Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton's laws of motion explained
Uploaded by
Bri_SinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Newton's laws of motion explained
Uploaded by
Bri_SinaCopyright:
Available Formats
an object at rest will remain at rest
E.g: Book Resting on a table For Falling Object, when Weight = Air Resistance, No Resultant Force -> No Acceleration -> Falling at a constant velocity (Terminal Velocity) Factors Affecting Terminal Velocity Mass The greater the mass, the greater the terminal velocity Surface Area The greater the surface area, the smaller the terminal velocity
When Forces are balanced (Newton 1st Law)
an object in motion will continue in motion at constant speed in a straight line in the absence of a resultant force acting on it.
Terminal Velocity
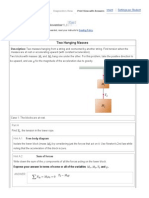
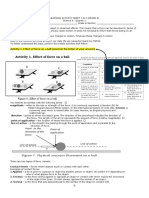
Force that opposes motion Advantages and Disadvantages of Frictions Ways to Reduce Friction Newtons second law of motion states that the resultant force acting upon an object is equal to the product of the mass and the acceleration of the object. Fr = ma Resultant of Parallel Forces
Friction
Simple Diagram to show all the forces acting on a body Help to solve problems
Free Body Diagrams
When Forces are UN-Balanced (Newton 2nd Law)
Forces (Newton's Laws of Motion)
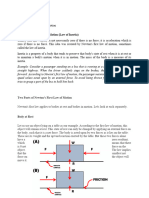
Newtons third law of motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction If object A exerts a force on object B, then B exerts an equal but opposite force on A Newtons third laws tells us 4 characteristics of forces: 1. Forces always occur in pair. Each pair is made of an action and reaction. 2.Action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude. 3.Action and reaction forces are opposite in direction. 4.Action and reaction forces act on different bodies.
Resultant of Non-Parallel Forces (use vector diagram)
Newton 3rd Law
Use to solve
Scale Diagram to solve for forces
Resultant Forces Use Parallelogram/Triangle Method Resultant force must have double arrow head Forces in Equilibrium ( No balanced forces) Use closed triangle method
Things to include in diagram: 1. Scale (1 cm rep 100N) 2. Parallelogram/ Triangle Method 3. Answer must include: Magnitude of Force and direction (means angle to which force)
You might also like
- Newton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyIrene QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Motion and Design VocabDocument2 pagesMotion and Design Vocabapi-289447020100% (1)
- 4.3newtons 1st Law and 2nd LawDocument6 pages4.3newtons 1st Law and 2nd Lawnegad607No ratings yet
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Motion PDFDocument9 pagesNewton's Law of Motion PDFSam Dy100% (3)
- What Is A ForceDocument12 pagesWhat Is A ForceSyed M HassanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNo ratings yet
- Newtons LaDocument9 pagesNewtons La金 Abigail RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Basic Physics SE-Force Difficulty LevelDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Basic Physics SE-Force Difficulty LeveltsoniffNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument16 pagesExam 2 SolutionssuccinumNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 ForcesDocument38 pagesWeek 8 ForcesSALMA AREKATNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument13 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedChinmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionMiralvNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 - Dynamic NotesDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 - Dynamic Notesnigusayele06No ratings yet
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument44 pagesLaws of Motion Explainedmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Sci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyDocument7 pagesSci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyCherry Beth PagenteNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument24 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Previewnanio_7No ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument56 pagesNewton's Lawskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument3 pagesDynamics NotesShamsherNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Organic2Document18 pagesCHM1 Organic2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- PHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Document7 pagesPHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Kenneth SilvaNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument10 pagesNewtons LawsJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - 2Document25 pagesChapter 5 - 2Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of MotionDocument2 pagesNewton's First Law of MotionSiddharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument39 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionKevin Joseph E. MarceloNo ratings yet
- statics of rigid bodies (1)Document14 pagesstatics of rigid bodies (1)Mariya MariyaNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument23 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument26 pagesPhysics Projectakash singh100% (4)
- Dynamics Summary NotesDocument7 pagesDynamics Summary NotesArlo SeasenNo ratings yet
- L1 Newton'sLawsDocument61 pagesL1 Newton'sLawsArafat AnikNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Easy As Apple Pie!Document44 pagesNewton's Laws: Easy As Apple Pie!RITUPARNA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesThree Laws of MotionCamille Neriza FeLicianoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion by JoyDocument49 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion by JoyMjoyTibayNo ratings yet
- 1.5newton's LawDocument39 pages1.5newton's LawEaintNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ConceptDocument15 pagesChapter 1 ConceptSiti KhalijahNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument7 pagesForces and Motion ExplainedMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument9 pagesForceMohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion ExplainedDocument16 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion ExplainedJoelle PoweNo ratings yet
- Physics Newton'sLawsofMotionDocument44 pagesPhysics Newton'sLawsofMotionCamela LacsamaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- PH110-CHAPTER 4 DynamicsDocument17 pagesPH110-CHAPTER 4 DynamicsNtape Knox SiwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 NotesYuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument27 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionJayhia Malaga JarlegaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument10 pagesNewton's First LawmatwaNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawDocument10 pagesNewton's LawKyla Desiree BedienesNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion: ContinuedDocument37 pagesForces and Newton's Laws of Motion: ContinuedPrasanta NaskarNo ratings yet
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocument22 pages05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Forces, Newton's Laws, and DynamicsDocument10 pagesForces, Newton's Laws, and DynamicsCai MingleiNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion1Document6 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion1darlei byerotNo ratings yet
- ANSWER-KEYDocument11 pagesANSWER-KEYPETER SALIVIONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 DynamicsTutor_KLNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 2 Newtons LawsDocument33 pagesMechanics 2 Newtons LawsParth ParakhNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - 1: 5.1. Newtons First LawDocument16 pagesForce and Motion - 1: 5.1. Newtons First Laweka123No ratings yet