Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study - Will Philips' Attempt at Repositioning Its Products Work - Business Today
Uploaded by
Sayan KarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study - Will Philips' Attempt at Repositioning Its Products Work - Business Today
Uploaded by
Sayan KarCopyright:
Available Formats
8/29/13
Case study: Will Philips' attempt at repositioning its products work? : Business Today
Close
Case study: Will Philips' attempt at repositioning its products work?
Manu Kaushik September 18, 2012
Executive Summary: Once a household name, Dutch consumer electronics major Philips has slipped over the years to become an 'also ran'. Its repeated attempts to rekindle its mojo have failed. Will its attempt at repositioning its products at the youth work? This case study looks at what went wrong and what the company needs to do in order to succeed. In April 2010, when Philips Electronics India Ltd announced its plan to outsource its TV business to Videocon Industries, the decision came as no surprise. The five-year pact, under which Videocon is handling Philips's TV manufacturing, distribution and sales in India, is aimed at restoring the profitability of the TV business. Philips was once a dominant player in the segment, with a market share of around 15 per cent in the early 1990s, but business eroded as Korean and Indian brands grabbed market share. As volumes fell, the company struggled to run its TV factory in Pune efficiently. It took the third-party route to manufacture CRTs and imported LCD screens, but this didn't help. Then the company licensed the unit to Videocon. Through the arrangement, Philips will get royalty income based on turnover. Videocon's economies of scale in manufacturing and its strong distribution network will help the Philips brand reach more outlets and reduce the cost per unit. The downfall of Philips's consumer business - especially TV - began in late 1990s. The reasons were beyond the control of the management. The entry of Korean chaebols The downfall of Philips's consumer such as Samsung and LG started eating into the market business - especially TV - began in late 1990s share of older players such as Onida, Videocon and Philips. Philips decided to stick to its usual strategy: relying on technology rather than strengthening distribution and marketing. It didn't want to compete with the Koreans on pricing, and thought the superior technology of its products, be it picture or sound quality, would stand out. "We took a conscious decision not to cut prices," says Kris Ramachandran, former CEO of Philips Electronics India.
businesstoday.intoday.in/storyprint/187786
1/4
8/29/13
Case study: Will Philips' attempt at repositioning its products work? : Business Today
{blurb}In no time, the strategy flopped. The slow-moving Philips couldn't sustain its top position and its market share fell to some 3.5 per cent by 1999. After losing its relevance in the consumer business, Philips did take some steps to address the situation. In early 2000, it roped in PwC to revamp its consumer products portfolio, set up new processes and overhaul the supply chain. After this, it launched a new range of CRT TVs under the brand name EyeQ. "The idea was to Indianise products to suit local tastes," says Rajeev Karwal, who headed Philips's consumer electronics division in 1999. The new sets had 300 channels, as opposed to 60 channels in older ones. High-end plasma TVs were also introduced. "The earlier TVs were more suited for Europeans, who like subtle colours. Indians, on the other hand, have a fondness for saturation and bright colours. The later versions of our TVs focused on targeting this issue," says S. Venkataramani, NonExecutive Director, Philips India. "Philips was strong in innovation, but lacked aggressive marketing," says Karwal. "When I joined Philips, I brought in fresh blood to challenge internal systems. A country like India requires go-to-market strategies. We tied up with dealers and proved that the technologies of our Korean counterparts are no superior to ours." Philips also rejigged its skills portfolio. Its workforce went from more than 11,000 in the early 1990s to around 3,500 by 2005. From six legal entities, it became one legal entity. "The focus was on reshaping the company to ensure sustainable, profitable growth," says Ramachandran. A 2001 survey by ad agency JWT further helped Philips improve its brand image. Although the brand was iconic in India for several decades with customers associating the transistor radio and incandescent bulbs with the Philips name, the survey found that people did not associate the brand with highend technology.
In lighting, Philips has historically been the segment leader in India, with a market share of around 30 per cent
So from 2001 on, most of Philips's ad campaigns emphasised the advanced features of its products. Gradually, the company reclaimed some lost ground. The TV market share went up to eight per cent in 2002. Although Philips sustained its TV market share at around six per cent in the following years, it lost the way when it shifted focus from TVs to lowmargin products such as DVD players, MP3 players and headphones.
To revive its past glory, Philips's product offerings have undergone a sea change
When the consumer electronics and appliances market exploded it went from Rs 20,000 crore in 2005 to Rs 33,000 crore in 2010 - Philips's revenues from
businesstoday.intoday.in/storyprint/187786 2/4
8/29/13
Case study: Will Philips' attempt at repositioning its products work? : Business Today
the consumer business declined - from nearly Rs 1,091 crore in 2005 to Rs 659 crore in 2010. The revenue mix got overhauled. From over 42 per cent of turnover in 2005, the consumer business fell to some 28 per cent in 2010. According to some senior executives, this was partly because the CRT division was given less importance at a time when the CRT market was growing in India. "Since the parent company exited the CRT industry in 2006, the Indian arm, too, showed little interest in the business, and it affected growth momentum," says A.D.A. Ratnam, President of Philips India's consumer lifestyle division. While the consumer business hit a brick wall, exponential growth in the lighting and health care segments kept Philips going. In lighting, the company has historically been the leader, with a market share of more than 30 per cent - more than twice that of its nearest competitors, Bajaj Electricals, Havells, Wipro Consumer Care and Lighting, and Surya Roshni. "Whether it's CFL or LED technology, Philips is a pioneer in bringing lighting solutions to India," says Nirupam Sahay, President of Philips's lighting division. "We have a big distribution network and reach out to one million electrical and non-electrical outlets." For professional lighting, Philips's client portfolio includes corporate and government customers such as Asian Paints, McDonalds India, Cognizant Technologies and Kolkata Municipal Corporation. In 2005, lighting accounted for slightly over 34 per cent of revenues. In the past five years, the company's dependence on this segment has grown - it now accounts for 51 per cent of Philips's revenues. But even the lighting business has seen plenty of ups and downs. To streamline this segment, the company had to shut down a factory each in Kolkata and Mumbai in the late 1990s. Later, the dumping of Chinese lighting products affected its market share. Timely government intervention in the form of anti-dumping laws helped CFL manufacturers. Today, Philips gets a big chunk of its revenues from audio video multimedia (AVM), which includes DVDs and home theatre systems. In fact, it leads the DVD market with a share of over 24 per cent. This, though, could be shortlived. Sector experts say changes in the AVM in-dustry will keep Philips's consumer electronics business under threat. "The DVD market is dying," says Deepa Doraiswamy, Industry Manager for electronics and security at Frost & Sullivan South Asia & Middle East. "The transition to store movies and music on a pen drive is already occurring at a fast clip." Still, Philips is doing all it can to revive its past glory. Product offerings across all three categories - consumer lifestyle, lighting and health care - have undergone a sea change. Starting with the launch of MP3 players in 2009, Philips has come out with new products, many of which target youth.
businesstoday.intoday.in/storyprint/187786
3/4
8/29/13
Case study: Will Philips' attempt at repositioning its products work? : Business Today
"India has a huge young population, so we decided our target customers should be 15 to 30 years old, because that's where buying is going to happen," says Ratnam. "We have to get into the lifecycle of consumers earlier." It has launched devices priced as low as Rs 150. "The focus is to make products that are not overengineered and are easy to replenish," says Ratnam. "Youngsters don't want to hold on to a product for 10 years." Philips has revamped its personal care portfolio, and introduced shavers, body groomers and epilators. It roped in John Abraham and Kareena Kapoor as brand ambassadors. This is the first time the Philips brand has been promoted by celebrities in India. Since 2009, Philips has opened 75 exclusive 'light lounges' in 40 cities. They sell decorative home lighting products priced between Rs 575 and Rs 45,000. Besides, Philips has 750 'light shoppes' - shop-in-shops in stores such as the Future Group's HomeTown and Lifestyle International's Home Centre. In 2011, Philips acquired leading appliances maker Maya Appliances, which owns the Preethi brand of kitchenware. "For each segment, Philips is trying to redefine the market," says Rajeev Chopra, Philips India's Managing Director and CEO. Philips's record inspires little confidence in its comeback attempt. Philips lacks a clearcut strategy for India, says Karwal, the former MD. "They are like a bull in a China shop." Will the current strategies work? Does Philips lack a clear vision in India? Does it need to focus more on marketing efforts? {blurb}
Print Close
URL for this article : http://businesstoday.intoday.in/story/philips-case-study/1/187786.html @ Copyright 2010 India Today Group.
businesstoday.intoday.in/storyprint/187786
4/4
You might also like
- Case Study VideoconDocument2 pagesCase Study VideoconKK0% (1)
- Philips' Failure to Harness its Brand Image in Rural IndiaDocument4 pagesPhilips' Failure to Harness its Brand Image in Rural IndiaSavita NeetuNo ratings yet
- Philips in Search of Its MojoDocument1 pagePhilips in Search of Its MojoSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Philips RepositioningDocument27 pagesPhilips RepositioningMayur GograNo ratings yet
- Case Study PhilipsDocument6 pagesCase Study PhilipsAnh Khôi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument22 pagesExecutive SummaryRupali RoyNo ratings yet
- Aayush Bansal - PGDM6/1903 - Strategic Management Assignment: Name Course Roll Number Subject Leader Topic Key WordsDocument20 pagesAayush Bansal - PGDM6/1903 - Strategic Management Assignment: Name Course Roll Number Subject Leader Topic Key WordsAayush BansalNo ratings yet
- PHILIPSDocument6 pagesPHILIPSbkarjinniNo ratings yet
- Philips ProjectDocument42 pagesPhilips Projectvikram89275% (4)
- Project of B2B MarketingDocument6 pagesProject of B2B MarketingARVIND PATELNo ratings yet
- HRM PhilipsDocument15 pagesHRM PhilipsJôy Gûptâ0% (1)
- Major Competitors of PhilipsDocument18 pagesMajor Competitors of PhilipsAditya Nayak100% (1)
- Company ProfileDocument3 pagesCompany ProfileAnushka GogoiNo ratings yet
- New Venture Integration (NVI)Document3 pagesNew Venture Integration (NVI)Sarvagya JhaNo ratings yet
- Philips-Analyzing The Marketing Environment in The Middle East PDFDocument2 pagesPhilips-Analyzing The Marketing Environment in The Middle East PDFHafiz Amanullah FarrukhNo ratings yet
- SM Cia 3Document17 pagesSM Cia 3Ritika HalderNo ratings yet
- Philips Lighting 2011Document21 pagesPhilips Lighting 2011Nitesh Kumar0% (1)
- Philips CaseDocument4 pagesPhilips CaseDe BuNo ratings yet
- BPL RepositioningDocument28 pagesBPL RepositioningImmanuel Joe ThomasNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document4 pagesCase 1Bint OsmanNo ratings yet
- Philips Company AnalysisDocument14 pagesPhilips Company AnalysisANJALI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Case Study of Royal Philips Corporation and The Intelligent Pill (Ipill)Document21 pagesCase Study of Royal Philips Corporation and The Intelligent Pill (Ipill)dsabol7534No ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument20 pagesExecutive SummaryShehzana MujawarNo ratings yet
- Final AssignmentDocument5 pagesFinal AssignmentRobin Rahman 1711948030No ratings yet
- Philips Electronics India Project Report on Market Footprint in IndoreDocument48 pagesPhilips Electronics India Project Report on Market Footprint in Indoremerchantsana_714No ratings yet
- philips[1]Document5 pagesphilips[1]tahirijaz603No ratings yet
- MM ZG611 Ec-3r Second Sem 2016-2017Document5 pagesMM ZG611 Ec-3r Second Sem 2016-2017ymsyaseenNo ratings yet
- Employee CommitmentDocument72 pagesEmployee CommitmentNavpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Royal Philips ElectronicsDocument4 pagesCompany Profile: Royal Philips ElectronicsVishal GargaNo ratings yet
- Misc Philips ROI FullDocument12 pagesMisc Philips ROI FullroahannikamNo ratings yet
- Prepare A SWOT Analysis of The Current Position of PhilipsDocument3 pagesPrepare A SWOT Analysis of The Current Position of PhilipsDhroov GoyalNo ratings yet
- LG PresentationDocument27 pagesLG Presentationpoojaarora_10_june50% (2)
- Assignment 8Document5 pagesAssignment 8Rehman MukarramNo ratings yet
- PhilipsDocument11 pagesPhilipsTYBMS B 2147 SALVI ROHITNo ratings yet
- LG Vs PhilipsDocument23 pagesLG Vs PhilipsGaurav Jeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Company Profile Marketing Strategy Objectives of The Study Scope of The Study Research MethodologyDocument42 pagesChapter-1: Company Profile Marketing Strategy Objectives of The Study Scope of The Study Research MethodologyMonu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Videocon ProjectDocument12 pagesVideocon Projectbabu_raj_9No ratings yet
- Philips CSR focuses on healthcare, environmentDocument19 pagesPhilips CSR focuses on healthcare, environmentMugilanNo ratings yet
- PhilipsDocument8 pagesPhilipsPrasanth Khanna100% (1)
- GM02 Economic and Social Environment of Business: Assignment No.IDocument4 pagesGM02 Economic and Social Environment of Business: Assignment No.IMahfooz AlamNo ratings yet
- Deloitte NL Culture Project Philips LightingDocument18 pagesDeloitte NL Culture Project Philips LightingRohan NandgaokarNo ratings yet
- Restructuring PhilipsDocument4 pagesRestructuring PhilipsPradeep BukarwalNo ratings yet
- 170106023459Document21 pages170106023459pulkitNo ratings yet
- PhilipsDocument9 pagesPhilipsAnkush DharNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of LG Electronics India (PVT.) Ltd.Document95 pagesMarketing Strategies of LG Electronics India (PVT.) Ltd.Md Naushad71% (7)
- Estrategias e Innovación: FODA Análisis de Apple y PhilipsDocument8 pagesEstrategias e Innovación: FODA Análisis de Apple y Philipsgabyfd87No ratings yet
- Info On LGDocument71 pagesInfo On LGbeejoyNo ratings yet
- Title: Consumer Behaviour Towards LG Television inDocument22 pagesTitle: Consumer Behaviour Towards LG Television inkunikithNo ratings yet
- Philips Versus MatsushitaDocument4 pagesPhilips Versus Matsushitaswati04sweetNo ratings yet
- BPL Colour Television - India's Top TV BrandDocument7 pagesBPL Colour Television - India's Top TV BrandPrakhyath BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Analisa Brand of PhilipsDocument6 pagesAnalisa Brand of PhilipsindrianiNo ratings yet
- How Philips Electronics is Making Things Better Through Innovation and Customer FocusDocument13 pagesHow Philips Electronics is Making Things Better Through Innovation and Customer Focusganguly86No ratings yet
- Case SynopsisDocument4 pagesCase SynopsisIndranil RoyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Sunil Gupta's Driving Digital StrategyFrom EverandSummary of Sunil Gupta's Driving Digital StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quantum Profits: Saving Western Manufacturing Using the Fourth DimensionFrom EverandQuantum Profits: Saving Western Manufacturing Using the Fourth DimensionNo ratings yet
- Summary of Oliver Gassmann & Karolin Frankenberger's The Business Model NavigatorFrom EverandSummary of Oliver Gassmann & Karolin Frankenberger's The Business Model NavigatorNo ratings yet
- Changeship - Workbook: Building and scaling next generation businesses in the digital polypol: Purpose driven - Customer dedicated - Sustainability enabledFrom EverandChangeship - Workbook: Building and scaling next generation businesses in the digital polypol: Purpose driven - Customer dedicated - Sustainability enabledNo ratings yet
- Netflix Success Decoded: The Key Factors That Led To Its Success: Learn Why Innovation, Disruption And User Experience Are So ImportantFrom EverandNetflix Success Decoded: The Key Factors That Led To Its Success: Learn Why Innovation, Disruption And User Experience Are So ImportantNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena ProblemDocument2 pagesTransport Phenomena ProblemSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Acroname: Sensor/Voltage Interface SessionDocument1 pageAcroname: Sensor/Voltage Interface SessionSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Simulating and Rendering FluidsDocument47 pagesSimulating and Rendering FluidsvdertiNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate TimeDocument1 pageHow To Calculate TimeSayan KarNo ratings yet
- MM653 EscaDocument58 pagesMM653 EscaSayan KarNo ratings yet
- METALLURGICAL ENGINEERING AND MATERIALS SCIENCE MCQDocument6 pagesMETALLURGICAL ENGINEERING AND MATERIALS SCIENCE MCQSayan KarNo ratings yet
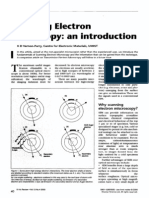
- SEM and Its Applications For Polymer ScienceDocument10 pagesSEM and Its Applications For Polymer ScienceSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution For Diffusion EquationDocument5 pagesNumerical Solution For Diffusion EquationSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Buddy Talk Tata SteelDocument2 pagesBuddy Talk Tata SteelSayan KarNo ratings yet
- SEM, XPS, TEM, ESCA, ThermalDocument1 pageSEM, XPS, TEM, ESCA, ThermalSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Surface Science and Methods in Catalysis CourseDocument85 pagesSurface Science and Methods in Catalysis CourseSayan Kar100% (1)
- SEM IntroDocument5 pagesSEM IntroSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution For Diffusion EquationDocument5 pagesNumerical Solution For Diffusion EquationSayan KarNo ratings yet
- THEORY OF POLYMER DYNAMICS - PaddingsDocument34 pagesTHEORY OF POLYMER DYNAMICS - PaddingsSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Modelling Studies On The Effects of Convection DuringDocument24 pagesModelling Studies On The Effects of Convection DuringSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Miller Indices & Bragg LawDocument4 pagesMiller Indices & Bragg LawSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Kinetics PFR PBR CSTR RTDDocument1 pageKinetics PFR PBR CSTR RTDSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Convections On SolidificationDocument1 pageEffects of Convections On SolidificationSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Polymer CompressionDocument4 pagesPolymer CompressionSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Transport TheoremDocument2 pagesTransport TheoremSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Galerkin Finite Element MethodsDocument9 pagesGalerkin Finite Element MethodsSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Ben Map Manual Oct 2012Document272 pagesBen Map Manual Oct 2012Sayan KarNo ratings yet
- 2007 - Urban Air Poll Analysis For UB Mongolia - ESDocument11 pages2007 - Urban Air Poll Analysis For UB Mongolia - ESSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Carbon-Based Field-Effect Transistors For NanoelectronicsDocument2 pagesCarbon-Based Field-Effect Transistors For NanoelectronicsSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Dynamic Simulation of Crystallization of Isotactic PolypropyleneDocument1 pageMolecular Dynamic Simulation of Crystallization of Isotactic PolypropyleneSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Practical Gauss PlumeDocument5 pagesPractical Gauss PlumeSaraswati DewiNo ratings yet
- IISc Interview 2013Document4 pagesIISc Interview 2013Sayan KarNo ratings yet
- 1dfem FDocument12 pages1dfem FSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Math 257: Finite Difference MethodsDocument8 pagesMath 257: Finite Difference MethodsSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Petri Net Modeling and ApplicationsDocument13 pagesPetri Net Modeling and ApplicationsRishiraj SenguptaNo ratings yet
- HVCB Timing ApplicationDocument52 pagesHVCB Timing Applicationbhuban mohanNo ratings yet
- Grove GMK 4080Document6 pagesGrove GMK 4080Deiver BarrazaNo ratings yet
- Address Book in JAVADocument18 pagesAddress Book in JAVAmelyfony100% (1)
- NASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsDocument17 pagesNASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsEgz AguilarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Power Transmission ReviewDocument17 pagesMechanical Power Transmission ReviewRoshan TiwariNo ratings yet
- GM300 SMDocument46 pagesGM300 SMSrboljub Milosavljevic100% (1)
- STP of Ethifen SyrupDocument5 pagesSTP of Ethifen SyrupBejoy KarimNo ratings yet
- What Is AmplifierDocument18 pagesWhat Is AmplifierEbayLunaNo ratings yet
- Sectional Results: Sofistik 2020Document28 pagesSectional Results: Sofistik 2020ec05226No ratings yet
- TASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)Document3 pagesTASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)frank 101No ratings yet
- Measurement & Calculation of Vehicle Center of Gravity Using Portable Wheel ScalesDocument11 pagesMeasurement & Calculation of Vehicle Center of Gravity Using Portable Wheel ScalesVedant KodagiNo ratings yet
- Quick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentDocument1 pageQuick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentMiguel FNo ratings yet
- The Weka Guard and Protector - Weka MarineDocument2 pagesThe Weka Guard and Protector - Weka MarineJoko SusiloNo ratings yet
- SSP 099 18 Tfsi 132kw 20 Tfsi 162kw Ea888Document60 pagesSSP 099 18 Tfsi 132kw 20 Tfsi 162kw Ea888Jose Ramón Orenes ClementeNo ratings yet
- PRJCTDocument10 pagesPRJCTrpkn541No ratings yet
- The Magnaflux Advantage (Whole Catalog)Document51 pagesThe Magnaflux Advantage (Whole Catalog)Andy StkNo ratings yet
- Earth Gravity and Satellite Orbits CalculationsDocument9 pagesEarth Gravity and Satellite Orbits CalculationsYoobsan Asaffaa FufaaNo ratings yet
- Desizing of CottonDocument16 pagesDesizing of CottonDeepali RastogiNo ratings yet
- Ee09 704 - Electrical Machine Design Model QPDocument2 pagesEe09 704 - Electrical Machine Design Model QPGīřïşh McNo ratings yet
- Hot Bolting FPSO BrazilDocument1 pageHot Bolting FPSO BrazilKhan Arshi100% (1)
- GRAS 46BE 1/4Document9 pagesGRAS 46BE 1/4nino16041973No ratings yet
- Trigonox101 PdsDocument3 pagesTrigonox101 PdsPaula RiveraNo ratings yet
- Appendix B - Design Examples: B.1 Multi-Span Precast Concrete Girder Made Continuous With Composite DeckDocument35 pagesAppendix B - Design Examples: B.1 Multi-Span Precast Concrete Girder Made Continuous With Composite DeckMICHAEL TADESSENo ratings yet
- RPVP Puerto PrincesaDocument8 pagesRPVP Puerto PrincesaRanny LomibaoNo ratings yet
- Goodyear Brochure Bandas-48Document1 pageGoodyear Brochure Bandas-48DavidNo ratings yet
- NPN Silicon Transistor: High Voltage Switch Mode ApplicationDocument6 pagesNPN Silicon Transistor: High Voltage Switch Mode ApplicationManuel PradoNo ratings yet
- Nitobond EP 0608Document2 pagesNitobond EP 0608James PittsNo ratings yet
- HW03 5ad S19 PDFDocument2 pagesHW03 5ad S19 PDFbobNo ratings yet
- Argelith Lieferprogramm GBDocument24 pagesArgelith Lieferprogramm GBmutyokaNo ratings yet

























![philips[1]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719654473/149x198/dfc5cd21e5/1712150764?v=1)