Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corries, Aretes and Pyramidal Peaks
Uploaded by
JDMcDougall0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
836 views4 pagesdescribe and explain corrie formation
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdescribe and explain corrie formation
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
836 views4 pagesCorries, Aretes and Pyramidal Peaks
Uploaded by
JDMcDougalldescribe and explain corrie formation
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
FORMATION OF
Corrie CORRIE, ARETE and PYRAMID PEAK.
Arête In this set of diagrams we shall see how the
processes of plucking and abrasion, as well as
Pyramidal ROTATIONAL FLOW and frost shattering create
peak the three most common features of UPLAND
glacial erosion.
Plucking
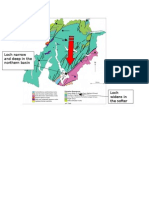
Abrasion Annotated photo of corrie and lochan in
Scottish Highlands
Frost
shattering Arête formed when two
Rotational flowof glacier scooped and corries erode back to
Rotational; deepened corrie at centre back
flow
Frost shattering
Tarn Lip-less eroded
(lochan)
Lip
Scoop
Excavate
Gouge
tear
Tarn//lochan formed as water
back wall steepened by collects in hollow
plucking
Corries, arêtes and pyramidal peaks are distinctive features of
upland glaciation, found in eg Cairngorms and Lake District. Drawing
labelled diagrams is a good way of explaining how they are formed
Corrie Formation
Practise drawing a sketch of the photo by
completing and labelling the outline sketch
Cairngorms
Plateau
Line of corries in the Cairngorm plateau.
Note how the snow lingers in the shaded
hollows
Rotational flowof glacier scooped and
deepened corrie at centre
You might also like
- Glaciation NotesDocument3 pagesGlaciation NotesRobNo ratings yet
- 197glaciation in ScotlandDocument5 pages197glaciation in Scotlandapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Review Lesson - GlaciersDocument48 pagesReview Lesson - GlacierssaipottahNo ratings yet
- 1 - Glaciation Chain Game - Print Out For LessonDocument2 pages1 - Glaciation Chain Game - Print Out For LessonJSVNo ratings yet
- Bamburgh Rock WalkDocument5 pagesBamburgh Rock WalkFinlay McDermidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PPT TwoDocument29 pagesLesson 2 PPT TwoJason AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Igneous Intrusions ExplainedDocument29 pagesIgneous Intrusions ExplainedFriska AyundaNo ratings yet
- Karst Landform FeaturesDocument26 pagesKarst Landform FeaturesA S Verma100% (1)
- Glaciation in East Africa and RiversDocument21 pagesGlaciation in East Africa and Riverskalule elvisNo ratings yet
- VI. SolusionalDocument30 pagesVI. SolusionalSitti Lasmi ManginsihNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Anagram Challenge - Print Out For LessonDocument1 page1 - The Anagram Challenge - Print Out For LessonJSVNo ratings yet
- Sryan Bruen Weathering Notes (JC Geography)Document2 pagesSryan Bruen Weathering Notes (JC Geography)Don MusogaNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument42 pagesGlacial LandformsKingsuk BurmanNo ratings yet
- Glaciers and GlaciationDocument10 pagesGlaciers and GlaciationMarshaNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalDocument40 pagesGlacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalSidra ShahNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalDocument35 pagesGlacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalTomáš PalánNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 GlaciersDocument15 pagesLesson 3 GlaciersNoelle Mc MahonNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalDocument40 pagesGlacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalAdil Javed ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument40 pagesGlacial LandformsJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Complete All The Tasks On The Following Sheets Name of LandformDocument5 pagesComplete All The Tasks On The Following Sheets Name of Landformdonotreply168436100% (1)
- Examine, With Reference To An Example You Have Studied, The Formation of One Rock-Type and How It Produces A Distinctive Landscape.Document4 pagesExamine, With Reference To An Example You Have Studied, The Formation of One Rock-Type and How It Produces A Distinctive Landscape.Paula SwalesNo ratings yet
- Glacierslandform 160625105649Document42 pagesGlacierslandform 160625105649Jann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument29 pagesGlacial LandformsABHAN InteliNo ratings yet
- Underground Waters Land FormsDocument23 pagesUnderground Waters Land FormsSahabzada Fahad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glaciers & Glaciation: Ice Sheets, Moraines & Climate ChangeDocument32 pagesGlaciers & Glaciation: Ice Sheets, Moraines & Climate Changeyatindra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Module D8 Information SheetsDocument6 pagesModule D8 Information SheetsKristopanus Patiung LantemonaNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms and DepositsDocument47 pagesGlacial Landforms and DepositsAarman SamiNo ratings yet
- Glaciers and Ice: Physical Properties and LandformsDocument31 pagesGlaciers and Ice: Physical Properties and LandformsIvanne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 - Glaciers and LandformsDocument86 pagesLecture9 - Glaciers and LandformsAniket KannoujiyaNo ratings yet
- Britain's Gypsum KarstDocument8 pagesBritain's Gypsum KarstDesai NileshNo ratings yet
- Geology Features Jan16 Low Res Locked For WebDocument2 pagesGeology Features Jan16 Low Res Locked For WebkazumicullaNo ratings yet
- 3 Karst LandformDocument40 pages3 Karst LandformVibha VermaNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document21 pagesCH 12kinggomzyNo ratings yet
- Glaciation in East Africa: Formation of The Ice (Glaciers)Document7 pagesGlaciation in East Africa: Formation of The Ice (Glaciers)Benjamin MukalaziNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalDocument40 pagesGlacial Landforms Shape Mountains: - Ice - Plumbing - Erosional - DepositionalZahid RaoNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument25 pagesGlacial Landformsabila asokNo ratings yet
- KS3 Geography Knowledge: CoastsDocument2 pagesKS3 Geography Knowledge: CoastsAbdellahNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2-Table ResGeo MindanaoDocument16 pagesActivityno.2-Table ResGeo Mindanao22-08420No ratings yet
- Glaciation and glacial landforms assignmentDocument11 pagesGlaciation and glacial landforms assignmentMu xiu LiNo ratings yet
- Limestone CavesDocument3 pagesLimestone CavesNIHARIKA SHAHNo ratings yet
- How Magma Forms and Creates Different Rock TypesDocument20 pagesHow Magma Forms and Creates Different Rock TypesJho Mil ButacNo ratings yet
- LimestoneDocument8 pagesLimestoneMatthew RamlochanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Friday 15-12-2012 GLACIAL LANDFORMSDocument42 pagesMODULE 2 - Friday 15-12-2012 GLACIAL LANDFORMSStephen ErickNo ratings yet
- Coastal Managemtn Holderness 2Document5 pagesCoastal Managemtn Holderness 2Grand OverallNo ratings yet
- Landforms Shaped by Erosion: Erosional Features and LandformsDocument4 pagesLandforms Shaped by Erosion: Erosional Features and LandformsYoumna BriguiNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument15 pagesGlacial LandformsRicha giriNo ratings yet
- Intro. To Geology and ReservoirDocument82 pagesIntro. To Geology and ReservoirRadwan AliNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Formation and Karst Topography FeaturesDocument2 pagesGround Water Formation and Karst Topography FeaturesMisylee HubillaNo ratings yet
- GROUND COVERED BY SNOW AND ICE LAYERSDocument6 pagesGROUND COVERED BY SNOW AND ICE LAYERSTrishia Lean ArgullanoNo ratings yet
- Glaciation The Formation of Glaciers and The Process by WhichDocument20 pagesGlaciation The Formation of Glaciers and The Process by Whichbethturner12No ratings yet
- 8 Glacial Deposition FeaturesDocument37 pages8 Glacial Deposition FeaturesKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Glacial Deposition: Librea, MarianDocument12 pagesGlacial Deposition: Librea, MarianJackielyn AbasNo ratings yet
- GeomorphologysummaryDocument2 pagesGeomorphologysummaryMária NemesNo ratings yet
- Geology 107L - Lecture 4: Glacial Deposits and Landforms of Eastern North DakotaDocument36 pagesGeology 107L - Lecture 4: Glacial Deposits and Landforms of Eastern North DakotaDeron ZiererNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2 TableDocument16 pagesActivityno.2 Table22-08420No ratings yet
- Bat - Beku SedimenDocument64 pagesBat - Beku SedimenvitaNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetHarold The GreatNo ratings yet
- Karstic Relief: Ana M Artacho AcedoDocument27 pagesKarstic Relief: Ana M Artacho AcedoJuan Sánchez-Garrido EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GlaciersDocument18 pagesLesson 1 GlaciersNoelle Mc MahonNo ratings yet
- Dendrochronolgy: Knowledge and UnderstandingDocument5 pagesDendrochronolgy: Knowledge and UnderstandingJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane MitchDeclanDocument2 pagesHurricane MitchDeclanJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- The Educators-Summary of Radio 4 Series: Sir Ken Robinson-Schools Are A Barrier To Creativity, As He Has Argued OnDocument5 pagesThe Educators-Summary of Radio 4 Series: Sir Ken Robinson-Schools Are A Barrier To Creativity, As He Has Argued OnJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Wind PowerDocument4 pagesWind PowerJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Mitch Defeats Countries of Central AmericaDocument2 pagesHurricane Mitch Defeats Countries of Central AmericaJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Archaeological MethodsDocument64 pagesArchaeological MethodsJDMcDougall100% (3)
- Physical PpqsDocument4 pagesPhysical PpqsJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Environmental Archaeology 2ndDocument49 pagesEnvironmental Archaeology 2ndDjumboDjett100% (1)
- The FarmerDocument2 pagesThe FarmerJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- British Isles ScriptDocument5 pagesBritish Isles ScriptJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- National ParksDocument1 pageNational ParksJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Mitch2Document2 pagesHurricane Mitch2JDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Physical PpqsDocument4 pagesPhysical PpqsJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- As Archaeology SpecificationDocument8 pagesAs Archaeology SpecificationJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane MitchOKrimDocument2 pagesHurricane MitchOKrimJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane MitchJaiDocument2 pagesHurricane MitchJaiJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- MississippiDocument3 pagesMississippiJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane MitchDocument1 pageHurricane MitchJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- The Yellow RiverDocument2 pagesThe Yellow RiverJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Geography River VolgaDocument3 pagesGeography River VolgaJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Mitch Strikes The CaribbeanDocument2 pagesHurricane Mitch Strikes The CaribbeanJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Dillon Geography Hurricane MitchDocument1 pageDillon Geography Hurricane MitchJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Sample Answer For Ink ExerciseDocument1 pageSample Answer For Ink ExerciseJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- River IndusDocument2 pagesRiver IndusJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Colorado RiverDocument2 pagesColorado RiverJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- SectionsDocument2 pagesSectionsJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- GlaciationDocument2 pagesGlaciationJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Loch Lomond Geology MapDocument1 pageLoch Lomond Geology MapJDMcDougallNo ratings yet
- Glaciation and Loch LomondDocument2 pagesGlaciation and Loch LomondJDMcDougall100% (1)