Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability and Statistics Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Bose ChanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Statistics Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Bose ChanCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Statistics
Formula Sheet
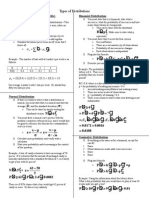
I. Descriptive Statistics
Sample Mean Sample Mean Depth of Median Midrange Range
(List of Data) (Freq. Distrib.)
∑x ∑ xf n +1 H +L
x= x= d ( x )= Midrange= R=H −L
n ∑f 2 2
Sample Variance Pop. Variance Sample St. Deviation Pop. St. Deviation
(List of Data) (List of Data) (List of Data) (List of Data)
∑ ( x− x ) ∑ ( x−µ ) ∑ ( x− x ) ∑ ( x−µ )
2 2 2 2
s2 = σ 2= s= σ=
n −1 N n −1 N
Variance St. Deviation
(Grouped Data) (Grouped Data)
( ∑ f ⋅ xm ) 2 ( ∑ f ⋅ xm ) 2
∑ f ⋅ xm −
2
∑ f ⋅ xm −
2
n n
s2 =
s=
n −1 n −1
Chebyshev’s Standard Score Percentile of a Piece of Data kth Percentile Interquartile
Theorem z-score Range
1 x −µ number of values below + 0.5 nk
at least 1− 2 z= percentile= ⋅100 Pk = IQR =Q3 −Q1
k σ total number of values 100
II. Probability
Permutation Rule: The arrangement of n objects in a specific order using r objects at a time is called a permutation of n objects taken
n!
r objects at a time. It is written n Pr and the formula is n Pr =
( n − r )!
n
Combination Rule: The number of combinations of r objects selected from n objects is denoted by n Cr , or , and is given by the
r
n!
formula n Cr = .
r !( n − r )!
Empirical Theoretical Complement General Special Addition Rule
Probability Probability Rule Addition Rule Mutually Exclusive Events
n ( A) n ( A)
P′( A) = P ( A) = P ( A ) =1− P ( A) P ( Aor B ) =P ( A) + P ( B )− P ( Aand B ) P ( Aor B or ... D ) =P ( A) + P ( B )+...+ P ( D )
n n( S )
General Special Multiplication Rule Conditional
Multiplication Rule for Independent Events Probability
P ( Aand B )
P ( Aand B ) = P ( A)⋅P ( B| A) P ( Aand B and ... and D ) = P ( A)⋅P ( B )⋅...⋅ P ( D ) P ( A|B ) =
P( B)
Mean of a Variance of a St. Deviation of a Binomial
Prob. Distribution Prob. Distribution Prob. Distribution Prob. Function
n
µ =∑ [ x ⋅ P ( x )] σ 2 =∑ x 2 ⋅ P ( x ) − µ 2 σ = ∑ x 2 ⋅ P ( x ) − µ 2 P ( x ) = ⋅ p x ⋅ q n−x for x =0,1,2,...
x
Mean of a Variance of a Standard Deviation of a
Binomial Random Variable Binomial Random Variable Binomial Random Variable
µ =np σ 2 =npq σ = npq
III. Inferential Statistics
z-score z-score Standard Error Confidence Interval Sample Size Needed for an
(Piece of Data) (Sample Mean) of the Mean Estimate for µ , ( σ Known) Interval Estimate of Pop. Mean
2
x −µ x −µx σ σ zα ⋅σ
z= z= σx= x±z ⋅
α n = 2
σ σx n 2 n E
Confidence Interval Confidence Iterval Sample Size Needed for an
Estimate for µ , ( σ Unknown) Estimate for p Interval Estimate of Pop. Proportion
2
s ˆˆ
pq zα
x ± tα ⋅ pˆ ± zα ⋅ ˆ ˆ 2
n = pq
2 n 2 n E
Test Statistic – Mean Test Statistic – Mean Test Statistic – Proportions
( σ Known) ( σ Unknown)
x −µ x x −µx pˆ − p x
z* = t* = with df = n −1 z* = with pˆ =
σ s pq n
n n n
Equation for Slope for y-intercept for Pearson’s Product
Line of Best Fit Line of Best Fit Line of Best Fit Moment r
∑ ( x − x )( y − y ) 1 x − x y − y
ŷ =b0 +b1 x b1 = b0 = y −b1 x r= ∑
∑ ( x− x ) n −1 sx s y
2
Test Statistic Confidence Interval Confidence Interval
Variance or St. Deviation Variance Standard Deviation
( n −1) s 2 ( n −1) s 2 ( n −1) s2 ( n −1) s 2 ( n −1) s2
χ2= with df = n −1 <σ 2 < 2 <σ <
σ2 χ larger
2
χ smaller χ larger
2
χ 2 smaller
Goodness-of-Fit Chi-Square
Chi-Square Test Test for Independence
(O − E ) 2 (O − E ) 2
χ 2 =∑ χ 2 =∑
E E
df = # categories – 1 df = (rows - 1)(columns – 1)
row sum×column sum
expected value =
grand total
You might also like
- STAT 400 Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSTAT 400 Midterm 1 Cheat SheetterencezhaoNo ratings yet
- Stats Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesStats Cheat SheetEdriana Isabel Bougrat Fermin50% (4)
- Statistics SymbolsDocument7 pagesStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- Statistics FormulasDocument8 pagesStatistics Formulascem9066100% (3)
- STATISTICS FORMULAE SHEET CHEATDocument4 pagesSTATISTICS FORMULAE SHEET CHEATWaqar MughalNo ratings yet
- Measures of SpreadDocument19 pagesMeasures of Spreadapi-2046991620% (2)
- Probability Cheatsheet v1.1.1 Key ConceptsDocument8 pagesProbability Cheatsheet v1.1.1 Key ConceptsMo Ml100% (1)
- STAT 251 Statistics Notes UBCDocument292 pagesSTAT 251 Statistics Notes UBChavarticanNo ratings yet
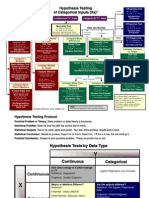
- Hypothesis Testing RoadmapDocument2 pagesHypothesis Testing RoadmapRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument10 pagesLinear Regressionapi-204699162No ratings yet
- STrategic AuditDocument4 pagesSTrategic AuditIshan DewvediNo ratings yet
- Differences in Perceptions of Training by Coaches and AthletesDocument5 pagesDifferences in Perceptions of Training by Coaches and AthletesPootrain ConductorNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- Statistics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesStatistics Formula Sheetmeolinh0% (1)
- Business MathematicsDocument61 pagesBusiness MathematicsVishal BhadraNo ratings yet
- List of Important AP Statistics Concepts To KnowDocument9 pagesList of Important AP Statistics Concepts To Knowm234567No ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument195 pagesDescriptive StatisticssammyyankeeNo ratings yet
- Formulacard PDFDocument8 pagesFormulacard PDFnoramirahNo ratings yet
- Statistics NotesDocument46 pagesStatistics Noteshsrinivas_7No ratings yet
- Statistics FormulaDocument5 pagesStatistics FormuladeenawantsNo ratings yet
- Summary of Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesSummary of Statistics FormulasAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Review Key Statistical ConceptsDocument55 pagesReview Key Statistical ConceptsMaitrayaNo ratings yet
- Important Statistics Formulas GuideDocument6 pagesImportant Statistics Formulas GuideFe OracionNo ratings yet
- Formula sheet for descriptive statistics, probability, and distributionsDocument2 pagesFormula sheet for descriptive statistics, probability, and distributionsJane Chun100% (1)
- AP Statistics 1st Semester Study GuideDocument6 pagesAP Statistics 1st Semester Study GuideSusan HuynhNo ratings yet
- I10064664-E1 - Statistics Study Guide PDFDocument81 pagesI10064664-E1 - Statistics Study Guide PDFGift SimauNo ratings yet
- Ap StatsDocument8 pagesAp StatsStella ChenNo ratings yet
- Summary of Formula - StatisticsDocument9 pagesSummary of Formula - StatisticsEzekiel D. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Types of Distributions: Probablity Distribution (Non Specific) Binomial DistributionDocument1 pageTypes of Distributions: Probablity Distribution (Non Specific) Binomial DistributionhellokeetyNo ratings yet
- TABLE 20: Formulas For Descriptive Statistics: Basic Moments Population Data Sample DataDocument2 pagesTABLE 20: Formulas For Descriptive Statistics: Basic Moments Population Data Sample DatageorgeNo ratings yet
- 2.2 The Gamma DistributionDocument4 pages2.2 The Gamma DistributionMorrizon RdzNo ratings yet
- AP Stats ReviewDocument59 pagesAP Stats ReviewSamer MetriNo ratings yet
- Refresher Probabilities Statistics PDFDocument3 pagesRefresher Probabilities Statistics PDFprabu2125No ratings yet
- Statistical Formulas (Business Stats)Document4 pagesStatistical Formulas (Business Stats)Peter BentNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulaDocument6 pagesStatistics FormulaमधुNo ratings yet
- Bus173 Chap03Document42 pagesBus173 Chap03KaziRafiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Probability Distributions: 4.1 Random VariablesDocument53 pagesChapter 4: Probability Distributions: 4.1 Random VariablesGanesh Nagal100% (1)
- CME 106 Introduction to Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesCME 106 Introduction to Probability and StatisticsDaniel JueNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Statistical InferenceDocument23 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Statistical Inferencecannickg100% (2)
- Probablity and StatisticsDocument11 pagesProbablity and StatisticsJeevitha BandiNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric StatisticsDocument20 pagesNon Parametric StatisticsshhanoorNo ratings yet
- Lec Generating FunctionDocument18 pagesLec Generating FunctionRaisa RashidNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Fundamental Stat Maths2 (D)Document28 pagesUnit4 Fundamental Stat Maths2 (D)Azizul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument35 pagesMeasures of Central Tendencykartikharish100% (1)
- Probablity DistributionDocument10 pagesProbablity DistributionsolomonmeleseNo ratings yet
- Important Statistics FormulasDocument12 pagesImportant Statistics FormulasSNo ratings yet
- Stats Formulas &tablesDocument21 pagesStats Formulas &tablesChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula SheetDocument7 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheetmrbass1234No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document39 pagesChapter 3api-3729261No ratings yet
- Ed - MathMajor12 Elementary Statistics and PRobabilityDocument3 pagesEd - MathMajor12 Elementary Statistics and PRobabilityHans RomeroNo ratings yet
- AP-Statistics ExamDocument23 pagesAP-Statistics Examldlewis100% (1)
- Hypothesis Tests for the Mean, t distribution, and Proportions Formula SheetDocument11 pagesHypothesis Tests for the Mean, t distribution, and Proportions Formula SheetdonatchangeNo ratings yet
- Categorical Data Analysis and Chi-SquareDocument27 pagesCategorical Data Analysis and Chi-SquareajiNo ratings yet
- 091 - MA8451 MA6451 Probability and Random Processes - Important Question PDFDocument19 pages091 - MA8451 MA6451 Probability and Random Processes - Important Question PDFSivanarulNo ratings yet
- Phi CoefficientDocument2 pagesPhi CoefficientRez Tacmo100% (1)
- AP Statistics Test ReviewDocument3 pagesAP Statistics Test ReviewPongman92100% (2)
- Formulae-posterDocument2 pagesFormulae-posterhemishab2007No ratings yet
- Prob StatDocument21 pagesProb StatJohn Paul AlegreNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- MTV Case StudyDocument12 pagesMTV Case Studylittlerobie100% (11)
- NonverbalprofsitDocument5 pagesNonverbalprofsitBose ChanNo ratings yet
- Clarion Logic CH6 NotesDocument23 pagesClarion Logic CH6 NotesBose ChanNo ratings yet
- TI-84 Plus Silver Edition ManualDocument696 pagesTI-84 Plus Silver Edition Manualjsmith96No ratings yet
- A Study On E Recruitment During Pandemic at Allsec TechnologiesDocument50 pagesA Study On E Recruitment During Pandemic at Allsec TechnologiesShanthiNo ratings yet
- Walmart's Supply Chain Excellence in Integration, Distribution and OperationsDocument44 pagesWalmart's Supply Chain Excellence in Integration, Distribution and OperationsProsenjit RoyNo ratings yet
- Conscious BusinessDocument19 pagesConscious BusinessparadescartarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikDocument5 pagesSyllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikRuchi HumaneNo ratings yet
- Local Media392447226283119720Document78 pagesLocal Media392447226283119720Apple James Orpiza IbitNo ratings yet
- p3 PiliavinDocument2 pagesp3 PiliavinSwimmyCj xoxoNo ratings yet
- Research Design and Development Lectures 1-1Document26 pagesResearch Design and Development Lectures 1-1georgemarkNo ratings yet
- ApplicationForm Academic SviasDocument6 pagesApplicationForm Academic Sviassenthuran amalathasNo ratings yet
- Ule 2015Document22 pagesUle 2015jhgfjgvjbhNo ratings yet
- VDCA Guideline SrilankaDocument31 pagesVDCA Guideline SrilankaVinay PathakNo ratings yet
- Challenges of International Standards On AuditingDocument7 pagesChallenges of International Standards On AuditingMuhammad Haiqhal Bin Mohd Noor AzmanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Tourism Development: A CritiqueDocument4 pagesSustainable Tourism Development: A CritiqueDanfil SalacNo ratings yet
- NASADocument5 pagesNASAPriya5sri349No ratings yet
- Small Business Management - Theory and Practice, 4e (Tim Mazzarol, 2020)Document597 pagesSmall Business Management - Theory and Practice, 4e (Tim Mazzarol, 2020)Trí Từ100% (2)
- Climate Change Strategies' Model in Teaching Science 7Document10 pagesClimate Change Strategies' Model in Teaching Science 7Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Prototype Lesson Plan in Inquiries, Investigation, and ImmersionDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Prototype Lesson Plan in Inquiries, Investigation, and ImmersionGlenn Quinlog OfficialNo ratings yet
- EAPP LECTURE 2 Danica Espinosa 11 CharityDocument10 pagesEAPP LECTURE 2 Danica Espinosa 11 CharityNicki EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Street Vendors: Their Business Challenges and SolutionsDocument10 pagesStreet Vendors: Their Business Challenges and SolutionsAshraful Islam ShowrovNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce in The Distribution Management: Shu-Hung HsuDocument8 pagesE-Commerce in The Distribution Management: Shu-Hung HsuAinul mardziahNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis To Prevent Fractures in Men and Women: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update From The American College of PhysiciansDocument28 pagesTreatment of Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis To Prevent Fractures in Men and Women: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update From The American College of PhysiciansRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- Content Writer ResumeDocument6 pagesContent Writer Resumekylopuluwob2100% (2)
- Bine 1Document4 pagesBine 1Dawit yirNo ratings yet
- Chapter16 PDFDocument23 pagesChapter16 PDFAbdullah BingaziNo ratings yet
- We Googled YouDocument6 pagesWe Googled Yousam_anshumanNo ratings yet
- Fyp BriefingDocument12 pagesFyp BriefingsalahNo ratings yet
- What Is Strategic Management and Why Is It Important?Document3 pagesWhat Is Strategic Management and Why Is It Important?Marco RegunayanNo ratings yet
- SAS 9.2 CDISC Procedure - User's GuideDocument101 pagesSAS 9.2 CDISC Procedure - User's GuidePuli SreenivasuluNo ratings yet
- 1st Uoi Planner Where We Are in Place and Time 2010 2011 NewDocument4 pages1st Uoi Planner Where We Are in Place and Time 2010 2011 NewAlka SaxenaNo ratings yet