Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry 1
Uploaded by
Sulaiman MohamadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry 1
Uploaded by
Sulaiman MohamadCopyright:
Available Formats
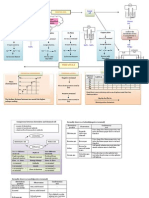
The process of BREAKING DOWN an electrolyte into CONSTITUENT ELEMENTS by passing ELECTRIC CURRENT through it.
E/plating
Iron ring Silver AgNO3 Electrode Half equation Products Observation Cathode (-) Ag+ + e Ag Ag Anode (+) Ag++ e
molten
ELECTROLYSIS
Silver atom Grey shiny solid deposited
Silver ions Anode become thinner
Electrolyte Purification Electrode Ions presence Moving of ions Half equation Products Observation Cathode (+) Anode (-) Br- , Pb2+ Br2BrBr2 + 2e Bromine gas Brown gas released Pb2+ Pb2+ + 2e Lead Pb Compound that CONDUCT ELECTRICITY in MOLTEN or AQUEOUS STATE undergoes CHEMICAL CHANGES CuSO Electrode Half equation Products Observation POSITION in ECS Carbon CONCENTRATION Cathode (-) Cu2+ + 2e Cu atom Brown solid deposited Cu Cu Anode (+) Cu2+ + 2e Impure Cu pure Cu
Grey solid formed
Aqueous
Cu2+ ion Anode become thinner
TYPE of ELECTRODE Carbon 1.0 mol dm-3 CuCl2 Cu electrode Cu electrode CuCl2 OH-, ClION PRESENCE MOVING OF ION half Equation (Selected ions to discharged) PRODUCT OBSERVATION
0.01 mol dm-3 CuCl2
Cu2+ , H+ Cathode
Position in E.C.S
Cu2+ , H+ Cathode
Position in E.C.S
ION PRESENCE MOVING OF ION
OH-, ClAnode
Position in E.C.S
Cu2+ , H+ Cathode
Position in E.C.S
ION PRESENCE MOVING OF ION half Equation (Selected ions to discharged) PRODUCT OBSERVATION
OH-, ClAnode Anode
Factor of Conc. Factor of electrode
Cu2+ + 2e Copper atom Brown solid deposited
Cu
half Equation (Selected ions to discharged) PRODUCT OBSERVATION
4OHO2 + 4e
2H2O +
Cu
Cu2+ + 2e
Cu2+ + 2e Copper atom Brown solid deposited
Cu
Cu2+ + 2e Copper atom Brown solid deposited
Cu
2Cl-
Cl2 + 2e
Oxygen gas Colourless gas released
Chlorine gas Greenish yellow gas released
Copper (II) ions Copper become thinner
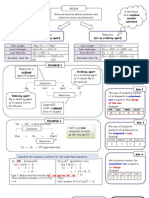
Blue colour of copper (II) chloride solution turn to colourless. Explain why? -Because concentration of Cu2+ ions decreases
Blue colour of copper (II) chloride solution turn to colourless. Explain why? -Because concentration of Cu2+ ions decreases
Blue colour of copper (II) chloride solution remain unchanged. Explain why ? because rate Cu2+ change to Cu is same with rate Cu change to Cu2+
Normally observe at Cathode in an electrolysis(negative terminal)
Abe Ki te
Electrolysis product
Observation Greenish yellow gas released
Confirmatory test Put a damp blue litmus paper into test tube, the litmus paper turn to red and bleach it Put a damp blue litmus paper into test tube, the litmus paper turn to red and bleach it Add starch solution into test tube, the starch solution turn to dark blue Put a glowing wooden splinter into test tube, the glowing wooden splinter will light up
Chlorine gas
e-
<
Ki te-
Bromine gas
Brown gas Brown (in aqeous)/purpe in gas Colourless gas released
Iodine
<
Oxygen gas
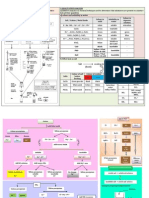
Comparison between electrolytic and chemical cell
-consist of electrolyte - consist of anode and cathode - electron flow from anode to cathode
similarities
Electrolytic cell Difference s Two or different electrode Used to produce chemical reaction Elect to chem. -ve terminal +ve terminal +ve terminal to ve terminal Made of Electric current Energy change Cathode Anode Flow of electron
Voltaic cell
Normally observe at anode in electrolysis (positive terminal) Electrolysis product Almost all metal (except Cu metal) Cu metal Observation Grey solid formed Brown solid formed Colourless gas released Confirmatory test Put a lighted wooden splinter into test tube, a pop sound is produced
Two different electrode Produced from chemical reaction Chem. To Elect +ve terminal -ve terminal -ve terminal to +ve terminal
Hydrogen gas
You might also like
- Tips Dan Ramalan SPM KIMIA 2011Document2 pagesTips Dan Ramalan SPM KIMIA 2011Sulaiman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Stage II Stage III: Sulphur Sulphur Dioxide Sulphur TrioxideDocument6 pagesStage II Stage III: Sulphur Sulphur Dioxide Sulphur TrioxideSulaiman Mohamad100% (1)
- A CidDocument3 pagesA CidSulaiman Mohamad100% (4)
- Simple Cell VOLTAIC CELL Daniel CellDocument2 pagesSimple Cell VOLTAIC CELL Daniel CellShamshul DidarellyNo ratings yet
- Salt 2Document3 pagesSalt 2Sulaiman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Formula KimiaDocument1 pageFormula KimiaShamshul DidarellyNo ratings yet
- State of Matter2Document2 pagesState of Matter2Sulaiman Mohamad100% (1)
- REDOX REACTIONSDocument3 pagesREDOX REACTIONSSulaiman Mohamad100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Data Sheet For BRASS SPECIFICATIONS PDFDocument5 pagesData Sheet For BRASS SPECIFICATIONS PDFvkmsNo ratings yet
- As 2738-2000Document29 pagesAs 2738-2000Sherry PorlayaganNo ratings yet
- Design in Brass: Properties and ApplicationsDocument16 pagesDesign in Brass: Properties and Applicationsjohn_progecoNo ratings yet
- Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination Heavy MetalsDocument11 pagesFlame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination Heavy MetalsSamir LimaNo ratings yet
- CHAP2 Bioavailability of Metals David Jhon LeventhalDocument9 pagesCHAP2 Bioavailability of Metals David Jhon LeventhalCrisThian PaucaNo ratings yet
- Product: ISO 9001:2008 Certified CompanyDocument5 pagesProduct: ISO 9001:2008 Certified CompanySharad KokateNo ratings yet
- Aalco Metals LTD Aluminium AlloyDocument2 pagesAalco Metals LTD Aluminium Alloyanwarali1975No ratings yet
- Cabletec Metal Braids Bonding Leads CatalogDocument28 pagesCabletec Metal Braids Bonding Leads CatalogРоман ДяченкоNo ratings yet
- Japanese Ind StandardsDocument4 pagesJapanese Ind Standardsemi_aeyNo ratings yet
- A Review of Solder Evolution in Electronic ApplicationDocument10 pagesA Review of Solder Evolution in Electronic ApplicationMasdio JoNo ratings yet
- Antamina 2010Document47 pagesAntamina 2010Roberto SalasNo ratings yet
- Copper GlycerolDocument7 pagesCopper Glycerolerem90No ratings yet
- Serge Lakhovsky CoilDocument2 pagesSerge Lakhovsky Coilandremdm2008No ratings yet
- Stoecker, John G. (Eds.) - A Practical Manual On Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, Volume 2 (2001, NACE International) PDFDocument280 pagesStoecker, John G. (Eds.) - A Practical Manual On Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, Volume 2 (2001, NACE International) PDFNatalia MagaquianNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Vs COPPERDocument4 pagesAluminum Vs COPPERTapi SkNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and PartnershipDocument2 pagesMixtures and Partnershipvijendra maurya0% (1)
- SD8B 4 Part2Document109 pagesSD8B 4 Part2Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Omega Product Price List PDFDocument10 pagesOmega Product Price List PDFVCNo ratings yet
- Mgps ManualDocument9 pagesMgps ManualMandeep Singh Kahlon100% (2)
- Ambient Air and Carbon DisulphideDocument2 pagesAmbient Air and Carbon DisulphideGopal MallickNo ratings yet
- TSA - Registrable Prospectus For Exposure DraftDocument435 pagesTSA - Registrable Prospectus For Exposure DraftmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolDocument4 pagesDiffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolhaydeeNo ratings yet
- Babbitt Metal: A Key Bearing MaterialDocument11 pagesBabbitt Metal: A Key Bearing MaterialMeghali BorleNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Organic Solvents For Extraction of Copper From Ammoniacal Carbonate Solution Hu2010Document6 pagesComparative Study of Organic Solvents For Extraction of Copper From Ammoniacal Carbonate Solution Hu2010mtanaydinNo ratings yet
- ASTM B88 - 1996 - Standard Specification For Seamless Copper Water TubeDocument14 pagesASTM B88 - 1996 - Standard Specification For Seamless Copper Water Tubefininho555100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Conductors and InsulatorsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Conductors and InsulatorsKeith yacoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Eng I 02 Dub BDocument318 pagesProperties of Eng I 02 Dub BspocajtNo ratings yet
- 266 - Sulphuric AcidDocument20 pages266 - Sulphuric AcidKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Properties and Uses of Zinc MetalDocument9 pagesProperties and Uses of Zinc Metalshahin azNo ratings yet
- Copper Nanoparticles: Synthetic Strategies, Properties and Multifunctional ApplicationDocument23 pagesCopper Nanoparticles: Synthetic Strategies, Properties and Multifunctional ApplicationardianNo ratings yet