Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Sheet
Uploaded by
Milan ZivkovicCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Sheet
Uploaded by
Milan ZivkovicCopyright:
Available Formats
TCA 785
Phase Control IC
TCA 785
Bipolar IC
Features
G G G G G G G G
Reliable recognition of zero passage Large application scope May be used as zero point switch LSL compatible Three-phase operation possible (3 ICs) Output current 250 mA Large ramp current range Wide temperature range
P-DIP-16-1
Type TCA 785
Ordering Code Q67000-A2321
Package P-DIP-16-1
This phase control IC is intended to control thyristors, triacs, and transistors. The trigger pulses can be shifted within a phase angle between 0 and 180 . Typical applications include converter circuits, AC controllers and three-phase current controllers. This IC replaces the previous types TCA 780 and TCA 780 D. Pin Definitions and Functions Pin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Pin Configuration (top view) Semiconductor Group 14 15 16 1 Symbol GND Q2 QU Q2 VSYNC I QZ V REF R9 C10 V11 C12 L Q1 Q2 VS Function Ground Output 2 inverted Output U Output 1 inverted Synchronous voltage Inhibit Output Z Stabilized voltage Ramp resistance Ramp capacitance Control voltage Pulse extension Long pulse Output 1 Output 2 Supply voltage 09.94
TCA 785
Functional Description The synchronization signal is obtained via a high-ohmic resistance from the line voltage (voltage V5). A zero voltage detector evaluates the zero passages and transfers them to the synchronization register. This synchronization register controls a ramp generator, the capacitor C10 of which is charged by a constant current (determined by R9). If the ramp voltage V10 exceeds the control voltage V11 (triggering angle ), a signal is processed to the logic. Dependent on the magnitude of the control voltage V11, the triggering angle can be shifted within a phase angle of 0 to 180. For every half wave, a positive pulse of approx. 30 s duration appears at the outputs Q 1 and Q 2. The pulse duration can be prolonged up to 180 via a capacitor C12. If pin 12 is connected to ground, pulses with a duration between and 180 will result. Outputs Q 1 and Q 2 supply the inverse signals of Q 1 and Q 2. A signal of +180 which can be used for controlling an external logic,is available at pin 3. A signal which corresponds to the NOR link of Q 1 and Q 2 is available at output Q Z (pin 7). The inhibit input can be used to disable outputs Q1, Q2 and Q 1 , Q 2 . Pin 13 can be used to extend the outputs Q 1 and Q 2 to full pulse length (180 ).
Block Diagram Semiconductor Group 2
TCA 785
Pulse Diagram
Semiconductor Group
TCA 785
Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Supply voltage Output current at pin 14, 15 Inhibit voltage Control voltage Voltage short-pulse circuit Synchronization input current Output voltage at pin 14, 15 Output current at pin 2, 3, 4, 7 Output voltage at pin 2, 3, 4, 7 Junction temperature Storage temperature Thermal resistance system - air Operating Range Supply voltage Operating frequency Ambient temperature VS f TA 8 10 25 18 500 85 V Hz C Symbol min. VS IQ V6 V11 V13 V5 VQ IQ VQ Tj Tstg Rth SA 55 0.5 10 0.5 0.5 0.5 200 Limit Values max. 18 400 VS VS VS
Unit V mA V V V
A
200
VS 10 VS 150 125 80
V mA V C C K/W
Characteristics 8 VS 18 V; 25 C TA 85 C; f = 50 Hz Parameter Supply current consumption S1 S6 open V11 = 0 V C 10 = 47 nF; R 9 = 100 k Synchronization pin 5 Input current R 2 varied Offset voltage Control input pin 11 Control voltage range Input resistance Semiconductor Group Symbol min. IS 4.5 Limit Values typ. 6.5 max. 10 Unit Test Circuit mA 1
I5 rms
V5
30 30 0.2 15 4
200 75 V10 peak
mV 4 V k 1 5
V11 R11
TCA 785
Characteristics (contd) 8 VS 18 V; 25 C TA 85 C; f = 50 Hz Parameter Ramp generator Charge current Max. ramp voltage Saturation voltage at capacitor Ramp resistance Sawtooth return time Inhibit pin 6 switch-over of pin 7 Outputs disabled Outputs enabled Signal transition time Input current V6 = 8 V Input current V6 = 1.7 V Deviation of I10 R 9 = const. VS = 12 V; C10 = 47 nF Deviation of I10 R 9 = const. VS = 8 V to 18 V Deviation of the ramp voltage between 2 following half-waves, VS = const. Long pulse switch-over pin 13 switch-over of S8 Short pulse at output Long pulse at output Input current V13 = 8 V Input current V13 = 1.7 V Outputs pin 2, 3, 4, 7 Reverse current VQ = VS Saturation voltage IQ = 2 mA Symbol min. I10 V10 V10 R9 tf 10 100 3 225 80 Limit Values typ. max. 1000 V2 2 350 300 Unit Test Circuit
A V mV k s
1 1.6 1 1
V6 L V6 H tr I6 H I6 L I10
4 1
3.3 3.3 500
2.5 5 800 200 5
V V s A
A
1 1 1 1 1 1
80 5
150
% %
I10
20
20
V10 max
V13 H V13 L I13 H I13 L
3.5
2.5 2.5
2 10 100
V V A
A
1 1 1 1
45
65
ICEO Vsat 0.1 0.4
10 2
2.6 2.6
Semiconductor Group
TCA 785
Characteristics (contd) 8 VS 18 V; 25 C TA 85 C; f = 50 Hz Parameter Outputs pin 14, 15 H-output voltage I Q = 250 mA L-output voltage IQ = 2 mA Pulse width (short pulse) S9 open Pulse width (short pulse) with C12 Internal voltage control Reference voltage Parallel connection of 10 ICs possible TC of reference voltage Symbol min. V14/15 H V14/15 L tp tp VS 3 0.3 20 530 Limit Values typ. VS 2.5 0.8 30 620 max. VS 1.0 2 40 760 Unit Test Circuit V V
s s/ nF
3.6 2.6 1 1
VREF
REF
2.8
3.1 2 10 4
3.4 5 10 4
1/K 1
Semiconductor Group
TCA 785
Application Hints for External Components min Ramp capacitance C10 500 pF V11 R9 C10 VREF K VREF K R9
2)
max 1 F1)
2)
The minimum and maximum values of I10 are to be observed
Triggering point
tTr =
Charge current
I10 =
Ramp voltage V10 max = VS 2 V V10 =
VREF K t R9 C10
2)
Pulse Extension versus Temperature
1) 2)
Attention to flyback times K = 1.10 20 %
Semiconductor Group
TCA 785
Output Voltage measured to + VS
Supply Current versus Supply Voltage
Semiconductor Group
TCA 785
It is necessary for all measurements to adjust the ramp with the aid of C10 and R 9 in the way that 3 V Vramp max V S 2 V e.g. C10 = 47 nF; 18 V: R 9 = 47 k; 8 V: R 9 = 120 k
Test Circuit 1 Semiconductor Group 9
TCA 785
The remaining pins are connected as in test circuit 1
Test Circuit 2
The remaining pins are connected as in test circuit 1 Test Circuit 3
Semiconductor Group
10
TCA 785
Remaining pins are connected as in test circuit 1 The 10 F capacitor at pin 5 serves only for test purposes Test Circuit 4
Test Circuit 5 Semiconductor Group 11
Test Circuit 6
TCA 785
Inhibit 6
Long Pulse 13
Pulse Extension 12
Reference Voltage 8
Semiconductor Group
12
TCA 785
Application Examples Triac Control for up to 50 mA Gate Trigger Current
A phase control with a directly controlled triac is shown in the figure. The triggering angle of the triac can be adjusted continuously between 0 and 180 with the aid of an external potentiometer. During the positive half-wave of the line voltage, the triac receives a positive gate pulse from the IC output pin 15. During the negative half-wave, it also receives a positive trigger pulse from pin 14. The trigger pulse width is approx. 100 s. Semiconductor Group 13
TCA 785
Fully Controlled AC Power Controller Circuit for Two High-Power Thyristors Shown is the possibility to trigger two antiparalleled thyristors with one IC TCA 785. The trigger pulse can be shifted continuously within a phase angle between 0 and 180 by means of a potentiometer. During the negative line half-wave the trigger pulse of pin 14 is fed to the relevant thyristor via a trigger pulse transformer. During the positive line half-wave, the gate of the second thyristor is triggered by a trigger pulse transformer at pin 15. Semiconductor Group 14
TCA 785
Half-Controlled Single-Phase Bridge Circuit with Trigger Pulse Transformer and Direct Control for Low-Power Thyristors Semiconductor Group 15
TCA 785
Half-Controlled Single-Phase Bridge Circuit with Two Trigger Pulse Transformers for Low-Power Thyristors Semiconductor Group 16
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Coil Measuring-, and Q-MetersDocument10 pagesCoil Measuring-, and Q-MetersNiket Sali SureshNo ratings yet
- Control IC For Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4718 ADocument17 pagesControl IC For Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4718 ASledge HammerNo ratings yet
- WP01062F24EN0117-Frequency and Antenna Selection Effects On Accuracy of Free Space Radar-V002Document6 pagesWP01062F24EN0117-Frequency and Antenna Selection Effects On Accuracy of Free Space Radar-V002kfathi55No ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Different Types of PCB Base MaterialsDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of PCB Base Materialsmatrixworld20No ratings yet
- Tca 785 DatasheetDocument18 pagesTca 785 DatasheetCarlos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Datashep Tca 785Document18 pagesDatashep Tca 785johan andresNo ratings yet
- Tca 785 DatasheetDocument18 pagesTca 785 Datasheetnur shintaNo ratings yet
- TLE4266G SiemensSemiconductorGroupDocument9 pagesTLE4266G SiemensSemiconductorGroupDuranRod2013No ratings yet
- CD1517 Long SemiDocument9 pagesCD1517 Long Semiamir baroughNo ratings yet
- Amplificador de Audio CD1517CPDocument9 pagesAmplificador de Audio CD1517CPAntonio ChavezNo ratings yet
- High-Power 2x6W Stereo Amplifier ICDocument9 pagesHigh-Power 2x6W Stereo Amplifier ICamir baroughNo ratings yet
- LM1815 Adaptive Variable Reluctance Sensor AmplifierDocument6 pagesLM1815 Adaptive Variable Reluctance Sensor AmplifierAbbode HoraniNo ratings yet
- Utc3842 YouwangelectronicsDocument9 pagesUtc3842 YouwangelectronicsMindSet MarcosNo ratings yet
- soldadora UTC3843DDocument9 pagessoldadora UTC3843DChristian ormeñoNo ratings yet
- Bay Linear Current Mode PWM Controller SpecificationsDocument11 pagesBay Linear Current Mode PWM Controller SpecificationsShashikant PatilNo ratings yet
- Dual Operational Amplifiers: FeatureDocument7 pagesDual Operational Amplifiers: FeatureAndres Fernandez Fernandez100% (1)
- SCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationDocument13 pagesSCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationEzequiel Posadas BocacaoNo ratings yet
- SCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationDocument14 pagesSCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationNaveedNo ratings yet
- 22W Car Radio Power Amplifier IC with Integrated Class-B OutputDocument11 pages22W Car Radio Power Amplifier IC with Integrated Class-B OutputamdatiNo ratings yet
- IRAMS10UP60A Integrated Power Module for Appliance Motor DriveDocument18 pagesIRAMS10UP60A Integrated Power Module for Appliance Motor DriveAnselmo LimaNo ratings yet
- PDF Irams10up60b IRFDocument19 pagesPDF Irams10up60b IRFAndy LNo ratings yet
- Fy700 Series TaieDocument9 pagesFy700 Series TaieHưng Phan HữuNo ratings yet
- L4981ADocument17 pagesL4981AMcu CdiiNo ratings yet
- VB027BSP: High Voltage Ignition Coil Driver Power IcDocument8 pagesVB027BSP: High Voltage Ignition Coil Driver Power IcmiyerNo ratings yet
- SCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationDocument13 pagesSCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationlubnaNo ratings yet
- ZS6312 V1.0Document12 pagesZS6312 V1.0Franzua PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- KA2131 SamsungDocument4 pagesKA2131 SamsungTito PerezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument8 pagesDatasheet PDFJavier Moscol YamunaqueNo ratings yet
- Ka7632 PDFDocument8 pagesKa7632 PDFenriqueNo ratings yet
- UTC TL1451 Linear Integrated Circuit: Dual Pulse-Width-Modulation Control CircuitsDocument5 pagesUTC TL1451 Linear Integrated Circuit: Dual Pulse-Width-Modulation Control CircuitsMarcos Gomes MisselNo ratings yet
- stps20s100cfp SCHOTTKY DIODEDocument7 pagesstps20s100cfp SCHOTTKY DIODEANDREASBOULNo ratings yet
- Borro ToDocument9 pagesBorro TomaugrysNo ratings yet
- STMicroelectronics L4981AD DatasheetDocument17 pagesSTMicroelectronics L4981AD Datasheetgafesa electronicsNo ratings yet
- 3842a DatasheetDocument8 pages3842a DatasheetVịnh DemoNo ratings yet
- Very High Speed, Ultra Low Power Consumption 5V Powered Rs-232 Drivers and ReceiversDocument10 pagesVery High Speed, Ultra Low Power Consumption 5V Powered Rs-232 Drivers and Receiversdurgesh100No ratings yet
- Proportional Amplifier PV: For The Control of A Proportional SolenoidDocument8 pagesProportional Amplifier PV: For The Control of A Proportional SolenoidIvan BeljinNo ratings yet
- Utc 4558Document4 pagesUtc 4558Ysrrael SilvaNo ratings yet
- Power Driver IC for CD PlayersDocument8 pagesPower Driver IC for CD PlayersAdnanDeğerliyurtNo ratings yet
- 3842Document12 pages3842luisNo ratings yet
- Ka3882/3/4/5 Smps Controller: Current Mode PWM ControllerDocument6 pagesKa3882/3/4/5 Smps Controller: Current Mode PWM Controllerjoil alvesNo ratings yet
- KA2410 DatasheetDocument6 pagesKA2410 Datasheetauyantepuy73No ratings yet
- Carlo - Gavazzi RGC2P60V75C1DFM Datasheet PDFDocument29 pagesCarlo - Gavazzi RGC2P60V75C1DFM Datasheet PDFmikeNo ratings yet
- Dual Bridge Driver IC Technical SpecificationDocument10 pagesDual Bridge Driver IC Technical SpecificationAndi HarsonoNo ratings yet
- REN R07ds1031ej0300 bcr16cm12lc DST 20190201Document9 pagesREN R07ds1031ej0300 bcr16cm12lc DST 20190201Purwanto B012No ratings yet
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKYPER 32 R L6100102Document18 pagesSEMIKRON DataSheet SKYPER 32 R L6100102Faisal AfzalNo ratings yet
- 6脚电源IC资料及代换Document7 pages6脚电源IC资料及代换Justin NgNo ratings yet
- Quad Channel High Side Driver: So-28 (Double Island)Document20 pagesQuad Channel High Side Driver: So-28 (Double Island)julianNo ratings yet
- T2117 Zero-Voltage Switch With Adjustable Ramp PDFDocument16 pagesT2117 Zero-Voltage Switch With Adjustable Ramp PDFnenadNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Ignition Coil Driver IC Technical SpecificationsDocument8 pagesHigh Voltage Ignition Coil Driver IC Technical SpecificationsJuan Jose Leon PaedesNo ratings yet
- LA6520 3-Output Power Operational AmplifierDocument2 pagesLA6520 3-Output Power Operational AmplifierElec ThaihoaNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuit: Current Mode PWM ControllerDocument6 pagesLinear Integrated Circuit: Current Mode PWM ControllernermeenelnaggarNo ratings yet
- Toshiba 8-Channel High Voltage Source DriverDocument10 pagesToshiba 8-Channel High Voltage Source DriverLider Ch CuevaNo ratings yet
- KA3842A IC Datasheet PDFDocument5 pagesKA3842A IC Datasheet PDFagarcosNo ratings yet
- LM386 DatasheetDocument6 pagesLM386 DatasheetJamie ValentineNo ratings yet
- MG17 K802 DanfossDocument98 pagesMG17 K802 DanfossMr.K chNo ratings yet
- Lead-Acid Battery Spec SheetDocument2 pagesLead-Acid Battery Spec SheetJean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- rg6 Gripper Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesrg6 Gripper Datasheet PDFRaj RajNo ratings yet
- Brosur Line Post InsulatorDocument2 pagesBrosur Line Post InsulatorHizbul MaulanaNo ratings yet
- physicLAB EA1Document17 pagesphysicLAB EA1marc San joseNo ratings yet
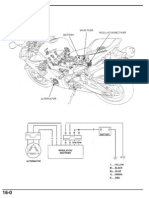
- 954 16 Charging SystemDocument9 pages954 16 Charging SystemgenuineswedeNo ratings yet
- PH Converter Ph402gDocument87 pagesPH Converter Ph402gvjNo ratings yet
- Cmsq200a7w1b PDFDocument280 pagesCmsq200a7w1b PDFLeonardusNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode ApplicationsDocument3 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode Applicationsdonatello84No ratings yet
- Manual H2 Purity AnalyzerDocument92 pagesManual H2 Purity AnalyzerPrima RadiansyahNo ratings yet
- No 52-G breaker consequences and standardsDocument7 pagesNo 52-G breaker consequences and standardsschauhan12No ratings yet
- Jameco Part Number 1390194: Distributed byDocument31 pagesJameco Part Number 1390194: Distributed byfox7878No ratings yet
- Havells ConsumerCables2020Document6 pagesHavells ConsumerCables2020juga2013No ratings yet
- Fixed Attenuators: Designer's Kit K3-GAT+Document1 pageFixed Attenuators: Designer's Kit K3-GAT+ppanagos5664No ratings yet
- Icecom 2023 Program v2bDocument18 pagesIcecom 2023 Program v2basarolicNo ratings yet
- BP Res U2 Elect Symbols Outlets NoteDocument23 pagesBP Res U2 Elect Symbols Outlets NoteEdev Paula De VeraNo ratings yet
- 327 DatatakomDocument2 pages327 DatatakomNorman RuizNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1E Module 13 Light and OpticsDocument46 pagesPHYSICS 1E Module 13 Light and OpticsClaire G. MagluyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Nonlinear and Anisotropic MaterialsDocument25 pagesLecture Nonlinear and Anisotropic MaterialsJabir Khan JadoonNo ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering & Science Ips Academy Indore: Major Project ReportDocument33 pagesInstitute of Engineering & Science Ips Academy Indore: Major Project Reportshruti20_mittalNo ratings yet
- Current Clamp Adaptor For Multimeters: by John ClarkeDocument7 pagesCurrent Clamp Adaptor For Multimeters: by John Clarkemor3danNo ratings yet
- C 102Document1 pageC 102Nicky DragutescuNo ratings yet
- PANEL LED 600 X 600 40 W 6500 KDocument3 pagesPANEL LED 600 X 600 40 W 6500 KEzhilNo ratings yet
- Simple Fire Alarm Circuits at Low CostDocument5 pagesSimple Fire Alarm Circuits at Low CostRobert CervantesNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Implementation in India - A Case Study of Puducherry Pilot ProjectDocument9 pagesSmart Grid Implementation in India - A Case Study of Puducherry Pilot Projectswapna44No ratings yet
- Survey of Control Methods For DC-DC Converters: KeywordsDocument6 pagesSurvey of Control Methods For DC-DC Converters: KeywordsBernardo GalvanoNo ratings yet
- Protect USB Data and Charging with Low Capacitance TVS ArrayDocument10 pagesProtect USB Data and Charging with Low Capacitance TVS ArrayhernanNo ratings yet