Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pro57 MultipleTrauma
Uploaded by
noorgianilestariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pro57 MultipleTrauma
Uploaded by
noorgianilestariCopyright:
Available Formats
T
r
a
u
m
a
P
r
o
t
o
c
o
l
s
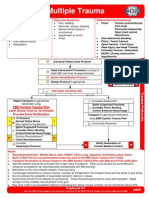
Multiple Trauma
History
Time and mechanism of injury
Damage to structure or vehicle
Location in structure or vehicle
Others injured or dead
Speed and details of MVC
Restraints / protective equipment
Past medical history
Medications
Signs and Symptoms
Pain, swelling
Deformity, lesions, bleeding
Altered mental status or
unconscious
Hypotension or shock
Arrest
Pearls
Recommended Exam: Mental Status, Skin, HEENT, Heart, Lung, Abdomen, Extremities, Back, Neuro
Items in Red Text are key performance measures used in the EMS Acute Trauma Care Toolkit
Transport Destination is chosen based on the EMS System Trauma Plan with EMS pre-arrival notification.
Geriatric patients should be evaluated with a high index of suspicion. Often occult injuries are more difficult to
recognize and patients can decompensate unexpectedly with little warning.
Mechanism is the most reliable indicator of serious injury.
In prolonged extrications or serious trauma, consider air transportation for transport times and the ability to give blood.
Do not overlook the possibility of associated domestic violence or abuse.
Scene times should not be delayed for procedures. These should be performed en route when possible. Rapid
transport of the unstable trauma patient is the goal.
Bag valve mask is an acceptable method of managing the airway if pulse oximetry can be maintained above 90%
Differential (Life threatening)
Chest Tension pneumothorax
Flail chest
Pericardial tamponade
Open chest wound
Hemothorax
Intra-abdominal bleeding
Pelvis / Femur fracture
Spine fracture / Cord injury
Head injury (see Head Trauma)
Extremity fracture / Dislocation
HEENT (Airway obstruction)
Hypothermia
Protocol 57
Any local EMS System changes to this document must follow the NC OEMS Protocol Change Policy and be approved by OEMS
2009
Rapid Transport to appropriate
destination using
EMS System Trauma Plan
Limit Scene Time to 10 minutes
Provide Early Notification
Consider
Head Injury Protocol
Splint Suspected Fractures
Consider Pelvic Binding
Control External Hemorrhage
IV Protocol
Normal Saline Bolus
May repeat for hypotension
Tension Pneumothorax?
Chest Decompression
Complete Assessment
Notify Destination or
Contact Medical Control
M M
Universal Patient Care Protocol
Adult Assessment Procedure focusing on
initial ABC and level of responsiveness
Spinal Immobilization Protocol
Airway Protocol if appropriate
Vital Signs including GCS
I I
Transport to appropriate destination
using EMS System Trauma Plan
EMT- I
EMT
EMT- P
Legend
Medical Control
B
I
P
B
I
P
M M
MR
Normal
P P
Abnormal
Splint Suspected Fractures
Consider Pelvic Binding
Control External Hemorrhage
Continually Reassess
You might also like
- Primary Trauma CareDocument48 pagesPrimary Trauma CareKABERA RENENo ratings yet
- Multiple Trauma ManagementDocument1 pageMultiple Trauma ManagementSetiawan Arif WibowoNo ratings yet
- Trauma Assessment: Aims of The Initial Evaluation of Trauma PatientsDocument6 pagesTrauma Assessment: Aims of The Initial Evaluation of Trauma Patientsece142No ratings yet
- Initial Assessment and Management of Multiply Injured PatientsDocument30 pagesInitial Assessment and Management of Multiply Injured PatientsSikaNo ratings yet
- W1L1 - Initial Assessment For Trauma - 2Document44 pagesW1L1 - Initial Assessment For Trauma - 2Baihaqi SaharunNo ratings yet
- Trauma OverviewDocument48 pagesTrauma OverviewFrancescoBarbero100% (1)
- General Surgery 27-03-07Document7 pagesGeneral Surgery 27-03-07Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Liver Trauma: DR Tarik El Batrawy Specialist General SurgeryDocument50 pagesLiver Trauma: DR Tarik El Batrawy Specialist General Surgerykata61No ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument18 pagesCardiac Tamponadeyelsinosmin romeroalvaradoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: Signs, Symptoms and DiagnosisDocument20 pagesCardiac Tamponade: Signs, Symptoms and Diagnosismuhammad iqbal mahfuzhNo ratings yet
- Management of Multiple Traumatised PatientDocument4 pagesManagement of Multiple Traumatised PatientOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Early Warning Score & Rapid Response TeamDocument26 pagesEarly Warning Score & Rapid Response TeamAsim IdreesNo ratings yet
- Fractures of The Lower LimbDocument50 pagesFractures of The Lower LimbVishwajit Hegde100% (1)
- Patient Safety: Early Warning ScoreDocument50 pagesPatient Safety: Early Warning ScoreAiko himeNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapDavis KallanNo ratings yet
- ABCs of Thoracic TraumaDocument5 pagesABCs of Thoracic TraumaAlice S ChangNo ratings yet
- Documenting A Transfusion Reaction: Chart SmartDocument2 pagesDocumenting A Transfusion Reaction: Chart SmartTracyNo ratings yet
- Patients Safety - Key Issues and ChallengesDocument4 pagesPatients Safety - Key Issues and ChallengeskabirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Patient SafetyDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Patient Safetyrejoicedear2020No ratings yet
- Revised Introduction To Pathology11Document42 pagesRevised Introduction To Pathology11windeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases GuidelineDocument100 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases GuidelineGalo PinosNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Trauma - Navy - PSPD 2021Document45 pagesThoracic Trauma - Navy - PSPD 2021Naavy LaksmonoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of ImmunityDocument11 pagesDiseases of ImmunityRAFAELLA SALVE MARIE GAETOSNo ratings yet
- Hypertency Emergency Acute PDFDocument12 pagesHypertency Emergency Acute PDFmasdika09No ratings yet
- Essentials of Effective Doctor-Patient CommunicationDocument43 pagesEssentials of Effective Doctor-Patient CommunicationRZ NgNo ratings yet
- Abdominal and Pelvic Injury: Associate Professor Visokai V., PH.DDocument65 pagesAbdominal and Pelvic Injury: Associate Professor Visokai V., PH.DRoman Mamun100% (1)
- Initial Assessment and Management Initial Assessment and ManagementDocument6 pagesInitial Assessment and Management Initial Assessment and Managementjc_sibal13No ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Intraabdominal InjuriesDocument88 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Intraabdominal Injuriessgod34No ratings yet
- TRAUMA ORGAN ABDOMEN: ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF BLUNT AND PENETRATING ABDOMINAL TRAUMADocument47 pagesTRAUMA ORGAN ABDOMEN: ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF BLUNT AND PENETRATING ABDOMINAL TRAUMAreginaNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- 10.08.07 Cardiac Tamponade HaagDocument16 pages10.08.07 Cardiac Tamponade HaagfoetorNo ratings yet
- Triage in Polytauma: Prof. Dr. A. Chandrasekaran M.S., PH.D.Document73 pagesTriage in Polytauma: Prof. Dr. A. Chandrasekaran M.S., PH.D.ShrutiNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Strategies in Health EducationDocument11 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Strategies in Health EducationEduardNo ratings yet
- Sefety and InjuryDocument24 pagesSefety and Injuryswing.sujuNo ratings yet
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) : Evann R. Casoy, RN Nurse Deployment ProjectDocument19 pagesHuman Papillomavirus (HPV) : Evann R. Casoy, RN Nurse Deployment ProjectEva CastuloNo ratings yet
- EN Primary SurveyDocument32 pagesEN Primary SurveythoriqNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument46 pagesEndocrinology[161]Shuaib AktherNo ratings yet
- Intro HADocument38 pagesIntro HAMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- Keep Physicians Up-to-Date with Current Clinical PracticeDocument242 pagesKeep Physicians Up-to-Date with Current Clinical PracticexguerratNo ratings yet
- Emergency Ortho BCS 2017Document80 pagesEmergency Ortho BCS 2017Priza RazunipNo ratings yet
- ABC AbdomenDocument57 pagesABC AbdomenSyahmi KhalidNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps Patient SafetyDocument58 pages7 Steps Patient SafetyDanissa Fidia PuteriNo ratings yet
- Torso TraumaDocument58 pagesTorso TraumaAbidisHereNo ratings yet
- Vascular System: - Arteries Arterioles - Capil ExchDocument35 pagesVascular System: - Arteries Arterioles - Capil ExchMikaelle GasparNo ratings yet
- Hildegard E. Peplau Nursing Nurse: - Client Relationship inDocument4 pagesHildegard E. Peplau Nursing Nurse: - Client Relationship inNicolette LeeNo ratings yet
- ATLS DRDocument45 pagesATLS DRNeNeei HenNieNo ratings yet
- Innate ImmunityDocument29 pagesInnate ImmunityAsad MirzaNo ratings yet
- ThrombophlebitisDocument3 pagesThrombophlebitismirrejNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment For Hypertensive Emergencies: New Concepts and Emerging Technologies For Emergency PhysiciansDocument0 pagesDrug Treatment For Hypertensive Emergencies: New Concepts and Emerging Technologies For Emergency PhysiciansRajihah JihahNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Injury-Dr - SayedDocument48 pagesAbdomen Injury-Dr - SayedAnonymous xmw6mrNo ratings yet
- Initial Assessment and Management of Trauma PatientsDocument8 pagesInitial Assessment and Management of Trauma PatientsAlvin De LunaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing Care: An OverviewDocument38 pagesPerioperative Nursing Care: An OverviewGeremew GizawNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol AcidosisDocument3 pagesSalbutamol AcidosisAccounts OfficerNo ratings yet
- CPR Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesCPR Checklist PDFSakura SaitoNo ratings yet
- Reducing Medical Error and Increasing Patient Safety: Richard Smith Editor, BMJDocument29 pagesReducing Medical Error and Increasing Patient Safety: Richard Smith Editor, BMJNOORAIMAH MURAHNo ratings yet
- Approach To Trauma: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument54 pagesApproach To Trauma: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesAhmed Tawfig GamalNo ratings yet
- Atp4 - 25x13 Casuality Evacuation PDFDocument88 pagesAtp4 - 25x13 Casuality Evacuation PDFbdavid2012-1No ratings yet
- Case Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMADocument5 pagesCase Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMAjisooNo ratings yet
- Bradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsDocument3 pagesBradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Radial Club Hand TreatmentDocument4 pagesRadial Club Hand TreatmentAshu AshNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian yoga techniqueDocument12 pagesAncient Indian yoga techniqueRandhir SinghNo ratings yet
- Lourdes College Nursing Program Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLourdes College Nursing Program Drug Studypinksapphire929100% (2)
- Proctor Tobacco History Report Canadian Trial Rapport - Expert - ProctorDocument112 pagesProctor Tobacco History Report Canadian Trial Rapport - Expert - Proctorkirk_hartley_1No ratings yet
- 837 Institutional 5010 PDFDocument610 pages837 Institutional 5010 PDFtrkreddyNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric StudyDocument8 pagesReliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric Studyedy harahapNo ratings yet
- 50 Bed Hospital Design in 1320 sqmDocument16 pages50 Bed Hospital Design in 1320 sqmNayana Bharathi83% (6)
- Evaluation MyocarditisDocument5 pagesEvaluation MyocarditisRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- The Functions and Types of AntibioticsDocument3 pagesThe Functions and Types of AntibioticsFida TsabitaNo ratings yet
- Mel Tappans Personal Survival Letter Issue 11 (Tappan)Document24 pagesMel Tappans Personal Survival Letter Issue 11 (Tappan)buckonbeach100% (1)
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmDocument1 pageLocal Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmSydney JenningsNo ratings yet
- ProspectusDocument52 pagesProspectusRabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Phobic EncounterDocument1 pagePhobic EncounterEmanuel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Canadian Standards For Hospital LibrariesDocument4 pagesCanadian Standards For Hospital LibrariesFernando HernandezNo ratings yet
- District: Rajkot Name of Institute: P.D.U. Medical CollegeDocument9 pagesDistrict: Rajkot Name of Institute: P.D.U. Medical CollegeManas K. TrivediNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Perio DZDocument2 pages4 Levels of Perio DZKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- Effects of Boiling Time On Mineral and Vitamin C Content of Three Varieties of Hibiscus Sabdriffa Drink in NigeriaDocument6 pagesEffects of Boiling Time On Mineral and Vitamin C Content of Three Varieties of Hibiscus Sabdriffa Drink in NigeriariniyuliasamosirNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument46 pagesMemoryMaha Al AmadNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Issues Solutions For PharmaDocument109 pagesIfrs Issues Solutions For PharmaSrinivasa Rao100% (1)
- Meningitis Pediatrics in Review Dic 2015Document15 pagesMeningitis Pediatrics in Review Dic 2015Edwin VargasNo ratings yet
- The New ILAE Seizure Classification, 63 Seizure TypesDocument3 pagesThe New ILAE Seizure Classification, 63 Seizure TypesAndreea AtănăsoaeiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Pulmonary Rehabilitation On Physiologic and Psychosocial Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument10 pagesEffects of Pulmonary Rehabilitation On Physiologic and Psychosocial Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseElita Urrutia CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Rectal Cancer Grossing Guide Optimizes Margin AssessmentDocument18 pagesRectal Cancer Grossing Guide Optimizes Margin Assessmentionut216100% (1)
- Critical Perspectives - Dissertation OgrDocument15 pagesCritical Perspectives - Dissertation OgrPipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 DiscussionDocument3 pagesChapter 6 DiscussionyughaNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE-B-Master-list-of-Learners-for-the-Pilot-Implementation-of-F2F-Classes-for-S.Y.-2021-2022Document7 pagesTEMPLATE-B-Master-list-of-Learners-for-the-Pilot-Implementation-of-F2F-Classes-for-S.Y.-2021-2022Resa Consigna MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Manage Odontogenic Infections Stages Severity AntibioticsDocument50 pagesManage Odontogenic Infections Stages Severity AntibioticsBunga Erlita RosaliaNo ratings yet