Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deform Intro
Uploaded by
Manu JhaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deform Intro
Uploaded by
Manu JhaCopyright:
Available Formats
Deformation Processing &
Forging Introduction
ver. 1
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 1
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Overview
• Types of Deformation Processing
• Forging
• Wire drawing
• E t i
Extrusion
• Rolling
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 2
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Types of deformation processing
• Forging
• Wire drawing
• Extrusion
• R lli
Rolling
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 3
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 4
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Wire drawing
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 5
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Extrusion
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 6
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Rolling
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 7
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
What is deformation processing?
• Process to make parts without material
removal
• Deformation occurs on parts with L/D ≈1
• High volume
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 8
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Examples of products
• Connecting rods
• Wire
• Bars
• Wi d
Window fframes
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 9
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Railroad engine
g connecting
g rod
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 10
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Typical product dimensions
• Small:
– coins
– surgical
i l wire
i
• Large:
– power plant turbine shafts
– aircraft landing gear
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 11
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Aircraft landing gear
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 12
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Process characteristics
• Material is deformed
– improvement of material properties
• grain refinement
• grain orientation
• work hardening
σ t = σ oε n
• Material is conserved
– minimal trimming and machining
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 13
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Important parameters
• Plasticity
• Friction
• Elasticity negligible
– usually
ll much h smaller
ll magnitude
it d
than plastic deformation
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 14
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Plasticity analysis
Forging force
• Slab method
– plane strain Platen
– plane stress Forging
Platen
Forging force
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 15
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Strain hardening
σt
fracture
σt = σoεn K
ε
1
• Tresca (maximum shear stress)
yield criterion: τflow = σflow / 2
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 16
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Energy / unit volume (u)
ε1 γ1
u = ∫ σ flow dε = ∫ τ flow dγ
0 0
∴ Δγ = 2 Δ ε
by Tresca (maximum shear stress)
criterion
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 17
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Working temperature
Recrystallization temperature = 0.5 Tmelting (K)
• Cold: T < 0.4
0 4 Tmelting(K)
– strain hardening effect
– no strain rate effect
σ = Kε n
• Hot: T > 0.6 Tmelting(K)
– no strain hardeningg effect
– strain rate effect
σ = Cε& m
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and 18
Systems Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 19
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging
g g
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 20
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Old Hammer Forge
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 21
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging
g g
• Part formation by pressing
between dies
– Dies are hard metal shapes
• Temperature
– Hot (usually)
– Cold
• Dies
– Open (no lateral constraints)
– Closed (lateral constraints)
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 22
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Open Die Forging
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 23
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Ring Forging
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 24
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Open die forging
Forging force
Platen
Forging
Platen
Forging force
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 25
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Closed Die Forging
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 26
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Closed die forging
F i force
Forging f
Flash
Forging
Forging force
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 27
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forgings
• Coins
• Landing gear
• Crank shafts
• T bi shafts
Turbine h ft
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 28
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging presses
• Large machines
– hold dies
– form parts
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 29
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Press types
yp
• Hydraulic
y presses
p
• Mechanical presses
• Screw presses
• Hammers
– gravity
i d drop
– power drop
– counter blow (two rams)
– high pressure gas
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 30
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
50 000 tton press
50,000
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 31
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forges
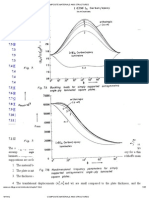
Schematic illustration of the principles of various forging machines. (a) Hydraulic
press. (b) Mechanical press with an eccentric drive; the eccentric shaft can be replaced
by a crankshaft to give the up-and-down motion to the ram. (continued)
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 32
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forges
Schematic illustration of the principles of various forging machines. (c) Knuckle-joint
press. (d) Screw press. (e) Gravity drop hammer.
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 33
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Dies
• Final p
part shape
p determined byy die
accuracy
• Multiple parts can be made in one die
• Progressive shaping can be done in one
die set
• Need to be stronger than highest
forging stress
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 34
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging hammer capabilities
Moving mass Energy at
((kg)
g) strike ((J))
Gravity drop 500 - 5,000 6,000 -
hammers 75,000
Power drop 500 - 18,000 18,000 -
hammers 600,000
High energy 500,000 -
rate forming 5,000,000
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and 35
Systems Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging press parameters
Load S tr o k e s Pow er
c a p a c ity p e r m in u te (k W )
M e c h a n ic a l p r e s s e s
O p e n -b a c k , 1 5 0 - 1 ,2 5 0 200 - 100 3 - 15
in c lin a b le kN
H ig h - s p e e d , s tr a ig h t 3 0 0 - 2 ,0 0 0 2000 - 200
s id e KN
L a r g e r s tr a ig h t s id e 1 - 6 MN 100 - 20 10 - 60
T r a n s fe r p r e s s e s 2 - 40 M N 50 - 10
F o r g in g p r e s s e s 3 - 80 M N 100 - 30 20 -
500
H y d r a u li
lic p r e s s e s
U n iv e r s a l 4 - 25 M N
F o r g in g p r e s s e s 2 - 500 M N 150 -
1000
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 36
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Hot upsetting machine parameters
Rate
R t size
i ((mm)) Forging
F i fforce St k / i
Strokes/min P
Power (kW)
(upset diameter) (MN)
25 0.5 90 5
38 1 65 10
50 2 60 15
75 4 45 25
100 6 35 40
125 8 30 50
150 10 27 60
175 13 25 90
200 16 23 110
225 20 20 150
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and 37
Systems Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging steps
• Prepare slug
– saw
– flame cut
– shear
• Clean
Cl slug
l surfaces
f
– shot blast
– flame
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 38
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging
g g steps
p
• For hot forging
– heat up and descale forging
– make sure press is hot
• Lubricate
– oil
– soap
– MoS
oS2
– glass
– graphite
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 39
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Lubrication purposes
• Reduce friction
• Reduce die wear
• Thermally insulate part
– to
t keep
k it warm
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 40
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging steps
• Forge
• Remove flash
– trim
– machine
• Check dimensions
• Post processing, if necessary
– heat
h t treat
t t
– machine
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 41
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Effect on grain structure
• Large grains are broken up.
• Grains can be made to flow
flow.
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 42
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Main forging defect
• Surface cracks
– due to sticking and barreling, leading to
tensile forces on the surface.
forging
operation
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 43
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Forging Defects
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 44
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
Summary
• Types of deformation processes
• Material deformation review
• Forging introduction
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 45
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
ME 6222: Manufacturing Processes and Systems 46
Prof. J.S. Colton © GIT 2009
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DA - 1 - Strength of MaterialsDocument4 pagesDA - 1 - Strength of MaterialsRudransh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 1 Grip BoltsDocument2 pages1 Grip BoltsJithinRajNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Dept. of Chemistry M. M. Arts and Science College, SirsiDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure: Dept. of Chemistry M. M. Arts and Science College, SirsiElish RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Lab Level 0Document34 pagesLab Level 0redz00No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Energy EntropyDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer: Energy EntropyKeybee AcquiatNo ratings yet
- Analysis, Design, and Detailing of Various Foundation LayoutsDocument28 pagesAnalysis, Design, and Detailing of Various Foundation LayoutsRamez Bou-RizkNo ratings yet
- 6 Uniform Circular MotionDocument83 pages6 Uniform Circular MotionRamachandranPerumal0% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument39 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFAgustin Jr., Reynold P.No ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics ApplicationDocument88 pagesFluid Dynamics Applicationkyledarbymanalo1437No ratings yet
- D. V. Ritzel, J. Crocker and D. Whitehouse - Blast Response of Soft-Skinned Shelters and Occupant VulnerabilityDocument26 pagesD. V. Ritzel, J. Crocker and D. Whitehouse - Blast Response of Soft-Skinned Shelters and Occupant VulnerabilityMallamaxNo ratings yet
- Filtration: Batch Filtration (Small Scale)Document6 pagesFiltration: Batch Filtration (Small Scale)Anonymous ZAr1RKNo ratings yet
- Research On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019Document7 pagesResearch On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019ait oubella marouaneNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials and StructuresDocument35 pagesComposite Materials and StructuresGundoju SreenivasNo ratings yet
- BellowsDocument34 pagesBellowsRicky Ocktavi RizkyNo ratings yet
- Cold-Formed Steel Structures: AS/NZS 4600:2018Document9 pagesCold-Formed Steel Structures: AS/NZS 4600:2018kiz0% (1)
- 2.the Lagrangian For Electromagnetic FieldsDocument4 pages2.the Lagrangian For Electromagnetic FieldsMizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Quality ReviewDocument6 pagesQuality ReviewShashi Kumar SNo ratings yet
- LQuiz (TOV1) # 14 (Eng)Document4 pagesLQuiz (TOV1) # 14 (Eng)PkrNo ratings yet
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocument22 pagesAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderNo ratings yet
- The Theory of One-Dimensional Consolidation of Saturated Clays-Gibson, England & HuseyDocument13 pagesThe Theory of One-Dimensional Consolidation of Saturated Clays-Gibson, England & HuseyAnonymous GnfGTwNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity Ishan Sharma 2148139Document12 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Ishan Sharma 2148139Ishan SapkotaNo ratings yet
- 131 - Physics 2Document4 pages131 - Physics 2nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Assessment of Soil Nailing Performance by Using Finite Element and Finite Difference MethodsDocument14 pagesAssessment of Soil Nailing Performance by Using Finite Element and Finite Difference MethodsnidhisasidharanNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: SciencedirectDedi AfandiNo ratings yet
- ENGN.2060 Assignment 06 SolutionDocument3 pagesENGN.2060 Assignment 06 SolutionSandeep PetwalNo ratings yet
- Guided Waves IDocument85 pagesGuided Waves IDeepjyoti Das100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological UniversitySandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2005Document41 pagesAieee 2005Vicky JeetNo ratings yet
- Public Release: Topic 4: Plane and Spherical Waves, Density, Intensity, and ImpedanceDocument39 pagesPublic Release: Topic 4: Plane and Spherical Waves, Density, Intensity, and ImpedanceKomay Abo ShakraNo ratings yet