Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcohol and Workouts
Uploaded by
TheGlobeandMailCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcohol and Workouts
Uploaded by
TheGlobeandMailCopyright:
Available Formats
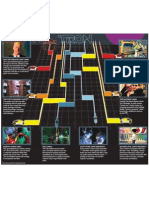
Researchers at Massey University in New Zealand put volunteers through
a strenuous leg workout that left them sore for several days. Drinking 1 gram
of alcohol per kilogram of bodyweight after the workout delayed muscle
recovery compared to a control group drinking straight orange juice,
but a dose of 0.5 grams had no effect.
9 HIGH DOSE 9 LOW DOSE
1 G ETHANOL / KG BODY WEIGHT 0.5 G ETHANOL / KG BODY WEIGHT
LEG MUSCLE TORQUE
300 300
(NEWTON-METRES)
ORANGE JUICE ORANGE JUICE
ALCOHOL ALCOHOL
250 250
ALCOHOL
200 200
150 150
Pre 36 60 Pre 36 60
TIME AFTER EXERCISE (HOURS) TIME AFTER EXERCISE (HOURS)
1 GRAM OF ALCOHOL/KG BODY 0.5 GRAMs ALCOHOL/KG BODY
WEIGHT CORRESPONDS TO: WEIGHT CORRESPONDS TO:
50 70 90 WEIGHT (KG) 50 70 90
63.4 88.7 114.1 ALCOHOL (ML) 31.7 44.4 57
3.7 5.2 6.7 1.9 2.6 3.3
BEER - 5%
341 ml
4.2 5.9 7.6 2.1 3.0 3.8
WINE - 12%
125 ml
2.1 3.0 3.9 1.1 1.5 1.9
EGG NOG - with 74 ml
double shot brandy or rum
TRISH McALASTER/THE GLOBE AND MAIL 8 SOURCES: BARNES ET AL.,
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND MEDICINE IN SPORT, EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSIOLOGY
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Babine Inspection Report 01/21Document10 pagesBabine Inspection Report 01/21TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- A National Strategy For High-Growth EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesA National Strategy For High-Growth EntrepreneurshipTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Babine Inspection Report 04/02Document6 pagesBabine Inspection Report 04/02TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- BRISON-Privilege-production of Document FINA-Final-EnDocument3 pagesBRISON-Privilege-production of Document FINA-Final-EnGlenn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Final Q4 2010 VC Data Deck - EnglishDocument33 pagesFinal Q4 2010 VC Data Deck - EnglishTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- The Wall - Anatomy of A Rock ExtravaganzaDocument1 pageThe Wall - Anatomy of A Rock ExtravaganzaTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Tron LegacyDocument1 pageTron LegacyTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Releases: General Social Survey: Victimization, 2009Document6 pagesReleases: General Social Survey: Victimization, 2009TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Ontario Superior Court of Justice Sentencing of Fahim AhmadDocument37 pagesOntario Superior Court of Justice Sentencing of Fahim AhmadTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Special Report: TD EconomicsDocument6 pagesSpecial Report: TD EconomicsTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- CFIB Business Barometer, Sept., 2010Document4 pagesCFIB Business Barometer, Sept., 2010TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- RBC Small Business SurveyDocument10 pagesRBC Small Business SurveyTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- New Evidence of Childcare in CanadaDocument44 pagesNew Evidence of Childcare in CanadaTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- The Fiscal Monitor: HighlightsDocument6 pagesThe Fiscal Monitor: HighlightsTheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Photos of Initial Scene 0001 Hrs 08 02 03Document20 pagesPhotos of Initial Scene 0001 Hrs 08 02 03TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet
- Recall and Initiative Amendment Act 2010Document3 pagesRecall and Initiative Amendment Act 2010TheGlobeandMailNo ratings yet