Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Anatomy Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Rosette Go0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesMASTICATION ARTICULATION INGESTION taste SPEECH DIGESTION DEGLUTATION RESPIRATION lips - are two fleshy borders of the mouth that are connected at the commissure. The labial commission - the area where the upper lip meets the lower lip - is a shallow depression extending from the corner ala of the nose down to the corner of the mouth. The LABIOMENTAL SULCUS - a conve
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMASTICATION ARTICULATION INGESTION taste SPEECH DIGESTION DEGLUTATION RESPIRATION lips - are two fleshy borders of the mouth that are connected at the commissure. The labial commission - the area where the upper lip meets the lower lip - is a shallow depression extending from the corner ala of the nose down to the corner of the mouth. The LABIOMENTAL SULCUS - a conve
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesOral Anatomy Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Rosette GoMASTICATION ARTICULATION INGESTION taste SPEECH DIGESTION DEGLUTATION RESPIRATION lips - are two fleshy borders of the mouth that are connected at the commissure. The labial commission - the area where the upper lip meets the lower lip - is a shallow depression extending from the corner ala of the nose down to the corner of the mouth. The LABIOMENTAL SULCUS - a conve
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
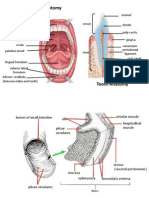
ORAL ANATOMY LESSON 3 • TUBERCLE OF THE UPPER LIP –
is a midline protrusion in the
PARAORAL TISSUES – are red zone of the upper lip
structures functionally associated • PHILTRUM – a shallow
with the oral cavity depression extending from the
center of the nose down to the
FUNCTIONS OF THE PARAORAL center of the upper lip
TISSUES:
• MASTICATION CHEEKS – is the lateral boundary of
• ARTICULATION the oral vestibule by the upper
• INGESTION vestibular fornix superioirly, the
• TASTE lower vestibular fornix inferiorly
• SPEECH and the pterygomandibular raphe
• DIGESTION laterally
• DEGLUTATION
STRUCTURES OF THE CHEEKS:
• RESPIRATION
• BUCCINATOR MUSCLE – the
muscle of the cheeks
LIPS – are two fleshy borders of the
mouth that are connected at the • BUCCAL FAT PAD OF BICHAT –
commissure and are basically the fat of the cheeks that
made up of muscles and salivary usually decrease in size with
glands age and is called the SUCKLING
PAD in infants
STRUCTURES OF THE LIPS: • PAROTID PAPILLA – found
• MUCOCUTANEOUS JUNCTION – opposite the buccal vestibule
the area of the lips between the • LINEA ALBA – a white line found
skin of the face and the red part at the occlusal plane where it
of the lips extends horizontally along the
• RED ZONE/VERMILLION AREA – midline of the cheeks
is the red/pink part of the lips
that is covered by a non- TONGUE – a flat broad muscular
keratinized mucosa organ found at the floor of the
mouth and is the principal organ
• WET LINE/WET-DRY LINE – is the
for taste
area separating the red zone
and the labial mucosa
STRUCTURES OF THE TONGUE:
• LABIAL COMMISSURE – the area
• ANTEROIR 2/3 OF THE TONGUE
where the upper lip meets the
– or the BODY is the one that is
lower lip
facing the palate
• NASOLABIAL GROOVE – a
• POSTERIOR 1/3 OF THE TONGUE
shallow depression extending
– or the BASE is the one that is
from the corner ala of the nose
facing the floor of the mouth
down to the corner of the mouth
• LINGUAL PAPILLA – covers the
• LABIOMARGINAL SULCUS – a
dorsal anterior 2/3 of the
shallow depression extending
tongue
downward from the corner of
the mouth • LINGUAL FOLLICLES – covers the
dorsal posterior 1/3 of the
• LABIOMENTAL GROOVE – a
tongue and is called LINGUAL
convex depression separating
TONSILS collectively
the lower lip from the chin
• TERMINAL SULCUS – a V-shaped papilla that contains the taste
area separating the anterior buds for sweet and salty tastes
and posterior dorsal part of the and is clinically seen as dark red
tongue scattered spots on the tongue
• FORAMEN CECUM – the slight • FOLIATE PAPILLA – are large
depression of the tongue raised papillae on the sides of
• MEDIAN SULCUS – a shallow the tongue that contains the
groove extending along the taste buds which are sensitive
midline of the tongue ending in to the sour taste
a slight depression
• DORSAL MUCOSA – lined by EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF THE
specialized mucosa TONGUE:
• VENTRAL MUCOSA – smooth • GENIOGLOSSUS MUSCLE – the
and thin strongest extrinsic muscle of
the tongue
• MANDIBULAR TORI – a non-
o Origin: GENIAL TUBERCLE
pathological excess of bone
OF THE MANDIBLE
* The TRIGEMINAL NERVE o Insertion: TONGUE
innervates the anterior 2/3 of the o Action: depressor
tongue while the protractor of the tongue
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE • STYLOGLOSSUS MUSCLE
innervates the posterior 1/3 of the o Origin: ANTERIOR
tongue SURFACE OF THE
STYLOID PROCESS
LINGUAL PAPILLA OF THE DORSAL o Insertion: TONGUE
ANTERIOR 2/3 OF THE TONGUE: o Action: elevate and
• CIRCUMVALLATE PAPILLA – is retract the tongue
arranged in a V-shaped manner • PALATOGLOSSUS MUSCLE
and is usually 8 in number o Origin: LOWER SURFACE
shaped as a very big mushroom OF THE PALATINE
papilla found in front of the APONEUROSIS
foramen cecum that contains o Insertion: TONGUE
the taste buds which are o Action: a sphincter
sensitive to the bitter taste muscle that closes the
• FILIFORM PAPILLA – is the most oronasal opening
numerous papilla which is • HYOGLOSSUS MUSCLE
scattered throughout the o Origin: HYOID BONE
tongue but is the only papilla o Insertion: TONGUE
that doesn’t contain taste buds o Action: depressor of the
and it is hair-like, it has a tongue
conical shape, it is highly
keratinized and it is the one INTRINSIC MUSCLES OF THE
responsible for giving the TONGUE:
tongue its grayish-pink velvety • LONGITUDINAL
appearance • VERTICAL
• FUNGIFORM PAPILLA – is found • TRANSVERSE
on the apex o the tongue. It is a
mushroom shaped papilla
smaller than the circumvallate
SALIVARY GLANDS – a fluid • POSTERIOR LINGUAL GLANDS –
material made up mostly of water found on the lingual tonsils on
that moistens the oral cavity the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
• INCISIVE GLANDS – found
STRUCTURES OF THE SALIVARY basically on the floor of the
GLANDS: mouth behind the 2 lower
• SUBLINGUAL CARUNCULA – is a incisors
site on either side of the
frenulum linguae on the TONSILS – lymphoid tissues
sublingual surface that denotes contained within the pharyngeal
the site at which the fauces
submandibular gland empties
into the oral cavity PHARYNGEAL LYMPHATIC RING OF
• PAROTID GLAND – the largest of WALDEYER:
the 3 salivary glands that is • PHARYNGEAL
found at the side of the face in • PALATINE
front of the ear and behind the • LINGUAL
ramus of the mandible that
mostly secretes the serous type PARANASAL SINUSES – are air-filled
• SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND – is cavities that lessens the weight of
about the size of a walnut the skull
secretes 80% serous and 20% • SPHENOID
mucous (WHARTON’S DUCT) • FRONTAL
• SUBLINGUAL GLAND – the • ETHMOID
smallest of the 3 salivary glands • MAXILLARY (ANTRUM OF
located at the floor of the HIGHMORE)
mouth and secretes mucous
primarily (BARTHOLIN’S DUCT)
• MINOR SALIVARY GLANDS –
very small glands with very
short ducts delivering small
amounts of saliva
• LABIAL GLANDS – numerous and
found within the labial area
• BUCCAL GLANDS – found within
the cheek area
• PALATINE GLANDS – found at
the posterior 1/3 of palate and
soft palate
• LINGUAL GLANDS – found at the -Rosette Go 070308
tongue
• ANTERIOR LINGUAL GLANDS –
also known as glands of
BLANDIN & NUHN is located at
the apex of the tongue
• LINGUAL GLANDS OF VON
EBNER – glands found beneath
the circumvallate papilla
You might also like
- Go Smile Dental Clinic - Pcpi ProposalDocument4 pagesGo Smile Dental Clinic - Pcpi ProposalRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Endodontics Final ReviewerDocument27 pagesEndodontics Final ReviewerRosette Go100% (5)
- King Saud University Dental Residents' Continuing Education Course in Oral BiologyDocument6 pagesKing Saud University Dental Residents' Continuing Education Course in Oral BiologyMuhamad Andika Arief PutranamiNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis Prelims ReviewerDocument16 pagesOral Diagnosis Prelims ReviewerRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Facial Danger Zones - Avoiding Nerve Injury in Facial Plastic SurgeryDocument63 pagesFacial Danger Zones - Avoiding Nerve Injury in Facial Plastic Surgeryramarchiori100% (1)
- DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING HEAD & NECK - Rick Harnsberger PDFDocument1,003 pagesDIAGNOSTIC IMAGING HEAD & NECK - Rick Harnsberger PDFAlina Tashnic100% (2)
- Oral Anatomy NotesDocument20 pagesOral Anatomy NotesMyrian V. Legaspi100% (1)
- Oral Anatomy Lesson 1Document2 pagesOral Anatomy Lesson 1Rosette Go100% (2)
- 2 Salivary GlandsDocument20 pages2 Salivary GlandsKaty SanchezNo ratings yet
- First Aid Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesFirst Aid Anatomy NotessethrbNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument10 pagesOral AnatomyRobins DhakalNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument10 pagesTongueBhuwanesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument65 pagesFacial NerveprashanthsumsaiarjunNo ratings yet
- Maxillary SinusDocument25 pagesMaxillary Sinusshreya dasNo ratings yet
- Anat 4.3 GIT Histo - ZuluetaDocument8 pagesAnat 4.3 GIT Histo - Zuluetalovelots1234No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Salivary Glandstheibban89No ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Anatomy and HistologyDocument37 pagesMaxillary Sinus Anatomy and HistologySkAliHassan100% (2)
- Orbicularis Oculi and Other Facial MusclesDocument10 pagesOrbicularis Oculi and Other Facial MusclesPATRICE ANNE ALCOREZANo ratings yet
- ENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Document4 pagesENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Tj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PharynxDocument31 pagesAnatomy of PharynxMuhammad KamilNo ratings yet
- Skull Normas and Facial BonesDocument36 pagesSkull Normas and Facial BonesVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument36 pagesOral Mucous MembraneFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves V, Vii, Viii, Ix, X, Xi, Xii: DR Nan Ommar FMHS, UnimasDocument32 pagesCranial Nerves V, Vii, Viii, Ix, X, Xi, Xii: DR Nan Ommar FMHS, UnimasMerriNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesSalivary GlandsNithish Reddy100% (1)
- Periodontium NotesDocument12 pagesPeriodontium NotesClarisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Oral Cavity & Tongue PDFDocument16 pagesOral Cavity & Tongue PDFLisa Denton100% (1)
- Maxillary SinusDocument67 pagesMaxillary SinusDR. NEETI TATIYANo ratings yet
- Histology of Ear and EyeDocument2 pagesHistology of Ear and EyeAnny AlvrzNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument112 pagesSalivary GlandSwati SawalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Major Salivary GlandsDocument46 pagesAnatomy of Major Salivary Glandswaniya irumNo ratings yet
- Development of The FaceDocument76 pagesDevelopment of The Facedr parveen bathla100% (1)
- Head+and+neck Mcqs With AnswersDocument178 pagesHead+and+neck Mcqs With Answersbadar_aqNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor PDFDocument93 pagesOdontogenic Tumor PDFEmad Alriashy100% (1)
- MnemonicsDocument11 pagesMnemonicsanon-626602No ratings yet
- Morphologic Patterns of Acute InflammationDocument51 pagesMorphologic Patterns of Acute Inflammationحفصه حسينNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal Duct CystDocument2 pagesThyroglossal Duct CystPulkitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- Head NeckDocument99 pagesHead NeckElena NazâruNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of Oral Soft TissuesDocument73 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of Oral Soft Tissuesvellingiriramesh53040% (1)
- Dental Anatomy Final ReviewDocument10 pagesDental Anatomy Final ReviewSalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Regional AnatomyDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Regional Anatomyapi-324160601100% (4)
- Tissue - SeeleyDocument61 pagesTissue - SeeleyJuli Damayanty HarahapNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandsDocument25 pagesSalivary Glandsapi-3777487100% (2)
- OHNS 2.1 Nose Paranasal Sinuses Nasal Obstruction Epistaxis Capinpin JMSales 1Document12 pagesOHNS 2.1 Nose Paranasal Sinuses Nasal Obstruction Epistaxis Capinpin JMSales 1Paolo BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Pathology of InfectiousDocument39 pagesPathology of InfectiousDeEo OnoNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal Tumours2Document46 pagesPharyngeal Tumours2miramirajalalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pathology Infectious DiseasesDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Pathology Infectious DiseasesNirav PatelNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Cells (Most Numerous Immune Cells)Document13 pagesDendritic Cells (Most Numerous Immune Cells)Emma RanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of NoseDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Noserizgah jawas100% (1)
- SkullDocument48 pagesSkulldavid100% (1)
- Facial Nerve & Its Applied Aspects: By-Dr. Abdul RazakDocument45 pagesFacial Nerve & Its Applied Aspects: By-Dr. Abdul RazakAbdul Razak100% (1)
- Pharyngeal Arch Derivatives Chart!Document5 pagesPharyngeal Arch Derivatives Chart!Suphadetch LeungNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumors of Oral Cavity: Dr. Deepak K. GuptaDocument44 pagesOdontogenic Tumors of Oral Cavity: Dr. Deepak K. GuptaBinek NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination and Histological Techniques OverviewDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination and Histological Techniques OverviewBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Histology of the Urinary System: Kidneys, Nephrons, and PassagewaysDocument46 pagesHistology of the Urinary System: Kidneys, Nephrons, and PassagewaysAnonymous EzxZg4uQ63100% (1)
- Management of Lefort FracturesDocument93 pagesManagement of Lefort FracturesKassim OboghenaNo ratings yet
- Tooth Numbering System Word FileDocument15 pagesTooth Numbering System Word FileRonak PatelNo ratings yet
- Periodontium (4) : Periodontal LigamentsDocument6 pagesPeriodontium (4) : Periodontal Ligamentsمحمد محمود القحيفNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument270 pagesCysts of The Oral CavitySally Mahfouz100% (6)
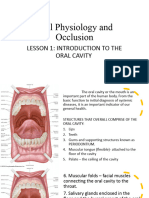
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- W2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFDocument69 pagesW2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- TONGUE Seminar by MeDocument84 pagesTONGUE Seminar by MeArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Accessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyDocument172 pagesAccessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyManisha RaoNo ratings yet
- L. 10 The Oral CavityDocument79 pagesL. 10 The Oral CavityAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Tongue Anatomy, Development, Histology & FunctionsDocument100 pagesTongue Anatomy, Development, Histology & FunctionsAPARNA AARATHI SREEKUMARNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology Midterm ReviewerDocument4 pagesAnesthesiology Midterm ReviewerRosette Go100% (1)
- Presence of Fever InfectionDocument1 pagePresence of Fever InfectionRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Guest Ice Breaker SampleDocument1 pageGuest Ice Breaker SampleRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom F3Document1 pagePom F3Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M2Document2 pagesPom M2Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M7Document2 pagesPom M7Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Know The Systemic Diseases Suffered by The PatientsDocument2 pagesKnow The Systemic Diseases Suffered by The PatientsRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M8Document2 pagesPom M8Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M1Document1 pagePom M1Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M5Document1 pagePom M5Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Instruments & MaterialsDocument1 pageInstruments & MaterialsRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M6Document2 pagesPom M6Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom M3Document2 pagesPom M3Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom F7Document2 pagesPom F7Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom F6Document2 pagesPom F6Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis m4Document2 pagesOral Diagnosis m4Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pom F5Document2 pagesPom F5Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis m2Document3 pagesOral Diagnosis m2Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis m3Document3 pagesOral Diagnosis m3Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Medicine Prelim ReviewerDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Medicine Prelim ReviewerRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis m5Document2 pagesOral Diagnosis m5Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Conditions - MidtermsDocument13 pagesUlcerative Conditions - MidtermsRosette Go100% (1)
- Ulcerative Conditions Associated With Immunlogic DysfunctionsDocument32 pagesUlcerative Conditions Associated With Immunlogic DysfunctionsRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Practice Management Prelim ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractice Management Prelim ReviewerRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery 2 Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesOral Surgery 2 Midterm ReviewerRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Pedodontics MidtermsDocument4 pagesPedodontics MidtermsRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology 2 Vesicular LesionsDocument5 pagesOral Pathology 2 Vesicular LesionsRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2 All in OneDocument102 pagesAnatomy 2 All in OneDragoiu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Presented Before The Annual Meeting of The American Association of Orthodontists, Dal-Las, Texas, April, 1953Document13 pagesPresented Before The Annual Meeting of The American Association of Orthodontists, Dal-Las, Texas, April, 1953Paola LoloNo ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck Dr. BanezDocument6 pagesAnterior Triangle of The Neck Dr. BanezMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- LidahDocument2 pagesLidahNur AsiahNo ratings yet
- 4 Cotofana 2016Document8 pages4 Cotofana 2016Thamyres Branco100% (1)
- Facial Make-Up ApplicationDocument38 pagesFacial Make-Up ApplicationJezel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Memorize ophtha layers, structures, and diseasesDocument51 pagesMemorize ophtha layers, structures, and diseasesPatryk Dionisio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Thyroid CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Thyroid CancerKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Use of Iowa Spaces For The Orthodontic Management of Mandibular Postsurgical Skeletal RelapseDocument6 pagesUse of Iowa Spaces For The Orthodontic Management of Mandibular Postsurgical Skeletal RelapseRamya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Speech & Its Prosthodontic ConsiderationDocument74 pagesTongue, Speech & Its Prosthodontic ConsiderationmujtabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Anatomy, Physiology (Essentials of Dental Assisting)Document35 pagesChapter 3 - Anatomy, Physiology (Essentials of Dental Assisting)mussanteNo ratings yet
- Thyroiditis: Evaluation and TreatmentDocument9 pagesThyroiditis: Evaluation and Treatmentรติรัตน์ หนูนุ่นNo ratings yet
- EYE FOCUS MECHANISM: ACCOMMODATIONDocument11 pagesEYE FOCUS MECHANISM: ACCOMMODATIONThadei Mruma100% (1)
- Auditory PhoneticsDocument8 pagesAuditory PhoneticsمثنىالبريطانيNo ratings yet
- A To Z Orthodontics Vol 11 Functional Orthodontic AppliancesDocument22 pagesA To Z Orthodontics Vol 11 Functional Orthodontic AppliancesNisa Ulil AmriNo ratings yet
- CVS, Respi Heent ExamDocument8 pagesCVS, Respi Heent ExamDranreb Berylle MasangkayNo ratings yet
- Examen Neurológico en Pequeños AnimalesDocument30 pagesExamen Neurológico en Pequeños AnimalesHelem MoreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Human Eye Class XDocument11 pagesLesson Plan Human Eye Class Xminakshi tiwari75% (8)
- Organs of SpeechDocument27 pagesOrgans of SpeechSanjit MishraNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument22 pagesMatrixMark Jonell EsguerraNo ratings yet
- How I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesDocument29 pagesHow I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesMartín Avellaneda SantoméNo ratings yet
- Examination of Lacrimal ApparatusDocument23 pagesExamination of Lacrimal ApparatusDr. T. BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Causes of VertigoDocument6 pagesCauses of VertigoSUALI RAVEENDRA NAIKNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma & Management: Dr. Utham Murali. M.S M.B.A. Asso - Prof of Surgery IMS / MSU / MalaysiaDocument48 pagesHead Trauma & Management: Dr. Utham Murali. M.S M.B.A. Asso - Prof of Surgery IMS / MSU / MalaysiaNinaNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Neuroanatomy and ObstetricsDocument13 pagesMCQs on Neuroanatomy and ObstetricsAbdullah TanoliNo ratings yet
- Mandibular RotationDocument70 pagesMandibular RotationMaitreye Priyadarshini100% (1)
- ICD 10 Codes AudiologyDocument57 pagesICD 10 Codes AudiologyEdi AhsaniNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Tacurong College College of NursingDocument4 pagesNotre Dame of Tacurong College College of NursingJona Phie Montero NdtcnursingNo ratings yet