Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Doms Drugs
Uploaded by
Mikz JocomCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Doms Drugs
Uploaded by
Mikz JocomCopyright:
Available Formats
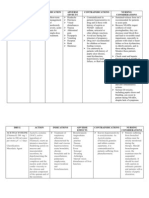
DRUG
DOSAGE
MECHANISM OF ACTION The exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, but the primary mechanism responsible for its anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic action is thought to be inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX).
INDICATION AND CONTRAINDICATION Indication: Acute or long-term treatment of mild to moderate pain
SIDE AND ADVERSE EFFECTS
Side Effects: Headache Dizziness Insomnia Fatigue Tinnitus, Ohthamologic effects Rash Stomatitis Diarrhea Nausea &Vomiting Adverse Effects: Bleeding Peripheral edema Anaphylactoid reactions to fatal anaphylactic shock
NURSING CONSIDERATION
Assess pain and limitation of movement; note type, location and intensity before annd 30-60 mins after administration Observe and report signs of bleeding (e.g, bleeding gums, bloody or black stools, cloudy or bloody urine) Monitor for signs and symptoms of GI irritation and ulceration. Monitor for increased serum sodium and potassium in patients receiving potassiumsparing diuretics Monitor weight and report gains greater than 1 kg (2 lb)/24 h
Generic Name: Diclofenac Brand Name: Cataflam Therapeutic Class: Analgesic and Antiinflammatory Functional Class: NSAIDs
Dose: 75mg Route: TIV Frequency: q12o (x4 doses)
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to NSAIDs, significant renal impairment
Why client is receiving the drug based on the history of present illness? Patient is having pain (Post OP)
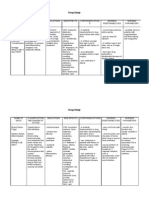
DRUG Generic Name: Pantoprazole Brand Name: Protonix IV Therapeutic Class: Antiulcer Agents Functional Class: Proton Pump Inhibitor Why client is receiving the drug based on the history of present illness? Patient was placed on NPO. (Pre-Op)
DOSAGE Dose: 40mg *While on NPO Route: TIV Frequency: Once a day
MECHANISM OF ACTION Binds to an enzyme in the presence of acidic gastric pH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen. Therapeutic Effects: Diminished accumulation of acid in the gastric lumen, with lessened acid reflux.
INDICATION AND CONTRAINDICATION Indication: Prevent serious problems caused by acid damage to your digestive system (Ulcers, CA of Esophagus)
Contraindication: Hypersensitivity
SIDE AND ADVERSE EFFECTS Side Effects: CNS: Headache, Nausea GI: Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea, Eructation, Flatulence, Constipation Skin: Pain/Redness/Swelling of the injection site, Rash, Pruritus, Urticaria Adverse Effects: Hematologic: Thrombophlebitis Leukopenia Musculoskeletal: Myalgia, Rhabdomyolysis Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Immune System Disorder: Anaphylaxis Renal and Urinary Disorder: Interstitial Nephritis Psychiatric Disorder: Somnolence Endo: Hyperglycemia
NURSING CONSIDERATION Asses for any hypersensitivity to any proton pump inhibitor or any drug component Switch patients on IV therapy to oral dosage as soon as possible Monitor for immediately report S of S angioedema or a severe skin reaction Urea breath test 46 weeks after completion of therapy Provide additional comfort measures to alleviate discomfort from GI effects and headache
DRUG
DOSAGE
MECHANISM OF ACTION It inhibits the synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Therapeutic Actions: Bactericidal Action
INDICATION AND CONTRAINDICATION Indication: Surgical Prophylaxis/Reducing or eliminating infections Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and other related antibiotics
Generic Name: Cefuroxime Brand Name: Zinacef Therapeutic Class: Antibacterial Antibiotic Functional Class: 2nd Generation Cephalosporins Why client is receiving the drug based on the history of present illness? Surgical prophylaxis(PreOP)
Dose: 750mg Route: TIV Frequency: q8o
SIDE AND ADVERSE EFFECTS Side Effects: Vomiting Abdominal Pain Diarrhea Rash Pruritus Urticaria Colitis Increased Serum Creatinine Decreased creatinine clearance Adverse Effects: Thrombophlebitis Pseudomonas Colitis Hemolytic Anemia Aplastic Anemia Haemorrhage Seizures Angioedema Cutaneous Vasculitis Anaphylaxis Nephrotoxicity
NURSING CONSIDERATION Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosophorins, penicillins and history of allergies particularly to drugs before therapy is initiated. Perform culture and sensitivity before initiation of therapy. Monitor periodically BUN and creatinine clearance. Inspect IM/IV sites for signs of phlebitis Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea, though pseudomonas colitis rarely occurs, this potentially lifethreatening
complication should be ruled out. Monitor for manifestations of hypersensitivity. Discontinue drug and report their appearance promptly. Monitor I and O rates and patterns. Report any significant changes.
DRUG
DOSAGE
MECHANISM OF ACTION Binds to mu-opioid receptors and inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS. Tramadol works primarily by acting directly on the brain. The primary mode of action is to decrease the brain's perception of pain. Therapeutic Effects: Decreased pain
INDICATION AND CONTRAINDICATION Indication: Moderate to moderately severe pain
Generic Name: Tramadol Brand Name: Ultram Therapeutic Class: Analgesic Why client is receiving the drug based on the history of present illness? The patient is having pain
Dose: 300mg Route: TIV (side drip)
Contraindication: Known hypersensitivity to tramadol, any other component of this product, or opioids
SIDE AND ADVERSE EFFECTS Side Effects: Fever Diarrhea Nausea and Vomiting Fainting Tachycardia Drowsiness Headache Dizziness Upset Stomach
NURSING CONSIDERATION Assess type, location, and intensity of pain before and 2-3 hr (peak) after administration. Assess BP & RR before and periodically during administration. Assess bowel function routinely. Monitor patient for seizures Overdose may cause respiratory depression and seizures Encourage patient to cough and breathe deeply every 2 hr to prevent atelactasis and pneumonia.
Adverse Effects: Angioedema Seizures Loss of coordination Overactive reflexes Shallow breathing
You might also like
- Drug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeDocument7 pagesDrug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- DiarryDocument10 pagesDiarryVan Ryan CondenoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- RUSS Emergency DrugDocument6 pagesRUSS Emergency DrugKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument70 pagesDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and UsesDocument11 pagesDrug Study Effects and UsesVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Drug Study CompilationDocument9 pagesDrug Study CompilationRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GanDocument34 pagesPentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GankotonashiNo ratings yet
- Ncp&drugstudDocument12 pagesNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDocument7 pagesNeuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyJomabee TuArNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationthomasfinley44No ratings yet
- Omeprazole Mechanism Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertDocument19 pagesOmeprazole Mechanism Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertCzarinah Ela MesiasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Document12 pagesMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Document2 pagesAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument6 pagesCefuroximetrinkets0914No ratings yet
- Drug and NCPDocument15 pagesDrug and NCPgeelawlietNo ratings yet
- Dugs CVADocument10 pagesDugs CVAMarie AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- Case Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisDocument34 pagesCase Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisVivian Montesena BreganzaNo ratings yet
- Cva Smh301 (Next)Document14 pagesCva Smh301 (Next)Christine OjedaNo ratings yet
- COX-2 inhibitor relieves arthritis painDocument5 pagesCOX-2 inhibitor relieves arthritis painDiolan Novero BagorioNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument6 pagesAtropine SulfateManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesDexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- VIII. Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDDocument17 pagesDRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 pagesDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Managing corticosteroids and their side effectsDocument6 pagesManaging corticosteroids and their side effectsKrista Madranca CastroNo ratings yet
- PARACETAMOLDocument2 pagesPARACETAMOLMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsnurse_nurseNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Drugs and Nle FeedbacksDocument106 pagesTop 40 Drugs and Nle FeedbacksGeraldin Buyagao KinlijanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name, Dose, Indications, Side Effects, Nursing Care, Rationale, Patient Teaching (38Document7 pagesGeneric Name, Dose, Indications, Side Effects, Nursing Care, Rationale, Patient Teaching (38Joanna Marie Datahan EstomoNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument3 pagesDrug OrderSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac NSAID Drug StudyDocument5 pagesKetorolac NSAID Drug StudyMary Grace IlaganNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- CaniDocument1 pageCaniMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument9 pagesAcid BaseMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- EffusionDocument1 pageEffusionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- EffusionDocument1 pageEffusionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- HypotensionDocument2 pagesHypotensionMikz Jocom0% (1)
- NX ManagementDocument1 pageNX ManagementMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- NX Floor PlanDocument1 pageNX Floor PlanMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and DiagnosticDocument1 pageLaboratory and DiagnosticMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Pillitteri EditedDocument34 pagesPillitteri EditedSheenah Parpan0% (1)
- 100 Item Obstetrics KeysDocument32 pages100 Item Obstetrics KeysChieChay Dub100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Obstetrics KeysDocument32 pages100 Item Obstetrics KeysChieChay Dub100% (1)
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- AbgDocument2 pagesAbgMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Epic Lab UpdateDocument3 pagesEpic Lab UpdateMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Re VeiwerDocument5 pagesRe VeiwerMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Pillitteri EditedDocument34 pagesPillitteri EditedSheenah Parpan0% (1)
- NCLEX-RN Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillDocument9 pagesNCLEX-RN Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillAko Si PisangNo ratings yet
- Renal OutlineDocument5 pagesRenal OutlineMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleDocument21 pages100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleAijem Ryan93% (15)
- Etiology: Environmental Factors in Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageEtiology: Environmental Factors in Bipolar DisorderMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- NCLEX-RN Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillDocument9 pagesNCLEX-RN Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillAko Si PisangNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Environmental Factors in Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageEtiology: Environmental Factors in Bipolar DisorderMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument2 pagesHaloperidolMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Viruses Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesBacteria Viruses Lesson Planapi-665322772No ratings yet
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- Neonatal Glycaemia and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis.Document11 pagesNeonatal Glycaemia and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis.Alma Iris Rodriguez D PadillaNo ratings yet
- VA Trans Resource ListDocument23 pagesVA Trans Resource ListMallory O'SheaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Ulcer, A Case StudyDocument4 pagesMarginal Ulcer, A Case StudySailaja NandennagariNo ratings yet
- Balanced Diet ChartDocument2 pagesBalanced Diet ChartjosephNo ratings yet
- Study of Incidence and Risk Factors For Surgical Site Infection After Cesarean Section at First Referral UnitDocument3 pagesStudy of Incidence and Risk Factors For Surgical Site Infection After Cesarean Section at First Referral UnitFaozan FikriNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Managing Student StressorsDocument173 pagesUnderstanding and Managing Student StressorsKhritish SwargiaryNo ratings yet
- Incident Reporting and Investigation ProcedureDocument8 pagesIncident Reporting and Investigation ProcedureWitara Saja67% (3)
- Allergen Awareness Training PresentationDocument32 pagesAllergen Awareness Training Presentationaprilia tunggal dewi100% (2)
- Drugs and Magic Remedies Objectionable Advertisements Act 1954Document9 pagesDrugs and Magic Remedies Objectionable Advertisements Act 1954Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- 9 Wireframe DocumentDocument7 pages9 Wireframe Documentharshaddanawale.nbnssoe.compNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Analysis 4Document3 pagesNursing Case Analysis 4Luna GrayNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors - KY Cancer RegistryDocument45 pagesBrain Tumors - KY Cancer RegistryMohammad Galih PratamaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2 (Postpartum Hemorrhage)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2 (Postpartum Hemorrhage)Killa BischeNo ratings yet
- Answer Key CicDocument3 pagesAnswer Key Cictiburshoc16No ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer: Anh Q. Truong MS-4 University of Washington, SOMDocument33 pagesLaryngeal Cancer: Anh Q. Truong MS-4 University of Washington, SOMSri Agustina0% (1)
- DSM Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesDSM Comparison ChartAJ commsNo ratings yet
- Career CounselingDocument13 pagesCareer CounselingPooja PatelNo ratings yet
- Twisted Risk Assesment 2Document2 pagesTwisted Risk Assesment 2api-306671250100% (1)
- Artificial RespirationDocument3 pagesArtificial RespirationRenju JoseNo ratings yet
- Tle ActivityDocument4 pagesTle ActivityManayam CatherineNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance / Preparation and of The Company / UndertakingDocument3 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance / Preparation and of The Company / UndertakingnbagarNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Diagnosing Infectious DiseasesDocument35 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Diagnosing Infectious DiseasesJehu C LanieNo ratings yet
- Constructive Programme for Complete IndependenceDocument15 pagesConstructive Programme for Complete IndependenceRanit MaitiNo ratings yet
- How To Take Your Blood Pressure at HomeDocument1 pageHow To Take Your Blood Pressure at HomePratyush VelaskarNo ratings yet
- Crossm: George R. Thompson, III, Phoebe Lewis, Stuart Mudge, Thomas F. Patterson, Bruce P. BurnettDocument11 pagesCrossm: George R. Thompson, III, Phoebe Lewis, Stuart Mudge, Thomas F. Patterson, Bruce P. BurnettarchikaNo ratings yet
- Scoring The Survey: Maysi 2 Scoringkey ScoringkeyDocument11 pagesScoring The Survey: Maysi 2 Scoringkey Scoringkey7 MNTNo ratings yet
- Case Study Fnes 366Document6 pagesCase Study Fnes 366api-347761303No ratings yet
- Pengisian Tanggal3Document32 pagesPengisian Tanggal3gusrina simamoraNo ratings yet