Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solid Waste Management
Uploaded by
Ashish DeotaleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid Waste Management
Uploaded by
Ashish DeotaleCopyright:
Available Formats
MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE
1. Municipal Solid Waste Garbage is generally referred to Waste and is also termed as rubbish, trash, junk, unwanted or undesired material.As per the Municipal Solid Waste (Management &Handling) Rule,2000 garbage is define as Municipal Solid Waste which includes commercial and residential wastes generated in a municipal or notified areas in either solid or semi-solid form excluding industrial hazardous wastes but including treated bio-medical wastes Municipal solid waste consists of household waste, construction and demolition debris, sanitation residue, and waste from streets. This garbage is generated mainly from residential and commercial complexes.
2. Main Sources of Municipal Waste
House hold waste Commercials: Street sweeping Hotels and restaurants Clinics and dispensaries Construction and demolition Horticulture Sludge
3. Composition of Municipal Solid Waste in India In India the biodegradable portion dominates the bulk of Municipal Solid Waste. Generally the biodegradable portion is mainly due to food and yard waste
With rising urbanization and change in lifestyle and food habits, the amount of municipal solid waste has been increasing rapidly and its composition changing. There are different categories of waste generated, each take their own time to degenerate (as illustrated in the table below).
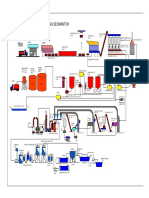
4. Life Cycle of Municipal Solid Waste
5. Municipal Solid Waste Management Practices in India The term municipal solid waste refers to solid waste from houses, streets and public places, shops, offices, and hospitals. Management of these types of waste is most often the responsibility of Municipal or other Governmental authorities. Except in the metropolitan cities, SWM is the responsibility of a health officer who is assisted by the engineering department in the transportation work. The activity is mostly labour intensive, and 2-3 workers are provided per 1000 residents served. The municipal agencies spend 5-25% of their budget on SWM A typical waste management system in a low- or middle-income country like India includes the following elements:
Waste generation and storage
Segregation, reuse, and recycling at the household level Primary waste collection and transport to a transfer station or community bin Street sweeping and cleansing of public places Management of the transfer station or community bin Secondary collection and transport to the waste disposal site Waste disposal in landfills
But in most of the Indian cities open dumping is the Common Practices which is adversely affecting on environment and Public health. 6. Adverse Effect of open dump An open dumping is defined as a land disposal site at which solid wastes are disposed of in a manner that does not protect the environment, are susceptible to open burning, and are exposed to the elements, vectors, and scavengers. Open dumping can include solid waste disposal facilities or practices that pose a reasonable probability of adverse effects on health or the environment. Health Effect
The health risks associated with illegal dumping are significant. Areas used for open dumping may be easily accessible to people, especially children, who are vulnerable to the physical (protruding nails or sharp edges) and chemical (harmful fluids or dust) hazards posed by wastes. Rodents, insects, and other vermin attracted to open dump sites may also pose health risks. Dump sites with scrap tires provide an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes, which can multiply 100 times faster than normal in the warm stagnant water standing in scrap tire causing several illnesses. Poisoning and chemical burns resulting from contact with small amounts of hazardous, chemical waste mixed with general waste during collection & transportation. Burns and other injuries can occur resulting from occupational accidents and methane gas exposure at waste disposal sites.
Environment pollution Air pollution Dust generated from on-site vehicle movements, and placement of waste and materials Water pollution Runoff from open dump sites containing chemicals may contaminate wells and surface water used as sources of drinking water open dumping can also impact proper drainage of runoff, making areas more susceptible to flooding when wastes block ravines, creeks, culverts, and drainage basins & also contamination of groundwater resources and surface water from leachate emissions. Soil Contamination Permanent or temporary loss of productive land Global Warming and Climate Change In most of the cities & towns the municipal solid waste is being dumped & burnt in open spaces without understanding the adverse impacts on the environment. The waste in the dumping ground undergoes various anaerobic reactions produces offensive Green House gases such as CO2, CH4 etc. These gases are contributing potentially to Global Warming & Climate Change phenomenon. Effects of MSW on environment and human health 1. Report - Occupational and Environmental Health Issues of Solid Waste Management Special Emphasis on Middle- and Lower-Income Countries - Sandra Cointreau A World Bank
2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8.
Report. http://www.wiego.org/occupational_groups/pdfs/waste_collectors/Urban_Paper_H ealth_SolidWaster_Mgt.pdf Information - Health and Environmental Effects of Burning Municipal Solid Waste (pdf) http://www.saskh2o.ca/PDF/EPB185.pdf Information Municipal Solid Waste effect on public health and Environment(Pdf) http://www.cepis.ops-oms.org/bvsacd/scan/033333/033333-03d.pdf Case Study- Health Implications Of Solid Waste Disposal: Case Study Of Olusosun Dumpsite, Lagos, Nigeria (pdf) http://www.ijpas.com/article/viewFile/3979/2809 Presentation -Impact of Solid Waste on Health and the Environment - A presentation by Arnold ,Funmilayo Akinbode,Walden Universityhttp://environmentalhealthtoday.files.wordpress.com/2009/08/app7akinbodefpp2.ppt Research Paper -Solid Waste Treatment and Disposal: Effects on public Health and Environment Safety Paper by Odhiambo E.O. Thomas ,Rotich Henry (PDF)http://paper.solidwaste.com.cn/onload/200701081310434744383.pdf Article - Health hazards and waste management by Lesley Rushto http://bmb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/68/1/183 Municipal Solid Waste and Green house gas emission http://www.westernclimateinitiative.org/archived_comments/98422.pdf
7. Integrated Solid waste Management Integrated Solid Waste Management (ISWM) is a tool to determine the most energy-efficient, least-polluting ways to deal with the various components & items of a communitys Solid Waste stream. The twin goals of ISWM are to:
Retain as much as possible of that energy & those materials in a useful state. Avoid releasing that energy or matter into the environment as a pollutant.
Benefits of Integrated Solid waste management The concept of ISWM plan derives from the necessity to look at alternative sources of collection, transportation and most importantly, disposal to ensure a healthy living environment in urban cities. Local and regional economies benefit by the continued exchange value of the reclaimed materials and products and the jobs created in reprocessing and reselling them. National and global resource natural depletion is reduced, contributing to a more sustainable longterm economy. Pollution from landfills is reduced because many toxic or otherwise polluting materials are diverted from the landfills, and because the overall volume of land filled material is reduced.
8. Legal framework for Municipal Solid Waste in India Municipal Solid Waste (Managment & Handling ) Rule was notified by the Ministry of Environment and Forest, Govt. of India [vide No.S.O.908 (B) dated the 25th September 2000]. The objective of these Rules was to make every municipal authority responsible for the implementation of the various provisions of the Rules within its territorial area and also to develop an effective infrastructure for collection, storage, segregation, transportation, processing and disposal of Municipal Solid Wastes. The Civic bodies have the responsibility to enforce these rules. The major functions of civic body include
Prohibiting littering of street Organizing house to house waste collection. Conducting awareness programs to disseminate information to public.
Providing adequate community storage facilities. Use of colour code bins and promotion of waste segregation. Transport of wastes in covered vehicles. Processing of wastes by adopting an appropriate combination of composting, anaerobic digestion, Pellatisation etc. Upgradation of the existing dump sites and Disposal of inert wastes in sanitary landfills.
As per the Rules, the citizens are responsible for
Segregation of wastes at source. Avoid littering of streets. Delivery of wastes in accordance with the delivery system notified by the respective Civic body.
Detail Municipal Solid Waste (Management & Handling) Rule ,2000 http://envfor.nic.in/legis/hsm/mswmhr.html
Other Countries Municipal Solid Waste Rules and Regulations EPA -Rule and Implementation Information for Standards of Performance for Municipal Solid Waste Landfills - http://www.epa.gov/ttn/atw/landfill/landflpg.html EPA-Non-hazardous Waste Regulations- http://www.epa.gov/waste/laws-regs/regs-non-haz.htm EPA Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Regulationshttp://www.epa.gov/waste/nonhaz/municipal/landfill/msw_regs.htm#icr Statutes, Regulations, and Regulatory Guidance- http://www.bordercenter.org/wastewatcher/milawlist.html Articles /News 1. 24 duniya.com - all the Articles & News related to Solid Waste Management from national Newspaper and Magazines http://www.24dunia.com/english-news/search/solid-waste-management-in-mumbai.html 2. The Views paper Environment -Urban Waste Management-February6, 2010 http://theviewspaper.net/urban-waste-management/ 3. Manure from Municipal Solid Waste Sumeet Kumar Sharma (Chemical Weekly ) http://203.199.213.48/1543/1/Manure_from_municipal_waste.pdf 4. The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management http://www2.widener.edu/~sxw0004/abstract36.html 5. The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management - Abstract from recent issue http://www2.widener.edu/~sxw0004/abstract36.html
You might also like
- Training Africa's Youth in Waste Management and Climate Change: A Textbook for the Youth in Africa's Primary and Junior Secondary SchoolsFrom EverandTraining Africa's Youth in Waste Management and Climate Change: A Textbook for the Youth in Africa's Primary and Junior Secondary SchoolsNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Solid Waste Management in AgraDocument16 pagesSustainable Solid Waste Management in AgraSagar AroraNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Plan for Statewide Afterschool NetworkDocument4 pagesSustainability Plan for Statewide Afterschool NetworkLawrence Patrick Ladia Limen100% (1)
- SOLID WASTE ManagementDocument77 pagesSOLID WASTE ManagementFahmi FesoolNo ratings yet
- Solid and Liquid Waste ManagementDocument13 pagesSolid and Liquid Waste Managementpunam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Solid and Liquid Waste ManagementDocument116 pagesSolid and Liquid Waste ManagementNP100% (3)
- The Many Benefits of Cleaning Our EnvironmentDocument6 pagesThe Many Benefits of Cleaning Our EnvironmentAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Waste Management - IDocument91 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste Management - Isairam2103No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management of Dhaka CityDocument10 pagesSolid Waste Management of Dhaka CityFiroz Reza100% (1)
- Lecture 9 On FisheriesDocument36 pagesLecture 9 On Fisheriesii muNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Bihar PDFDocument2 pagesAir Pollution Bihar PDFVikash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ecotourism Study to Develop Maco's Sustainable Tourism PlanDocument6 pagesEcotourism Study to Develop Maco's Sustainable Tourism PlanYlloy AnalabNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management 2011Document10 pagesSolid Waste Management 2011Global Unification International100% (1)
- Importance of MangrovesDocument22 pagesImportance of MangrovesDivya ChawhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Pollution Is SylhetDocument17 pagesAssignment On Pollution Is SylhetAhad Zaman RonyNo ratings yet
- Polluter Pays Principle in IndiaDocument3 pagesPolluter Pays Principle in IndiaAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management ProjectDocument12 pagesSolid Waste Management ProjectShahbaz Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Soyabean Production in Malawi PDFDocument9 pagesSoyabean Production in Malawi PDFChikondi Tembo100% (1)
- Waste ManagementDocument23 pagesWaste ManagementRishi Raj CharanNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in IslamabadDocument41 pagesSolid Waste Management in IslamabadDurrayy Mahmood100% (4)
- Template Letter Post DoctoralDocument3 pagesTemplate Letter Post DoctoralPamela Grace AnzuresNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Be MPDocument658 pagesWaste Management Be MPAnwar Haji JavedNo ratings yet
- Health-Care Waste ManagementDocument7 pagesHealth-Care Waste Managementscience worldNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste PresentationDocument29 pagesSolid Waste PresentationSyed Bakhtyar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Environmental DegradationDocument89 pagesEnvironmental DegradationSTELLA ANETOR100% (1)
- Solid Waste Audit of LandfillDocument71 pagesSolid Waste Audit of LandfillPutt LaLuNo ratings yet
- SWM Project Report NewDocument20 pagesSWM Project Report NewKarthik MadhokNo ratings yet
- Equator PrinciplesDocument10 pagesEquator Principlesemma monica100% (2)
- Solid Waste MangementDocument23 pagesSolid Waste Mangementoqp98949No ratings yet
- Philippine Initiatives To Address Environmental IssuesDocument2 pagesPhilippine Initiatives To Address Environmental IssueschikkietingNo ratings yet
- Biogas in GhanaDocument18 pagesBiogas in GhanaShannon SeaNo ratings yet
- Sphere Standards: Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygiene Promotion (WASH)Document29 pagesSphere Standards: Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygiene Promotion (WASH)Sote BrilloNo ratings yet
- Impact of Organic Farming and Food on Citizens of PakistanDocument30 pagesImpact of Organic Farming and Food on Citizens of PakistanFraz RazaNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Perception of Higher Diploma Program As Opportunity For Promoting Professional Development in Arba Minch University (Ethiopia) : A Qualitative InquiryDocument24 pagesTeachers' Perception of Higher Diploma Program As Opportunity For Promoting Professional Development in Arba Minch University (Ethiopia) : A Qualitative InquiryDessalegn EjiguNo ratings yet
- Report On Solid Waste Management AgraDocument195 pagesReport On Solid Waste Management AgraHimanshu Sethi100% (4)
- Report 3 - WACSDocument64 pagesReport 3 - WACSiking balonNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument53 pagesWaste ManagementBenison MathewNo ratings yet
- How Can Agricultural and Rural Development Best Be PromotedDocument9 pagesHow Can Agricultural and Rural Development Best Be PromotedNicole Andrea TuazonNo ratings yet
- Delivering Sustainable Development: A Principled Approach To Public-Private FinanceDocument8 pagesDelivering Sustainable Development: A Principled Approach To Public-Private FinanceOxfamNo ratings yet
- Constraints To Promoting People Centred Approaches in RecyclingDocument10 pagesConstraints To Promoting People Centred Approaches in RecyclingAhm MehrNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation Goals & ObjectivesDocument1 pageWater Conservation Goals & ObjectivesDipayan0% (1)
- Good Practices in SWM - A Collection of LGU ExperiencesDocument72 pagesGood Practices in SWM - A Collection of LGU Experiencesmalapatan menroNo ratings yet
- Vol4 - 4-Yaptenco - FullPaper - A Paper On Open BurningDocument14 pagesVol4 - 4-Yaptenco - FullPaper - A Paper On Open BurningJosmae MaskianolangNo ratings yet
- Waste Management DraftDocument41 pagesWaste Management DraftSnehaNo ratings yet
- Background of Study Waste Management at BGH: A STUDYDocument1 pageBackground of Study Waste Management at BGH: A STUDYKhrys Anne ReyesNo ratings yet
- Annual - Crop - EHS Guidelines - 2ndconsult - Comparison - 2007vs2016 PDFDocument43 pagesAnnual - Crop - EHS Guidelines - 2ndconsult - Comparison - 2007vs2016 PDFIFC SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assesment Final011x80Document23 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assesment Final011x80Saurav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineer resume titleDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Engineer resume titleDennie DennyNo ratings yet
- OPIF Reference GuideDocument106 pagesOPIF Reference GuidesketchesdomainNo ratings yet
- Effective Waste ManagementDocument2 pagesEffective Waste ManagementJoshua Cocks100% (5)
- Eia Developing Countries Asia PDFDocument349 pagesEia Developing Countries Asia PDFJohn Gilbert GopezNo ratings yet
- 5.10thasia3r QuezonDocument14 pages5.10thasia3r QuezonTribung ManggugubatNo ratings yet
- Asha For Education ProposalDocument12 pagesAsha For Education ProposalMinatiBindhani100% (2)
- Project Proposal On Lecture and Demonstration Programme On "Biodiversity Conservation in The Face of Climate Change.-2021Document13 pagesProject Proposal On Lecture and Demonstration Programme On "Biodiversity Conservation in The Face of Climate Change.-2021MinatiBindhaniNo ratings yet
- Curiculum VitaeDocument4 pagesCuriculum VitaeRashid BumarwaNo ratings yet
- Pertcpm 4Document70 pagesPertcpm 4John BanielNo ratings yet
- How to Empower Children in the World: Earth Leaders for Environmental MonitoringFrom EverandHow to Empower Children in the World: Earth Leaders for Environmental MonitoringNo ratings yet
- Effects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost on Soil Microbial BiomassDocument17 pagesEffects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost on Soil Microbial BiomassKhushboo KhannaNo ratings yet
- EEDM Notes Unit-5Document34 pagesEEDM Notes Unit-5Hardik JhalaniNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste AssignmentDocument19 pagesSolid Waste AssignmentAlfatah muhumed0% (1)
- NKVSDocument1 pageNKVSAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Trusses 1Document3 pagesTrusses 1Esmaeil Na0% (1)
- Electrical Invoice Template from SwapnasiddhiDocument2 pagesElectrical Invoice Template from SwapnasiddhiAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity SangliDocument7 pagesBiodiversity SangliAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument35 pagesAcid RainAshish Deotale100% (4)
- Young Indian ScientistDocument18 pagesYoung Indian ScientistAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Electrical Invoice Template from SwapnasiddhiDocument2 pagesElectrical Invoice Template from SwapnasiddhiAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- S.No State City JEE (Offline) 2018 JEE (Online) 2018Document6 pagesS.No State City JEE (Offline) 2018 JEE (Online) 2018Ashish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- IIT Bombay UCEED 2019 important dates registration exam centersDocument1 pageIIT Bombay UCEED 2019 important dates registration exam centersAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Importance of family values and relationships discussedDocument8 pagesImportance of family values and relationships discussedAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Kundali SthansDocument1 pageKundali SthansAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Birds LifeDocument6 pagesBirds LifeAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor SeminarDocument15 pagesAir Compressor SeminarAshish Deotale75% (4)
- Acid RainDocument35 pagesAcid RainAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Noise Pollution ObjectivesDocument1 pageNoise Pollution ObjectivesAshish Deotale67% (6)
- List of Diploma Institutes in Pune RegionDocument28 pagesList of Diploma Institutes in Pune RegionAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Fav ShayriDocument3 pagesFav ShayriAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Extinct BirdsDocument3 pagesExtinct BirdsAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Sports Person EnglishDocument4 pagesSports Person EnglishAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Extinct BirdsDocument3 pagesExtinct BirdsAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- HSC Mar 17 General PDFDocument8 pagesHSC Mar 17 General PDFAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Electronic PartsDocument23 pagesElectronic PartsAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Sandpani Sheti MarathiDocument6 pagesSandpani Sheti MarathiAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University Engg FeDocument9 pagesShivaji University Engg FeAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Sainya Padak MarathiDocument1 pageSainya Padak MarathiAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Indian Singers and MusiciansDocument6 pagesIndian Singers and MusiciansAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- PLC & SCADA Automation CourseDocument2 pagesPLC & SCADA Automation CourseAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Water ProjectDocument8 pagesWater ProjectAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- List of Diploma Institutes in Pune RegionDocument28 pagesList of Diploma Institutes in Pune RegionAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument4 pagesWater PollutionAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Enhanced H2S Recovery From Sour Water StrippersDocument12 pagesNovel Approach For Enhanced H2S Recovery From Sour Water Strippersmksscribd100% (1)
- SP 046 - SP Booster Plus - InternationalDocument6 pagesSP 046 - SP Booster Plus - InternationalJeremiah WalkerNo ratings yet
- ABB Distribution Transformer HandbookDocument92 pagesABB Distribution Transformer Handbookanon_532189789No ratings yet
- Solids Separation Study Guide: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Wastewater Operator CertificationDocument44 pagesSolids Separation Study Guide: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Wastewater Operator CertificationkharismaaakNo ratings yet
- Plastic Waste Recycling PaperDocument17 pagesPlastic Waste Recycling PaperKaila AnisyaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black - Properties PDFDocument15 pagesCarbon Black - Properties PDFdan_geplNo ratings yet
- Green Marketing PPT NewDocument18 pagesGreen Marketing PPT NewDipak Vakrani100% (2)
- Economic-Environment Interactions MatrixDocument7 pagesEconomic-Environment Interactions MatrixArya Malik100% (1)
- DESIGN of Biological Systems For 4MLD Waste Water TreatmentDocument34 pagesDESIGN of Biological Systems For 4MLD Waste Water TreatmentInigo JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Site (Hirac)Document4 pagesCleaning Site (Hirac)jovyNo ratings yet
- Sewer and Water Line Layout: P 7 7 Froilan S. Florendo, JRDocument1 pageSewer and Water Line Layout: P 7 7 Froilan S. Florendo, JRRA CruzNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper: Republic Act - 8749 Philippine Clean Air ACT OF 1999Document6 pagesReaction Paper: Republic Act - 8749 Philippine Clean Air ACT OF 1999George Evan BabasolNo ratings yet
- Flowsheet PKS Tanjung SeumentohDocument1 pageFlowsheet PKS Tanjung SeumentohRizki AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Novacron Bril - Yellow H-4gnDocument4 pagesNovacron Bril - Yellow H-4gnTanzimul IslamNo ratings yet
- You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.: Essay 1 Group (tên nhóm) (họ và tên không dấu) (số thứ tự) TopicDocument4 pagesYou should spend about 40 minutes on this task.: Essay 1 Group (tên nhóm) (họ và tên không dấu) (số thứ tự) TopicNhi SongNo ratings yet
- Mesa Adensadora de Lodo AndritzDocument2 pagesMesa Adensadora de Lodo AndritzLara PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Oil Containment Operational Requirements For Major Substations PDFDocument29 pagesOil Containment Operational Requirements For Major Substations PDFCarlos PereiraNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Q2 Week 2Document21 pagesScience 4 Q2 Week 2MELISSA BAYAWANo ratings yet
- AL MARAI HADCO ETP - Process Description and SeqDocument43 pagesAL MARAI HADCO ETP - Process Description and SeqHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 20% Development Fund: Function/Program Appropriations Allotments Obligation Unobligated Project/Activity BalanceDocument3 pages20% Development Fund: Function/Program Appropriations Allotments Obligation Unobligated Project/Activity BalanceJonson PalmaresNo ratings yet
- 8° Inglés Caring For The EnvironmentDocument4 pages8° Inglés Caring For The EnvironmentRivera Niño Karen LorenaNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of A Switched Reluctance MotorDocument4 pagesEnvironmental and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of A Switched Reluctance MotorAmgad_A_Salama_239No ratings yet
- E Waste Management and Recycling Mechanism in Japan Sugimoto SanDocument17 pagesE Waste Management and Recycling Mechanism in Japan Sugimoto SanBeepul BhartiNo ratings yet
- Suction 7000Document15 pagesSuction 7000Payasito Naricitas Naricita SombrerinNo ratings yet
- Vortex Pump Market - Innovations & Competitive Analysis - Forecast - Facts and TrendsDocument2 pagesVortex Pump Market - Innovations & Competitive Analysis - Forecast - Facts and Trendssurendra choudharyNo ratings yet
- Laser Peening-A Processing Tool To Strengthen Metals or AlloysDocument11 pagesLaser Peening-A Processing Tool To Strengthen Metals or AlloysAB CabralNo ratings yet
- UDS LocktonDocument23 pagesUDS LocktonNicoleVerosilNo ratings yet
- 8 Wastewater Collection, Treatment and Disposal: 8.1 The ApproachDocument11 pages8 Wastewater Collection, Treatment and Disposal: 8.1 The ApproachVirah Sammy ChandraNo ratings yet
- Class 12 LA FlamingoDocument42 pagesClass 12 LA FlamingoHome Grown CreationNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution in Maharashtra - ReportDocument16 pagesWater Pollution in Maharashtra - ReportShaurya ParnamiNo ratings yet