Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodic Table: Part One: General Trends
Uploaded by
adikmukOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periodic Table: Part One: General Trends
Uploaded by
adikmukCopyright:
Available Formats
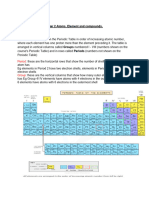
Periodic Table : Part One
General Trends
Classifying elements and its use
to predict properties of elements
The elements are systematically arranged which
helps us in remembering their properties.
Prediction of molecular formulae, nature of
oxides and types of chemical bonding can be
made.
Prediction of new elements.
On the basis of properties, correct electronic
configuration can be given.
Periodicity
Refers to the gradual change of physical and
chemical properties across the period
Group
I
Group
II
Transition
Metals
Group
III
Group
VII
Group
0
GROUP
Electronic Configuration of Lithium: 2.1
Electronic Configuration of Sodium: 2.8.1
Electronic Configuration of Potassium: 2.8.8.1
Electronic Configuration of Rubidium: 2.8.18.8.1
What do they share in common?
GROUP Vertical Columns
Same no. of valence electrons
Similar chemical properties
Reacts in similar ways
Down the group,
More metallic in character
Proton no. increases
Atomic radius/size increases
Period 1
Period 2
Period 3
PERIOD
Electronic configuration of Sodium: 2.8.1
Electronic configuration of Magnesium: 2.8.2
Electronic configuration of Silicon: 2.8.4
Electronic configuration of Argon: 2.8.8
What do they share in common?
PERIOD Horizontal Rows
Same no. of electron shells
From the left to the right,
Metallic character decreases
Non-metallic character increases
Metal usually has 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons in
its atom
Non-metal usually has 5, 6, 7 or 8 valence
electrons in its atom
http://www.privatehand.com/flash/elements.html
You might also like
- Unit 1 Part 4 The Periodic TableDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Part 4 The Periodic TableI LOVE JAKENo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic Table PropertiesDocument13 pagesModern Periodic Table PropertiesAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Periodicity: Learning OutcomesDocument16 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicity: Learning OutcomesAshley KuwodzaNo ratings yet
- PERIODIC TABLE ELEMENTSDocument7 pagesPERIODIC TABLE ELEMENTSOtgon OrgilNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Periodic Table and Atomic StructureDocument16 pagesCH 1 Periodic Table and Atomic StructuretanhuikuanNo ratings yet
- Key IdeasDocument11 pagesKey Ideasapi-261372832No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Document66 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNo ratings yet
- Summarised Yearly Teaching Plan F4Document14 pagesSummarised Yearly Teaching Plan F4FatimahHishamuddinNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of The ElementsDocument26 pagesThe Periodic Table of The ElementsRubén De Gracia Santo100% (1)
- Topic Flow Year 1Document4 pagesTopic Flow Year 1Prity PramanikNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Atoms, Elements and Compounds Igcse NotesDocument4 pagesCH 2 Atoms, Elements and Compounds Igcse NotesKim BoraNo ratings yet
- Science-8 Q3 Episode-3 SLMDocument4 pagesScience-8 Q3 Episode-3 SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- MR Osho/1 Term/Chemistry/Ss2Document34 pagesMR Osho/1 Term/Chemistry/Ss2jeremiah oseniNo ratings yet
- chemistry periodic trends class notesDocument3 pageschemistry periodic trends class notesdevanshuekandeNo ratings yet
- 69 Trends in Physicalpropsrevised PDFDocument3 pages69 Trends in Physicalpropsrevised PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 Module 2 The Periodic TableDocument10 pagesCHM 111 Module 2 The Periodic TableAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 The Periodic Table - Docx FINAL PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 6 The Periodic Table - Docx FINAL PDFProf Samuel KashinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manualthrenodyvoxlkio100% (26)
- CBCS - B.sc. With Chemistry - Generic ElectiveDocument17 pagesCBCS - B.sc. With Chemistry - Generic ElectiveMd RaselNo ratings yet
- SSS 2 E-Note 1st Term ChemistryDocument23 pagesSSS 2 E-Note 1st Term ChemistryDave Blessed90% (10)
- Periodic Classification of The Element - Lesson - 2Document14 pagesPeriodic Classification of The Element - Lesson - 2samsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesUnit 6 The Periodic TableVKNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - Chemistry - Week 1 - 8Document5 pagesScheme of Work - Chemistry - Week 1 - 8api-272169187No ratings yet
- Unit-3 In-Organic Chemistry: PCT-112 IHS GabsDocument34 pagesUnit-3 In-Organic Chemistry: PCT-112 IHS GabsMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Chemical FamiliesDocument32 pages2.2 Chemical Familiespeter ogencheNo ratings yet
- 41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptDocument70 pages41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptSanthi SriNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument41 pagesPeriodic TableMahmoud AladdasiNo ratings yet
- 2023 H1 H2 Periodic Table - Notes and TutorialDocument37 pages2023 H1 H2 Periodic Table - Notes and TutorialElean NgNo ratings yet
- PDF ViewerDocument11 pagesPDF ViewerAnjaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesChemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions ManualRicardoPetersJrdstf100% (50)
- Periodic Trends, Valence e- & LEDSDocument5 pagesPeriodic Trends, Valence e- & LEDSJoseph ZafraNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Chemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Chemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual PDFelijah3oa4knight100% (8)
- The Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument12 pagesThe Periodic Table and PeriodicityNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFDeepak GH100% (1)
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument13 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsOasisEducation OesNo ratings yet
- Bishop Study Guide 2Document10 pagesBishop Study Guide 2Faisal Mohad Al SakhenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument24 pagesChapter Two: Atoms, Molecules and IonsYusuf AbdirisakNo ratings yet
- Trends in Group IIDocument5 pagesTrends in Group IIEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- IB MYP Chemistry Term End AssessmentDocument2 pagesIB MYP Chemistry Term End AssessmentKrishna Teja100% (2)
- Chemistry Igcse (Cie) Break Down of Topics CoveredDocument15 pagesChemistry Igcse (Cie) Break Down of Topics CoveredketamineNo ratings yet
- Periodicclassificationofelements Notes&QuestionsDocument5 pagesPeriodicclassificationofelements Notes&QuestionsAngelic ShineNo ratings yet
- CHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFDocument89 pagesCHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Notes Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument4 pagesCH 5 Notes Periodic Classification of Elementskashvi goelNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Organization of The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesA Brief History of The Organization of The Periodic TableLucila QuinquilleriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateTonald DrumpNo ratings yet
- First 5 Chapters Chemistry XiiDocument201 pagesFirst 5 Chapters Chemistry XiiIkram ali khan100% (2)
- Periodic Classification of Elements: Chapter - 5Document6 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements: Chapter - 5makapra007No ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument4 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 8Document68 pagesChe101 Chap 8Ruhi AfsaraNo ratings yet
- Science 8 14.2 Features of The Periodic TableDocument21 pagesScience 8 14.2 Features of The Periodic TableAngel MoranNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Checklist LatymerDocument4 pages4.1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Checklist LatymerEashwar RajakumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Periodic TableDocument2 pagesUnderstanding the Periodic TablewakakkaNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University, Phagwara: INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN (For Lectures)Document13 pagesLovely Professional University, Phagwara: INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN (For Lectures)Er Vishal Vaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 AnsDocument5 pagesCh4 AnsKarm VeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Assessment PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 6 Assessment PDFMichael Foster67% (3)
- Principles of Chemistry 1: Chapter 1. Matter-MeasurementDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Chemistry 1: Chapter 1. Matter-MeasurementHải Đăng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- SS2 Chemistry 1st Term Lesson Note PDFDocument73 pagesSS2 Chemistry 1st Term Lesson Note PDFAugustine AmaechiNo ratings yet
- Latihan Menulis AbjadDocument26 pagesLatihan Menulis AbjadadikmukNo ratings yet
- Partion FailDocument2 pagesPartion FailadikmukNo ratings yet
- Bintik ButaDocument2 pagesBintik ButaadikmukNo ratings yet
- Soalan Acid Bases (Quiz1)Document1 pageSoalan Acid Bases (Quiz1)adikmukNo ratings yet
- Mole and Molarity..DifferencesDocument1 pageMole and Molarity..DifferencesadikmukNo ratings yet
- Bintik ButaDocument2 pagesBintik ButaadikmukNo ratings yet
- Sulit: Do Not Open The Question Booklet Until Being Told To Do SoDocument25 pagesSulit: Do Not Open The Question Booklet Until Being Told To Do SoarulapanNo ratings yet
- Quiz ALKENE Form 5semekarDocument1 pageQuiz ALKENE Form 5semekaradikmukNo ratings yet
- Ujian Setara 2 Chemistry Form 4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesUjian Setara 2 Chemistry Form 4 QuestionsadikmukNo ratings yet
- Concentration of Acid (Quiz2)Document3 pagesConcentration of Acid (Quiz2)adikmukNo ratings yet
- Circle II Students HandoutDocument8 pagesCircle II Students HandoutadikmukNo ratings yet
- Similarity HANDOUT Form 3Document4 pagesSimilarity HANDOUT Form 3adikmukNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRYadikmuk100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4-Paper 2Document19 pagesChemistry Form 4-Paper 2adikmuk50% (2)
- Graf Fungsi Form 3Document14 pagesGraf Fungsi Form 3adikmukNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument17 pagesRedox ReactionsadikmukNo ratings yet
- Determine copper oxide formulaDocument4 pagesDetermine copper oxide formulaadikmukNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 - Paper 1Document13 pagesChemistry Form 4 - Paper 1adikmuk0% (1)
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument16 pagesParticulate Nature of MatteradikmukNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRYadikmuk100% (1)
- Collision TheoryDocument9 pagesCollision TheoryHasbullah Md SukurNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument8 pagesAcid and BasesadikmukNo ratings yet
- Kegunaan Asid Dan Alkali Dalam Kehidupan SeharianDocument2 pagesKegunaan Asid Dan Alkali Dalam Kehidupan Seharianadikmuk100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument18 pagesAtomic StructureadikmukNo ratings yet
- Kegunaan Asid Dan Alkali Dalam Kehidupan SeharianDocument2 pagesKegunaan Asid Dan Alkali Dalam Kehidupan Seharianadikmuk100% (1)
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument9 pagesOxidation and ReductionAziah HusainNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument27 pagesSeparation TechniquesadikmukNo ratings yet
- Natural RubberDocument20 pagesNatural RubberadikmukNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument27 pagesSeparation TechniquesadikmukNo ratings yet