Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STWG3 24-8800C
Uploaded by
StonyTony0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
184 views4 pagesOriginal Title
STWG3.24-8800C
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
184 views4 pagesSTWG3 24-8800C
Uploaded by
StonyTonyCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
BEOOG siepwateh 1/5 second, 30 minutes, accumulated)
1) Specifications
Casing diameter 40.25 mm
Height 7.55 mm
Vibrations per hour 18,000
“Diashock” Shock-resistant Device
2) Features
By utilizing SEIKO’s wealth of experience
in the stopwatch manufacturing field
easy-to-use characteristics are pursued.
Shockproofing is additionally increased
by adopting the “Diashock” and by im-
proving the dial securing system.
Many rational designs are realized~such as
miniature and high-performance escape-
ment, nonsymmetrical heart cams, and so
forth. An adjustment disk of hammer
which facilitates the hands returning fune-
tion, a stud holder. for easy adjustment of
off beut, and so on are adopted. To
fucilitate aftersales service, the int
changeability of parts is also considered.
3) Disassembly and Assembly
Disassemble the stopwatch according to
the procedures shown in Figs.(1)toG I).
Assemble the stopwatch according to the
procedures shown in Figs. Dto().
4) Lubrication
Colored symbols printed in the figures
show types of oil and lubrication points
© Mobius SyntA-Lube
© Seiko watch oil S-4.
Oil quantity
© Extremely small quantity
© Normal quantity
oem Suificient quantity
© Oil must not be applied
NOTE)Portions with no indications do
not require lubrication,
5) Checking
Starting and stopping condition
‘The operating lever, hammer.
balance stop lever condition.
Hands returning condition:
The fly-back lever returns to zero
position
ced amplitude of balance:
Under the stopping condition, the
balance wheel should be started cor-
rectly from the impulse surface of the
disengaging pallet jewel.
Erroneous early stop of watch:
When depressing the crown slowly,
confirm that the second hand does not
stop just before the crown falls in
abruptly.
Position of minute hand:
When stopping the second hand on
zero position during operation, check
Whether or not the minute hand is on
the minute graduation
Actual measurement
Finally, perform actual measurement at
30 minutes to confirm watch accuracy.
and
Ki
~ 8006
1
8800C
When removing the. di
‘out gradually dizecy from above
cS sms attached to prevent the
fonand fourth whee! Pinion
from breaking
fo Dial screws @
Apply sufficient Iubricant to the
column and ratchet wheel (four por-
tions on the column and over three
portions on the ratchet whea))
mot {— —— opening erg nee BD
go N ing
Scenes nna
—eancs nine (8
seonsatisoeroe((9)
Secondsetting ever (20)
et naira rn (9)
Spr spring a
pein er (96)
[2+ one
a
Fly back lever spring
{3} sev fr acusiman ik of naneer ~~)
Since a rubber gasket is provided,
use alcohol rather than washing with
volatile oil (benzine). After assemb-
ling, confirm the synchronizing com
Adjustment disk of hammer
dition (fourth wheel & pinion).
eter to hands returning mechanism
After assembling the balance stop
lever, check for end shake, Carefully
hhandie the balance stop lever pin to
prevent deforming the pin. IC it is
‘bent foo much, the watch will stop
caulicr than the normally contest
time when depressing the quick
stopping button.
VU!
8800 ~ 2 —
8800C
——Fiatenet wneat screw (5)
cron wre! aara(1Q)
Qe —, | Sy een sf
, = Sliding crown wheel spring. 0)
ihe] 5 a 1 is arn 0 moe te
Diasnock How to assemble the sliding
hel
& ily position the
mn the grooved portion
of the Bridge, then insert the
Tower pivot of the sliding
Crown “wheel” between the,
Tong hole and spring, seting =
the spring correctly,
same cock somes
Oss ©
Om —— ay
oe
By svvees pallet fork & “i ,
pore & aia ite com (Q)
Barre! & train-whee! ae
Center whet & pinion (20)
Fount mt 8 sinon/ 3)
G eaare wnt oige wren ——P
Dee wren =r gS Tie hel 8 oron
(Dees me
cb ing secre 2
Big, nD
Winai ina sem 94)
Casing clamp screw
inaing pinion (9B)
‘Assemble the winding pinion o that
the cuttings are on the crown side
(Casing clamp
It is unnacesary to. remove
the winding stem cock for
‘ordinary disassembling.
—8800¢ — 3 —
8800C
6) Structure
6-1 Mechanism of starting and stopping
device
When depressing the crown, the pillar
wheel turns through action of the operat-
ing lever, and the balance stop lever stops
the balance. At the same time, the second
setting lever correctly holds the tooth end
of the fourth wheel and pinion, stopping
it. By this action, errors due to amount of
backlash return is completely prevented
while the hands are being returned,
6-2 Mechanism of hands returning device
When the hammer is located between the
columns of the pillar wheel (stopped
condition), if the returning button is
depressed, the fly-back lever releases the
| motion of the hammer, and the hammer
strikes the minute and second heart cams,
returning the hands to zero position.
When the hammer is located on the
column of the pillar wheel (moving condi-
tion), the hands will not return to a zero
position even though the returning button
is depressed.
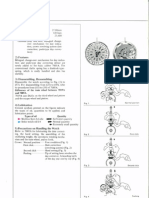
Adjustment disk of hammer (adjust
ment of hammer) (Fig. 1)
It is necessary to adjust the hammer so
that the hammer returns to zero position
(it should touch the shoulder of the
second heart cam) and the hammer effects
a slight clearance with the minute heart
| cam, To accomplish these adjustments
easily, this adjustment disk of hammer has
| been newly devised.
The adjustment disk of hammer is a
circular disk having a tube which becomes
a revolving shaft of the hammer on its
center, with six holes for determining the
Find
—8800¢ — 4 —
Distance between the center tube to each
hole on the circumference is slightly
different; however, the center distance of
two holes which confront each other over
the center tube is the same. Consequently,
by setting either pair of holes on two pins
of the plate, position of the revolving
shaft on the hammer can be moved,
adjusting the clearance between the
hammer and the minute heart cam.
| There are two adjustment disk of hammer
| types according to whether a large or
small quantity is used to change positions
of the two pins; one or two marks (dot)
are engraved on the disk. One dot (A) has
an adjusting width of 0-0.048m/m and
| two dots (B) have an adjusting width of
0.072m/m—0.12m/m,
|
Relations between the selecting method
of the hole and position of the shaft are
shown in Fig. 2
© Heart cams
Shape of the heart cams is a nonsym-
metrical type, especially devised to con-
stantly maintain a zero-returning torque
applied to the heart cams when the hands
are returned,
SETS
O02 6
Oo oO
You might also like
- Seiko Crystal CodesDocument4 pagesSeiko Crystal CodesStonyTony50% (2)
- Seiko 6139Document16 pagesSeiko 6139demo1967100% (1)
- Seiko Gasket Coding SystemDocument2 pagesSeiko Gasket Coding SystemStonyTony100% (3)
- STWG3 22-7016aDocument9 pagesSTWG3 22-7016aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 17-6138aDocument10 pagesSTWG3 17-6138aStonyTony100% (1)
- STWG3 14-5606aDocument7 pagesSTWG3 14-5606aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 15-5619aDocument2 pagesSTWG3 15-5619aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 20-6309aDocument7 pagesSTWG3 20-6309aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 23-7019aDocument2 pagesSTWG3 23-7019aStonyTony100% (1)
- STWG3 06-2206aDocument3 pagesSTWG3 06-2206aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 13-5206aDocument8 pagesSTWG3 13-5206aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 09-2706aDocument10 pagesSTWG3 09-2706aStonyTonyNo ratings yet
- STWG3 00-CalibresDocument3 pagesSTWG3 00-CalibresStonyTony100% (1)
- STWG3 04-2202aDocument4 pagesSTWG3 04-2202aStonyTonyNo ratings yet