Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ampicillin
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ampicillin
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright:
Available Formats
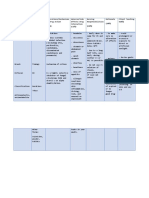
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name Pharmacologic Bactericidal action against General Concentrations CNS: Lethargy, Before
Ampicillin Class sensitive organisms; inhibits Indications - Allergies to penicillins, hallucinations, seizures - Observe 15 rights in drug
Penicillin synthesis of bacterial cell wall, - Treatment of cephalosporins, or other administration.
Trade Name causing cell death. infections caused allergens CV: Heart failure - Assess for allergies to penicillins,
Principen Therapeutic Class by susceptible cephalosporins, or other allergens.
Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics strains of Shigella, Precaution GI: Glossitis, stomatitis, - Assess for renal disorders or lactation.
Minimum Dose D: Crosses placenta; enters Salmonella, - Renal disorders gastritis, sore mouth, - Culture infected area before treatment.
8 g/day Pregnancy Risk breast milk Escherichia coli, furry tongue, black - If patient is a woman and she uses
Factor M: Not known Haemophilus Drug interaction “hairy” tongue, nausea, hormonal contraceptive, she should use
Maximum B E: Urine, unchanged influenzae, Proteus Drug to drug vomiting, diarrhea, a second form of birth control for 1-2
Dose mirabilis, Neisseria - Increased ampicillin effect abdominal pain, bloody weeks while taking this drug.
14 g/day Drug Half Life gonnorhoeae, with probenecid diarrhea, enterocolitis,
1-2 hours enterococci, gram- - Increased risk of rash with pseudomembranous During
Contents positive organisms allopurinol colitis, nonspecific - Administer oral drug on an empty
Ampicillin (penicillin G- - Increased bleeding effect hepatitis stomach, 1 hour before or 2 hours after
sodium sensitive with heparin, oral meals.
staphylococci, anticoagulants GU: Nephritis - Administer with a full glass of water. Do
Availability streptococci, - Decreased effect with not give with fruit juice or soft drinks.
and color pneumococci) tetracyclines, Hematologic: Anemia, - Do not give IM injections in the same
Capsules: 250, - Meningitis caused chloramphenicol thrombocytopenia, site; atrophy can occur.
500 mg by Neisseria - Decreased efficacy of leukopenia, - For IV administration, give slowly over
Powder for oral meningitidis hormonal contraceptives, neutropenia, prolonged 3-5 mins.
suspension: - Unlabeled use: atenolol with ampicillin bleednig time - Use within 1 hour after preparation
125 mg/5 mL, Prophylaxis in because potency may decrease
250 mg/5 mL cesarean section in Drug to food Hypersensitivity: significantly after that.
Powder for certain high-risk - Oral ampicillin may be less Rash, fever, wheezing,
injection: 250, patients effective with food; take on anaphylaxis After
500 mg, 1, 2 g empty stomach - Dispose of used materials properly.
Local: Pain, phlebitis, - Educate patient about side effects.
Routes of Drug to lab test thrombosis at injection - Instruct to report pain or discomfort at
administration - False-positive Coombs' test site sites, unusual bleeding or bruising,
Oral if given IV mouth sores, rash, hives, fever, itching
Intramuscular - Decrease in plasma Other: Superinfections severe diarrhea, difficulty breathing.
Intravenous estrogen concentrations in – oral and rectal - Instruct patient not to use antibiotic to
pregnant women moniliasis, vaginitis self-treat other infections.
- False-positive urine glucose - Instruct to take the full course of drug
tests if Clinitest, Benedict's therapy.
solution or Fehling's solution - Do proper documentation.
is used
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide,
Lippincott’s Nursing Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 126-127 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Drug Guide, pp. 127-128 Nursing Drug Guide, p. 128 pp. 127-128
Drug Guide, p. 126- Guide, p. 126 Guide, pp. 126-127
127
You might also like
- Ampicillin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin - Drug StudyLegendX100% (4)
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin Drug StudyTimothyMangrobang50% (2)
- Ampicillin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesAmpicillin DRUG STUDYMarvie Cadena100% (1)
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin Drug Studymilkv92% (12)
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidinecen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesGentamycin DRUG STUDYMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- MSU-IIT Nursing Student Drug Study on ZyvoxDocument3 pagesMSU-IIT Nursing Student Drug Study on ZyvoxAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus Influenzae, Proteus Mirabilis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, Enterococci, GramDocument2 pagesHaemophilus Influenzae, Proteus Mirabilis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, Enterococci, GramLegendXNo ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Amikacin SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amikacin Sulfateichiro017100% (7)
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY AmoxicillinKhylamarie VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- DRUG STUDY: PARACETAMOLDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY: PARACETAMOLShanel Aubrey Aglibut100% (1)
- Drug Study Vitamin KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Vitamin KFlorence NightingaleNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsPeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- STREPTOMYCINDocument3 pagesSTREPTOMYCINChad InongNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDocument5 pagesDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Fluconazole Dose Indications Side Effects Nursing TeachingDocument2 pagesFluconazole Dose Indications Side Effects Nursing Teachingryan100% (1)
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalSherwin LauronNo ratings yet
- WVSU College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesWVSU College of Nursing Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- Gatchalian Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGatchalian Drug StudyAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- DRUG AmikacinDocument2 pagesDRUG Amikacinrholiboi100% (1)
- Gentamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGentamycin Drug StudyShin Guevara100% (3)
- Ampicillin Sodium - Sulbactam Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmpicillin Sodium - Sulbactam Sodium Drug StudyMelissa Marie Custodio100% (3)
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- MebendazoleDocument1 pageMebendazolegiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument1 pageMethergineCharissa Magistrado De Leon0% (1)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocument64 pagesDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Drug SummDocument1 pageGentamicin Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- PHENYLEPHRINEDocument3 pagesPHENYLEPHRINERoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- School Nursing Common DRUG STUDYDocument10 pagesSchool Nursing Common DRUG STUDYMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyDocument7 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyGabriel Rosales RM RNNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument1 pageGentamicinreinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Misoprostol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Misoprostol)Danica NuevaexcijaNo ratings yet
- Nursery Drug StudyDocument9 pagesNursery Drug StudyNiña Dianne Rubin RustiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study in GentamicinDocument2 pagesDrug Study in Gentamicinanthony_alviar100% (1)
- Sample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYDocument8 pagesSample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYSherina BolosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Piperacillin / TazobactamDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Piperacillin / Tazobactammyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageAmoxicillin DRUG STUDYChristine IbiasNo ratings yet
- Patient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGDocument4 pagesPatient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGJackieMae100% (1)
- Co TrimoxazoleDocument2 pagesCo TrimoxazoleGrace Donato100% (1)
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudySiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY RabiesDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY RabiesFranz RolfNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- Balido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayDocument1 pageBalido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayEmman BalidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeMikko McDonie VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityDocument2 pagesDoctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- LTD Finals Cases Batch 1Document29 pagesLTD Finals Cases Batch 1Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- LTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Document18 pagesLTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsDocument22 pagesFreedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Document1 pageAffidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Procedural Due Process Case DigestsDocument8 pagesProcedural Due Process Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Document18 pagesCONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digests For Canons 10-13Document6 pagesCase Digests For Canons 10-13Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- The Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodDocument17 pagesThe Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler67% (6)
- Legal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Document34 pagesLegal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Digests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Document1 pageDigests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law I NotesDocument59 pagesConstitutional Law I NotesIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Cases 1 15Document11 pagesCases 1 15Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Persons - Notes For MidtermsDocument10 pagesPersons - Notes For MidtermsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- Affidavit of Loss - CabrerosDocument1 pageAffidavit of Loss - CabrerosIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Rgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchDocument40 pagesRgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- Guideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsDocument7 pagesGuideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsLisna K. RezkyNo ratings yet
- Antigen & Antibody: Structure, Function & Immune ResponseDocument48 pagesAntigen & Antibody: Structure, Function & Immune Responsebook keedaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepDocument24 pagesExamples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepJatro100% (1)
- Emergency Action Principles CPR First AidDocument7 pagesEmergency Action Principles CPR First AidRonald Michael QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis: 1) Introduction 2) Basic Elements in Assessment 3) Physical AssessmentDocument36 pagesClinical Assessment and Diagnosis: 1) Introduction 2) Basic Elements in Assessment 3) Physical AssessmentTrixieCamposano100% (1)
- Ecg PDFDocument2 pagesEcg PDFNaveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Guideline ManualDocument157 pagesTrauma Guideline Manualsgod34No ratings yet
- What Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsKeneth Dave AglibutNo ratings yet
- IJOH Vol. 6Document92 pagesIJOH Vol. 6Shud MnNo ratings yet
- Itrack Advance BrochureDocument2 pagesItrack Advance BrochureHaag-Streit UK (HS-UK)No ratings yet
- ClinicalfeaturesDocument11 pagesClinicalfeaturesapi-526590140No ratings yet
- 2-1 박종설.rev1 PDFDocument77 pages2-1 박종설.rev1 PDFNam LeNo ratings yet
- ShineDocument37 pagesShineMohd SaifNo ratings yet
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNo ratings yet
- Spermac Stain Analysis of Human SpermDocument5 pagesSpermac Stain Analysis of Human SpermNatasyaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis DiagramDocument1 pageHematopoiesis DiagramApril Rose Airoso - AramburoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TablesDocument19 pagesMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Hearing Screening in Speech and Language Delay PatientsDocument5 pagesHearing Screening in Speech and Language Delay PatientsrezkiwjNo ratings yet
- Myasis, Tungiasis and LoiasisDocument34 pagesMyasis, Tungiasis and LoiasisMateo LópezNo ratings yet
- L Hi Appt Results 06252021Document7 pagesL Hi Appt Results 06252021C RealNo ratings yet
- Gene Reports: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesGene Reports: SciencedirectautomationenggNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument6 pagesJaundiceNiaNo ratings yet
- Health CareDocument1 pageHealth CareMikeNo ratings yet
- What Light Source Is Used in Most Flow CytometersDocument4 pagesWhat Light Source Is Used in Most Flow CytometersMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- (7P) Host-Microbial Interactions in Periodontal DiseasesDocument6 pages(7P) Host-Microbial Interactions in Periodontal DiseasesNegrus StefanNo ratings yet
- IKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRDocument2 pagesIKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRikman nibosNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Products - CatalogueDocument4 pagesSri Sri Products - CatalogueSiva Saravana ManiNo ratings yet
- Nhs Clinical Evaluation Team Clinical Review Safety Peripheral Intravenous Cannula Report October 2018Document44 pagesNhs Clinical Evaluation Team Clinical Review Safety Peripheral Intravenous Cannula Report October 2018imaguestuserNo ratings yet
- Newborn Hearing ScreeningDocument8 pagesNewborn Hearing ScreeningGina BARCENANo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Unit Orientation: Prof. Precy P. LantinDocument17 pagesIntensive Care Unit Orientation: Prof. Precy P. LantinJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet