Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perinialism and Other Facts
Uploaded by
MaheshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Perinialism and Other Facts
Uploaded by
MaheshCopyright:
Available Formats
T-109
Table 11.1
Branches of Philosophy
Branch Metaphysics Description An attempt to determine what is real Key Questions What is the meaning of life? Does life have a purpose? Are people born good or evil? Does the universe have a design or purpose? What are the limits of knowledge? Where do we find the sources of knowledge? How do we acquire knowledge? Are there ways of determining the validity of knowledge? What is the truth? What is the validity of ideas and how can this be determined? How can we communicate with others without contradicting ourselves? What do our arguments mean?
Epistemology
Questions about knowledge and knowing
Logic
Procedures for arguing that bring people to valid conclusions Seeking wisdom about the nature of ethical and aesthetic values
Axiology
Ethical:
What are values and why are they important? How should we live our lives? What is right and what is wrong?
Aesthetic:
How do we judge what we see, touch and hear? What is beauty?
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-110
Table 11.2
Types of Reasoning
Type of Reasoning Deductive Description Example
Reasoning from general to specific
Generalization: All students at this school wear
uniforms.
Specifics:
Uniforms help students feel part of the group. Uniforms discourage labeling due to economic status. Inductive Reasoning from specific to general
Specifics:
Students benefit from clear expectations for their conduct. School policies help identify uniform procedures for all teachers and staff.
Generalization:
Because of its benefits, the school should develop a handbook that clearly states expectations for students.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-111
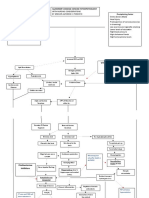
Figure 11.1
Components of an Educational Philosophy
Perceptions of Students Beliefs about Teaching and Learning
Philosophy of Education
An Understanding of Knowledge
Determining What is Worth Knowing
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-112
Table 11.3
Perennialist Perspectives on Education
Perceptions of Students Human nature is constant. All students learn and grow in similar ways.
Beliefs About Teaching and Learning Teaching is orderly and carefully articulated. Traditional subjects of study emphasized.
Understanding of Knowledge Internalizing wisdom of the ages. Teacher dispenses knowledge, students absorb.
What is Worth Knowing Eternal truths learned through studying great books.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-113
Table 11.4
Progressivist Perspectives on Education
Perceptions of Students Learners are active, selfmotivated. Every student has unique needs and interests.
Beliefs About Teaching and Learning Teacher serves as a facilitator.
Understanding of Knowledge Knowledge is obtained by students as they interact with people and things. Students construct knowledge from what they see, hear, and do.
What is Worth Knowing Information and skills are of interest to the student. Process of knowing is more important than product.
Students learn best from active involvement.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-114
Table 11.5
Essentialist Perspectives on Education
Perceptions of Students Student motivation frequently comes from teacher. Students need to be disciplined and work hard to learn.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Beliefs About Teaching and Learning Teacher is responsible for motivating students.
Understanding of Knowledge Knowledge comes from memorizing content and internalizing skills of traditional subjects.
What is Worth Knowing Traditional academic subjects, plus technology, seen as valuable. Vocational education not encouraged.
Teacher dispenses knowledge of traditional subjects, Knowledge students absorb. comes from hard work.
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-115
Table 11.6
Existentialist Perspectives on Education
Perceptions of Students
Beliefs About Teaching and Learning
Understanding of Knowledge Knowledge is discovering who we are as individuals.
What is Worth Knowing Individually determined learning is based on life experiences and understanding of the world.
Every student Teachers role is is an to demonstrate individual. importance of discipline in Students pursuing should have academic goals. freedom to choose, take Individualized responsibility educational for actions. experiences are promoted.
Personalized information is needed to make responsible Knowledge that choices in life. leads to selfdiscovery and responsible choice is sought.
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
T-116
Table 11.7
Social Reconstructionist Perspectives on Education
Perceptions of Students Students are the hope for future growth and change in society. Students are capable of changing society if given necessary knowledge and skills.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Beliefs About Teaching and Learning Teachers lead by modeling democratic actions and exciting students about the needs for social change. Much of true learning occurs outside the classroom as students work to change society.
Understanding of Knowledge The information and skills needed to be a part of society while working to implement positive change are important.
What is Worth Knowing Life skills necessary for serving as successful change agents in society are sought.
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-117
Table 11.8
Philosophical Perspectives on Curriculum Content
Perennialism Train the mind in traditional subjects. Progressivism Individual topics are learned through meaningful experiences. Integrated curriculum includes topics of interest to students. Essentialism Rigorous common core of traditional courses is taught. Computer literacy is also considered important. Existentialism Individual curriculum is designed to help students understand selves and lifes meanings. Social Reconstructionism Understanding social justice and equity issues are important.
Core curriculum consists of social studies, mathematics, the sciences, music, and art.
Strategies are needed to implement social change.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-118
Table 11.9
Philosophical Perspectives on Instructional Methods
Perennialism Direct instruction, Socratic method used. Progressivism Constructive and cooperative learning is preferred. Essentialism Traditional methods such as direct instruction and Socratic method are used. Other methods are used when they can be effective. Existentialism Methods model decision making and choosing between alternatives such as story telling and discussions of existential questions. Social Reconstructionism Methods vary, with their intent being to guide students to an understanding of social issues and constructive methods of dealing with them.
Traditional methods of instruction are used.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
T-119
Table 11.10
Philosophical Perspectives on Management and Discipline
Perennialism Traditional methods emphasizing control and student respect for the teacher as educational leader are used. Progressivism Students actively participate in planning for and implementing classroom management and discipline. Essentialism Students are expected to follow the rules, work hard, and allow others to engage in learning. Character training is also emphasized. Existentialism Open approach to management and discipline in which students are given equal responsibility with teacher for dealing with problems and conflict. Social Reconstructionism Stresses importance of community building. Students need skills for effective group action.
Henniger The Teaching Experience: An Introduction to Reflective Practice
Copyright 2004 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- CH11Document11 pagesCH11Zahida AfzalNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching Techniques: by Evelyn Jepkemei Chief Advisor Inside Out Learning (IOL)Document25 pagesEffective Teaching Techniques: by Evelyn Jepkemei Chief Advisor Inside Out Learning (IOL)Evelyn JepkemeiNo ratings yet
- TTP ReviewerDocument4 pagesTTP ReviewerJohn Ray FelixNo ratings yet
- Concept of Effective TeachingDocument16 pagesConcept of Effective TeachingUmme FarwahNo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument89 pagesPrinciples of TeachingAnne Anne Cabeltis-MañaboNo ratings yet
- Local Media8699183543187838904Document19 pagesLocal Media8699183543187838904Daniel Titular100% (1)
- The Professional TeacherDocument30 pagesThe Professional TeacherKyrie Irving CastañaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2Sambala AbbeyNo ratings yet
- Unit#4 TEACHINGDocument6 pagesUnit#4 TEACHINGUmar DrazNo ratings yet
- Education PhilosophiesDocument3 pagesEducation PhilosophiesCanute McinnisNo ratings yet
- Draft Personal Philosophy v3 WeeblyDocument5 pagesDraft Personal Philosophy v3 Weeblyapi-402677865No ratings yet
- Legal Education: Journal ofDocument19 pagesLegal Education: Journal ofArif Papanya ArfaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Education Module 1Document6 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Education Module 1Allysa Shane Paningbatan RascoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FaciDocument6 pagesModule 1 FaciALLYSA RASCONo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Principles Module 1 Unit 1Document8 pagesLearner Centered Principles Module 1 Unit 1Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching StrategiesDocument20 pagesEffective Teaching StrategiesEzrah Uriah OliverosNo ratings yet
- Teaching AptitudeDocument26 pagesTeaching AptitudeAmlan DeNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Teaching StrategiesDocument30 pagesLearner-Centered Teaching StrategiesЛана Шаманаева100% (2)
- Principles of Teaching and LearningDocument48 pagesPrinciples of Teaching and Learningorangebackpack100% (1)
- The Concept of Effective TeachingDocument10 pagesThe Concept of Effective TeachingSukay NahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesTheories of Learning in 40 CharactersElizabethNo ratings yet
- Philosophies that influence curriculumDocument5 pagesPhilosophies that influence curriculumAngel Mae H. SolaminNo ratings yet
- GEE PMT Module 3Document4 pagesGEE PMT Module 3Ryan AmaroNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Theories of LearningDocument57 pagesLearner-Centered Theories of LearningAnonymous E8yT3R4iNo ratings yet
- Activity #1Document5 pagesActivity #1Alna Gamulo LosaNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology Research MethodsDocument32 pagesEducational Psychology Research MethodsVukashin.meNo ratings yet
- Teaching Philosophy StatementsDocument6 pagesTeaching Philosophy StatementsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Module 2M Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDocument48 pagesModule 2M Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeAubrey Justine Galeon100% (1)
- Effective Teaching Strategies and PrinciplesDocument17 pagesEffective Teaching Strategies and PrinciplesFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Power of Experience in Your Learning and Your Students' LearningDocument5 pagesThe Power of Experience in Your Learning and Your Students' LearningFaryz Tontok Tinan 오빠No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes AndragogyDocument3 pagesLecture Notes AndragogyVenus FernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pedagogy: Pedagogy and Andragogy (2) Teaching and Learning (3) Learning StylesDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Pedagogy: Pedagogy and Andragogy (2) Teaching and Learning (3) Learning StylesAdAm JazzNo ratings yet
- R-Educ 201Document34 pagesR-Educ 201Kwin KwinNo ratings yet
- Towards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDocument6 pagesTowards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDarwin RosendeNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope: EssentialismDocument3 pagesNature and Scope: EssentialismKashmir FajardoNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning Principles and Theories Orientation PresentationDocument42 pagesAdult Learning Principles and Theories Orientation PresentationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Asian Development Foundation College Philosophy of EducationDocument8 pagesAsian Development Foundation College Philosophy of EducationBernard RosarioNo ratings yet
- Test Your Understanding of The PhilosophiesDocument3 pagesTest Your Understanding of The PhilosophiesRey Razel Cave100% (4)
- Principles of Teaching and Learning: Key Concepts ExplainedDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Teaching and Learning: Key Concepts Explainedimee eusebio100% (1)
- UNit 1chapter1 3principles of TeachingfinalDocument29 pagesUNit 1chapter1 3principles of TeachingfinalJona MagnoNo ratings yet
- Educ 3Document19 pagesEduc 3Kurt Louie LiwanaganNo ratings yet
- Definition of TeachingDocument40 pagesDefinition of TeachingSim BelsondraNo ratings yet
- Philosophical and Pedagogical Approach of Curriculum and Curriculum DevelopmentDocument7 pagesPhilosophical and Pedagogical Approach of Curriculum and Curriculum DevelopmentCherry Ann Hernandez Yamat100% (4)
- Philosophies of EducationDocument6 pagesPhilosophies of EducationBob FloresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EducationDocument13 pagesIntroduction To EducationKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Welcome To EDBE 8P03... : Cognition and The Exceptional Learner (P/J/I)Document42 pagesWelcome To EDBE 8P03... : Cognition and The Exceptional Learner (P/J/I)aleiyah.liguori1616No ratings yet
- Pedagogical ConcernsDocument5 pagesPedagogical ConcernsSrijesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Major philosophies and psychologies shaping curriculum developmentDocument22 pagesMajor philosophies and psychologies shaping curriculum developmentEllen Joy Peniero67% (3)
- Pedagogy COTEMDocument177 pagesPedagogy COTEMEskindir JembereNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 4Document13 pagesProf Ed 4jomar alingasaNo ratings yet
- FL-Module UNIT 1 Learner-centered-Teaching - .-Foundations-And-CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesFL-Module UNIT 1 Learner-centered-Teaching - .-Foundations-And-CharacteristicsJr Ramos100% (1)
- Edu321 NotesDocument6 pagesEdu321 NotesMak SenNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument38 pagesFoundations of EducationRachel May DiestroNo ratings yet
- Teacher Attitude and SkillsDocument9 pagesTeacher Attitude and SkillssanjeevchsNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Strategy in ChemistryDocument47 pagesTeaching and Learning Strategy in ChemistryLidya PurwasihNo ratings yet
- Principle and Strategies of TeachingDocument25 pagesPrinciple and Strategies of TeachingGilbert Mendoza100% (1)
- School Based InsetDocument35 pagesSchool Based InsetJhune Valdez Gandola100% (1)
- Introduction To Philosophies of EducationDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Philosophies of EducationGrecii SarmientoNo ratings yet
- English for Students of Educational Sciences: Educational SciencesFrom EverandEnglish for Students of Educational Sciences: Educational SciencesNo ratings yet
- Classroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- Theories of Leadership Traits and BehaviorsDocument35 pagesTheories of Leadership Traits and BehaviorsMaheshNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership4647Document45 pagesEffective Leadership4647Jay AdonesNo ratings yet
- Basic Assumptions Principles of CBTDocument12 pagesBasic Assumptions Principles of CBTMahesh100% (1)
- Goals and Types of Psychological Assessment and EvaluationDocument13 pagesGoals and Types of Psychological Assessment and EvaluationMaheshNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSDocument15 pages(Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSVaibhav NikharNo ratings yet
- Visual CommunicationDocument73 pagesVisual CommunicationMahesh100% (1)
- Unit 3 Probability Distributions: StructureDocument38 pagesUnit 3 Probability Distributions: StructureMaheshNo ratings yet
- Exide Life InsuranceDocument26 pagesExide Life InsuranceMaheshNo ratings yet
- The Roles of Educational Technology in LearningDocument15 pagesThe Roles of Educational Technology in LearningMaheshNo ratings yet
- Cognative Behavioural TherapyDocument32 pagesCognative Behavioural TherapyMaheshNo ratings yet
- Information Brochure-2019 PDFDocument70 pagesInformation Brochure-2019 PDFhapshitaNo ratings yet
- Indian Nuclear Society: 13 Annual Conference - INSAC 2002Document7 pagesIndian Nuclear Society: 13 Annual Conference - INSAC 2002MaheshNo ratings yet
- Visual Communication2Document14 pagesVisual Communication2MaheshNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals PDFDocument30 pagesTransition Metals PDFMaheshNo ratings yet
- Present Status and Improvement of Industrial Safety at Construction SitesDocument12 pagesPresent Status and Improvement of Industrial Safety at Construction SitesMaheshNo ratings yet
- Accident InvestigationDocument5 pagesAccident InvestigationMaheshNo ratings yet
- Fire SafetyDocument5 pagesFire SafetyMaheshNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms To Correct For InstrumentalDocument6 pagesGenetic Algorithms To Correct For InstrumentalMaheshNo ratings yet
- Workplace Accident Investigation GuideDocument5 pagesWorkplace Accident Investigation GuideMaheshNo ratings yet
- IGP CSAT Paper 1 Science Biology Muscular and Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesIGP CSAT Paper 1 Science Biology Muscular and Skeletal SystemMaheshNo ratings yet
- Development of A Remotely OperatedDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Remotely OperatedMaheshNo ratings yet
- Fire Risk Assessment For Workplaces Containing Flammable SubstancesDocument12 pagesFire Risk Assessment For Workplaces Containing Flammable SubstancesMaheshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Transition MetalsDocument56 pagesChemistry of Transition MetalsHamad Mohamad100% (1)
- Present Status and Improvement of Industrial Safety at Construction SitesDocument12 pagesPresent Status and Improvement of Industrial Safety at Construction SitesMaheshNo ratings yet
- Transparent Solid-State Lithiated Neutron Scintillators Based On Self-Assembly of Polystyrene-Block - Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Copolymer ArchitecturesDocument5 pagesTransparent Solid-State Lithiated Neutron Scintillators Based On Self-Assembly of Polystyrene-Block - Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Copolymer ArchitecturesMaheshNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSDocument15 pages(Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSVaibhav NikharNo ratings yet
- S 140106235848 Phpapp02Document20 pagesS 140106235848 Phpapp02viraivil9417No ratings yet
- Basic Coordination ChemistryDocument17 pagesBasic Coordination ChemistryMaheshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument16 pagesChemical Engineering DepartmentMaheshNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Pressure Effects On SolubilityDocument4 pagesTemperature and Pressure Effects On SolubilityMaheshNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Further ReadingDocument17 pagesAdverbs Further ReadingᅳNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Clea 2022-2023Document2 pagesSoal Uts Clea 2022-2023estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Jsi Eng Paper 1Document4 pagesJsi Eng Paper 1Sharifah Jannatul AjilahNo ratings yet
- 7 Hemolytic Anemias PDFDocument44 pages7 Hemolytic Anemias PDFWin Ni del PîlarNo ratings yet
- Juvy Ciocon-Reer v. Juddge Lubao (DIGEST)Document1 pageJuvy Ciocon-Reer v. Juddge Lubao (DIGEST)Glory Grace Obenza-Nodado100% (1)
- School Memo Reada A ThonDocument6 pagesSchool Memo Reada A ThonJanine EspinedaNo ratings yet
- Câu bị động (tiếp)Document6 pagesCâu bị động (tiếp)GIANG NGUYỄNNo ratings yet
- Article 9 of Japan ConstitutionDocument32 pagesArticle 9 of Japan ConstitutionRedNo ratings yet
- Yoga Poses For Back Pain ReliefDocument11 pagesYoga Poses For Back Pain Reliefshiv yoga100% (2)
- Doctors not guilty of negligence in patient's deathDocument1 pageDoctors not guilty of negligence in patient's deathAlleine TupazNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Cws FinalDocument13 pagesCws Finalapi-282878271No ratings yet
- Language Assistant in ColombiaDocument2 pagesLanguage Assistant in ColombiaAndres CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Marketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storesDocument18 pagesMarketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storescandyNo ratings yet
- v4 Nycocard Reader Lab Sell Sheet APACDocument2 pagesv4 Nycocard Reader Lab Sell Sheet APACholysaatanNo ratings yet
- AI technologies improve HR analysisDocument4 pagesAI technologies improve HR analysisAtif KhanNo ratings yet
- The Tonal Style of Sergei Prokofiev's "Romeo and Juliet"Document252 pagesThe Tonal Style of Sergei Prokofiev's "Romeo and Juliet"John WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- RIZALDocument36 pagesRIZALRichard GonowonNo ratings yet
- Earnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)Document27 pagesEarnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)jeetNo ratings yet
- Exl - Exterior Lighting System PDFDocument336 pagesExl - Exterior Lighting System PDFAxxNo ratings yet
- Cooking Taoshobuddha Way Volume 2Document259 pagesCooking Taoshobuddha Way Volume 2Taoshobuddha100% (3)
- Solar CompendiumDocument19 pagesSolar CompendiumCasey Prohn100% (4)
- Forbidden TextsDocument179 pagesForbidden TextsThalles FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Roy FloydDocument2 pagesRoy FloydDaniela Florina LucaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 DLL English 4 q4 Week 7Document3 pagesGrade 4 DLL English 4 q4 Week 7Cristina Singsing100% (1)
- Nurses Qualityof Work LifeDocument5 pagesNurses Qualityof Work LifeAnissa septianiNo ratings yet
- JTH 14015Document4 pagesJTH 14015Catherine MorrisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying by S.K. RoyDocument613 pagesFundamentals of Surveying by S.K. RoyChalamaiah Vadlamudi100% (1)
- Math 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDDocument18 pagesMath 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDJosh T CONLUNo ratings yet
- TEST Lop 5Document3 pagesTEST Lop 5tan nguyen vanNo ratings yet