Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gel A Pot
Uploaded by
Gela Pielago0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesGeneric name Brand name Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Contraindicated to patients with allergies to penicillins, cepahlosporins. Do not mix with aminoglycoside solutions, administer these drugs separately.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gel a Pot
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGeneric name Brand name Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Contraindicated to patients with allergies to penicillins, cepahlosporins. Do not mix with aminoglycoside solutions, administer these drugs separately.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesGel A Pot
Uploaded by
Gela PielagoGeneric name Brand name Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Contraindicated to patients with allergies to penicillins, cepahlosporins. Do not mix with aminoglycoside solutions, administer these drugs separately.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
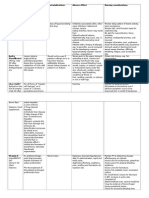
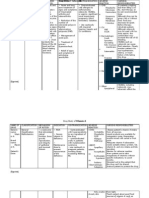
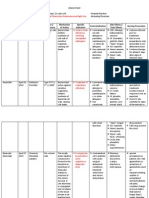
Generic name Ceftazidime
Brand name Tazidime
Classification • Antibiotic
• Cephalosporin (third generation)
Dosage 0-4 weeks (<1200 g): 50 mg/kg/dose IV q12h
< 7d (>1200 g): 50 mg/kg/dose IV q12h
>7d (>1200 g): 50 mg/kg/dose IV q8h
Mechanism of Action ♥ Inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell
death.
Indication ☻ CNS infections
Contraindication ☼ Contraindicated to patients with allergies to penicillins,
cepahlosporins.
Adverse Effects CNS: Headache, dizziness, thethargies, paresthesias
GI: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain,
flatulence, psuedomembranous colitis, liver toxicity
GU: Nephrotoxicity
Hematologic: bone marrow depression- decreased WBC,
decreased platelets, decrease Hct
Hypersensitivity: ranging from rash to fever to
anaphylaxis, serum sickness reaction
Local: Pain, abscess at injection site, phlebitis,
inflammation at IV site
Other: Superinfections, disulfiram-like reactions with
alcohol
Nursing Intervention ☻ Assess for liver and renal dysfunction
and Precautions ☻ Culture infection, and arrange sensitivity tests before
and during therapy if expected response is not seen.
Warning:
☻ Do not mix with aminoglycoside solutions, administer
these drugs separately.
☻ Powder and reconstituted solution darken with
storage.
☻ Have Vit. K available in case hypoprothrombinemia
occurs
☻ Discontinue if hypersensitivity occurs
☻ Teach SO that patients may experience upset stomach
or diarrhea but must report severe diarrhea, difficulty
breathing, fatigue, pain at injection site.
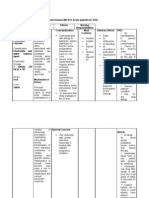
Generic name Sodium Bicarbonate
Brand name Sodium Bicarbonate Injection 4.2%
Classification Urinary alkalinizer, System alkalinizer, Electrolyte,
Antacid
Dosage Resuscitation: 2 mEq/kg IV over 3-5 minutes.
*Full correction of metabolic acidosis=Wt (kg) x Base
deficit (mEq/L) x 0.3 = mEq of HCO3. Give ½ of this dose.
Mechanism of Action ♥ Treats metabolic acidosis. Give slowly over several
hours for VLBW. Must have adequate ventilation. Do not
give in presence of hypercarbia.
Indication ☻Treatment of metabolic acidosis; promotion of gastric,
systemic, and urinary alkalinization; replacement therapy
in severe diarrhea; used to reduce incidence of chemical
phlebitis (used as neutralizing additive solution).
Contraindication ☼ Loss of chloride from vomiting or continuous GI suction
when patient is receiving diuretics known to produce
hypochloremic alkalosis; metabolic and respiratory
alkalosis; hypocalcemia in which alkalosis may produce
tetany, hypertension, convulsions, or CHF; when
administration of sodium could be clinically detrimental.
Adverse Effects
Cardiovascular
Exacerbation of CHF.
GI
Rebound hyperacidity; milk-alkali syndrome.
Lab Tests
Hypernatremia; alkalosis.
Miscellaneous
Extravasation with cellulitis, tissue necrosis, ulceration,
and sloughing; local pain; venous irritation; tetany;
edema.
Nursing Intervention • Instruct patient not to take medication with milk
and Precautions because renali calculi can develop.
• Explain need to avoid OTC medications
containing sodium bicarbonate, such as Alka-Seltzer
. Excessive use of sodium bicarbonate can result in
increase acid secretion or systemic alkalosis.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Animal Viruses and HumansDocument201 pagesAnimal Viruses and HumansPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- History of DohDocument3 pagesHistory of Dohleslie ann gaspar100% (2)
- HIV/AIDS Concept MapDocument1 pageHIV/AIDS Concept MapAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- PEMF Machine Destroys Parasitic InfectionsDocument2 pagesPEMF Machine Destroys Parasitic InfectionskjprnewsNo ratings yet
- Dietary Analysis ProjectDocument3 pagesDietary Analysis ProjectMichelle Davis0% (1)
- Drug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsLovely Saad TubañaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Marked Myelosuppression, Previous Treatment With Cumulative Doses ofDocument5 pagesMarked Myelosuppression, Previous Treatment With Cumulative Doses ofMac Mac100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- SpirometryDocument11 pagesSpirometryTrandafirulNegruNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocument17 pagesThyroid Disease in Pregnancydaniel100% (1)
- Compilation Drugstudy, NCP Cva (1) - BadetDocument14 pagesCompilation Drugstudy, NCP Cva (1) - BadetLizette Villanueva-UntalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (AFP)Document10 pagesDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CefuroximeLyana Stark92% (39)
- Backup NclexDocument61 pagesBackup NclexSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Celecoxib drug guideDocument10 pagesCelecoxib drug guidejessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument36 pagesDruggecalian100% (1)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument44 pagesDrug StudyLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNo ratings yet
- Imci Drug StudyDocument4 pagesImci Drug StudyDea Sabelle CastroNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- 8copd DrugtabncpDocument18 pages8copd DrugtabncpMaristelaMolinaNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocument5 pagesAmpicillin Drug StudyAna Mae ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeDocument5 pagesTreatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyJJASGHDocument7 pagesDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument8 pagesDrugsWinalyn PaderoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesMcDo DonatoNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin (: Drug ClassDocument8 pagesClindamycin (: Drug ClassWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin, Prednisone, Ciprofloxacin: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesAmoxicillin, Prednisone, Ciprofloxacin: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Classifi-Cation Action Indication / Uses Common Adverse Effects Contra-Indications Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesGeneric Name Classifi-Cation Action Indication / Uses Common Adverse Effects Contra-Indications Nursing ConsiderationsMe-joy CortezNo ratings yet
- GI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseDocument4 pagesGI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseNerissa Neri NatataNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsDocument5 pagesRanitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsAyanne ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyPrincess CavestaniNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Online AudioDocument4 pagesFurosemide: Online AudioDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- CloxacillinDocument3 pagesCloxacillinRoberto Manuel IINo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- GenericDocument4 pagesGenericGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter VDocument2 pagesChapter VGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Gel ADocument1 pageGel AGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Gel ADocument2 pagesGel AGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- NomerDocument2 pagesNomerGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Role of Yoga in Gastro-Intestinal Problems W.S.R. To Constipation (Vibandha) in GeriatricsDocument8 pagesRole of Yoga in Gastro-Intestinal Problems W.S.R. To Constipation (Vibandha) in GeriatricsPriyanka SinghviNo ratings yet
- Cefixime oral suspension SPC summaryDocument9 pagesCefixime oral suspension SPC summaryPharmacist ipsNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Immunity Deciphering An EnigmaDocument204 pagesThe Logic of Immunity Deciphering An EnigmaSatyabrataSahaNo ratings yet
- Nurses Guide 2010 WEBDocument290 pagesNurses Guide 2010 WEBSunita AbrahamNo ratings yet
- ArslanDocument11 pagesArslanHappy LadybugNo ratings yet
- Dental X-Ray ExamsDocument2 pagesDental X-Ray ExamsSara Loureiro da LuzNo ratings yet
- Intermittent FastingDocument13 pagesIntermittent FastingGina DeStefano RolfsmeierNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Impact of COVID-19 in India PDFDocument7 pagesThe Rise and Impact of COVID-19 in India PDFAryan MistryNo ratings yet
- Impact BariatricDocument8 pagesImpact BariatricHar YudhaNo ratings yet
- AKIN DİL Prepositions-AdverbsDocument15 pagesAKIN DİL Prepositions-AdverbsSerpil AyNo ratings yet
- Unit-X: Meeting Needs of PatientDocument16 pagesUnit-X: Meeting Needs of PatientMuneeswaran SmpNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia SDocument4 pagesThalassemia SShofa NisaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes INSIPIDUSDocument6 pagesDiabetes INSIPIDUSavinash dhameriya100% (1)
- Heart Disease in PregnancyDocument5 pagesHeart Disease in PregnancyAngeliqueNo ratings yet
- INQVESTDocument10 pagesINQVESTCruz Abigail C.No ratings yet
- Designed To Move Full ReportDocument142 pagesDesigned To Move Full ReportAktibiliNo ratings yet
- Thomas Bowers v. Carolyn Colvin, 4th Cir. (2015)Document10 pagesThomas Bowers v. Carolyn Colvin, 4th Cir. (2015)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Leptin, abdominal obesity and risk of depression onset in older menDocument15 pagesLeptin, abdominal obesity and risk of depression onset in older menandinitaaaNo ratings yet
- Neuropathology With Kartik Rangaraj MDDocument21 pagesNeuropathology With Kartik Rangaraj MDBen DjamaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument43 pagesPediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lateral Elbow PainDocument62 pagesChronic Lateral Elbow Painloopy100No ratings yet
- Why You Should Exercise - Persuasive SpeechDocument3 pagesWhy You Should Exercise - Persuasive Speechbrittbivins75% (4)
- Master of Science in Tropical and Infectious DiseasesDocument13 pagesMaster of Science in Tropical and Infectious DiseasesYalem ZewduNo ratings yet