Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Myocardial Infarction/ Heart Attack
Uploaded by
Jet Bautista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesTable summary
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTable summary
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesMyocardial Infarction/ Heart Attack
Uploaded by
Jet BautistaTable summary
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
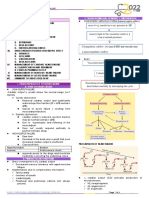
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION REFERENCE: Principles of Medical-Surgical Nursing, LeMone and Burke, Volume 2, 3rd ed.
, pp 982-991
DEFINITION AND RISK PATHOPHYSIOL MANIFESTATIONS DIAGNOSTIC TESTS MANAGEMENT
FACTORS OGY
MF: interruption of blood Occlusion 1. Chest Pain 1. Creatinine kinase (CK) PHARMACOLOGIC
supply to part of the heart, ↓ Sudden onset Normal: 12-80 (M), 10-70 (F) 1. Aspirin – platelet aggregation
most commonly due to Blood clot Not associated with activity Elevation indicates cardiac 2. Nitroglycerin (0.4mg) - pain
occlusion causing myocardial formation Mostly occurs in the early tissue damage 3. Morphine sulfate (DOC) – oxygen demand
cell necrosis, resulting to ↓ morning 2. CK-MB 4. Striptokinase – fibrinolytic
ischemia and oxygen shortage Impaired blood Crushing, severe, pressure, Normal: 0% to 3% of total CK 5. Verapamil/Esmolol – atrial fibrillation or other dysrhythmias
flow heavy, squeezing, tightness Most sensitive indicator of MI 6. Propranolol, Atenolol, Metoprolol – decrease cardiac work
RF: ↓ or burning Elevation of greater than 5% 7. ACE inhibitors – reduce risk of subsequent HF and
Non-modifiable: Ischemia Begins substernally and indicates MI reinfarction
1. Pre-existing coronary heart ↓ may radiate to shoulder, 3. Cardiac-specific troponin T 8. Abciximab – maintain coronary patency
diseases, including a previous Necrosis neck, jaw, or arms (cTnT) 9. Heparin – prevent systemic or pulmonary embolism
heart attack, prior angioplasty ↓ Lasts more than 15 to 20 Normal: <0.2 mcg/L 10. Dopamine – improves renal perfusion, myocardial
or bypass surgery, or Scar formation, minutes Elevation indicates acute MI, contractility, CO and BP
angina O2, Glycogen Not relieved by rest or unstable angina MEDICAL
2. Age and ATP nitroglycerin 4. Cardiac-specific troponin I 1. Bed rest for the first 12 hours to reduce cardiac workload
M >45, W>55 depletion 2. Anxiety; Sense of impending (cTnI) 2. Allow sitting at bedside after 12 hours
3. Gender – M>F ↓ doom Normal: <3.1 mcg/L 3. Gradually increase activity as tolerated
4. Heredity: Family history of Anaerobic 3. Tachycardia Elevation indicates acute MI, 4. Provide a quiet, calm environment
early heart disease metabolism 4. Cool, clammy, mottled skin, unstable angina 5. Limit visitors
Modifiable: ↓ diminished peripheral pulses 5. CBC (elevated WBC and ESR) 6. Administer O2 by NC at 2-5LPM
Smoking Acidosis, due to vasoconstriction 6. ABG (blood O2 levels, and A-B 7. Liquid diet for the first 4 to 12 hours, followed by Low-fat,
Alcoholism. electrolyte 5. Tachypnea, Dyspnea, SOB imbalance) Low-cholesterol, Low-sodium diet
Stress. imbalances, due to blood chemistry 7. ECG (inverted T, elevated ST, 8. Small, frequent feeding
High blood pressure. hormone changes stimulating the formation of Q) 9. Limit caffeine
High blood release , ↓MC, respiratory center 8. Echocardiography (cardiac wall SURGICAL
cholesterol ↓SV, ↓CO, ↓BP, 6. Diaphoresis motion and left ventricular 1. Percutaneous Coronary Revascularization (e.g. angioplasty
Overweight and ↓tissue 7. elevation of temperature function) and stent replacement) to restore blood flow to myocardium
obesity perfusion 8. N&V 9. Radionuclide imaging 2. Intra-aortic balloon pump to augment CO, used after cardiac
Physical inactivity 9. Hypotension or hypertension (myocardial perfusion) surgery
10. Palpitations, dysrhythmias 3. Ventricular Assistive Devices which takes partial or complete
control of cardiac function
ALAGAO, Jerome, SN IV/BAUTISTA, Jesther Rowen, SN IV
ALAGAO, Jerome, SN IV/BAUTISTA, Jesther Rowen, SN IV
You might also like
- Myocardial Infarction Nursing CareDocument28 pagesMyocardial Infarction Nursing Caresusi jNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIDocument5 pagesCoronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIAila HinlogNo ratings yet
- Final Internal MedicineDocument14 pagesFinal Internal MedicinemusthajabhassimNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EmergencyDocument34 pagesCardiac EmergencyRima HannaniNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument27 pagesMyocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentKyrajane EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical NursingMaria TagubaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementDocument8 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementOdai AL KarkiiNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromem3d1k100% (1)
- Polycystic NCP1Document4 pagesPolycystic NCP1Mary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- 2022 Pharmacology s2t2 HeartfailureDocument6 pages2022 Pharmacology s2t2 Heartfailurejed larsen capulong gavinoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: by Ho NisaDocument58 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: by Ho NisaShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Common Cardiovascular Diseases Often Found DailyDocument121 pagesCommon Cardiovascular Diseases Often Found Dailyandikaagus13No ratings yet
- CASE 1 TG Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock 2014Document52 pagesCASE 1 TG Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock 2014biandaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health King Fahad Hofuf Hospital Nursing EducationDocument33 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health King Fahad Hofuf Hospital Nursing EducationAqeelNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome GuideDocument50 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome GuideWinda Ayu PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Case study of Anterior Wall MIDocument32 pagesCase study of Anterior Wall MIسوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- Oxy Nov 9Document4 pagesOxy Nov 9Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Cardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesCardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaMariana NannettiNo ratings yet
- Cardiology HFDocument11 pagesCardiology HFdhayemaruNo ratings yet
- 5,6.heart FailureDocument12 pages5,6.heart FailureKUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANNo ratings yet
- Circulation Failure (Shock) : Pediatric Emergency Department Medical FacultyDocument18 pagesCirculation Failure (Shock) : Pediatric Emergency Department Medical FacultySukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- DR Rahul VarshneyDocument64 pagesDR Rahul VarshneyIMNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Ischaemic Heart Disease (IHD)Document29 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Ischaemic Heart Disease (IHD)Mahum SohailNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Protocol On Shock 2019Document16 pagesAIIMS Protocol On Shock 2019gaddam narasimhaNo ratings yet
- PATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)Document13 pagesPATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)vikashchahal1987No ratings yet
- HF DeaDocument53 pagesHF DeaSyifa Mahmud Syukran AkbarNo ratings yet
- Cardio - HPN HFDocument8 pagesCardio - HPN HFHgielNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument9 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseKarisaNo ratings yet
- Systolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureDocument13 pagesSystolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureElisabeth F. OjhaNo ratings yet
- Banan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBanan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiSarahNo ratings yet
- Managing Ischemic Heart DiseasesDocument14 pagesManaging Ischemic Heart DiseasesNoveno CNo ratings yet
- Prometric High-Yield NOTES PDFDocument135 pagesPrometric High-Yield NOTES PDFDr-Jahanzaib Gondal100% (3)
- Clinical PharmacyDocument8 pagesClinical PharmacyMissy NaguitNo ratings yet
- Cardio Notes, Heart FailureDocument17 pagesCardio Notes, Heart FailureJoy DunwanNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument7 pagesCardioGerald AndrinNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument2 pagesCardiac ArrestKaja MatovinovicNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure and Shockfrenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Causes, Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment of Different Types of ShockDocument4 pagesCauses, Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment of Different Types of ShockKory Christina100% (2)
- Manage Cardiac EmergenciesDocument56 pagesManage Cardiac Emergencies21rayhanf100% (1)
- Cardiac Disease NotesDocument4 pagesCardiac Disease NotesKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- AcutDocument27 pagesAcutyulanda fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationDocument8 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationReiche GomezNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Investigations and ManagementDocument4 pagesChest Pain Investigations and ManagementYY_1992No ratings yet
- 4.heart Failure HandoutDocument108 pages4.heart Failure HandoutGetachewNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Applied To Practice (GAP) : American College of Cardiology, Puerto Rico ChapterDocument27 pagesGuidelines Applied To Practice (GAP) : American College of Cardiology, Puerto Rico ChapterYenza FaheraNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic Crisis & Disaster NursingDocument80 pagesAcute Biologic Crisis & Disaster NursingprinceBel21No ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHADocument46 pagesHeart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHAYuanita WahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-ShockDocument5 pagesLecture 6-ShockMadiha MadiNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Family MedicineDocument49 pagesStudy Notes Family MedicineMedShare85% (27)
- Unstable Angina, STEMI, NSTEMI Diagnosis and ManagementDocument21 pagesUnstable Angina, STEMI, NSTEMI Diagnosis and ManagementNabil Mosharraf Hossain100% (2)
- Heart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument48 pagesHeart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSanjay SathasevanNo ratings yet
- Ipd - KardiologiDocument116 pagesIpd - KardiologiWynda MuljonoNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 2Document21 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 2Giovanni Mictil100% (1)
- Problem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupDocument47 pagesProblem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupClaudia Narinda R. PNo ratings yet
- Cardiac FailureDocument63 pagesCardiac FailureNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Uterine BleedingJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- 10 Rights of Drug Administration With Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pages10 Rights of Drug Administration With Nursing ImplicationsJet Bautista100% (6)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- NCP - Acute Abdominal PainDocument3 pagesNCP - Acute Abdominal PainJet Bautista100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Sample Curriculum VitaeDocument1 pageSample Curriculum VitaeJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - FinalDocument2 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding - FinalJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Journal PACUDocument11 pagesNursing Journal PACUJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP HypertensionJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Captopril CefuroximeDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Captopril CefuroximeJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition problem due to substance abuseDocument2 pagesNutrition problem due to substance abuseLouie James Velasco OstreaNo ratings yet
- THINK AGAIN: Revisiting IM Injections: Bautista, Jesther Rowen B. BSN Iii-1 BLDH, 7-3, WARDDocument4 pagesTHINK AGAIN: Revisiting IM Injections: Bautista, Jesther Rowen B. BSN Iii-1 BLDH, 7-3, WARDJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cord Care Case Slip - Lorma CollegesDocument1 pageCord Care Case Slip - Lorma CollegesJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study - MetronidazoleJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CelebrexDocument1 pageDrug Study - CelebrexJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- DR Case Slip - Lorma CollegesDocument1 pageDR Case Slip - Lorma CollegesJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Captopril CefuroximeDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Captopril CefuroximeJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Or Case Slip - Lorma CollegesDocument1 pageOr Case Slip - Lorma CollegesJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmpicillinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmpicillinJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- OR Case Reaction - Sponge CountDocument3 pagesOR Case Reaction - Sponge CountJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Summary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseDocument1 pageSummary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODocument1 pageDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Hyoscine Butylbromide IVDocument1 pageDrug Study - Hyoscine Butylbromide IVJet Bautista80% (5)
- Me Reference Statistical Analysis Research GateDocument7 pagesMe Reference Statistical Analysis Research Gatesooho32No ratings yet
- (PDHPE) Chap 01 HSC CORE 1Document31 pages(PDHPE) Chap 01 HSC CORE 1RobinHoodCookiesNo ratings yet
- ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IDocument4 pagesABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IIgnacio Aguilar ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontics Key Points by DANESHDocument21 pagesProsthodontics Key Points by DANESHNoor HaiderNo ratings yet
- Medication History Interview Form-MCP+OGH-PharmD VI Year InternshipDocument2 pagesMedication History Interview Form-MCP+OGH-PharmD VI Year InternshipMarifuddin HussainiNo ratings yet
- XDocument186 pagesXLavanya Priya SathyanNo ratings yet
- Conservation GeneticsDocument24 pagesConservation GeneticsAmrutha BaskerNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Properties of Coconut Shell OilDocument12 pagesAntimicrobial Properties of Coconut Shell OilBalakrishna GopinathNo ratings yet
- Standardizing Urine Conditions for NMR Metabolomics StudiesDocument24 pagesStandardizing Urine Conditions for NMR Metabolomics StudiesJessicaNo ratings yet
- AFA Cancer Care PolicyDocument32 pagesAFA Cancer Care PolicyCori RothNo ratings yet
- LIC Jeevan Shiromani 9 Inch X 8 Inch EngDocument22 pagesLIC Jeevan Shiromani 9 Inch X 8 Inch EngNithin KKNo ratings yet
- MumpsDocument3 pagesMumpsAbeer FatimaNo ratings yet
- 29 Days Study Plan and Important Stuff by Hafiz Bilal For 4TH Year MBBS PDFDocument3 pages29 Days Study Plan and Important Stuff by Hafiz Bilal For 4TH Year MBBS PDFDaneyal Arshad100% (2)
- Wastage Operational SummaryDocument5 pagesWastage Operational SummaryWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- An Update On Treatment Options For Pancreatic AdenocarcinomaDocument43 pagesAn Update On Treatment Options For Pancreatic AdenocarcinomaNatalindah Jokiem Woecandra T. D.No ratings yet
- Maternity Exam 181920Document99 pagesMaternity Exam 181920Johanna Erazo Padilla100% (3)
- Ban Xia Bai Zhu Tian Ma TangDocument14 pagesBan Xia Bai Zhu Tian Ma TangHung NguyenNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 13 - Preparation of The Mouth For R - 2011 - McCracken S Removable Parti PDFDocument20 pagesCHAPTER 13 - Preparation of The Mouth For R - 2011 - McCracken S Removable Parti PDFFlorin Razvan CurcăNo ratings yet
- Hand Washing and Oral CareDocument4 pagesHand Washing and Oral CaremejulNo ratings yet
- AspergillosisDocument36 pagesAspergillosisganesa ekaNo ratings yet
- 1.edebiyat Sınavı B GrubuDocument3 pages1.edebiyat Sınavı B GrubuyaseminNo ratings yet
- Skin Infection Lab ReportDocument6 pagesSkin Infection Lab Reportthe someone100% (2)
- Chronic Cough Differential DiagnosisDocument6 pagesChronic Cough Differential DiagnosisUbaidillah HafidzNo ratings yet
- Pathway AUBDocument1 pagePathway AUBIqbalNo ratings yet
- Harrison Powerpoint Pt2Document33 pagesHarrison Powerpoint Pt2bioe07011No ratings yet
- Animal Product ManualDocument748 pagesAnimal Product ManualrohishaakNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Management of DiseasesDocument25 pagesAyurvedic Management of DiseasesShreyaNo ratings yet
- Lafarge Fly Ash MSDSDocument6 pagesLafarge Fly Ash MSDSVăn phòng Phân xưởng Vận hành 1No ratings yet
- (PIH) CASE PRESENTATION (Group11)Document41 pages(PIH) CASE PRESENTATION (Group11)Kaye Drexcel SequilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction HIV AIDSDocument36 pagesIntroduction HIV AIDSKwaku Oppong AsanteNo ratings yet