Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure and Care of a Compound Microscope
Uploaded by
Sakkunthala ElilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure and Care of a Compound Microscope
Uploaded by
Sakkunthala ElilCopyright:
Available Formats
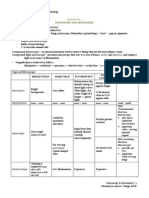
Practical 1: Investigating the structure, functions and care of a compound light
microscope
Objective: To study the structure, functions and care of a compound light microscope
Purpose: To determine the proper ways of conducting an experiment using a compound
light microscope
Introduction: The first microscope to be developed was the optical microscope, although
the original inventor is not easy to identify. An early microscope was made in 1590 in ,
Middelburg . Two eyeglass makers are variously given credit: Hans Lippershey and Hans
Janssen. Giovanni Faber coined the name microscope for Galileo Galilei's compound
microscope in 1625
Materials/ Apparatus: lens paper, glass cover slips, oil immersion, human blood smear
specimen, rabbit's heart specimen, artery and vein specimen, aorta specimen, compound
microscope
Methodology:
1. The provided specimen is placed on the stage of the microscope and the low
power objective lens are selected. (4X)
2. The lenses are raised using the coarse focus knob until you see the image come
into focus and then go out again, then focus back until you find center focus. The
fine focus knob is used when the specimen was near the objective lens.
3. The image is centered and the light is adjusted using the diaphragm.
4. The objective lens are now switched to the highest power objective lens (40x).
The fine focus is read and light (diaphragm) as needed. Before the observation, oil
are added to the specimen as a buffer.
After use of microscope, ensure
1. The respective lenses are cleaned up using lens solution.
2. Glass slides and cover slips are cleaned.
3. The compound light microscope is covered with plastic to avoid contact with dust
and dirt.
Discussion:
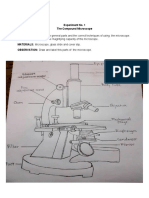
Eyepiece:
the lens you look through, magnifies the specimen
Base:
supports the microscope
Nosepiece:
holds objective lenses
High and Low Power Objective Lens:
magnify the specimen
Arm:
supports upper parts of the microscope, used to carry the microscope
Fine Focus Knob:
used to focus when using the high power objective
Stage:
where the slide is placed
Diaphragm:
regulates the amount of light reaching the objective lens
Course Focus Knob:
used to focus when using the low power objective
Light Source:
provides light
Stage Clips:
hold slide in place on the stage
Conclusion: the microscope should be handle carefully while oil immersion was using
during large magnification as a buffer. The structure of a cell such as cell membrane and
nucleus can be observe through the microscope.
You might also like
- The Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)Document11 pagesThe Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)JheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Zoology 2Document4 pagesLab Report Zoology 2Rebecca UyNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Parts and Functions GuideDocument2 pagesCompound Microscope Parts and Functions Guidemydiamondstar17No ratings yet
- EXP1Document8 pagesEXP1Marife CompraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Microscopy: A Guide to Proper Compound Microscope Use and MaintenanceDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Microscopy: A Guide to Proper Compound Microscope Use and Maintenancecharles mepaniaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsIrish Mejia100% (1)
- Microscope Parts WorksheetDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts WorksheetNidafe VillasNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Enabling Assessment 2.1 Intoduction To MicrosDocument4 pagesEnabling Assessment 2.1 Intoduction To MicrosAvrick GoNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts Notes PDFDocument1 pageMicroscope Parts Notes PDFArquero NosjayNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document5 pagesLab Report 1yosaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1Document4 pagesLab Exercise 1Alessandra WyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 1. MicroscopeDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise 1. MicroscopeJohn Christian100% (1)
- Plant and Animal LabDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Labapi-312828959No ratings yet
- Compund MicroscopeDocument6 pagesCompund MicroscopebellarosyNo ratings yet
- Microscopy & MicrometryDocument4 pagesMicroscopy & MicrometryChristine Jo Ann ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)Document5 pagesMicroscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)JASMIN DAMIANNo ratings yet
- Compound Monocular Microscope Parts and UseDocument5 pagesCompound Monocular Microscope Parts and UseDiana BoladoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportNor HafizahNo ratings yet
- Experiment of Angiosperm PlantDocument4 pagesExperiment of Angiosperm Plantganu8950% (2)
- Instruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationDocument3 pagesInstruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 MicrosDocument5 pagesExercise No 1 MicrosJm Gutierrez0% (1)
- Parts and Functions of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageParts and Functions of A MicroscopeDivine Josol CamposanoNo ratings yet
- 2 Microscope Letter e Lab Handout This OneDocument2 pages2 Microscope Letter e Lab Handout This Onejimmy dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Pratical 1 - MicrosDocument7 pagesPratical 1 - MicrosanthorNo ratings yet
- Microscopes Lab Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMicroscopes Lab Lesson Planapi-412438755No ratings yet
- Lab Report Cells Seen Under The MicroscopeDocument5 pagesLab Report Cells Seen Under The Microscopeorlandoe2560% (1)
- Phet Inquiry Bending LightDocument6 pagesPhet Inquiry Bending Lightapi-326963627No ratings yet
- Microscope UseDocument7 pagesMicroscope UsebegNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab ReportDocument3 pagesMicroscope Lab ReportKarina Gonzalez70% (10)
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageParts and Function of A MicroscopejinmenchieNo ratings yet
- Microscope ActivityDocument5 pagesMicroscope ActivityDharlynette MungcalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 - Mic102Document10 pagesLab Report 1 - Mic102Suhada IdayuNo ratings yet
- Microscopes Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMicroscopes Parts and Functionweng100% (6)
- Microscope CareDocument5 pagesMicroscope Care3ciaGarcia20No ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts and Function of The MicroscopeStephen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Histology of Plant and Animal CellsDocument4 pagesHistology of Plant and Animal Cellscikaifa25% (4)
- 2 Microscopy LabDocument18 pages2 Microscopy Lablux0008No ratings yet
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageParts and Function of A Microscopevanessa81% (16)
- Microscope Labeling 1Document1 pageMicroscope Labeling 1api-318387471No ratings yet
- Hay InfusionDocument1 pageHay Infusioninnoaruta_22No ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document14 pagesLab Report 1api-340424634100% (5)
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 7 Activity 1Document2 pagesQ2 Science 7 Activity 1Jaen RociosNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of OrganellesDocument18 pagesWhat Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of Organellestdukes546No ratings yet
- Punnett Square WorksheetDocument9 pagesPunnett Square WorksheetBeatrice AnnNo ratings yet
- Bino Laboratory Manual 3DDocument48 pagesBino Laboratory Manual 3DAndrea TamundongNo ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument3 pagesCompound MicroscopeTaehyung Kim100% (1)
- Microscopes and Microscopy TechniquesDocument2 pagesMicroscopes and Microscopy TechniquesJeanel SamonteNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesJhon Carlo Bataller Monleon100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Laboratory Worksheet 1: The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Laboratory Worksheet 1: The Compound Light MicroscopeBastin ChamNo ratings yet
- Extracting DNA From A BananaDocument8 pagesExtracting DNA From A BananaJHASMIN NICOLE MANCERANo ratings yet
- What Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Document10 pagesWhat Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Alejandra NuñezNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise: Microscopy: Care of The MicroscopeDocument13 pagesLab Exercise: Microscopy: Care of The Microscopeblackforest8No ratings yet
- Microscope Skills Year 11 WorksheetDocument1 pageMicroscope Skills Year 11 WorksheetNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMicroscope Lesson PlanAmanda0% (1)
- Lab 1 - The Use & Care of The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLab 1 - The Use & Care of The MicroscopeFatin Ahmad100% (1)
- Lab Exercise 1 MicrosDocument7 pagesLab Exercise 1 MicrosaluapNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument4 pagesMicroscopelawandlatif36No ratings yet
- Guide to Microscopy TechniquesDocument17 pagesGuide to Microscopy TechniquesSathvik BangiramaneNo ratings yet
- Aries Laser PointerDocument2 pagesAries Laser PointersheshidharrajubNo ratings yet
- Hasselblad 500CMDocument29 pagesHasselblad 500CMcleansweeper100% (1)
- Instruction Manual for Nikon AF240SV/AF240SV QD CameraDocument19 pagesInstruction Manual for Nikon AF240SV/AF240SV QD CameraGerman RuizNo ratings yet
- History Of Photography From Pinhole To DigitalDocument22 pagesHistory Of Photography From Pinhole To DigitalDatulna Benito Mamaluba Jr.No ratings yet
- Microscope Review GuideDocument34 pagesMicroscope Review GuideWwwanand111100% (1)
- Raft Version ULY: Inaldi ANDDocument17 pagesRaft Version ULY: Inaldi ANDLuis David Trejos RojasNo ratings yet
- Sony Dsr-pd177p (Dsr-pd175p Dsr-pd175) Camcorder PalDocument11 pagesSony Dsr-pd177p (Dsr-pd175p Dsr-pd175) Camcorder PalherrystynNo ratings yet
- Optical Instruments CH9bDocument14 pagesOptical Instruments CH9bRishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- CollimatorDocument5 pagesCollimatorskc3128No ratings yet
- Chaotic Behavior in Erbium-Doped Fiber-Ring Lasers: Liguo Luo, T. J. Tee, and P. L. ChuDocument7 pagesChaotic Behavior in Erbium-Doped Fiber-Ring Lasers: Liguo Luo, T. J. Tee, and P. L. ChuVastavikta SinghNo ratings yet
- Using the Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesUsing the Compound MicroscopeEarl JohnNo ratings yet
- Qty Items Part Numbers: D D D D Object TelescopeDocument7 pagesQty Items Part Numbers: D D D D Object TelescopekamdidoelNo ratings yet
- Canon Eos 70dDocument2 pagesCanon Eos 70dSandro Campagnoli0% (1)
- OTDR Report: Job InfoDocument2 pagesOTDR Report: Job InfoneonetwirelessNo ratings yet
- Consumables PICOWAY MAR 2023 REV.1Document1 pageConsumables PICOWAY MAR 2023 REV.1Admin LuminkaNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE76K0T-EXLPF Datasheet 20230605Document4 pagesDS-2CE76K0T-EXLPF Datasheet 20230605Jorge CaleroNo ratings yet
- Alexa: Price List - EU 05/2017Document81 pagesAlexa: Price List - EU 05/2017arindam dasNo ratings yet
- Studio Lighting GuideDocument3 pagesStudio Lighting GuideStojan TashurovNo ratings yet
- Ds 2ce16a2n Vfir3 BRWDocument1 pageDs 2ce16a2n Vfir3 BRWivangunawan71No ratings yet
- UAV Mapping Tool V2.1Document14 pagesUAV Mapping Tool V2.1Andi BakarovNo ratings yet
- Avanar 200mm f3.5 Prime Lens: MoiraDocument4 pagesAvanar 200mm f3.5 Prime Lens: MoiraBill Chan ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 26 BinocularsDocument18 pages26 BinocularsAnasmawwatNo ratings yet
- Robtics Officina Stellare Veloce RH 300 - 300mm f3 Riccardi Honders - Ota enDocument4 pagesRobtics Officina Stellare Veloce RH 300 - 300mm f3 Riccardi Honders - Ota enIlarion MogaNo ratings yet
- Light MicroscopeDocument10 pagesLight MicroscopeAnkit MishraNo ratings yet
- Lubitel 166bDocument10 pagesLubitel 166bCarlos NeriNo ratings yet
- MOZA MINI-P Camera Compatibility List: Shutter Record Auto Focus Note Function Brand Camera CableDocument2 pagesMOZA MINI-P Camera Compatibility List: Shutter Record Auto Focus Note Function Brand Camera CableFlorian BuicanNo ratings yet
- Bushnell 2004 Catalog PDFDocument45 pagesBushnell 2004 Catalog PDFCraig ThompsonNo ratings yet
- History of The CameraDocument18 pagesHistory of The CameraGayle OmisolNo ratings yet
- 7 Fashion Photo and Lighting Setup With Beauty DishDocument1 page7 Fashion Photo and Lighting Setup With Beauty DishdvduronNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Star AdventurerDocument36 pagesInstruction Manual: Star AdventurerGustavo GuilhermeNo ratings yet