Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
Alynna ValbuenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP
Uploaded by
Alynna ValbuenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Alynna Cherise T.
Valbuena N4A
NURSING CARE PLAN
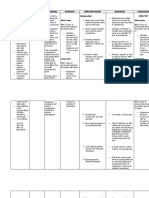
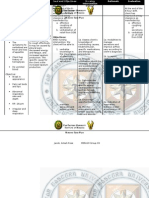
ASSESSMENT
Subjective: The patient complaints of easy fatigability. Objective: BP: 160/90 Protruding abdomen with purple striae over the abdomen and buttocks Round face Develoment of facial hair Numerous bruises on the skin Thin lower extremities Difficulty climbing from one stair to another Diagnostic tests reveal the ff: Glucose: 186 mg/dl Na: 152 mEq/L K: 3.2 mEq/L Ca: 4.3 mEq/L Cortisol: 35 ug/dl
DIAGNOSIS
Activity Intolerance r/t muscle weakness and fatigues as manifested by inability to maintain usual routines.
PLANNING
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will achieve slight increase in activity tolerance evidenced by acceptable level of fatigue/weakness.
INTERVENTIONS
Assess sleep patterns and note changes in thought processes/behaviors.
RATIONALE
Multiple factors can aggravate fatigue, including sleep deprivation, emotional distress, side effects of medication, and progression of disease process. Prevents overexertion, allows for some activity within patient ability.
EVALUATION
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient has achieved slight increase in activity tolerance evidenced by acceptable level of fatigue/weakness.
Recommend scheduling activities for periods when patient has most energy. Adjust activities as necessary, reducing intensity level/discontinuing activities as indicated. Encourage patient to do whatever possible, e.g., self-care, sit in chair, visit with family/friends. Instruct patient/family/caregiver in energy conservation techniques. Stress necessity of allowing for frequent rest periods following activities. Demonstrate proper performance of ADLs, ambulation/position changes. Identify safety issues, e.g., use of assistive devices, temperature of bath water, keeping travel-ways clear of furniture. Encourage nutritional intake/use of supplements as appropriate.
Provides for sense of control and feeling of accomplishment.
Enhances performance while conserving limited energy, preventing increase in level of fatigue.
Protects patient/caregiver from injury during activities.
Necessary to meet energy needs for activity.
You might also like
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPAbbie TantengcoNo ratings yet
- NCP SviDocument4 pagesNCP SviEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaKen100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Diarrhea 2Document1 pageNursing Care Plan For Diarrhea 2Skyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument7 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Surgical Ward RotationDocument3 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Surgical Ward RotationEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection - NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection - NCPHamil BanagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ExampleDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ExampleBrittanyNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP SEIZURE DISORDERDocument2 pagesNCP SEIZURE DISORDERPatricia FaraonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Actual Nursing Care Plan GT DisorderDocument3 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan GT DisordermandzkievonnieNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan: Involution (Bubble He)Document4 pagesTeaching Plan: Involution (Bubble He)Pamela BagabaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP For Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageNCP For Activity IntoleranceKristine LonyenNo ratings yet
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationPJNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPMichael John F. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1Rommelie CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida NCPDocument3 pagesSpina Bifida NCPShahzad GulfamNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocument3 pagesNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- NCP For CipDocument22 pagesNCP For CipBing DayaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocument1 pageCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- NCP Lack of KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNCP Lack of KnowledgeFaye BartianaNo ratings yet
- NCP LymphomaDocument3 pagesNCP Lymphomamahmoud fuqahaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug Namecheanne003No ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAnn AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument13 pagesNCPLee Da HaeNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- NCP (Fatigue)Document1 pageNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanjmichaelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Revised ResearchDocument14 pagesRevised ResearchAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument2 pagesArthritisAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- First and Second Level of Assessment Inadequate Living SpaceDocument2 pagesFirst and Second Level of Assessment Inadequate Living SpaceAlynna Valbuena60% (5)
- FNCP For Community UTI ProblemDocument9 pagesFNCP For Community UTI ProblemAlynna Valbuena100% (1)
- First and Second Level of Assessment Unsanitary Waste DisposalDocument2 pagesFirst and Second Level of Assessment Unsanitary Waste DisposalAlynna Valbuena0% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Pedia With LeukemiaDocument14 pagesPedia With LeukemiaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Function Food SampleDocument3 pagesNutrition Function Food SampleAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet