Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alpha Receptors Classification
Uploaded by
rajeshmangalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alpha Receptors Classification
Uploaded by
rajeshmangalCopyright:
Available Formats
Alpha 1 agonists Because of their properties as vasoconstrictive agents they are used to reduce edema and inflammation.
Common decongestant drugs include naphazoline, phenylephrine and propylhexedrine. Alpha 1 antagonists These drugs act by causing vasodilation and decreased peripheral resistance, therefore they are used in the treatment of hypertension (prazosin). Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia is another clinical use of alpha 1 antagonists: tamsulosin is a subtype-selective alpha 1A receptor that has more specificity toward smooth muscle in genitourinary tract; thus tamsulosin has lower incidence of orthostatic hypotension. Alpha 2 agonists By activating central alpha 2 receptors, alpha 2 adrenergic agonists inhibit sympathetic outflow from CNS. Clonidine is used for the rteatment of hypertension and symptoms associated with opioid withdrawal. Alpha-methyldopa is a precursor to the alpha 2 agonist alpha-methylnorepinephrine, it is the drug of choice for the treatment of hypertension during pregnancy. Alpha 2 antagonists Yohimbine blockade of alpha 2 receptors leads to increased release of norepinephrine with susequent stimulation of cardiac beta 1 receptors and peripheral vasculature alpha 1 receptors. Yohimbine was used in the past to treat erectile dysfunction. References and further reading Golan, David E (editor). Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy, 2nd edition. LWW: 2008. Katzung, B. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 10th Edition. Mc Graw Hill Medical: 2007 Harvey, Richard; Champe, Pamela (series editors). Lippincott illustrated reviews: Pharmacology, 4th edition. LWW: 2009 Written By:Flavio Guzmn, MD Last updated: November 22, 2010. Read related articles about: Antihypertensives, Autonomic Pharmacology, Cardiovascular Previous Post Next Post
You might also like
- Reference Literature ReviewDocument1 pageReference Literature ReviewrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel BlockersDocument3 pagesCalcium Channel BlockersrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Baker RC Armstrong Ma Young Is Mcclean E O Rourke D Campbell FC Dsa Aa Mcbride WTDocument5 pagesBaker RC Armstrong Ma Young Is Mcclean E O Rourke D Campbell FC Dsa Aa Mcbride WTrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Illnes1Document2 pagesFoodborne Illnes1rajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Risks From Smoking During Pregnancy: Effects On MothersDocument1 pageRisks From Smoking During Pregnancy: Effects On MothersrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
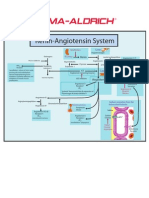
- Angio Ren inDocument1 pageAngio Ren inEndang Dwi KurniaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Process of 5-HT and Noradrenaline NeurotransmissionDocument1 pageThe Normal Process of 5-HT and Noradrenaline NeurotransmissionrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument1 pageVirusesrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Paecilomyces Fungal Species, Associated With A Range of Moldy and Rotting Fruits andDocument2 pagesPaecilomyces Fungal Species, Associated With A Range of Moldy and Rotting Fruits andrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Foodborne PathogensDocument1 pageBacterial Foodborne PathogensrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Jejuni 77.3%, Salmonella 20.9%, Escherichia Coli O157:H7 1.4%, and All Others Less ThanDocument1 pageJejuni 77.3%, Salmonella 20.9%, Escherichia Coli O157:H7 1.4%, and All Others Less ThanrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Arasites: The Scolex of Tenia Solium, A Pork TapewormDocument1 pageArasites: The Scolex of Tenia Solium, A Pork TapewormrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic AgentsDocument1 pagePathogenic AgentsrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Chloroquine: Adverse EffectsDocument1 pageChloroquine: Adverse EffectsrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Preventing Bacterial Food PoisoningDocument1 pagePreventing Bacterial Food PoisoningrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Illness (Also Foodborne Disease and Referred To As Food Poisoning) IsDocument1 pageFoodborne Illness (Also Foodborne Disease and Referred To As Food Poisoning) IsrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Folin-Wu Prodedure of Glucose EstimationDocument3 pagesFolin-Wu Prodedure of Glucose EstimationrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument1 pageStages of MitosisrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel AntagonistsDocument1 pageCalcium Channel AntagonistsrajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Gene Mapping 1Document1 pageGene Mapping 1rajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)