusan EmosiAbu Hanafi Abu SamahNo ratings yet
- Soal Ujian SarafDocument5 pagesSoal Ujian SarafAntonia TwistinaNo ratings yet
- Operasi Radikal MastoidektomiDocument8 pagesOperasi Radikal Mastoidektomicoco satryaNo ratings yet
- Hyaline Membrane Disease - TasyaDocument30 pagesHyaline Membrane Disease - TasyaSetiafanjNo ratings yet
- 9 Fisiologi GehDocument45 pages9 Fisiologi GehPutri Aswariyah RamliNo ratings yet
- Referat Obat Pelumpuh OtotDocument15 pagesReferat Obat Pelumpuh OtotUmmul Khair Imaduddin100% (1)
- MOVEMENT DISORDERDocument184 pagesMOVEMENT DISORDERNurul RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGI THORAX ESSENSIALDocument72 pagesRADIOLOGI THORAX ESSENSIALRahmat AzimiNo ratings yet
- Gagal JantungDocument7 pagesGagal JantungMila Nur KholilaNo ratings yet
- Aca - DotDocument15 pagesAca - DotAga S ImandaNo ratings yet
- Referat DeliriumDocument21 pagesReferat DeliriumDella SeptaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Psikiatri HilDocument17 pagesLaporan Kasus Psikiatri HilNurul Hildayanti ILyasNo ratings yet
- Silabus Pembekalan CBT FK UmsuDocument45 pagesSilabus Pembekalan CBT FK Umsunuralisalim79No ratings yet
- Hiv Aids ToxoplasmaDocument22 pagesHiv Aids ToxoplasmaMenda SuciNo ratings yet
- TUMOR OTAK DAN MEDULA SPINALISDocument24 pagesTUMOR OTAK DAN MEDULA SPINALISayfanNo ratings yet
- HIDRANENSEFALIDocument14 pagesHIDRANENSEFALInashqonashNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM KardioDocument12 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM KardioFerdy IlhamNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cara Memanfaatkan Buku Ini Dengan BaikDocument3 pages1.2 Cara Memanfaatkan Buku Ini Dengan BaikKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Pengantar Teknik Anamnesis Pada OSCEDocument4 pages2.0 Pengantar Teknik Anamnesis Pada OSCEKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Apakah OSCE ItuDocument2 pages1.1 Apakah OSCE ItuKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Wanita Muda Dengan Sesak NapasDocument7 pages2.2 Wanita Muda Dengan Sesak NapasKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Formulir Monitoring Pelaksanaan Program Uks Ukgs UkgmDocument2 pagesFormulir Monitoring Pelaksanaan Program Uks Ukgs UkgmKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Kak Audit Internal 2018Document9 pagesKak Audit Internal 2018Keyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Halaman Depan Laporan KasusDocument3 pagesHalaman Depan Laporan KasusKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Stase NEFRO Gea DaraDocument12 pagesStase NEFRO Gea DaraKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- PP 21 Tahun 2014Document9 pagesPP 21 Tahun 2014niztgirlNo ratings yet
- Panduan Praktik Mandiri - BestDocument7 pagesPanduan Praktik Mandiri - BestKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Cuap2 LyrikDocument8 pagesCuap2 LyrikKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Griya TBDocument2 pagesGriya TBKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Cover Lepbang DandyDocument25 pagesCover Lepbang DandyKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Griya TBDocument2 pagesGriya TBKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Satuan Acara Penyuluhan DemensiaDocument6 pagesSatuan Acara Penyuluhan DemensiaHarrie Az NaNo ratings yet
- Puisi - Mengais Masa LaluDocument1 pagePuisi - Mengais Masa LaluKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Skedule PijenanDocument1 pageSkedule PijenanKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Form Surat Lamaran BPOM PDFDocument1 pageForm Surat Lamaran BPOM PDFarum suciati100% (9)
- Rekap Dahlia 3 TGL 26 Agustus EditedDocument7 pagesRekap Dahlia 3 TGL 26 Agustus EditedKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- BronkopneumoniaDocument14 pagesBronkopneumoniafildafadilahNo ratings yet
- GIPSDocument3 pagesGIPSKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Rincian Kebutuhan Pegawai Dan Alokasi ASN Di Badan Pengawas Obat Dan Makanan 2017 PDFDocument7 pagesRincian Kebutuhan Pegawai Dan Alokasi ASN Di Badan Pengawas Obat Dan Makanan 2017 PDFLiyana IlmiyatiNo ratings yet
- Stomatitis KontakDocument5 pagesStomatitis KontakKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Urtikaria PDFDocument2 pagesUrtikaria PDFAulya Adha DiniNo ratings yet
- Stomatitis DentureDocument5 pagesStomatitis DentureKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Fraktur Suprakondiler HumerusDocument5 pagesFraktur Suprakondiler HumerusKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet