Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3 - Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
Hayati Aini AhmadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3 - Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
Hayati Aini AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Coordinate Geometry
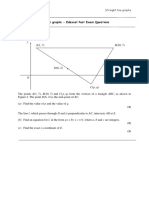
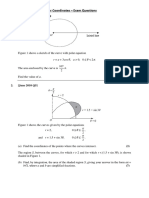
1. Diagram 1 shows two straight lines, SP and PQ, intersect each other perpendicular at point
P, which lies on the y-axis.
S
x
0 Q
Given that the equation of the straight line PQ is , find
(a) the coordinates of points P and Q [2 marks]
(b) the equation of line SP [2 marks]
(c) the coordinates of point R if 2PQ = 3QR [3 marks]
(d) the area of triangle SPR [3 marks]
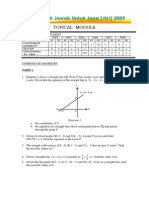
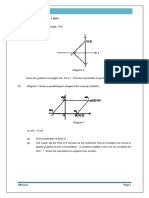
2. Diagram 2 shows a triangle PQR. Point S lies on the line PR. Given that the equation of line
PQ is given by .
y
S
5
x
P 0
Q
(a) Find the coordinate of point R if 3PS = 2SR [3 marks]
(b) Hence, find the equation of line QR. [2 marks]
(c) Calculate the area of [2 marks]
(d) A point T moves in such a way that its distance from point R is equal to the distance
between point S and point Q. Find the equation of the locus of T. [3 marks]
Add Maths Buddy Support SMK BBSL_2011
Coordinate Geometry
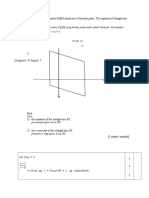
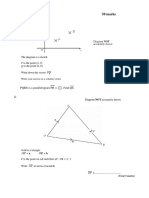
3. In Diagram 3, the straight line is perpendicular to ST. Q is the intersection point
of the lines such that SQ : QT = 1 : 2.
y Find
(a) the equation of ST [3 marks]
(b) the coordinates of Q [2 marks]
S (c) the coordinates of S [2 marks]
y Q R (d) the area of the quadrilateral
y T(3,1)
P x OPQR [3 marks]
O
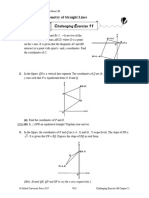
4. In Diagram 4, and the equation of straight line BC is .
y
A(-5,11)
B
x
C
(a) Find
(i) the equation of the straight line AB
(ii) the coordinates of B
(b) The straight line AB is extended to a point D such that AB : BD = 2 : 3 . Find the
coordinates of D.
(c) A point Q moves such that its distance from point A is always 6 units. Find the
equation of the locus of Q.
Add Maths Buddy Support SMK BBSL_2011
You might also like
- Straight Line Graphs - Edexcel Past Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesStraight Line Graphs - Edexcel Past Exam QuestionsAlisa PhanNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 10 Trigonometry)Document4 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 10 Trigonometry)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry2Document3 pagesCoordinate Geometry2Cah YeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Coordinate GeometryDocument11 pagesChapter 6: Coordinate GeometryHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument3 pagesCoordinate GeometryRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)Document4 pagesAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)HANIFAHNo ratings yet
- Juj 2009 PDFDocument36 pagesJuj 2009 PDFMohd Khir ZainunNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Paper 2. Sabah 2011 P2Q9Document2 pagesCoordinate Geometry Paper 2. Sabah 2011 P2Q9Loh AlexNo ratings yet
- LokusDocument8 pagesLokusroslizaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Add MathDocument13 pagesCoordinate Geometry Add MathAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Latihan Pengukuhan 4 Dec (Ahad)Document7 pagesLatihan Pengukuhan 4 Dec (Ahad)Yun XingNo ratings yet
- Quiz Ch7Document2 pagesQuiz Ch7Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Geometry CoordinateDocument13 pagesForm 4 Geometry CoordinateVaidehi UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Advance Level Subjective Questions For JEE Advance: Straight Lines Circles Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDocument22 pagesAdvance Level Subjective Questions For JEE Advance: Straight Lines Circles Parabola Ellipse HyperbolasushantNo ratings yet
- Mate Latih Tubi - Garis Lurus T4Document3 pagesMate Latih Tubi - Garis Lurus T4cgnashNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Part 1 TDocument19 pagesTopic 4 Part 1 TAsli GoncNo ratings yet
- I Love Maths Series Book 4 - Analytical GeometryDocument58 pagesI Love Maths Series Book 4 - Analytical GeometryBonga percyNo ratings yet
- Maths Soalan SetaraDocument8 pagesMaths Soalan SetarasiaoruiNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument6 pagesCoordinate GeometrySalmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Exam Preparation - Coordinate Geometry 21st OctDocument2 pagesExam Preparation - Coordinate Geometry 21st OctZantusNo ratings yet
- F3 Challenging Exercise 11Document3 pagesF3 Challenging Exercise 11pgkbgjrh5pNo ratings yet
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Document5 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhNo ratings yet
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Document5 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C1 Advanced Subsidiary Coordinate GeometryDocument7 pagesEdexcel GCE Core Mathematics C1 Advanced Subsidiary Coordinate GeometryArrow GamingNo ratings yet
- STPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsDocument3 pagesSTPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsMelody Ong0% (1)
- Mathematics: Revision QuestionsDocument16 pagesMathematics: Revision Questionsdarwisyah.yunosNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument41 pagesCh-11 Three Dimensional Geometryjaved alamNo ratings yet
- 5a. Mixed Exam-Style Questions On Coordinate GeometryDocument2 pages5a. Mixed Exam-Style Questions On Coordinate GeometrycindyNo ratings yet
- 11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: C, Correct To 3 Significant FiguresDocument2 pages11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: C, Correct To 3 Significant Figures(4C27) Wong Ching Tung, Zoey 20181D043spss.hkNo ratings yet
- FG200106Document10 pagesFG200106Tien Dung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3-ST&CR (15.04.2020)Document12 pagesAssignment - 3-ST&CR (15.04.2020)KaushikNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry (AM)Document11 pagesCoordinate Geometry (AM)Siti AiscyahNo ratings yet
- Focus Camp 2021 VectorsDocument5 pagesFocus Camp 2021 Vectorsfairprice tissueNo ratings yet
- NewProgress - AMaths TB - ch10Document3 pagesNewProgress - AMaths TB - ch10kkakilaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 6Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 6Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Constructing Loci and Finding Midpoints in Geometry ProblemsDocument2 pagesConstructing Loci and Finding Midpoints in Geometry ProblemsTan Kui GekNo ratings yet
- LAtihan F5Document9 pagesLAtihan F5rasidhaNo ratings yet
- C4 Vectors Exam QuestionsDocument26 pagesC4 Vectors Exam QuestionsswssNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- Kulai 2023 QDocument2 pagesKulai 2023 Qqian yee nguNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY AND ALGEBRA PROBLEMSDocument1 pageGEOMETRY AND ALGEBRA PROBLEMSaTIEN230991No ratings yet
- FP2 Chp7 PolarCoordinates ExamQuestionsDocument11 pagesFP2 Chp7 PolarCoordinates ExamQuestionsc16mk1No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledNicole WongNo ratings yet
- C1: Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: Learning ObjectivesDocument24 pagesC1: Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: Learning ObjectivesIsmail Medhat SalahNo ratings yet
- Xercise: Jee ProblemsDocument2 pagesXercise: Jee ProblemspandaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Terminal Weekend Task 1 22 09 23Document1 page2nd Terminal Weekend Task 1 22 09 23MR GAMERNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan Matematik 2010Document10 pagesKoleksi Soalan Matematik 2010khai_83No ratings yet
- AHL 3.12 Vector DefinitionsDocument52 pagesAHL 3.12 Vector Definitionspelin petekNo ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 Question Ans Er All Uestions (100 Marks) 1Document14 pagesH2 Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 Question Ans Er All Uestions (100 Marks) 1Emmanuel Elijah ErNo ratings yet
- Pure Maths Year 1 End of Unit Test 2Document2 pagesPure Maths Year 1 End of Unit Test 2fajrbilaNo ratings yet
- AMATH Coordinate GeometryDocument26 pagesAMATH Coordinate GeometryLeneNo ratings yet
- Circle Exam QuestionsDocument12 pagesCircle Exam Questionsgegopog372No ratings yet
- Bab8 Mathf2 PDFDocument1 pageBab8 Mathf2 PDFCeciliaHillaryNo ratings yet
- Vectors Prepared by ArafatDocument10 pagesVectors Prepared by ArafatArafathali Shaikdawood BasheeraliNo ratings yet
- Questions on Vectors and LinesDocument9 pagesQuestions on Vectors and LinesIshy HereNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Coordinate GeometryDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Coordinate GeometryforgamingNo ratings yet
- Linear Law 2014Document8 pagesLinear Law 2014Ainol Bazlin FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Top Performing Schools in Malaysia's Mathematics OlympiadDocument15 pagesTop Performing Schools in Malaysia's Mathematics OlympiadHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Modul Jom Tanya Sifu - Integrations & Vectors 2014Document16 pagesModul Jom Tanya Sifu - Integrations & Vectors 2014Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Set 1@2014Document1 pageQuadratic Equation Set 1@2014Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Index Number - Set1 @2010Document2 pagesIndex Number - Set1 @2010Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Index Number - Set 2@2010Document2 pagesIndex Number - Set 2@2010Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jom Tanya Sifu@Form 5: Chapter 1: PROGRESSIONSDocument15 pagesJom Tanya Sifu@Form 5: Chapter 1: PROGRESSIONSHayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Index Number Set3@2010Document2 pagesIndex Number Set3@2010Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Integration and DifferentiationDocument7 pagesIntegration and DifferentiationHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Triangle - Set 2Document2 pagesSolutions of Triangle - Set 2Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 6 (Revised)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 6 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jadual Trial SPM 2013Document1 pageJadual Trial SPM 2013Hayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Tutorial Vector Q1 - Paper 1Document1 pageTutorial Vector Q1 - Paper 1Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Paper 1) - Set 1@2013Document2 pagesDifferentiation (Paper 1) - Set 1@2013Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 4 (Revised Version 2013)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 4 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 8 (Revised)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 8 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 5 (Revised Version 2013)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 5 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progression Paper 1@set1 (Revised Version 2013)Document2 pagesProgression Paper 1@set1 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 7 (Revised)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 7 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 3 (Revised Version 2013)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 3 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Progressions Paper 1@set 2 (Revised Version 2013)Document2 pagesProgressions Paper 1@set 2 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3472 MT - Skema Kertas 2no.14Document1 page3472 MT - Skema Kertas 2no.14Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralDocument18 pagesQuadrilateralviralroshNo ratings yet
- USAJMO Math Olympiad SolutionsDocument9 pagesUSAJMO Math Olympiad SolutionsRUSDIN, S.Si100% (1)
- Teorema de Seno y Coseno. Area de TriánguloDocument24 pagesTeorema de Seno y Coseno. Area de Triángulomartha0% (1)
- Prisms - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPrisms - WorksheetChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Lampshade MathematicsDocument5 pagesLampshade MathematicsChai SilwanusNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 4Document2 pagesForm 4 Mathematics Chapter 4Chong Jie Mee67% (3)
- G.7 Polygon DemoDocument8 pagesG.7 Polygon DemoHoney Lou Cotingjo PaitonNo ratings yet
- 5 1 A CalculatingpropertiesshapesDocument8 pages5 1 A Calculatingpropertiesshapesapi-264767990No ratings yet
- Chart WorkDocument485 pagesChart WorkMika Marielle TrincheraNo ratings yet
- Application On Similar Triangles and Similarities in Right TrianglesDocument4 pagesApplication On Similar Triangles and Similarities in Right TrianglesCat PusaNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument27 pagesMensurationCalifornia KnightNo ratings yet
- Indices Logs Surds 11-21Document56 pagesIndices Logs Surds 11-21Ibraheem MassabNo ratings yet
- The Alternative IMOsDocument42 pagesThe Alternative IMOsPetar Nizić - NikolacNo ratings yet
- Solving Right TrianglesDocument8 pagesSolving Right TrianglesPatrick GuerraNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS TOPICS COVERED IN FIRST QUARTERDocument8 pagesCALCULUS TOPICS COVERED IN FIRST QUARTERVanessa May CasiñoNo ratings yet
- Mat 1a SmartDocument7 pagesMat 1a SmartAmukNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine Law: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesSine and Cosine Law: Name: - DateMark Ronald SuaisoNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines - JEE Mains Mini Capsule PDFDocument37 pagesStraight Lines - JEE Mains Mini Capsule PDFSouhardya DuttaNo ratings yet
- 9 1 Circles and CircumferenceDocument22 pages9 1 Circles and CircumferenceReham Mohamed Ahmed NoufalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MTAP Questions With SolutionsDocument12 pagesGrade 8 MTAP Questions With SolutionsMariella Gerelingo100% (1)
- 8.3-Area of CirclesDocument21 pages8.3-Area of CirclesBrett EdgerleNo ratings yet
- Horticulture Week 3Document19 pagesHorticulture Week 3Joyce PolintanNo ratings yet
- ISMC 2016 Primary 5 SolutionsDocument6 pagesISMC 2016 Primary 5 SolutionsAileen MimeryNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus - 1 & 2Document9 pagesDifferential Calculus - 1 & 2ArnavNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Quarter 3 Week 7 and 8Document2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Quarter 3 Week 7 and 8zaldy mendozaNo ratings yet
- Classifying Triangles by Angles and SidesDocument40 pagesClassifying Triangles by Angles and SidesSishira PattanNo ratings yet
- Loci Proofs Maths ChapterDocument40 pagesLoci Proofs Maths ChapterMovies buddyNo ratings yet
- GR-10 Assignment - 1Document6 pagesGR-10 Assignment - 1julianqophisoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W3Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W3Angelica GuillermoNo ratings yet
- 2013 Bookmatter PrinciplesOfPhysicsDocument66 pages2013 Bookmatter PrinciplesOfPhysicsGuilherme BrunoNo ratings yet