Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory of Knowledge Vocabulary2
Uploaded by
ibbiologycommackhlCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory of Knowledge Vocabulary2
Uploaded by
ibbiologycommackhlCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory of Knowledge Vocabulary List: Know what these terms mean as they relate to the particular areas of ToK
and be able to use them in your essay and presentationYou will get a better score.
Problem of Knowledge 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Argument adignorantiam Certainty coherence Common sense Confirmation bias Evidence Gullibility Judgment Mental map Open-mindedness Paradox of cartography Paranormal phenomena Relativism (know the dangers of and the strengths of) 13. Skepticism (what are the concerns associated with it) 14. Ways of knowing (what are they?) The Nature of Knowledge 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Authority worship Context Culture Expert opinion Indoctrination Information Justified true belief Knowledge by authority News media Primary knowledge Second-hand knowledge Sufficient condition Thick concept Urban legend
Ways of Knowing: Language 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Ambituity Back translation Body language Classification Communication Connotation Denotation Emotive meaning Euphemism Grammar Idiom Irony Linguistic determinism Metaphor Sapir-Worf hypothesis Stereotype Weasel words
Ways of Knowing: Perception 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Common-sense realism Empiricism Figure and ground Phenomenalism Scientific realism Sensation Visual agnosia Visual grouping
Ways of Knowing: Reason 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Adhominem Argument ad ignorantiam Betting the question Belief bias Binary thinking Circular reasoning Confirmation bias Contradiction Deduction Double standards Enthymeme Equivocation Fallacy False analogy False dilemma
16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32.
Hasty generalizations Induction/inductive inference Infinite regress Lateral thinking Laws of thought Loaded questions Post hoc ergo propter hoc Premise Prison of consistency quantifier Rationalization Rhetoric Special pleading Syllogism Validity Venn diagram Vested interest Vicious circle
6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16.
Deduction Empiricism Euclidean geometry Formal system Formalism Godels incompleteness theorem Goldbachs conjecture Idealization Platonism Synthetic Theorem
Areas of Knowledge: Natural Sciences 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Anomaly Conjectures and refutations Controlled experiment Empirical Empiricist Falsification Hypothesis Law Logical positivism Paradigm Physics envy Principle of simplicity Pseudo-science Rationalist Relativism Science worship Scientism
Ways of Knowing: Emotion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Apathy Debutting intuition Emotional coloring Emotive language Empathy intuitions James-Lange theory Primary emotions Rational fool Romanticism Social emotion Stoicism
Also know: 1. Four kinds of proposition a. Analytic statements b. Empirical statements c. Value-judgments d. Metaphysical statements 2. Paradigms as knowledge filters Areas of Knowledge: Mathematics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Analytic A posteriori A priori Axioms Conjecture
Areas of Knowledge: Human Sciences 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Bear market Behaviorism Bias Bull market Free-will/determinism Going native Holism Human free-will Law of large numbers Loaded questions Mirror test Nature-nurture debate Observer effect Phillips curve
15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc fallacy Reactance Reductionism Reductive fallacy Stream of consciousness Trends and laws Verstehen position
13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18.
Self-interest theory Self-regarding desires Special pleading Utilitarianism Value-judgment Veil of ignorance
Concluding Chapter: Truth and Wisdom 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Correspondence theory Coherence theory Pragmatic theory Dangers of Relativism Dangers of Dogmatism Wisdom Good judgment Breadth of vision Self-knowledge Responsibility Intellectual humility Circular reasoning Communal reinforcement Cubist theory of truth Defense mechanisms Intellectuals virtues Learned ignorance Rationalization Selective attention
Areas of Knowledge: History 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Bias Cubist history Economic determinism Empathy Great person theory of history Hindsight bias Primary source Secondary source Self-realizing expectations
Areas of Knowledge: The Arts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Aesthetics Avant-garde Beauty Canon Catharsis Disinterested Expert opinion Forgeries Form versus content Kitsch Mimesis
Areas of Knowledge: Ethics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Altruism Cultural imperialism Duty ethics Egoism Golden rule Moral absolutism Moral principle Moral relativism Other-regarding desires Relativism Rights Rule worship
You might also like
- Tok EhibihitionDocument5 pagesTok EhibihitionNicklaus ElliottNo ratings yet
- Anchoring EffectDocument20 pagesAnchoring EffectSvetlana Kononenko67% (3)
- E-BOOK Theory of Knowledge For The IB DiplomaDocument17 pagesE-BOOK Theory of Knowledge For The IB DiplomaT-girl100% (2)
- Ib Chemistry Revision PDFDocument27 pagesIb Chemistry Revision PDFSrushti71% (7)
- Extended Essay in Psychology ChecklistDocument3 pagesExtended Essay in Psychology Checklisttriptirathore100% (1)
- Families and Households Revision Notes for AS and A Level Sociology: AQA FocusFrom EverandFamilies and Households Revision Notes for AS and A Level Sociology: AQA FocusRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Genetic and Brain Technologies: What Sort of Future Should We Bring AboutDocument192 pagesGenetic and Brain Technologies: What Sort of Future Should We Bring AboutAmber CottonNo ratings yet
- TOK 2022 Course OutlineDocument21 pagesTOK 2022 Course OutlineAshita Naik100% (1)
- Final TOK Essay Rishabh RDocument4 pagesFinal TOK Essay Rishabh RRishabh RavalNo ratings yet
- Present knowledge dependent past knowledge TOK essayDocument6 pagesPresent knowledge dependent past knowledge TOK essay缪青玉100% (1)
- IB Psychology HL SyllabusDocument4 pagesIB Psychology HL SyllabusSathya ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- ESS IA Example - 10 - eDocument16 pagesESS IA Example - 10 - eMonika Mehta100% (1)
- Intro To TOK - Crash Course For TeachersDocument36 pagesIntro To TOK - Crash Course For TeachersAnonymous q6ffsM4ERr100% (1)
- IB Chemistry HL - Cameron Lumsden - Third Edition - OSC 2015 PDFDocument188 pagesIB Chemistry HL - Cameron Lumsden - Third Edition - OSC 2015 PDFAshwinNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA ChecklistDocument7 pagesIB Chemistry IA ChecklistOGswaggerNo ratings yet
- Thrust Bearing CalculationsDocument162 pagesThrust Bearing Calculationslahiru1983100% (1)
- Leviton ManualDocument82 pagesLeviton ManualRobby Larson100% (1)
- GMAT Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesGMAT Practice QuestionswithraviNo ratings yet
- Tok Essay ExemplarDocument38 pagesTok Essay Exemplarmgupta72No ratings yet
- ToK Essay and Presentation IntroductionDocument8 pagesToK Essay and Presentation IntroductionMr. Clark100% (2)
- TOK Essay FinalDocument9 pagesTOK Essay Finalsarahnxoxo47No ratings yet
- IB Theory of Knowledge EssayDocument8 pagesIB Theory of Knowledge EssayMomina Amjad100% (3)
- TOK EssayDocument3 pagesTOK EssayOlivier SorghoNo ratings yet
- IB TOK Ethics PresentationDocument22 pagesIB TOK Ethics PresentationAdam Zhang100% (1)
- Knowledge Under Bias and SelectionDocument8 pagesKnowledge Under Bias and SelectionFezaNo ratings yet
- TOK Natural Science SchemeDocument10 pagesTOK Natural Science SchemeSimon100% (3)
- TOK Annotated EssayDocument5 pagesTOK Annotated Essayhikarid100% (1)
- May 2021 TOK EssayDocument9 pagesMay 2021 TOK EssayShankar MutnejaNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry SL BookletDocument8 pagesIb Chemistry SL BookletBoshra NouriNo ratings yet
- Ethical judgments limit methods of knowledge production in science and artsDocument7 pagesEthical judgments limit methods of knowledge production in science and artsmuskaanNo ratings yet
- Natural Science Tok Presentation Part ADocument12 pagesNatural Science Tok Presentation Part Aapi-202268486No ratings yet
- TOK Essay Writing BookletDocument26 pagesTOK Essay Writing Bookletcybele100% (1)
- IB Extended EssayDocument2 pagesIB Extended EssayAmal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- TOK EssayDocument7 pagesTOK EssaySyco8785% (13)
- E-BOOK IB Theory of Knowledge Essay Writing GuideDocument24 pagesE-BOOK IB Theory of Knowledge Essay Writing GuideAhmed L'hopitaleNo ratings yet
- TOK Exhibition A EngDocument5 pagesTOK Exhibition A EngPinkSpaghettiBearNo ratings yet
- Cas EssayDocument2 pagesCas EssaySara AbouhilalNo ratings yet
- IB Extended EssayDocument17 pagesIB Extended EssayRichard BonettNo ratings yet
- ToK SoWDocument6 pagesToK SoWSagiparameshNo ratings yet
- IB TOK 1 Resources NotesDocument85 pagesIB TOK 1 Resources Notesxaglobal100% (1)
- IB TOK Essay ExampleDocument4 pagesIB TOK Essay ExampleLucy HanNo ratings yet
- TOK Essay Structure GuideDocument3 pagesTOK Essay Structure GuideVy DoNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA Guidance and HintsDocument4 pagesIB Chemistry IA Guidance and HintsGinevraPiccioniNo ratings yet
- IB Master Guide IB Extended Essay PDFDocument60 pagesIB Master Guide IB Extended Essay PDFVishnupriya Premkumar100% (2)
- Ib Academy Biology SL Study GuideDocument164 pagesIb Academy Biology SL Study GuideSuuz de Bruijn50% (2)
- Theory of Knowledge AOKsDocument15 pagesTheory of Knowledge AOKsRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Exhibition Unpacking DocumentDocument12 pagesExhibition Unpacking DocumentJamie Chung100% (1)
- TOK Science Unit PlannerDocument2 pagesTOK Science Unit PlannerxaglobalNo ratings yet
- TOK Language Unit PlannerDocument2 pagesTOK Language Unit PlannerxaglobalNo ratings yet
- TOK, ConceptsDocument2 pagesTOK, ConceptsJulie Vu100% (6)
- Object 1: Easy German BookDocument4 pagesObject 1: Easy German BookMelina Student - ChatzisymeonNo ratings yet
- Ibdp HandbookDocument42 pagesIbdp HandbookJefferson WidodoNo ratings yet
- Kritvi - TOK Exhibition CommentaryDocument6 pagesKritvi - TOK Exhibition CommentaryKritviiiNo ratings yet
- LBIS TOK Essay Guide Nov 2016Document74 pagesLBIS TOK Essay Guide Nov 2016CJ matthewNo ratings yet
- IB History Role of Language and ReasonDocument7 pagesIB History Role of Language and ReasonHimanshu MehtaNo ratings yet
- Myers Et Al - Clear and Present ThinkingDocument214 pagesMyers Et Al - Clear and Present ThinkingAENo ratings yet
- Physics Foibles: A Book for Physics, Math and Computer Science StudentsFrom EverandPhysics Foibles: A Book for Physics, Math and Computer Science StudentsNo ratings yet
- Craig E Knowledge & The State of Nature An Essay in Conceptual Synthesis 1991Document182 pagesCraig E Knowledge & The State of Nature An Essay in Conceptual Synthesis 1991Felipe Elizalde100% (1)
- Art of NecessityDocument167 pagesArt of NecessityunsurprisedNo ratings yet
- 2012 Book TopicalThemesInArgumentationTh PDFDocument339 pages2012 Book TopicalThemesInArgumentationTh PDFLetícia Pimenta100% (1)
- Training Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Document51 pagesTraining Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Ankita BharadwajNo ratings yet
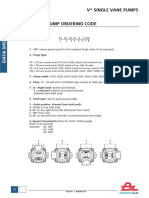
- V Single Vane Pumps: 1 - "F3" 2 - Pump TypeDocument14 pagesV Single Vane Pumps: 1 - "F3" 2 - Pump TypeJose Leandro Neves FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review (Students)Document16 pagesBasic Chemistry Review (Students)AnilovRozovaNo ratings yet
- VT2009B Eng 02 953680Document2 pagesVT2009B Eng 02 953680gabrieltracto100% (1)
- BRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessDocument2 pagesBRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessKhoa Bui AnhNo ratings yet
- Product Manual For Resilient Seated Cast Iron Air Relief Valves For Water Works Purposes ACCORDING TO IS 14845: 2000Document5 pagesProduct Manual For Resilient Seated Cast Iron Air Relief Valves For Water Works Purposes ACCORDING TO IS 14845: 2000Tanmoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled: Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained ConditionsDocument9 pagesUncontrolled: Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained ConditionsMohannad QutubNo ratings yet
- DT022BTFT v10Document12 pagesDT022BTFT v10Johny JongNo ratings yet
- Effect of Restraint, Volume Change, and Reinforcement On Cracking of Mass ConcreteDocument26 pagesEffect of Restraint, Volume Change, and Reinforcement On Cracking of Mass ConcreteDIDIER ANGEL LOPEZ RINCONNo ratings yet
- Pritchett Clock Repair Shop Breakeven Analysis ExcelDocument138 pagesPritchett Clock Repair Shop Breakeven Analysis ExcelMohd Yousuf MasoodNo ratings yet
- Quad Encoder Velocity Accel with CRIOLabVIEW FPGADocument5 pagesQuad Encoder Velocity Accel with CRIOLabVIEW FPGAChâu Tinh TrìNo ratings yet
- ACI229Document18 pagesACI229Francisco CalderónNo ratings yet
- Thermal Barrier Coatings Seminar ReportDocument6 pagesThermal Barrier Coatings Seminar ReportGanesh NandgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Quiz6 AnswerDocument8 pagesQuiz6 AnswerTrí Tạ MinhNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 - FactorizationDocument25 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 - FactorizationSATAMANYU BHOLNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Chemistry Past Papers January 2015Document20 pagesCSEC® Chemistry Past Papers January 2015Jonathan RamsundarNo ratings yet
- Solution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDocument4 pagesSolution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDrumil TrivediNo ratings yet
- BA (Hons) Philosophy CurriculumDocument123 pagesBA (Hons) Philosophy CurriculumDARSHAN RAAJANNo ratings yet
- 1) Computer Concepts NotesDocument6 pages1) Computer Concepts NotesVenus Leilani Villanueva-Granado100% (2)
- LCD Interfacing PDFDocument37 pagesLCD Interfacing PDFPeeyush Kp100% (1)
- Product Guide (English 140702)Document11 pagesProduct Guide (English 140702)Dineshkumar MahedranNo ratings yet
- Tecquipment - Flumes - Data SheetDocument3 pagesTecquipment - Flumes - Data SheetArthur BritoNo ratings yet
- StudenttextDocument15 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- Simulation and Implementation of Servo Motor Control With Sliding Mode Control (SMC) Using Matlab and LabviewDocument30 pagesSimulation and Implementation of Servo Motor Control With Sliding Mode Control (SMC) Using Matlab and Labviewmjohn87No ratings yet
- Carbolite CWF1313 004 - 3216Document44 pagesCarbolite CWF1313 004 - 3216dev-nullNo ratings yet
- House of CardsDocument2 pagesHouse of CardsHello misterNo ratings yet
- Temperarura4 PDFDocument371 pagesTemperarura4 PDFmario yanezNo ratings yet