Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproduction in Human Beings
Uploaded by
anjupalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproduction in Human Beings
Uploaded by
anjupalCopyright:
Available Formats
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS The period of adolescence where the rate of general body growth begins to slow down
and reproductive tissues begin to mature is called PUBERTY. CHANGES AT PUBERTY Increase in height Change in body shape Voice change Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands Development of sex organs Reaching Mental, Intellectual and Emotional Maturity Hormones from pituitary stimulate testes and ovaries to release testosterone( in male) and estrogen (in female)
Released in the blood stream and reach parts of the body ( Target site)
Stimulate changes in the body at onset of puberty
I)
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS Testis- Produces male gamete (sperm). Secretes male hormone (testosterone).
Located outside abdominal cavity in SCROTUM because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. Epididymis- Temporary storage of sperms. Vas deferens- Transports sperm into urethra. Urethra- forms a common passage for both the sperms and urine Penis- Copulatory organ II) ACCESSORY GLANDS Prostate glandSecretion keeps the sperms active. Seminal vesicleSecretion provides nourishment and mobility to sperm. Cowpers gland-Produces white viscous and alkaline secretion. SEMEN Sperm and secretion of assessor glands. SPERM consist of Head, Middle piece and Tail.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Ovaries- located close to the lateral walls of pelvic cavity. Maturation of ovum takes place and secretes female hormones ( estrogen and progesterone). Fallopian tube/oviduct- Site for fertilization Uterusembryo attaches here for further development o Nourishment of foetus o Contractions expel the baby out during birth. Cervix- the cervix projects slightly into an elastic muscular tube ,the vagina Vagina/birth canal- receives sperm and act as birth canal When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousand s of immature eggs which start maturing at the time of puberty. Menarche - commencement of menstrual cycle at puberty which marks the beginning of reproductive life of the human female.
Menopause - cessation of menstrual cycle which marks the end of the reproductive life of the human female. MENSTRUAL CYCLE The cycle includes the maturation of egg, its release, thickening of uterine wall and its breakdown if pregnancy does not occur. FERTILISATION The union of sperm and egg is called fertilization It takes place in fallopian tube The fertilized egg ( the zygote) gets implanted in the lining of the uterus The embryo gets nutrition and oxygen from the mothers blood with the help of PLACENTA. The child birth takes place after nine months as a result of rhythmic contraction of the muscles in the uterus.
Implantation- Attachment of embryo to the lining of uterus.
Placenta - A connection between the mother and the foetus. Gestation period - The period between fertilization and birth.
I. II.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH Need and methods of family planning To check population explosion To maintain general and reproductive health of women Birth control methods
Mechanical - i) Diaphragam ii) IUCD iii) Condom Surgical - i) Tubectomy in female ii) Vasectomy in male
Chemical - i) Vaginal pills ii) Oral pills STDs Infectious diseases which are spread by sexual contact. Examples; Syphilis, Gonorrhea, Trichomoniasis and AIDS.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thMadhav GourNo ratings yet
- A - Lecture 1 - The Bony PelvisDocument31 pagesA - Lecture 1 - The Bony PelvisShirline MillingtonNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of the Female Genital TractDocument170 pagesCongenital Anomalies of the Female Genital Tractonijino100% (1)
- Menstrual Cycle Fertilization and Embryogenesis 1Document71 pagesMenstrual Cycle Fertilization and Embryogenesis 1Siselle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of NewbornDocument4 pagesImmediate Care of NewbornjvjohnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Conference PDFDocument44 pagesLesson Plan of Conference PDFRahul DamorNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesDocument8 pagesUnit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesSudip Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- Constriction Band SyndromeDocument8 pagesConstriction Band SyndromesabistonNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis and EmbolismDocument43 pagesThrombosis and Embolismkanchana pvnNo ratings yet
- Procedures in O&GDocument7 pagesProcedures in O&GAbdulrahman NajiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemLiangkiuwiliuNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Physical Exam - StudentsDocument112 pagesNeonatal Physical Exam - StudentssanNo ratings yet
- Course Plan Post BasicDocument30 pagesCourse Plan Post Basicsumitgupta2391No ratings yet
- Obg Objective QuestionDocument1 pageObg Objective QuestionDESUN Nursing School100% (1)
- InfantDocument37 pagesInfantGwyneth Dane LaranangNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument18 pagesRenal SystemS GNo ratings yet
- Bone Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesBone Growth and DevelopmentTroy Albert MirandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment by DR Dahir123Document84 pagesNewborn Assessment by DR Dahir123Najjuma BettyNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Breast FeedingDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Breast FeedingRollan MaulasNo ratings yet
- 03 - Skeletal System 2019 Moodle-FullDocument90 pages03 - Skeletal System 2019 Moodle-FullSeanNo ratings yet
- Effective Midwifery: Fetal Skull LandmarksDocument11 pagesEffective Midwifery: Fetal Skull LandmarksRinkish DalliahNo ratings yet
- PPP PPHDocument26 pagesPPP PPHKuruvila L DanielNo ratings yet
- Placenta CirculationDocument11 pagesPlacenta CirculationJason Jimmy Lee PillayNo ratings yet
- RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN INFERTILITY TECHNIQUESDocument111 pagesRECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN INFERTILITY TECHNIQUESsanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- 03.chronic Supp Otitis MediaDocument33 pages03.chronic Supp Otitis MediaJumanne JayNo ratings yet
- Congenital Vascular Anomalies in Amniotic Band Syndrome of The LimbsDocument7 pagesCongenital Vascular Anomalies in Amniotic Band Syndrome of The LimbsDiana IacobNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practices in ObstetricsDocument46 pagesEvidence Based Practices in Obstetricsvikas takNo ratings yet
- Iv TherapyDocument3 pagesIv TherapylovlyNo ratings yet
- Fetal Malpresentations Diagnosis and ManagementDocument21 pagesFetal Malpresentations Diagnosis and ManagementEsther Ellise Abundo100% (1)
- Fetal MalpresentationDocument33 pagesFetal MalpresentationMichael Angelo Seña100% (1)
- Anatomy of The BreastDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The BreastJuliana Andres100% (1)
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument6 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitiesPrashant MundeNo ratings yet
- Sexual Dysfunctions and ParaphiliasDocument10 pagesSexual Dysfunctions and ParaphiliasGino Al Ballano BorinagaNo ratings yet
- Malpresentation and Malposition: Supervision By: DR Ashjan Tarayra Directed By: DR Montaser AsafrahDocument53 pagesMalpresentation and Malposition: Supervision By: DR Ashjan Tarayra Directed By: DR Montaser AsafrahMahmoud Asafrah100% (1)
- Fetal and Placental Physiology:: The PlacentaDocument14 pagesFetal and Placental Physiology:: The PlacentaTri GunawanNo ratings yet
- Malformations of Female Genital OrgansDocument28 pagesMalformations of Female Genital OrgansTommy SinghNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Early DevelopmentDocument73 pagesFertilization and Early DevelopmentSavita Hanamsagar100% (1)
- Growth and Developments PDFDocument3 pagesGrowth and Developments PDFAlok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fertilisasi Askeb IDocument19 pagesFertilisasi Askeb IPutry Utami0% (1)
- Nicu ReportDocument66 pagesNicu ReportEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- 2019 Midwife CVDocument2 pages2019 Midwife CVapi-455508133No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System ExplainedDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive System ExplainedJasmaine RivoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Pregnant Woman With HIVDocument34 pagesCare of The Pregnant Woman With HIVJenelle Melinda TullochNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual CycleDocument7 pagesThe Menstrual Cyclejoshua.brussell100% (1)
- Pyelonephritis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Kidney InfectionDocument12 pagesPyelonephritis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Kidney Infectionngee_markpatrick100% (1)
- Abnormalities of The PassengerDocument87 pagesAbnormalities of The Passengerapi-19641337100% (2)
- Abnormal LabourDocument12 pagesAbnormal Labourabidul hoqueNo ratings yet
- PAIN RELIEF IN LABOUR: ANESTHESIA OPTIONSDocument85 pagesPAIN RELIEF IN LABOUR: ANESTHESIA OPTIONSBrian Baxter100% (1)
- Menstrual CycleDocument3 pagesMenstrual CycleTHANGES THANGUNo ratings yet
- Vaginal CandidiasisDocument29 pagesVaginal CandidiasisMike Serge RazafiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument63 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Obstetrical OperationsDocument47 pagesLecture 9 Obstetrical OperationsgnpobsNo ratings yet
- THE MORAL ISSUES OF ABORTION: ONGOING DEBATES CHAPTERDocument38 pagesTHE MORAL ISSUES OF ABORTION: ONGOING DEBATES CHAPTERBHUKYA USHARANINo ratings yet
- Understanding Twin PregnancyDocument56 pagesUnderstanding Twin Pregnancyangel panchalNo ratings yet
- Newborn Reflexes ExplainedDocument2 pagesNewborn Reflexes ExplainedNEil モラレスNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument17 pagesAnatomy ReportMabeth PagatpatNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEjoannalyn gregorioNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8Document8 pagesReproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8anjupalNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination - Class XDocument7 pagesControl & Coordination - Class XanjupalNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument16 pagesHeredity and EvolutionanjupalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFanjupal80% (5)
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument11 pagesImprovement in Food Resourcesanjupal100% (2)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plantsanjupal100% (2)
- Sources of Energy - Class XDocument9 pagesSources of Energy - Class XanjupalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Science Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFDocument13 pagesScience Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFanjupalNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind MappingDocument12 pagesImprovement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind Mappinganjupal83% (6)
- Force and Laws of MotionDocument20 pagesForce and Laws of MotionanjupalNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument11 pagesHeatanjupalNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint - Vivek - X-ADocument33 pagesCarbon Footprint - Vivek - X-AanjupalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Control and CoordinationDocument17 pagesControl and Coordinationanjupal100% (1)
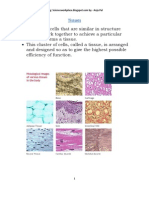
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesanjupalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument8 pagesNutrition in PlantsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument19 pagesNutrition in AnimalsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Cell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesCell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeanjupalNo ratings yet
- L-8 Motion: List of ConceptsDocument11 pagesL-8 Motion: List of ConceptsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument28 pagesLife Processesanjupal100% (1)
- Bulletin 13.9.22Document4 pagesBulletin 13.9.22dbq088sNo ratings yet
- Consent To Electronic CommunicationsDocument2 pagesConsent To Electronic CommunicationsVilmarie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titration Experiment ResultsDocument3 pagesAcid-Base Titration Experiment ResultsLim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- Archana PriyadarshiniDocument7 pagesArchana PriyadarshiniJagriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Crises ManagementDocument19 pagesCrises ManagementJinenus MosisaaNo ratings yet
- Early Christian Reliquaries in The Republic of Macedonia - Snežana FilipovaDocument15 pagesEarly Christian Reliquaries in The Republic of Macedonia - Snežana FilipovaSonjce Marceva50% (2)
- Reading SkillsDocument37 pagesReading SkillsShafinaz ZhumaNo ratings yet
- Bushing Conductor TypesDocument2 pagesBushing Conductor TypesSandeep BNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Brushless DC Motor Using Conventional ControllersDocument9 pagesSpeed Control of Brushless DC Motor Using Conventional ControllersMuhdnursalam ZolkepliNo ratings yet
- Curso de GaitaDocument24 pagesCurso de GaitaCarlosluz52No ratings yet
- 20 Đề Thi Thử Tiếng Anh Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết - LovebookDocument462 pages20 Đề Thi Thử Tiếng Anh Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết - LovebookPhương UyênNo ratings yet
- Under DronesDocument336 pagesUnder DronesRobert LewisNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise - Analysis of The Collapse of Silicon Valley BankDocument2 pagesPractical Exercise - Analysis of The Collapse of Silicon Valley Bankhanna.ericssonkleinNo ratings yet
- Controlled Vadose Zone Saturation and Remediation (CVSR)Document35 pagesControlled Vadose Zone Saturation and Remediation (CVSR)FranciscoGarciaNo ratings yet
- No. of Periods UNIT - 1: Antenna FundamentalsDocument8 pagesNo. of Periods UNIT - 1: Antenna Fundamentalsbotla yogiNo ratings yet
- Week Three Lesson Plan Bread and Jam For FrancesDocument2 pagesWeek Three Lesson Plan Bread and Jam For Francesapi-29831576No ratings yet
- Ear Discharge (Otorrhoea) FinalDocument24 pagesEar Discharge (Otorrhoea) Finaljaya ruban100% (1)
- Sally Su-Ac96e320a429130Document5 pagesSally Su-Ac96e320a429130marlys justiceNo ratings yet
- Reviews On IC R 20Document5 pagesReviews On IC R 20javie_65No ratings yet
- Curriculum Design and Development Part IDocument18 pagesCurriculum Design and Development Part IAngel LimboNo ratings yet
- Lewatit VP OC 1600 LDocument3 pagesLewatit VP OC 1600 Lphucuong2410No ratings yet
- File Download ActionDocument45 pagesFile Download Actionecarter9492No ratings yet
- Slides Iso 17021 Be LacDocument117 pagesSlides Iso 17021 Be Lacjorge.s1943No ratings yet
- Fire Resistance Ratings - ANSI/UL 263: Design No. U309Document4 pagesFire Resistance Ratings - ANSI/UL 263: Design No. U309DavidNo ratings yet
- Helical Axes of Skeletal Knee Joint Motion During RunningDocument8 pagesHelical Axes of Skeletal Knee Joint Motion During RunningWilliam VenegasNo ratings yet
- Nucor at A CrossroadsDocument10 pagesNucor at A CrossroadsAlok C100% (2)
- Lesson 4 - Learning AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson 4 - Learning AssessmentBane LazoNo ratings yet
- Verify File Integrity with MD5 ChecksumDocument4 pagesVerify File Integrity with MD5 ChecksumSandra GilbertNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System FundamentalsDocument4 pagesElectrical Power System FundamentalsArnab BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ExcaliburDocument113 pagesExcaliburYuvarajaa SomasundaramNo ratings yet