Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Guide Coastal Change and Conflict
Uploaded by
Mrs MitchellCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Guide Coastal Change and Conflict
Uploaded by
Mrs MitchellCopyright:
Available Formats
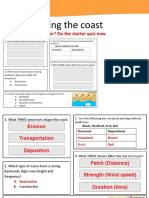
Question (2 marks) Name and describe one process of coastal erosion.
Question (/6 marks)
COASTAL CHANGE AND CONFLICT
Question (3 marks) Describe the process of longshore drift. You may use a diagram to help your answer.
Explain how a spit is formed. You may draw a diagram to help your answer. OR For a named location, explain the costs and benefits of using hard engineering techniques to protect a coastline from erosion.
The most important feature of a coast is often the type of rock in the area. Some rocks (e.g. granite) are more resistant to erosion than others (e.g. clay).
Longshore drift the movement of sediment down the coast in the direction of the wind.
There are 3 main types of coastal erosion: Hydraulic action water is forced into cracks in the rock and weakens the rock. Abrasion- loose rocks are thrown against the cliff by waves and wear the cliff away. Attrition Loose sediment continually collides with other sediment and gets smaller.
Coastal landforms at hard rock coasts include caves, arches, stacks, stumps, and wave cut platforms.
NAMED EXAMPLE : EROSION AND MANAGEMENT AT CHRISTCHURCH BAY Councils have 4 choices when choosing how to protect the coast: Conflict at the coast Not everyone agrees about how to deal with coastal erosion Local residents and businesses will be in favour of protecting the coastline, however they will not like ugly sea defences. Taxpayers may prefer to use cheaper methods as they do not want their taxes used for something that doesnt benefit them. Environmentalists may prefer to do nothing as they do not want to disrupt natural habitats. People who live downdrift may prefer to do nothing as they rely on sediment for their own beaches.
Christchurch Bay on the Uks coast has a severe problem. Thecoastline is made up of boulder clay, a very soft rock, which means this coastline is eroding at about 2 metres a year. This erosion threatens people and their property. Make sure you know how wave type influences beach profile. Constructive waves help to build up the beach, while destructive waves create steep beaches.
1. 2. 3. 4.
Hold the line Advance the line Strategic Retreat Do Nothing
Concordant coastlines where layers of rock are parallel to the coastline. We find coves and cliffs here. Discordant coastline where the layers of rock are perpendicular to the coastline. We find headlands and bays here.
Managing the coast There are many methods used to try to protect the coast from erosion. Hard Engineering (Traditional) using concrete and steel structures to stop waves e.g. sea walls, gabions, revetments. Hard engineering methods are effective but often costly and ugly. Soft Engineering (Modern) using smaller structures built from natural materials to reduce wave energy e.g. planting vegetation, beach nourishment, off shore breakwaters. These methods usually look more attractive and can be cheaper but they are sometimes not as effective. Dont forget, the issue of coastal erosion is likely to become more important due to sea level rise and increased storms due to climate change.
KEY WORD BANK EROSION DEPOSITION SPIT GROYNES
ABRASION GABIONS
HYDRAULIC ACTION RIP RAP BOULDER CLAY
ARCH SWASH
STACK
LONGSHORE DRIFT BACKWASH
You might also like
- Coastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)Document55 pagesCoastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)As 54bdNo ratings yet
- 03 Handout 3Document5 pages03 Handout 3fuenNo ratings yet
- Landforms of Coastal Erosion and Deposition: Erosional Features Teacher: Mrs. A. Reid-AllenDocument49 pagesLandforms of Coastal Erosion and Deposition: Erosional Features Teacher: Mrs. A. Reid-AllenRuksi CocoNo ratings yet
- Shore-Protection System, Case Study: FRIDAY, APRIL 16, 2021Document41 pagesShore-Protection System, Case Study: FRIDAY, APRIL 16, 2021SSNo ratings yet
- I. Hard and Soft EngineeringDocument25 pagesI. Hard and Soft EngineeringDomingo Brioso Gamis IIINo ratings yet
- Ow It Formed (Geograp Ical Processes)Document3 pagesOw It Formed (Geograp Ical Processes)Jaimie DonovanNo ratings yet
- Human Modification of The Caribbean Coastal EnvironmentalDocument6 pagesHuman Modification of The Caribbean Coastal Environmentalreeta ramNo ratings yet
- Coastal Defense: Rico Fuentes Jr. BSCE-5Document22 pagesCoastal Defense: Rico Fuentes Jr. BSCE-5Icz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Coastal - Marine and Coastal ProcessesDocument3 pagesCoastal - Marine and Coastal Processesjulius.storage2023No ratings yet
- Crowded Coasts AS Notes.Document7 pagesCrowded Coasts AS Notes.ultimop34No ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion Dissertation IdeasDocument6 pagesCoastal Erosion Dissertation IdeasPaySomeoneToDoMyPaperNewark100% (1)
- Coasts: Earth: Our HomeDocument32 pagesCoasts: Earth: Our HomeVernon100% (1)
- 08 Coastal ManagementDocument3 pages08 Coastal ManagementAlexandra ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Man's Impact On CoastlinesDocument35 pagesMan's Impact On CoastlinesLaura-Lee DownesNo ratings yet
- GA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3Document4 pagesGA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3geoboom12No ratings yet
- Coastal Processes and ManagementDocument28 pagesCoastal Processes and ManagementJoshuaHortonNo ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion 2Document3 pagesCoastal Erosion 2Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Beach Erosion Research PaperDocument6 pagesBeach Erosion Research Papergzrvpcvnd100% (1)
- Coastal Management TechniquesDocument17 pagesCoastal Management Techniqueshani sofia sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Curved Sea WallDocument1 pageCurved Sea WallTechno geoNo ratings yet
- Main Topic: River and Coast: I. Constructive Waves Ii. Destructive Waves I. Constructive WavesDocument6 pagesMain Topic: River and Coast: I. Constructive Waves Ii. Destructive Waves I. Constructive WavesAnthony HarrisNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Coastal ErosionDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Coastal Erosiongw10ka6s100% (1)
- Prepared By: Mensah Senoo Prince Ali Rageh Saad Fatema Begum Tareq KhaledDocument23 pagesPrepared By: Mensah Senoo Prince Ali Rageh Saad Fatema Begum Tareq KhaledpossiprinceNo ratings yet
- Coastal Protection StructuresDocument107 pagesCoastal Protection StructuresKhrl K Khrl88% (8)
- Chapter3 PDFDocument42 pagesChapter3 PDFElsayedNo ratings yet
- ReintroducingStructuresforErosionControlFINAL PDFDocument10 pagesReintroducingStructuresforErosionControlFINAL PDFBenedictus JohanesNo ratings yet
- L1 Coastal Protection System - NewDocument87 pagesL1 Coastal Protection System - NewNURSASHA FAREESHA MARZUKINo ratings yet
- 10.8-10.9 Coastal Management Hard and Soft Engineering (KMU)Document23 pages10.8-10.9 Coastal Management Hard and Soft Engineering (KMU)LaherNo ratings yet
- 3a. The Coastal ZoneDocument140 pages3a. The Coastal Zoneb_osborne100% (1)
- Walton On The Naze 2012-13Document46 pagesWalton On The Naze 2012-13Jack LinsteadNo ratings yet
- Coasts Under ThreatDocument9 pagesCoasts Under Threatapi-258813608No ratings yet
- Marine Coastal ErosionDocument1 pageMarine Coastal ErosionsukunyuNo ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Coastal StructuresDocument18 pagesTypes and Functions of Coastal StructuresMourad Nadeer100% (1)
- Coastal Processes and LandformsDocument33 pagesCoastal Processes and Landformslyana1234100% (4)
- Geography Notes-Half Yearly 2011.: Coastal ManagementDocument6 pagesGeography Notes-Half Yearly 2011.: Coastal ManagementannieaterNo ratings yet
- Coastal ProtectionDocument2 pagesCoastal Protectionapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Edexceligcsegeographychapter 2Document31 pagesEdexceligcsegeographychapter 2api-265424071No ratings yet
- Shoreline Protection Alternatives: Focus On..Document4 pagesShoreline Protection Alternatives: Focus On..Mohamed AtiaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Coastal ErosionDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Coastal Erosionaflstjdhs100% (1)
- L8 Defending The CoastDocument27 pagesL8 Defending The CoastRahma AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Coastal Management NotesDocument2 pagesCoastal Management Notesapi-330338837No ratings yet
- IGCSE Cambridge Geography - CoastsDocument17 pagesIGCSE Cambridge Geography - CoastsCrystal Berry100% (1)
- Igcse Geography CoastsDocument24 pagesIgcse Geography CoastsMunir LakhaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion Prevention MethodsDocument5 pagesCoastal Erosion Prevention MethodspoojaNo ratings yet
- Oce CoDocument41 pagesOce Coarimel11No ratings yet
- Design of Seawall PDFDocument39 pagesDesign of Seawall PDFAhmed Balah100% (1)
- 5 Coastal WikiDocument5 pages5 Coastal WikiVanja Damjanovic100% (1)
- Sea ReclamationDocument11 pagesSea Reclamationhani sofia sulaimanNo ratings yet
- 16 3 Shoreline Features and ProcessesDocument23 pages16 3 Shoreline Features and ProcessesRoland Rawlins IgaborNo ratings yet
- CP Against Wave EnergyDocument19 pagesCP Against Wave EnergyHafiz_Murni_4791No ratings yet
- Displacement of Land Along TheDocument3 pagesDisplacement of Land Along ThePavani Nisansala KulasekaraNo ratings yet
- His Article Is Recommended by The Editorial TeamDocument4 pagesHis Article Is Recommended by The Editorial TeamSwamy ManiNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument5 pagesGeographysmmaabzNo ratings yet
- f214412736 Recommendations For Non Structural Shore Erosion Control Projects Marsh Creation For Habitat and Shoreline StabilizationDocument26 pagesf214412736 Recommendations For Non Structural Shore Erosion Control Projects Marsh Creation For Habitat and Shoreline StabilizationMac allan ramosNo ratings yet
- Increasing RisksDocument5 pagesIncreasing Risksdebbie96No ratings yet
- Coastal and River StructuresDocument5 pagesCoastal and River StructuresAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNo ratings yet
- Jps - Kawalan Hakisan OmbakDocument21 pagesJps - Kawalan Hakisan OmbakPutera JasneyNo ratings yet
- Oceanography: Tom GarrisonDocument20 pagesOceanography: Tom GarrisonBond__001No ratings yet
- Csec GeographyDocument26 pagesCsec GeographyAmelia PitterNo ratings yet
- Oceans On The Edge RevisionDocument21 pagesOceans On The Edge RevisionMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide For Oceans On The EdgeDocument3 pagesRevision Guide For Oceans On The EdgeMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Revsion Guide For Water WorldDocument1 pageRevsion Guide For Water WorldMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Climate Change RevisionGuide Jle AmendedDocument1 pageClimate Change RevisionGuide Jle AmendedMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Revision StationsDocument8 pagesRevision StationsMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide For Restless EarthDocument1 pageRevision Guide For Restless EarthMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Battle For The BiosphereDocument1 pageRevision Guide Battle For The BiosphereMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- How Did You Kill This AlbatrossDocument6 pagesHow Did You Kill This AlbatrossMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- China Hail StormDocument11 pagesChina Hail StormMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Storm Chaser Video Note Taking StructuresDocument7 pagesStorm Chaser Video Note Taking StructuresMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- FrackingDocument11 pagesFrackingMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument6 pagesIntroMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Battle For The Biosphere RevisionDocument15 pagesBattle For The Biosphere RevisionMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Liftoff: Guide To Duo Deployment Best Practices: Version 2.1 Published October 3, 2019Document14 pagesLiftoff: Guide To Duo Deployment Best Practices: Version 2.1 Published October 3, 2019Johana RNo ratings yet
- Container Stowage Plans ExplainedDocument24 pagesContainer Stowage Plans ExplainedMohd akifNo ratings yet
- Development Approach PlanDocument15 pagesDevelopment Approach PlanGaurav UpretiNo ratings yet
- Long-Range FM Transmitter With Variable Power OutputDocument2 pagesLong-Range FM Transmitter With Variable Power OutputHaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540No ratings yet
- 365) - The Income Tax Rate Is 40%. Additional Expenses Are Estimated As FollowsDocument3 pages365) - The Income Tax Rate Is 40%. Additional Expenses Are Estimated As FollowsMihir HareetNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Introduction To XML: Exercise 1Document4 pagesLab 8 Introduction To XML: Exercise 1HasanNo ratings yet
- Postal-BSNL Meeting MinutesDocument5 pagesPostal-BSNL Meeting MinutesP Karan JainNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Khaled CVDocument2 pagesMohamed Khaled CVMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Vissim 11 - ManualDocument1,219 pagesVissim 11 - Manualmauricionsantos60% (5)
- Bigdata 2016 Hands On 2891109Document96 pagesBigdata 2016 Hands On 2891109cesmarscribdNo ratings yet
- Self Improvement Books To ReadDocument13 pagesSelf Improvement Books To ReadAnonymous oTtlhP67% (3)
- Certificate of IncorporationDocument1 pageCertificate of IncorporationVaseem ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Kokichi OmaSprite Gallery Danganronpa Wiki FDocument3 pagesKokichi OmaSprite Gallery Danganronpa Wiki Fmzcvxf9fwpNo ratings yet
- Intangible Capital: Key Factor of Sustainable Development in MoroccoDocument8 pagesIntangible Capital: Key Factor of Sustainable Development in MoroccojournalNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics 50 (2010) Editorial on 2009 Space Cryogenics WorkshopDocument1 pageCryogenics 50 (2010) Editorial on 2009 Space Cryogenics WorkshopsureshjeevaNo ratings yet
- Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionDocument15 pagesCiphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionJ_RameshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Evolution of Labour Laws in IndiaDocument13 pagesLecture 3 - Evolution of Labour Laws in IndiaGourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Material SelectionDocument99 pagesMaterial SelectionRaj Bindas100% (8)
- Agency Certificate of Compliance: IGHRS Update As of June 30, 2022Document2 pagesAgency Certificate of Compliance: IGHRS Update As of June 30, 2022Dacanay RexNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPDocument39 pagesConcepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPasadnawazNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elinor OstromDocument5 pagesTheory of Elinor OstromSanjana KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- Create Config Files Python ConfigParserDocument8 pagesCreate Config Files Python ConfigParserJames NgugiNo ratings yet
- InkscapePDFLaTeX PDFDocument3 pagesInkscapePDFLaTeX PDFFrancesco ReaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 OkDocument37 pagesChapter 8 OkMa. Alexandra Teddy Buen0% (1)
- Emergency Incidents AssignmentDocument4 pagesEmergency Incidents Assignmentnickoh28No ratings yet
- SPIE/COS Photonics Asia Abstract Submission Guidelines: Important DatesDocument1 pageSPIE/COS Photonics Asia Abstract Submission Guidelines: Important Dates李健民No ratings yet
- Comparison Between India and ChinaDocument92 pagesComparison Between India and Chinaapi-3710029100% (3)
- Project ProposalDocument6 pagesProject Proposalapi-386094460No ratings yet
- Jabiru Inc S Senior Management Recently Obtained A New Decision Support DatabaseDocument1 pageJabiru Inc S Senior Management Recently Obtained A New Decision Support DatabaseDoreenNo ratings yet