Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Riveted Joints: Hareesha N G Dept. of Aeronautical Engg Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering Bangalore-78
Uploaded by
Hareesha N G0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views22 pagesRiveted Joints
Original Title
Riveted Joints
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRiveted Joints
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views22 pagesRiveted Joints: Hareesha N G Dept. of Aeronautical Engg Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering Bangalore-78
Uploaded by
Hareesha N GRiveted Joints
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Riveted Joints
Hareesha N G Dept. of Aeronautical Engg Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering Bangalore-78
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
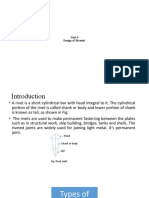
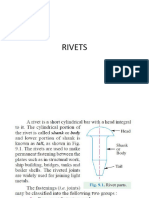
Introduction A rivet is a short cylindrical bar with a head integral to it. The cylindrical portion of the rivet is called shank or body and lower portion of shank is known as tail. The rivets are used to make permanent fastening between the plates such as in structural work, ship building, bridges, tanks and boiler shells. The riveted joints are widely used for joining light metals.
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
Types of Rivet Heads
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
Types of riveted joints
1. Lap joint 2. Butt joint
Lap joint: A lap joint is that in which one plate overlaps the
other and the two plates are then riveted together.
Butt joint: A butt joint is that in which the main plates are kept in alignment butting (i.e. touching) each other and a cover plate (i.e. strap) is placed either on one side or on both sides of the main plates. The cover plate is then riveted together with the main plates.
Butt joint
Lap joint
11/27/2013 Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78 4
Important Terms Used in Riveted Joints
The following terms in connection with the riveted joints are important from the subject point of view : 1. Pitch. It is the distance from the centre of one rivet to the centre of the next rivet measured parallel to the seam as shown in Fig. It is usually denoted by p. 2. Transverse pitch. It is the perpendicular distance between the centre lines of the successive rows as shown in Fig. It is usually denoted by pt. 3. Diagonal pitch. It is the distance between the centres of the rivets in adjacent rows of zig-zag riveted joint as shown in Fig. It is usually denoted by pd. 4. Margin or marginal pitch. It is the distance between the centre of rivet hole to the nearest edge of the plate as shown in Fig. It is usually denoted by m.
11/27/2013 Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78 5
Proportions of dimensions of riveted joints Thickness of plate
t = Thickness of the plate Diameter of rivets. the diameter of the rivet hole (d) may be determined by using Distance of centre of the rivet from edge of the plate = 1.5d Margin , m=d Longitudinal Pitch p=3d Transverse pitch pt = 0.8P for chain riveting = 0.6P for zig-zag riveting Thickness of butt strap. Single cover plate t1 = 1.125 t Double cover plate t2 = 0.7 to 0.8t
11/27/2013 Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78 6
Types of Riveted joints
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
Double Riveted lap joints
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
Double Riveted Zig zag Lap joint
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
Single riveted, single strap butt joint
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
10
Single riveted, double strap butt joint
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
11
Double riveted, double strap chain butt joint
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
12
Double riveted, double strap zig zag butt joint
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
13
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
14
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
15
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
16
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
17
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
18
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
19
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
20
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
21
11/27/2013
Hareesha N Gowda, DSCE, Blore-78
22
You might also like
- Rivet and Riveted JointsDocument20 pagesRivet and Riveted Jointsdeepbhagat100% (1)
- Strength Calculation and Dimensioning of Joints: Prepared By: Samson Yohannes Assistant ProfessorDocument45 pagesStrength Calculation and Dimensioning of Joints: Prepared By: Samson Yohannes Assistant ProfessorBK MKNo ratings yet
- 3.DME - ME3RD - UNIT-3.2 - Design of JointsDocument70 pages3.DME - ME3RD - UNIT-3.2 - Design of JointsCHITYALA YASHWANTH KRISHNA ,ECE18 Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- RivetsDocument28 pagesRivetsMS JAMWALNo ratings yet
- RIVETSDocument16 pagesRIVETSعبدالرحمن سيدNo ratings yet
- Design of Permanent Joints RivetsDocument37 pagesDesign of Permanent Joints RivetsAmunyela FelistasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 L-1 Bolt DesignDocument34 pagesChapter - 3 L-1 Bolt DesignBerihunNo ratings yet
- Threaded & Riveted JointsDocument43 pagesThreaded & Riveted JointsMadhurima BhandariNo ratings yet
- U-4 - Design of Riveted Joint - SRMDocument87 pagesU-4 - Design of Riveted Joint - SRMsiddharth GautamNo ratings yet
- L11 Mechanical FastenersDocument91 pagesL11 Mechanical FastenersSHADES 4 ALLNo ratings yet
- Ex. No Date Name of The Experiment Mark No Staff SignatureDocument35 pagesEx. No Date Name of The Experiment Mark No Staff SignaturesivagamipalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - BT 205 - AFDocument22 pagesUnit2 - BT 205 - AFyobingewatcher06No ratings yet
- Riveted Connections ExplainedDocument38 pagesRiveted Connections ExplainedKeerthana PNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of Riveted Lap JointDocument7 pagesStress Analysis of Riveted Lap JointMeck LotfiNo ratings yet
- DOS II PPT 2Document40 pagesDOS II PPT 2revathisasikumar5420No ratings yet
- MP II by RavindranDocument15 pagesMP II by Ravindranavijayakumar_1964No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 31-Aug-2020 Module 4 Design of Riveted Joint 8 PDFDocument53 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 31-Aug-2020 Module 4 Design of Riveted Joint 8 PDFAK PRODUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- Riveted Joint DesignDocument72 pagesRiveted Joint DesignROHAN PILLAI100% (1)
- Damaging: Permanent JointsDocument16 pagesDamaging: Permanent JointsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- 7 Bolted Connections-T8 T9Document24 pages7 Bolted Connections-T8 T9Bernardine BenedictNo ratings yet
- AE2259 Aircraft Component Drawing EDITED1Document49 pagesAE2259 Aircraft Component Drawing EDITED1db4911100% (2)
- MECH4914 Design Project B: Bolted Joint StiffnessDocument25 pagesMECH4914 Design Project B: Bolted Joint StiffnessahmedNo ratings yet
- 7 Riveted JointsDocument72 pages7 Riveted JointsanirudhNo ratings yet
- Rivet Joint Design & TypesDocument15 pagesRivet Joint Design & TypesThirumalaimuthukumaranMohan100% (1)
- Riveted JointDocument70 pagesRiveted JointAbhishek Saliya100% (1)
- Ae6413 - Cad & Aircraft Component DrawingDocument52 pagesAe6413 - Cad & Aircraft Component DrawingDamo Daran G50% (2)
- Design of Fastners - Screwed JointsDocument25 pagesDesign of Fastners - Screwed JointsKunal AhiwaleNo ratings yet
- Design & Drafting Lab ManualDocument49 pagesDesign & Drafting Lab ManualKalpit KauraseNo ratings yet
- THREADED FASTENERS: BOLTS, SCREWS, STUDS AND NUTSDocument31 pagesTHREADED FASTENERS: BOLTS, SCREWS, STUDS AND NUTSabdullah omar MohamedNo ratings yet
- Design of Rivets (Part 2)Document29 pagesDesign of Rivets (Part 2)Dhruv PancholiNo ratings yet
- Ae 6314 Acd Lab ManualDocument57 pagesAe 6314 Acd Lab ManualNaga SuryaNo ratings yet
- Design of shaft couplingsDocument48 pagesDesign of shaft couplingsAkshayNo ratings yet
- Riveted Joint Design: Middle Technical University Technical Engineering Material DepartmentDocument12 pagesRiveted Joint Design: Middle Technical University Technical Engineering Material DepartmentTokki TokkiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 DesignofshaftscouplingsDocument45 pagesUnit 7 DesignofshaftscouplingssuswagatNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5. Riveted ConnectionsDocument12 pagesLESSON 5. Riveted ConnectionsAdarsh bhatNo ratings yet
- Rivets as Permanent Mechanical JointsDocument21 pagesRivets as Permanent Mechanical JointsJatin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Joint Types in Machine DesignDocument28 pagesModule 3 - Joint Types in Machine DesignMahmud HassanNo ratings yet
- Shaft Coupling Design GuideDocument45 pagesShaft Coupling Design GuideSai Radha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Threaded JointsDocument23 pagesThreaded JointsSreejith MohanNo ratings yet
- ME 3011D MD1 Riveted JointDocument67 pagesME 3011D MD1 Riveted Jointvivek geddamNo ratings yet
- 15ME3112 Design of Machine ElementsDocument29 pages15ME3112 Design of Machine Elementslikhith saiNo ratings yet
- Riveted Joints: Presented By:-Tanuj Bansal PG/FET/1850257 Department of Food Engineering and Technology, SLIETDocument15 pagesRiveted Joints: Presented By:-Tanuj Bansal PG/FET/1850257 Department of Food Engineering and Technology, SLIETTanuj BansalNo ratings yet
- 7-Design of Riveted Joints - Introduction-03-Sep-2018 - Reference Material I - Module 4A - Rivetted JointsDocument62 pages7-Design of Riveted Joints - Introduction-03-Sep-2018 - Reference Material I - Module 4A - Rivetted Jointsakhil govindNo ratings yet
- ME 322 - Design of Bolted ConnectionsDocument50 pagesME 322 - Design of Bolted ConnectionsSindhu Reddy100% (1)
- Riveted Joint Design GuideDocument20 pagesRiveted Joint Design GuidegurdyalNo ratings yet
- Riveted JointsDocument28 pagesRiveted Jointsgnbabuiitg0% (1)
- Design of Shafts CouplingsDocument45 pagesDesign of Shafts CouplingsRavi Teja100% (2)
- THREADED FASTENERS AND DRAWING STANDARDSDocument31 pagesTHREADED FASTENERS AND DRAWING STANDARDSziadatz0% (1)
- Machine Design Lec3Document75 pagesMachine Design Lec3sam0415No ratings yet
- Designofshaftscouplings PPT 121011041653 Phpapp02Document45 pagesDesignofshaftscouplings PPT 121011041653 Phpapp02suswagatNo ratings yet
- Joining Methods: Tolerances: Fit Between PartsDocument11 pagesJoining Methods: Tolerances: Fit Between PartsChiara RipaltiNo ratings yet
- Keys and Couplings Types DesignDocument85 pagesKeys and Couplings Types DesignMannam Sarath Sarath100% (1)
- Shaft Lectures - Class4Document21 pagesShaft Lectures - Class4Atalelew ZeruNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Sheet Metal DesignDocument27 pagesPresentation On Sheet Metal Designniloy_67No ratings yet
- Threads and Thread CuttingDocument56 pagesThreads and Thread CuttingVenugopal MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Design of Riveted JointDocument12 pagesDesign of Riveted JointYogesh DandekarNo ratings yet
- 15CS35 - Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2018Document2 pages15CS35 - Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2018Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis Laboratory Manual VTU PDFDocument42 pagesModelling and Analysis Laboratory Manual VTU PDFHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- BAI and ASI Syllabus For QP Setting Aug 2020Document6 pagesBAI and ASI Syllabus For QP Setting Aug 2020Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 15CS35 - Unix and Shell Programming-July 2018Document2 pages15CS35 - Unix and Shell Programming-July 2018Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- File Identifier - StickersDocument50 pagesFile Identifier - StickersHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2011Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2011Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2014Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2014Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 10CS44 - Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2012Document2 pages10CS44 - Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2012Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-July 2011Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-July 2011Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2010Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Dec 2010Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2009Document2 pages06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2009Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- MOM COsDocument1 pageMOM COsHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2010Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2010Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2008Document1 page06CS36-Unix and Shell Programming-Jan 2008Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Practice Final SolutionsDocument41 pagesPractice Final SolutionsHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- JET ENGINE FundamentalsDocument18 pagesJET ENGINE FundamentalsHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- ARDB Rules - Grants PDFDocument38 pagesARDB Rules - Grants PDFHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Exam Question BankDocument1 pageExam Question BankHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Where To Approach For R&D Funds?Document15 pagesAppendix: Where To Approach For R&D Funds?malini72No ratings yet
- Application For Grant of Research/Development Project/Facilities Under Grants-In-Aid Scheme of Aeronautics R&D BoardDocument3 pagesApplication For Grant of Research/Development Project/Facilities Under Grants-In-Aid Scheme of Aeronautics R&D BoardHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Phase1 Closure July 2004Document27 pagesPhase1 Closure July 2004Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- PhaseII Final IITDocument26 pagesPhaseII Final IITHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Pert Chart MineDocument1 pagePert Chart MineHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Chapter NumbersDocument11 pagesChapter NumbersHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- 2015 Project TitlesDocument9 pages2015 Project TitlesHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Alg LabDocument22 pagesAlg LabShobha KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Q and ADocument47 pagesSample Q and AHareesha N G100% (1)
- Lab26 - Configure Endpoint and Access S3Document18 pagesLab26 - Configure Endpoint and Access S3Hareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Database AwsDocument15 pagesDatabase AwsHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Lab25 - Command Line InterfaceDocument22 pagesLab25 - Command Line InterfaceHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Artifact Entry Form - Ostp Standard 3Document1 pagePortfolio Artifact Entry Form - Ostp Standard 3api-253007574No ratings yet
- Mtle - Hema 1Document50 pagesMtle - Hema 1Leogene Earl FranciaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Document3 pagesNama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Yetri MulizaNo ratings yet
- Casting Procedures and Defects GuideDocument91 pagesCasting Procedures and Defects GuideJitender Reddy0% (1)
- Agricultural Engineering Comprehensive Board Exam Reviewer: Agricultural Processing, Structures, and Allied SubjectsDocument84 pagesAgricultural Engineering Comprehensive Board Exam Reviewer: Agricultural Processing, Structures, and Allied SubjectsRachel vNo ratings yet
- Polyol polyether+NCO Isupur PDFDocument27 pagesPolyol polyether+NCO Isupur PDFswapon kumar shillNo ratings yet
- QueriesDocument50 pagesQueriesBajji RajinishNo ratings yet
- Hyper-Threading Technology Architecture and Microarchitecture - SummaryDocument4 pagesHyper-Threading Technology Architecture and Microarchitecture - SummaryMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- 5511Document29 pages5511Ckaal74No ratings yet
- Zelev 1Document2 pagesZelev 1evansparrowNo ratings yet
- Krok2 - Medicine - 2010Document27 pagesKrok2 - Medicine - 2010Badriya YussufNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University Management Services ExamDocument16 pagesPolytechnic University Management Services ExamBeverlene BatiNo ratings yet
- ConductorsDocument4 pagesConductorsJohn Carlo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Towards A Human Resource Development Ontology Combining Competence Management and Technology-Enhanced Workplace LearningDocument21 pagesTowards A Human Resource Development Ontology Combining Competence Management and Technology-Enhanced Workplace LearningTommy SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Borello-Bolted Steel Slip-Critical Connections With Fillers I. PerformanceDocument10 pagesBorello-Bolted Steel Slip-Critical Connections With Fillers I. PerformanceaykutNo ratings yet
- Antenna VisualizationDocument4 pagesAntenna Visualizationashok_patil_1No ratings yet
- Reflection Homophone 2Document3 pagesReflection Homophone 2api-356065858No ratings yet
- TOGAF 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation GuideDocument114 pagesTOGAF 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation GuideRodrigo Maia100% (3)
- Marshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleDocument2 pagesMarshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleTewodros TadesseNo ratings yet
- Built - in BeamsDocument23 pagesBuilt - in BeamsMalingha SamuelNo ratings yet
- FINAL A-ENHANCED MODULES TO IMPROVE LEARNERS - EditedDocument22 pagesFINAL A-ENHANCED MODULES TO IMPROVE LEARNERS - EditedMary Cielo PadilloNo ratings yet
- IoT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEMDocument18 pagesIoT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEMArunkumar Kuti100% (2)
- Rtsa 2012Document7 pagesRtsa 2012Justin RobinsonNo ratings yet
- National Standard Examination in Astronomy 2018-19 (NSEA) : Question Paper Code: A423Document1 pageNational Standard Examination in Astronomy 2018-19 (NSEA) : Question Paper Code: A423VASU JAINNo ratings yet
- Insider Threat ManagementDocument48 pagesInsider Threat ManagementPatricia LehmanNo ratings yet
- Water Jet CuttingDocument15 pagesWater Jet CuttingDevendar YadavNo ratings yet
- AZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01Document21 pagesAZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01MgminLukaLayNo ratings yet
- Lankeda 3d Printer Filament Catalogue 2019.02 WGDocument7 pagesLankeda 3d Printer Filament Catalogue 2019.02 WGSamuelNo ratings yet
- Moor, The - Nature - Importance - and - Difficulty - of - Machine - EthicsDocument4 pagesMoor, The - Nature - Importance - and - Difficulty - of - Machine - EthicsIrene IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesInventory Control Review of Literatureaehupavkg100% (1)