Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SaO2 Versus SpO2
Uploaded by
jidongjc100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
17K views9 pagesThis file briefly describes the difference between SaO2 ans SpO2.
Original Title
SaO2 versus SpO2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis file briefly describes the difference between SaO2 ans SpO2.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
17K views9 pagesSaO2 Versus SpO2
Uploaded by
jidongjcThis file briefly describes the difference between SaO2 ans SpO2.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
SaO2 versus SpO2
With background knowledge
Types of haemoglobins
Deoxyhaemoglobin (Hb)
Oxyhaemoglobin (HbO2)
Methaemoglobin (Methb)
Carboxyhaemoglobin (COHb)
Sulfhaemoglobin (SfHb)
Carboxysulfhaemoglobin (COSfhb)
Where the concentration of
oxyhaemoglobin dominates in the
blood
SaO2
A parameter measured by CO-oximeter
The ratio of oxyhaemoglobin over all types of
haemoglobin
SpO2
A parameter measured by pulse-oximeter
The ratio of oxyhaemoglobin over the
concentration of oxyhaemoglobin and
deoxyhaemoglobin
CO-oximeter
measuring SaO2
Traditional way of measuring oxygen
saturation in arterial blood
Measurement taken on several wavelengths
of light
Achieved with the usage of blood gas
analyzer
Pulse-oximeter
measuring SpO2
Non-invasive way of oxygen level
measurement
Both transmission mode and reflection
modes available
Transmission : fingertip, earlobe
Reflection : forehead, cheek, calf, thigh
Poorer SNR occurs at reflection mode
Most-commonly dual-wavelength method
used
Malfunction of pulse-
oximetry
Consider a heavy smoker with 15% COhb
Pulse-oximeter is unable to distinguish
between COhb and HbO2
In the case where SaO2 is 84%
◦ A result of 99% SpO2 will be shown
◦ The reading is heavily affected
◦ Situation of user endangered when wrong action
taken
Summary of pulse oximetry
Measure blood saturation levels. Unable to
detect tissue hypoxia as a result of anaemia
Unable to distinguish the dysfunctional
haemoglobins – over estimate SaO2 level
Not an accurate devise.. Yet good indicator of
saturation and desaturation level
More reliable if reflective probe used to tape
to the body
Digital version not necessarily better than
analogue one
Summary of pulse oximetry
Venous pulsation artificially lower than SaO2
A guide to peripheral circulation
Aim to keep levels above 95%
Action taken quickly if below 90%
You might also like
- 2022 Pulse Oximetry and CapnographyDocument33 pages2022 Pulse Oximetry and CapnographyMohmmed MousaNo ratings yet
- Regional AnesthesiaDocument54 pagesRegional AnesthesiaIdza Fariha AfriNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Disorders - Lecture 45Document14 pagesAcid Base Disorders - Lecture 45yassin mostafaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureDocument30 pagesMechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureFlavius AnghelNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Document7 pagesVentilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Tarran PhagooNo ratings yet
- Dr. Arlene Jane Sy-Reodica Clinical Applications Specialist - ASEAN Monitoring SolutionsDocument43 pagesDr. Arlene Jane Sy-Reodica Clinical Applications Specialist - ASEAN Monitoring SolutionsArNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base - Ppt-How To ReadDocument22 pagesAcid-Base - Ppt-How To ReadnursaidahNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanDocument238 pagesBronchiectasis: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanKM Lakshmana Rajan0% (1)
- Pulsus ParadoxusDocument2 pagesPulsus ParadoxusHassan.shehriNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy: Housemanship Training Programme Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive CareDocument55 pagesOxygen Therapy: Housemanship Training Programme Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive CaretorreslysNo ratings yet
- Perioperative ManagementDocument16 pagesPerioperative ManagementMelvin NizelNo ratings yet
- Understanding Mechanical Ventilation Modes & WeaningDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Mechanical Ventilation Modes & WeaningDeepa BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- The Preoperative EvaluationDocument25 pagesThe Preoperative Evaluationnormie littlemonsterNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Sepsis:: Early Goal Directed Therapy and BeyondDocument86 pagesThe Treatment of Sepsis:: Early Goal Directed Therapy and BeyondAndreas OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Surfactant PresentationDocument18 pagesSurfactant PresentationMaadaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas MachineDocument33 pagesBlood Gas MachinenofearnofearNo ratings yet
- Monitoring PerioperatipDocument54 pagesMonitoring Perioperatipjavajavu100% (1)
- Max Surgical Blood Order PDFDocument6 pagesMax Surgical Blood Order PDFatina putriNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Liver FunctionDocument64 pagesEvaluation of Liver FunctionMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Permanent FormDocument4 pagesPermanent FormdgfuiNo ratings yet
- Spirometry E-Guide 2013Document28 pagesSpirometry E-Guide 2013Vidal Odon Ramos MermaNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Stabilitation in Critically Ill Patient - 2015Document36 pagesTransportation and Stabilitation in Critically Ill Patient - 2015Gustav Valentino100% (1)
- Anesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairDocument29 pagesAnesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairArop AkechNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy For Adults in Hospital Clinical GuidelineDocument10 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy For Adults in Hospital Clinical GuidelinePremaKurniaNo ratings yet
- Supraglottic Airway Devices A Review in A New Era of Airway Management 2155 6148 1000647Document9 pagesSupraglottic Airway Devices A Review in A New Era of Airway Management 2155 6148 1000647Riris SihotangNo ratings yet
- Shock (For Surgery)Document50 pagesShock (For Surgery)Emmanuel Rojith VazNo ratings yet
- 2013 Sepsis GuidelinesDocument58 pages2013 Sepsis GuidelinesMuhd Azam100% (1)
- DVT Pulmonary EmbolismDocument40 pagesDVT Pulmonary EmbolismDr. Shatdal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Capnometry: Dhanya VDocument49 pagesCapnometry: Dhanya VdaviddanamrajanNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 pagesSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13No ratings yet
- Essential Concepts for Airway ManagementDocument42 pagesEssential Concepts for Airway Managementkader abdiNo ratings yet
- Ivc FilterDocument15 pagesIvc FilterashishNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Preparation of Patient For SurgeryDocument23 pagesPreoperative Preparation of Patient For SurgeryFauzi SebunyaNo ratings yet
- Massive Blood Transfusion Protocol (MBTP) Definition and ManagementDocument17 pagesMassive Blood Transfusion Protocol (MBTP) Definition and ManagementevanNo ratings yet
- Coccidiosis Power PointDocument36 pagesCoccidiosis Power PointBob UrbandubNo ratings yet
- Venous Air EmbolismDocument16 pagesVenous Air EmbolismEylia MelikaNo ratings yet
- CPAP SlidesDocument52 pagesCPAP SlidesAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- 12.intraoperative Fluid ManagmentDocument54 pages12.intraoperative Fluid ManagmentyeabsraNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument24 pagesCardiopulmonary Bypass: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid Management in Pediatrics: By: Karim Kamal, MDDocument33 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management in Pediatrics: By: Karim Kamal, MDMohammed AKNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Fluid Therapy in Shock.10Document6 pagesOptimizing Fluid Therapy in Shock.10Paulo Victor100% (1)
- Perioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenDocument31 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenRashmi SahaNo ratings yet
- Opioid Analgesics & Antagonists: Dr. Hayder B Sahib Ph.D. PharmacologyDocument47 pagesOpioid Analgesics & Antagonists: Dr. Hayder B Sahib Ph.D. Pharmacologyarham pirachaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea PPTDocument82 pagesDiarrhea PPTIshwar HavaragiNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver FailureDocument69 pagesAcute Liver FailureAsif.N.IqbalNo ratings yet
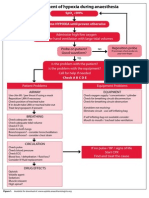
- Management of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaDocument5 pagesManagement of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaNurhafizahImfista100% (1)
- ABG Interpretation ActivityDocument16 pagesABG Interpretation ActivityArlly Faena AbadNo ratings yet
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument47 pagesPreoperative EvaluationCzerwin Juales100% (2)
- Icu Sop: TOPIC: Length of Stay in ICUDocument5 pagesIcu Sop: TOPIC: Length of Stay in ICURohit RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Useful Formulas for Fluid Therapy CalculationsDocument2 pagesUseful Formulas for Fluid Therapy CalculationsPrabhakar KumarNo ratings yet
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines PresentationDocument30 pagesSurviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines PresentationwisnusigitpratamaNo ratings yet
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesFrom EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- Business Communication 1: American Psychological Association (APA) Style CitationDocument28 pagesBusiness Communication 1: American Psychological Association (APA) Style CitationjidongjcNo ratings yet
- Bio Monitoring 01Document41 pagesBio Monitoring 01jidongjcNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Lighting An Energy-Economics PerspectiveDocument18 pagesSolid-State Lighting An Energy-Economics PerspectivejidongjcNo ratings yet
- National Day Rally SpeechDocument21 pagesNational Day Rally SpeechjidongjcNo ratings yet
- National Day Rally Speech - SummaryDocument1 pageNational Day Rally Speech - SummaryjidongjcNo ratings yet
- Bio Engineered Skin Substitute For Burn VictimsDocument19 pagesBio Engineered Skin Substitute For Burn VictimsjidongjcNo ratings yet
- SaO2 Versus SpO2Document9 pagesSaO2 Versus SpO2jidongjcNo ratings yet
- Background Knowledge of Pulse OximetryDocument9 pagesBackground Knowledge of Pulse Oximetryjidongjc100% (2)
- ATPL 040.human Factor NotesDocument22 pagesATPL 040.human Factor NotesAbu BrahimNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Wound Healing PDFDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Wound Healing PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonographic Examination of The Small Intestine, Large IntestineDocument6 pagesUltrasonographic Examination of The Small Intestine, Large IntestineYans PangerunganNo ratings yet
- Year 4 Science Learner's BookDocument106 pagesYear 4 Science Learner's BookFatme AllawaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exedrcises & TechniquesDocument4 pagesTherapeutic Exedrcises & Techniquesrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument12 pages0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersIf HassanNo ratings yet
- Emergent Properties of Individual OrganismsDocument33 pagesEmergent Properties of Individual OrganismsCharleneKronstedtNo ratings yet
- Delayed Awakening From AnaesthesiaDocument3 pagesDelayed Awakening From AnaesthesiaSenthooran ArudshivsmNo ratings yet
- (VCE Biology) 2005 Chemology Unit 2 Exam and Solutions PDFDocument22 pages(VCE Biology) 2005 Chemology Unit 2 Exam and Solutions PDFJustine LyNo ratings yet
- IPPA Procedures Guide for Nursing StudentsDocument5 pagesIPPA Procedures Guide for Nursing StudentsJulieeNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wDocument5 pagesTopic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wSeve ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument79 pagesNervous SystemAffan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Open Cloze IDocument2 pagesOpen Cloze IRadu BortesNo ratings yet
- THORAXDocument27 pagesTHORAXOleashedNo ratings yet
- Central Venous CatheterizationDocument16 pagesCentral Venous CatheterizationNavjot BajwaNo ratings yet
- Tube GuideDocument1 pageTube Guidezalam55No ratings yet
- Krok 1 Telegram Group ResultsDocument44 pagesKrok 1 Telegram Group ResultsHarsh NimavatNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant MorphologyDocument513 pagesFlowering Plant MorphologyVaibhav PanchalNo ratings yet
- Locomotary Organelles in ProtozoaDocument25 pagesLocomotary Organelles in Protozoaashley clintonNo ratings yet
- Examination of KneeDocument4 pagesExamination of KneeAdrian PopNo ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument22 pagesBehaviorismOlcay Sanem SipahioğluNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9JulieNo ratings yet
- Reflex ExercisesDocument43 pagesReflex ExercisesFlori100% (4)
- Neuroplasticity - Changing The Brain InfographDocument2 pagesNeuroplasticity - Changing The Brain InfographpamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Communication ModelsDocument19 pagesLesson 4-Communication ModelsChristine Mae MontesNo ratings yet
- Basirika Mary Carolyne Latest (Autorecovered)Document5 pagesBasirika Mary Carolyne Latest (Autorecovered)Carol BasirikaNo ratings yet
- Nanoelectromechanical Systems: Condensed Matter Physics 114-36, California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91125Document19 pagesNanoelectromechanical Systems: Condensed Matter Physics 114-36, California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91125Yash SakujaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Penata Muda Tk-1 / III BDocument6 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Penata Muda Tk-1 / III BLuciano NawaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lab Depex ReviewerDocument46 pages2nd Lab Depex ReviewerprincelfangorNo ratings yet
- Diagnose Cure and Empower Yourself by Currents of Breath - Authored by Acharya Shriram SharmaDocument78 pagesDiagnose Cure and Empower Yourself by Currents of Breath - Authored by Acharya Shriram SharmaGuiding Thoughts- Books by Pandit Shriram Sharma Acharya100% (19)