Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3 Chapter 1 - Respiration
Uploaded by
Mona MohtarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3 Chapter 1 - Respiration
Uploaded by
Mona MohtarCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE SCIENCE
WWW.SMKSP.COM
Intensive
FOR FOR FORM 3 FORM 3 FOR FORM 3
SCIENCE INTENSIVE PROGRAMME FOR FROM 3 CHAPTER 1 : RESPIRATION SMK SUNGAI PASIR , O8OOO SUNGAI PETANI , KEDAH DARULAMAN. TEL : 04-421 1764 FAX : 422 0203 LAMAN WEB : WWW.SMKSP.COM
1 Respiration is a chemical process whereby glucose react with oxygen to produce energy, carbon dioxide and water. Words equation
Glucose + Oxygen Energy + Carbon dioxide + Water
Transport of oxygen from the alveoli into the cells
Huamn Respiratory System
1.Nasal cavity
Trap dust, warmed and moistens air
2. Trachea
Trap dust and microorganisms
3. Brochus
Direct air into brochiole
6. Ribs
Protects lungs and heart 7Intercostal muscle Moves ribs
4. Bronchiole
Direct air into Alveoli
5. Alveoli
Diffuses air into blood capillaries
8. Diaphragm
Helps breathing mechanism
1 Oxygen from alveolus diffuses into the blood capillaries and combines with haemoglobin in the red blood cells to form oxyhaemoglobin. 2. The oxygenated blood then transport to the heart and pumps to all parts of the body. 3. When reach the body cells, oxyhaemoglobin break down and the oxygen diffuses into the cells and carries out the process of respiration 4. At the same time, carbon dioxide in the cells diffuses into the blood capillaries. 5. The deoxygenated blood then transport to the heart and pumps to the lungs. 6
Harmful substances Cigarette smoke Effects Tar - blackens the lungs. Nicotine - causes lung cancer Acid - corrodes lung's cells. Carbon monoxide - reduce ability of blood to transport oxygen
3 Pathway of air flow from the nose to the alveolus during inhalation :
BronNose Trachea Bronchus chiole Alveolus
Vehicles smoke
4 Using a functional model of the lungs to explain the process of inhalation.
Y-Shape tube Balloon Air space Bell jar Rubber sheet represented Trachea & bronchus represented represented represented represented Lung Thoracic cavity Rib cage Diaphragm
Using a model to explain the inhalation
1 2. 3. 4. When the rubber sheet is pulled down. Volume of bell jar increase. Air pressure inside the bell jar increase. Air from outside flow into the balloon and expand. represented 1 2. 3. 4.
Process of inhalation
When the diaphragm is move downward & flattens Volume of thoracic cavity is increase. Air pressure inside the thoracic cavity increase. Air from outside flow into the lung and inflate.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Science F4 Effect of Impurities On Boiling Point NewDocument1 pageScience F4 Effect of Impurities On Boiling Point Newzalifah74No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- m5 FractionsDocument2 pagesm5 Fractionszalifah74No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Module 7: Phythagoras' Theorem (Form 2)Document2 pagesModule 7: Phythagoras' Theorem (Form 2)zalifah74No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Module 3:percentage (Form 1)Document1 pageModule 3:percentage (Form 1)zalifah74No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Module 2: Basic Measurements (Form 1)Document7 pagesModule 2: Basic Measurements (Form 1)zalifah74No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
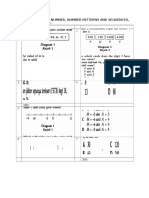
- m1 Whole Num, Num Pattern & Sequences, DecimalsDocument4 pagesm1 Whole Num, Num Pattern & Sequences, Decimalszalifah74No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Mathematical Reasoning Maths k2.Document12 pagesMathematical Reasoning Maths k2.zalifah74No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Plant CellDocument35 pagesThe Plant Cellzalifah74No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Cell: An Internet Laboratory On The Cell, Created by Wendy M. Rounds 5/3/00Document24 pagesThe Cell: An Internet Laboratory On The Cell, Created by Wendy M. Rounds 5/3/00zalifah74No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- What Happens During A HeartbeatDocument3 pagesWhat Happens During A Heartbeatzalifah74No ratings yet
- 2012 f5 Identifying VariablesDocument8 pages2012 f5 Identifying Variableszalifah74No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
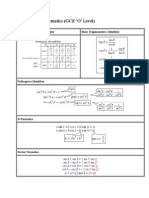
- Additional Mathematics (GCE 'O' Level) : TrigonometryDocument2 pagesAdditional Mathematics (GCE 'O' Level) : Trigonometryzalifah74No ratings yet
- Nitrogen CyclfeDocument1 pageNitrogen Cyclfezalifah74No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)