Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study Fracture 2 (Drug Study and NCP)
Uploaded by
chrom17Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study Fracture 2 (Drug Study and NCP)
Uploaded by
chrom17Copyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME INDICATION ACTION ADVERSE CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING
REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic:
Iron deficiency Provides GI: nausea, Contraindicated in patients - Tell the patient to take
FEROUS
elemental iron, epigastric pain, with hemosiderosis, tab. With juice or water,
SULFATE
an essential vomiting, primary hemochromatosis, but not milk or antacids.
component in constipation, hemolytic anemia, peptic
Brand:
the formation of black stools, ulceration, ulcerative - Instruct patient not to
Fer-Iron
hemoglobin diarrhea, anorexia colitis and in those crush or chew
receiving repeated blood extended-release forms.
Dosage:
Other: temporary transfusions.
200 mg tab, OD
stained teeth from -Advise patient to
liquid forms report constipation and
Classification:
change in stool color or
Iron supplement
consistency.
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME INDICATION ACTION ADVERSE CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING
REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic: Serious infections Inhibits protein CNS: Contraindicated in patients -Obtain specimen for
AMIKACIN caused by synthesis by neuromuscular hypersensitive to drug or culture and sensitivity
SULFATE sensitive strains binding directly blockade. other aminoglycosides. tests before giving first
of Pseudomonas to the 30s dose.
Brand: aeruginosa, ribosomal EENT: ototoxicity
Amikin E.coli, Proteus, subunit; -Watch for signs and
Klebsiella, or bactericidal GU: possible symptoms of super
Dosage: Staphylococcus increase in urinary infection, such as
500 mg IV q 12°
excretion of casts, continued fever, chills
x 5 days
nephrotoxicity and increased pulse
rate.
Classification:
Musculoskeletal:
Anti-infectives
arthralgia -Instruct patient to
promptly report adverse
Respiratory: reactions to prescriber.
apnea
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME INDICATION ACTION ADVERSE CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING
REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
Paracetamol Mild pain or fever Thought to produce Contraindicated in patients Advise patient that drug
Hematologic:
analgesia by hypersensitive to drug. is only for short-term
hemolytic
Dosage: blocking pain use.
anemia,
300 mg IV q 4° impulses by
neutropenia,
for temp. 38°C inhibiting synthesis Monitor vital signs.
leucopenia
of prostaglandin in
Classification: the CNS or other
Hepatic:
Analgesic substances that
jaundice
sensitize pain
receptors to
Metabolic:
stimulation. The
hypoglycemia
drug may relieve
fever through
Skin: rash,
central action in the
urticaria
hypothalamic heat-
regulating center.
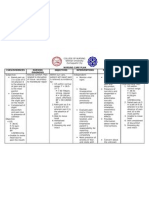
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS ANALYSIS
Subjective: Ø The extremities -establish rapport -to gain pt.’s
Impaired After series of After series of
cannot function trust and
Objective cues: physical nursing cooperation nursing
properly after a
mobility related interventions, -monitor vital signs –to have interventions,
-pale and weak fracture, thus,
in appearance to fractured patient will be baseline data patient was able
there is
femur able to -to immobilize to demonstrate
-difficulty in immobility -maintain
the extremity,
changing demonstrate temporary skin increasing
because normal and to relieve
positions while traction
increasing pain function of the
lying on bed function of the
function of the extremities.
muscle depends
-difficulty in extremities. -apply and
on the integrity -to control
moving the maintain sandbags
external rotation
extremities of the bones to or a trochanter roll
-to maintain
-inability to which they are -place a pillow bet.
abduction and
the legs
walk or stand attached. alignment
alone
Immobility of a
-limited ROM body part may
possibly
interrupt the -encourage the
-to promote
circulation of patient to exercise
blood through as much as muscle strength
possible by means
the circuitous
of overhead
network of trapeze
arteries and -turn the patient on
veins the affected or
unaffected -to prevent
extremity as bedsores
prescribed by the
physician
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS ANALYSIS
-establish rapport -to gain pt.’s At the end of the
Subjective: Pain r/t open The pain is Within the shift,
trust and
“Masakit parin fracture, soft continuous and patient will cooperation shift, patient’s
ung kaliwang tissue damage, increases alleviate pain. -monitor vital signs -to have baseline pain was
binti ko.”as muscle spasm in severity until data and to alleviated, AEB
monitor for pt.’s
verbalized by the and surgery the bone signs of
patient. fragment are infections verbalization,
immobilized. “hindi na
-assess type, masakit”.
The muscle degree and location -to have basis of
Objective cues: spasm that of pain treatment and
management
-wounds and accompanies
bruises noted fracture is a type
both in lower
and upper of
-position for
extremities natural splinting comfort and -to promote
function, and assist wellness and to
designed to prevent bedsores
with frequent
minimize further changes in position
-facial grimace -to promote
movement of he relaxation
noted when -encourage deep
moving lower fracture breathing exercises
extremities fragments.
-with complaints -to permit
of pain on left swelling and
knee aggravated -perform aseptic wound drainage,
by too much dressing changes with wound
with sterile gauze irrigation and
movement
debridement as
-with pain scale ordered
of 7 out of 10
-to minimize
-elevate the edema
extremity
-to promote
-promote intake of wound healing
adequate nutrition
-to relieve pain
-administer
analgesics as
prescribed by the
physician
HEALTH TEACHINGS
1. Explain the goals of frequent position changes.
Positioning (Goals)
* to prevent contractures
* stimulate circulation and prevent pressure sores
* prevent thrombophlebitis and pulmonary embolism.
* promote lung expansion and prevent pneumonia
* decrease edema of the extremities
* changing position from lying to sitting several times
a day can help prevent changes in the CVS known as deconditioning.
*the recommendation is to change body position at least
every 2 hours, and preferably more frequently in patients who have no spontaneous
movement.
2. Discuss the different therapeutic exercises.
Therapeutic Exercises
1. Positive range of motion exercise
2. active assistive range of motion
3. active range of motion
4. Resistive exercise
5. Isometric or muscle settings exercise.
3. Encourage patient to have adequate nutrition to promote healing of soft
tissue and bone.
4. Encouraged patient to increase oral fluid intake.
5. Teach patient and family to elevate the extremity to minimize edema.
6. Teach patient and family to perform wound care to flap or skin graft after
the wound is closed in 5 to 7 days.
You might also like
- The Human Body EnergyDocument4 pagesThe Human Body EnergyOdette Müller-Dogan100% (3)
- Case Study Myocardial InfarctionDocument23 pagesCase Study Myocardial InfarctionJester GalayNo ratings yet
- End Indifference - Pope: Stray Bullet Cases Hit 36 Firecrackers Injure 459Document56 pagesEnd Indifference - Pope: Stray Bullet Cases Hit 36 Firecrackers Injure 459Art JasmeNo ratings yet
- RMT TrainningDocument2 pagesRMT TrainningDita Nadya RizkitaNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- BICOM Treatment of Chronic Fatigue and FibromyalgiaCFS ReportDocument15 pagesBICOM Treatment of Chronic Fatigue and FibromyalgiaCFS ReportAnahata Fraydon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (2)
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- ELC590 Persuasive SpeechDocument5 pagesELC590 Persuasive SpeechmypinkladyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusNo ratings yet
- Drug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursingDocument1 pageDrug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursinghahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- COLCHICINE pptx1800128929Document15 pagesCOLCHICINE pptx1800128929April Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- LortabDocument1 pageLortabSheri490No ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyMariz Joy Gonzales Guillermo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl Drug Classification, Mechanism of Action, Indication, Contraindication and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageBisacodyl Drug Classification, Mechanism of Action, Indication, Contraindication and Nursing ConsiderationsJewel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 pagesDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine HydrochlorideRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- S: "Masakit Ang Ulo at Tiyan Niya" As Verbalized byDocument2 pagesS: "Masakit Ang Ulo at Tiyan Niya" As Verbalized bydenise-iceNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Post-Operative HypothermiaDocument2 pagesAssessing and Treating Post-Operative HypothermiaJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- NCP Mandibular)Document5 pagesNCP Mandibular)yellarfNo ratings yet
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 pagesDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- SilgramDocument6 pagesSilgramJacqueline SweetNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- AMARYL 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, 4mg: 1 Indications and UsageDocument16 pagesAMARYL 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, 4mg: 1 Indications and Usageddandan_2No ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Actibile: Formulation: Drug InteractionsDocument1 pageActibile: Formulation: Drug InteractionsNxxxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Ix. List of Priority ProblemDocument10 pagesIx. List of Priority ProblemshinloNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument2 pagesOMEPRAZOLEJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- TherablocDocument3 pagesTherablocianecunar100% (2)
- Brand Name: Aspirin Generic Name: Acetyl Salicylic Acid Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Aspirin Generic Name: Acetyl Salicylic Acid Drug ClassificationianecunarNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateMiEr Cañas AzenicNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanDocument5 pagesPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study Forms FINALDocument9 pagesNCP and Drug Study Forms FINALVince Troy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationastersisk1121No ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPVictor MurilloNo ratings yet
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETDocument6 pagesComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- CELINDocument9 pagesCELINaikoestrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain WDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain Wmiles sbNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY For SrugeryDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY For SrugeryZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Student Drug Study Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesStudent Drug Study Mefenamic AcidJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Toxicology Reports: Rekhadevi Perumalla Venkata, Rajagopal SubramanyamDocument8 pagesToxicology Reports: Rekhadevi Perumalla Venkata, Rajagopal SubramanyamPoetri MarboenNo ratings yet
- Kesesuaian StokDocument2 pagesKesesuaian StokResky OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- 02 1975 Act DdbiaDocument13 pages02 1975 Act DdbiaChuah C. KenNo ratings yet
- New Improved CV 2018 MayDocument4 pagesNew Improved CV 2018 MayGiorgos Allen WattsNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Abnormal CTG Pattern - 2Document17 pagesInterpretation of Abnormal CTG Pattern - 2Jaspreet Kaur100% (1)
- Posterior Open Bite CausesDocument30 pagesPosterior Open Bite CauseschaitreeNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Piezoelectric and Magnetostrictive Scaling DevicesDocument38 pagesThe Effect of Piezoelectric and Magnetostrictive Scaling Devicesnotaden1849No ratings yet
- Controlled and Novel Drug DeliveryDocument23 pagesControlled and Novel Drug Deliverynews information0% (1)
- pb980 Monitor Cuff Pressure Manager BrochureDocument4 pagespb980 Monitor Cuff Pressure Manager BrochuredohxlrpxsxnwnsumyiNo ratings yet
- Mtendere Community Cholera Prevention OutreachDocument2 pagesMtendere Community Cholera Prevention OutreachReal KezeeNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease: Overview of The LiverDocument6 pagesLiver Disease: Overview of The LiverMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- Planning Design and Analysis of G+1 Hospital Building For Iiit Srikakulam CampusDocument1 pagePlanning Design and Analysis of G+1 Hospital Building For Iiit Srikakulam CampusSaritha TejavathNo ratings yet
- IAT 1 Answer Key RHEDocument13 pagesIAT 1 Answer Key RHEAparna GanesenNo ratings yet
- Isak 1 2 ViennaDocument6 pagesIsak 1 2 Viennanifej15595No ratings yet
- National Affairs 2022 - Jan To September - TopicWise PDF by AffairsCloud 9Document160 pagesNational Affairs 2022 - Jan To September - TopicWise PDF by AffairsCloud 9Nilesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Timetable Theory-August 2023Document22 pagesTimetable Theory-August 2023SueNo ratings yet
- Geog 102 Topic 3Document41 pagesGeog 102 Topic 3Nikolamladenovac9No ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and Drug InformationDocument54 pagesCritical Thinking and Drug Informationapi-661456802No ratings yet
- Table of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Document9 pagesTable of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Raheem AhmedNo ratings yet
- TRAFFIC JAM in EVERESTDocument18 pagesTRAFFIC JAM in EVERESTSB100% (1)
- WWW Asc Alchemy Com Asc HTMLDocument4 pagesWWW Asc Alchemy Com Asc HTMLJimm NewtronNo ratings yet
- Providing Public Area ServicesDocument48 pagesProviding Public Area ServicesFONCY BUYANNo ratings yet
- Discussion of Dr. John Bowlby's PaperDocument11 pagesDiscussion of Dr. John Bowlby's PaperFrancisCevallosNo ratings yet