Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analisis Kriging
Uploaded by
Prahastomi Muttahari S.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analisis Kriging
Uploaded by
Prahastomi Muttahari S.Copyright:
Available Formats
ANALISIS KRIGING
Pengantar
Analisis dengan kriging digunakan untuk estimasi nilai yang tidak diketahui
berdasarkan nilai yang diketahui. Syarat metode kriging adalah variabel tersebut memilki
nilai yang lebih mirip untuk jarak yang lebih dekat, artinya untuk jarak yang lebih dekat
nilai variabel tersebut lebih mirip dibandingkan jarak yang lebih jauh. Misalnya
kedalaman air tanah, ketinggian wilayah, pendemik penyakit menular/virus. Kalaupun
terdapat perbedaan yang signifikan pada nilai daerah yang berdekatan, akan dimasukkan
pada variabel error sehingga pemilihan metode kriging harus meminimumkan error.
Langkah-langkah
Langkah-langkah pembuatan peta polygon adalah sebagai berikut:
1. Scanning Peta dari Bakosurtanal untuk mendapatkan file raster image (JPEG).
Simpan file tersebut dengan nama file dan direktori yang dikehendaki.
2. Melakukan registrasi file raster image (JPEG) yang didapatkan dengan
MapInfo. Buka file raster image (JPEG) di MapInfo dan klik pilihan register.
Pada proses registrasi, langkah yang harus dilakukan adalah memilih empat
titik kontrol dan memasukkan koordinat masing-masing titik kontrol yaitu x
untuk koordinat bujur dan y untuk koordinat lintang. Data masukan koordinat
berupa desimal sehingga perlu transformasi dari satuan derajat kedalam
desimal. MapInfo akan memberikan informasi error dari nilai koordinat yang
telah dimasukkan, proses digitasi akan memberikan hasil yang bagus apabila
error kurang dari lima pixel.
3. Sebelum melakukan on screen digitizing, tetapkan dulu skala yang digunakan
untuk menentukan derajat akurasi yang diinginkan. Pilih menu map, change
view, map scale, kemudian tetapkan skala yang diinginkan.
4. On screen digitizing pada raster image yang telah teregistrasi
1
yaitu dengan
mengaktifkan layer control pada cosmetic layer dan melakukan digitasi untuk
batas desa. Setelah semua batas desa terdigitasi simpan file ke dalam nama file
dan direktori yang dikehendaki, misalnya line.
2
5. Gunakan icon marquee select untuk memilih seluruh line hasil digitasi.
Pastikan pada masing-masing desa hanya dibatasi oleh garis yang merupakan
batas dari desa yang bersangkutan dan tidak menyambung dengan batas desa
dari desa yang bersebelahan. Hal ini penting dalam proses enclose. Namun
apabila kesalahan ini terjadi dapat dilakukan perbaikan, yaitu:
a) Klik pada garis yang terjadi kesalahan, ubah kedalam polyline dengan
memilih menu object, convert to polyline.
b) Pilih icon reshape untuk memunculkan node pada polyline.
c) Pilih node yang memotong garis tepat pada batas desa, pilih menu object,
polyline split add node sehingga garis terpotong tepat pada batas desa.
Apabila node yang tersedia tidak ada yang tepat pada batas desa, buat
node tersebut dengan mengaktifkan icon add node dan klik tepat pada titik
yang memisahkan garis pada batas desa.
d) Pastikan pula garis yang telah dibuat tidak ada yang terputus ataupun
terlalu panjang (dua node menyambung), meskipun hanya beberapa
1
Raster image yang telah teregistrasi disimpan dengan tipe file MapInfo Table File.
2
Cosmetic layer merupakan file yang bersifat sementara sehingga apabila file hasil digitasi masih dalam
cosmetic layer maka file dapat hilang.
milimeter. Jika hal ini terjadi, aktifkan icon reshape kemudian perpanjang
atau perpendek dengan menarik node sehingga antar dua node menjadi
terhubung.
6. Pilih menu object, snap, kemudian aktifkan object enable snap dan tentukan
snap tolerance.
3
7. Pilih menu object, enclose untuk mentransformasi line menjadi poligon.
8. File line sekarang terdiri dari poligon dan line. Untuk mendapatkan peta
dalam bentuk poligon, pilih seluruh area kelurahan,
4
copy kedalam cosmetic
layer dan simpan kedalam nama dan direktori yang diinginkan, misalnya
poligon.
9. Untuk membuat atribut dari peta Surabaya poligon, klik icon new browser.
Karena dibutuhkan field kode desa dan nama desa sebagai atribut, pilih menu
table, maintenance untuk menambahkan field. Klik pada salah satu desa maka
kursor akan aktif pada posisi baris yang bersesuaian dalam tabel.
10. Peta kelurahan telah selesai dibuat, akan tetapi format MapInfo tidak dapat
dibaca oleh ArcGis. Untuk itu dilakukan transformasi format yaitu dengan
memilih menu tools, universal translator. Tetapkan file source dan
destination, baik untuk nama file maupun formatnya
5
.
Untuk memasukkan titik yang nantinya menjadi input analisis, berikut keterangan dari
situs harvard university.
3
Snap tolerance dimaksudkan apabila terdapat node yang tidak menyambung, terlalu panjang atau terlalu
pendek, tetapi masih dalam batas toleransi snap maka dua node tersebut akan tersambung.
4
Pemilihan dengan cara memilih satu persatu (menggunakan tombol control) dan pastikan tidak ada garis
yang ikut terpilih.
5
Dalam kasus ini pilih ESRI shape agar dapat dibaca ArcGis.
1. You need to create a file with three columns: one for longitude, one for latitude, and
one for the variable that you wish to map. The first row of the file should contain the
variable names (e.g., x,y,z).
2. Note that ArcGIS assumes that input x and y coordinates correspond to the x and y
coordinates of the coordinate system of the data frame (longitude and latitude if you are
using a geographic coordinate system). If this is not the case for your data, you may need
to further examine the documentation to see how this might be handled.
3. For response variables that are constrained to be positive, such as concentrations, a
common approach is to take the natural logarithm of the values. This tends to produce
data that more closely match the underlying statistical assumptions involved in kriging.
This and other transformations could also be done within ArcGIS before doing kriging.
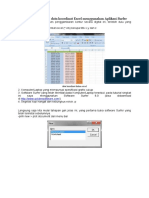
4. Your input file should be comma delimited, which means that there should be commas,
and only commas, between the values in the file. Each line should pertain to a single
location, with the x and y coordinates of the location and the response value, all separated
by commas. One way to create this format is in Microsoft Excel. Open the file that you
want to convert. Go to File->Save as, and under 'Save as type', select 'CSV'. Hit Save,
and Yes to the window that pops up. When you quit Excel, you do not need to save any
changes. In S-plus or R, if you use the write.table() function to create the data file, the
argument ' sep="," ' will create a comma delimited file. You can also use dbf files, which
can also be created with MS Excel.
5. Open your map in ArcMap, and go to Tools->Add XY data, click the folder icon on
the top right, and browse through the folders to find the .csv file that you just created.
Then hit OK. Your new layer should appear in the Layers column on the left. It will also
display the layer as individual points on your map.
Sedangkan pengolahan dalam ArcGis juga dijelaskan melalui geostatistical analysis.
Secara singkat dapat disusun langkah sebagai berikut:
1. Make sure the Geostatistical Analyst is enabled (Tools->Extensions) and the toolbar is
visible (View->Toolbars).
2. Select Geostatistical Wizard on the Geostatistical Analyst toolbar.
3. Select the input data (layer) to krige and the attribute (response, i.e., z) variable, as well
as the Kriging method in the lower left. Then choose Next.
4. (Step 1) Select Ordinary Kriging->Prediction Map. You also presumably have the
option of transforming the data, such as using the natural logarithm, if you haven't done
so already, though in my setup, ArcGIS gives me no options under Transformation.
Click Next(untuk asumsi kenormalan).
5. (Step 2) The next step involves estimating the covariance structure using the empirical
variogram or empiral covariogram. The default is the variogram, and there is some
evidence in the literature for preferring this when using the weighted least squares
approach, as in ArcGIS. I suggest using the K-Bessel (known more commonly as the
Matern) model; this has become popular in the spatial statistics literature. In particular,
the Matern model tends to produce surfaces that are more smooth locally (on a very fine
scale) than some other models (such as the exponential or spherical). This is often
desirable, since the unknown underlying surface can often plausibly be considered to be
locally smooth on a very fine scale. I suggest using the values for the Matern model
estimated by ArcGIS. If you wish to change the values, you will want to read the
documentation for ArcGIS and probably some basic material on spatial statistics. Note
that if the estimated value for the Parameter of the Matern is less than one, then the
estimated surface is not differentiable (0.5 is the exponential model and values
approaching infinity tend toward the Gaussian model). I also suggest clicking on
'Measurement Error' and sliding the bar to '100% Measurement Error', which indicates
that your data are measured with uncertainty. The documentation claims that by doing so,
you avoid interpolating the data (having the estimated surface go exactly through your
data points), although I have not seen any differences in the estimated surface whether
the Measurement Error box is clicked or not clicked. Still, to be safe, I suggest clicking
the box. Then click Next.
The one exception to using the default values is that you may want to investigate the
possibility that your data have directionality to them, for example if they are influenced
by prevailing winds or groundwater flow directions. An easy way to do this is to click on
anisotropy toward the upper right of the Step 2 box and allow ArcGIS to estimate the
necessary additional parameters automatically. To assess whether including directionality
in your model is warranted you could compare the root mean square prediction error
given in Step 4 for the models with and without anisotropy.
Gambar di atas jika estimasi tidak memperhatikan faktor arah (isotropi) sehingga estimasi
hanya berdasarkan jarak titik (semakin dekat suatu titik akan memiliki karakteristik yang
lebih mirip).
Jika estimasi memperhatikan jarak titik dan arah, maka korelasi spasial yang digunakan
adalah anisotopi (misal untuk kasus penyebaran penyakit, curah hujan).
6. (Step 3) The next step determines the details of how ArcGIS approximates the surface
estimate so that the computations can be done quickly. Theoretically, the estimated
surface at any point should be based on all of the data points, but ArcGIS uses only some
of the points, indicated in the Neighbors to Include field. From a statistical viewpoint,
there is more danger in using too few than too many points (since the kriging method
essentially ignores data points far from the location at which predictions are being made
anyway). I suggest using a sizable fraction of the data, to the extent that it does not take
too long to estimate the surface. For example for 100 data points, I would try to use at
least 25 neighbors, and more if possible. For 1000, I would use at least 25-50 and ideally
a few hundred, but the computations may be too slow with this many. I would unclick the
Include at Least box, which preferentially includes data points based on direction,
unless you have modeled directionality on the previous screen. Note that the colored map
of points indicates the relative weights assigned to each data point for use in predicting
the surface at the focal location at the center of the circle/ellipse. Click Next.
Untuk pemeriksaan neighbors selain cara diatas dapat juga dilakukan dengan voronoi
map. Masukkan jumlah titik yang memiliki warna sama.
Klik pada option tren analysis untuk mengetahui ada atau tidaknya tren pada data. Bila
proyeksi data pada sumbu x dan y menunjukkan garis non linier maka data
mengindikasikan ada tren. Maka untuk pengolahan ArcGis harus menggunakan tren
removal.
7. (Step 4) The next screen assesses how good your predictions are based on cross-
validation (leaving points out of the fitting and then estimating the value and comparing
to the actual value). The root-mean-square prediction error can be compared between
different models as a way of choosing a model (such as whether to include
directionality). The ArcGIS documentation gives more detail about this. Click Finish
and then OK to produce the surface map.
8. Your new layer should now appear on the map. If you would like to change the colors,
you can right-click on the layer from the Layers column and go to 'Properties'. On the top
menu, select 'Symbology'. You can then change the colors in 'Color Ramp'. You can also
change the number of colors that appear on the map by selecting a different number from
the drop-down menu.
9. Estimating the uncertainty in your predicted surface is an important aspect of spatial
analysis. If the uncertainty is so great that peaks and valleys in the surface may not truly
exist, then it would be ill-advised to try to interpret those peaks and valleys as
representing real features of your data. To estimate the standard errors at each location, as
presented in an additional map, use the exact same steps as above, but in Step 1, select
Ordinary Kriging->Prediction Standard Error Map. The interpretation of the confidence
level indicated by the standard error at each location is that if you repeated the
experiment many times, collecting data over and over again, in approximately 67% of the
experiments, the true surface at a point would lie within one standard error of the
estimated surface produce. Note that this uncertainty calculation does NOT account for
the uncertainty in fitting the covariance structure, which might be substantial.
Setelah didapatkan surface estimation nilai prediksi pada daerah yang ingin kita estimasi
dapat diketahui. Aktifkan layer KRIGING dan klik tepat pada titik yang nilainya ingin
dihitung. Jangan lupa aktifkan kursor pada identify maka apabila kita klik pada suatu
titik, nilai yang akan diperkirakan akan diketahui.
Berikut desa yang missing value untuk variabel kedalaman air tanah setelah diestimasi
dengan kriging
DESA
KOORDINAT PREDIKSI POSISI
DATA (U(i)) BUJUR LINTANG
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Kandangan 112
o
3907,920E 7
o
1504,559S 7,093208
Buntaran 112
o
4021,136E 7
o
1455,068S 4,825878
Tanjung Sari 112
o
4131,640E 7
o
1535,744S 4,420314
Jeruk 112
o
3835,380E 7
o
1818,446S 33,938166
Simomulyo 112
o
4240,789E 7
o
1550,658S 4,732769
Tegal Sari 112
o
4407,563E 7
o
1610,996S 4,750260
Ngagel 112
o
4442,815E 7
o
1640,825S 4,647249
Darmo 112
o
4349,937E 7
o
1726,923S 5,901477
Sawungaling 112
o
4340,446E 7
o
1730,991S 6,232151
Wonokromo 112
o
4349,937E 7
o
180,8200S 5,750904
Ngagel Rejo 112
o
4434,680E 7
o
1748,617S 4,718152
Pegirian 112
o
4504,509E 7
o
1331,005S 4,696463
Krembangan Utara 112
o
4404,852E 7
o
1354,005S 3,659426
Perak Barat 112
o
4343,158E 7
o
1332,361S 3,317181
Jagir 112
o
4425,189E 7
o
1819,802S 4,798393
Analisis kriging mempunyai banyak metode, penyesuaian, dan trik. Kondisi data yang
berbeda mengakibatkan perlakuan yang berbeda. Syarat utama data untuk dapat
dilakukan analisis kriging adalah kenormalan dan regionalized data.
You might also like
- Modul 5. Pemodelan Sistem Informasi Geografis (Site Suitability) + DEMDocument15 pagesModul 5. Pemodelan Sistem Informasi Geografis (Site Suitability) + DEMsiti mutawaliaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data RasterDocument9 pagesAnalisis Data RasterAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum SIG 5Document19 pagesLaporan Praktikum SIG 5Muhammad Agung Andika OktafiansyahNo ratings yet
- Tip ArcGISDocument20 pagesTip ArcGISrovidakamal100% (2)
- Modul Pelatihan Sig Menggunakan ArcgisDocument118 pagesModul Pelatihan Sig Menggunakan ArcgisErwin Hermawan67% (3)
- Manipulasi Dan Analisis Data SIG Melalui Proses Pemasukan DataDocument8 pagesManipulasi Dan Analisis Data SIG Melalui Proses Pemasukan DataN'rique SilvaNo ratings yet
- HGJHGLDocument15 pagesHGJHGLWeslyRambuLangi0% (1)
- GIS Level 1 GIS Workshop Exercises IdDocument5 pagesGIS Level 1 GIS Workshop Exercises IdIkrima Silvi HadzarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Spasial Berbasis RasterDocument14 pagesAnalisis Spasial Berbasis RasterIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Modul Pengenalan ArcGISDocument20 pagesModul Pengenalan ArcGISHizrianNo ratings yet
- Mengolah Data SRTMDocument0 pagesMengolah Data SRTMawienizef100% (3)
- ArcgisDocument10 pagesArcgisFauzan AchmadNo ratings yet
- Pelatihan Sistem Informasi Geografis - DasarDocument35 pagesPelatihan Sistem Informasi Geografis - DasarRakhma TikaNo ratings yet
- Modul Arcgis LanjutanDocument24 pagesModul Arcgis LanjutanUpik Upiko Fitra Saleh100% (1)
- CROSS_SECTION_ARCGISDocument8 pagesCROSS_SECTION_ARCGISpaulo de carvalhoNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Komputer PertemuanDocument11 pagesAplikasi Komputer PertemuanarifNo ratings yet
- SLOPE DAN KONTUR DI ARCGISDocument9 pagesSLOPE DAN KONTUR DI ARCGISmaruf291197No ratings yet
- Apa Itu ArcGISDocument12 pagesApa Itu ArcGISMicky DiohNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data SIGDocument41 pagesAnalisis Data SIGmasagus muhammad ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Mempelajari Penampilan Data SpasialDocument14 pagesMempelajari Penampilan Data SpasialAdy MentayadiputraNo ratings yet
- DISTRIBUSI DATADocument44 pagesDISTRIBUSI DATAJumadil Awaluddin100% (2)
- M1 - Pengenalan ArcMapDocument10 pagesM1 - Pengenalan ArcMapFARIZKI KharisaNo ratings yet
- M6 - Geoprocessing Dan Data Entry - ArcGISDocument15 pagesM6 - Geoprocessing Dan Data Entry - ArcGISSyahdan DzulhajNo ratings yet
- HaloDocument17 pagesHaloBrian Purnama PutraNo ratings yet
- Konversi Excel ke Shp ArcGISDocument16 pagesKonversi Excel ke Shp ArcGISsukardiNo ratings yet
- Tujuan Dan Definisi Aplikasi SurfacDocument6 pagesTujuan Dan Definisi Aplikasi Surfacindra subaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum SbdsDocument14 pagesLaporan Praktikum SbdsMuhammad ZidanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Sig Penjelasan Tool Di ArcgisDocument11 pagesTugas Sig Penjelasan Tool Di ArcgisGalih Adi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Analisis Geostatistik ArcgisDocument22 pagesTutorial Analisis Geostatistik ArcgisAhmad Amiruddin100% (4)
- Analisis Dan Pembuatan Digital Elevation ModelDocument6 pagesAnalisis Dan Pembuatan Digital Elevation ModelLa Ode IsraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ratih NewDocument4 pagesJurnal Ratih NewSylvia IpingNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data Raster PDFDocument8 pagesAnalisis Data Raster PDFRaji PriyadiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kuliah Tutorial ArcGISDocument49 pagesTugas Kuliah Tutorial ArcGISKurniawan Edy100% (2)
- GIS UPDATINGDocument12 pagesGIS UPDATINGEddie Ellis100% (1)
- Bab III Pengenalan Arcmap 10 Ver2Document29 pagesBab III Pengenalan Arcmap 10 Ver2shogy100% (1)
- Modul ArcGISDocument28 pagesModul ArcGISKhansaNo ratings yet
- Prosedur Pembuatan Database Dan Estimasi Sumberdaya Nikel Menggunakan SURPACDocument6 pagesProsedur Pembuatan Database Dan Estimasi Sumberdaya Nikel Menggunakan SURPACYofi Astaman DakundeNo ratings yet
- Materi 5Document14 pagesMateri 5D'ony GazeRockNo ratings yet
- SURFER8Document7 pagesSURFER8xtololxNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum SIG 9-10 Essa - ZioDocument6 pagesLaporan Praktikum SIG 9-10 Essa - ZioESHANUNo ratings yet
- 05 - Data SpasialDocument31 pages05 - Data SpasialAyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- OPTIMASI KEMIRINGAN LAHANDocument6 pagesOPTIMASI KEMIRINGAN LAHANRani AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- GEOSPATIAL ANALYSISDocument17 pagesGEOSPATIAL ANALYSISAyu Saraswati HvkNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data Vektor QGISDocument5 pagesAnalisis Data Vektor QGISrinatrismiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Acara Ii Praktikum SPDKDocument22 pagesLaporan Acara Ii Praktikum SPDKINSOS OYINo ratings yet
- Teori Dasar GeokomputasiDocument31 pagesTeori Dasar GeokomputasiYuda SatriaNo ratings yet
- Modul I: Pengenalan Software Arcgis 1.1. Deskripsi UmumDocument67 pagesModul I: Pengenalan Software Arcgis 1.1. Deskripsi Umumanik susilowatiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Interpretasi Ruang: Image Pre Processing Dan ExtensionDocument12 pagesLaporan Praktikum Interpretasi Ruang: Image Pre Processing Dan ExtensionNovi YantiNo ratings yet
- MEMBUAT PETA 3D DENGAN TINDocument267 pagesMEMBUAT PETA 3D DENGAN TINYuliasD.Mia0% (1)
- BAB 02 PENGENALAN ArcMAP OKDocument20 pagesBAB 02 PENGENALAN ArcMAP OKAgus Darma putraNo ratings yet
- SISTEM INFORMASI GEOGRAFISDocument23 pagesSISTEM INFORMASI GEOGRAFISRahmatu ArifaldiNo ratings yet
- GISDocument4 pagesGISLaw CeliciaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar USLE GIS REFDocument34 pagesBahan Ajar USLE GIS REFzsazsaNo ratings yet
- Acara 2 SigDocument5 pagesAcara 2 SigSusi AndrianiNo ratings yet
- SIG A M1 443675 Farizki IndrawanDocument19 pagesSIG A M1 443675 Farizki IndrawanFARIZKI KharisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Membuat Data Spasial Menggunakan ArcGIS 10Document35 pagesTutorial Membuat Data Spasial Menggunakan ArcGIS 10Ilham Hidayatullah100% (1)
- Kegunaan Surfer Dalam Bidang GeologiDocument28 pagesKegunaan Surfer Dalam Bidang GeologiYuda SatriaNo ratings yet
- Membuat Aplikasi Bisnis Menggunakan Visual Studio Lightswitch 2013From EverandMembuat Aplikasi Bisnis Menggunakan Visual Studio Lightswitch 2013Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Canda Ala Sufi LengkapDocument87 pagesCanda Ala Sufi LengkapFarahnisa MappasissiNo ratings yet
- Perintah Dasar LinuxDocument2 pagesPerintah Dasar LinuxSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Prisma Pemikiran Gus Dur PDFDocument211 pagesPrisma Pemikiran Gus Dur PDFSayid Simbadda100% (3)
- SongDocument1 pageSongSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Halaman Isi SYDK Rev 1g.pdf1192063692Document88 pagesHalaman Isi SYDK Rev 1g.pdf1192063692Panatalaga100% (1)
- A Book of Wisdom Menghimpun Cerita Menggali MaknaDocument321 pagesA Book of Wisdom Menghimpun Cerita Menggali MaknaSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Ipi 440608Document4 pagesIpi 440608Sayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- La TahzanDocument124 pagesLa TahzanFreddy Lesmana100% (15)
- 8 - Pola Pemboran Dan Pola Peledakan - 2015Document26 pages8 - Pola Pemboran Dan Pola Peledakan - 2015Sayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- 124.10.010 - Sayyidul US - PR1Document3 pages124.10.010 - Sayyidul US - PR1Sayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Uts PKNDocument6 pagesUts PKNSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Metode Ordinary Kriging Pada GeostatistikaDocument60 pagesMetode Ordinary Kriging Pada GeostatistikaYongki Andita Aiman100% (2)
- Kolok CT Full 200106Document86 pagesKolok CT Full 200106diedroc100% (1)
- Caliper LogDocument2 pagesCaliper LogSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Lumpur PengeboranDocument21 pagesLumpur PengeboranSayid Simbadda100% (1)
- Bab 2Document3 pagesBab 2Sayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Etika Dan Tanggung Jawab Sosial PerusahaanDocument24 pagesEtika Dan Tanggung Jawab Sosial PerusahaanAndistya Oktaning Listra100% (2)
- Data Diskrit Adalah Data Hasil Pengamatan Yang Hanya Menempati AngkaangkaDocument1 pageData Diskrit Adalah Data Hasil Pengamatan Yang Hanya Menempati AngkaangkaSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet
- Etika Dan Tanggung Jawab Sosial PerusahaanDocument24 pagesEtika Dan Tanggung Jawab Sosial PerusahaanAndistya Oktaning Listra100% (2)
- Kwitansi PembayaranDocument1 pageKwitansi PembayaranSayid SimbaddaNo ratings yet