Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C Example Programs
Uploaded by
Basit ShahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C Example Programs
Uploaded by
Basit ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
Computer Centre
Introduction to C.
C Example Programs
This document contains numerous example programs to provide a practical aid for learning C programming language.
Input and Output programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating the input and output functions. This program uses the scanf function.
#include <stdio.h> main() { float a , b , c; printf("Input two numbers... \n"); scanf("%f%f" , &a , &b); c = a*b; printf("%f times %f = %f\n" , a , b , c); }
This program combines printf and scanf whereby printf displays the input from scanf.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int i; printf("%c\n",scanf("%i",i)); }
This program demonstrates the use of getchar and putchar.
#include <stdio.h> main() { char ch; printf("Enter some text (type a period to quit)...\n"); do { ch = getchar(); putchar(ch+1); } while (ch != '.'); printf("\n\n"); printf("Enter some text (type a period to quit)...\n");
1 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
while ( (ch = getchar()) != '.') putchar(ch-1); printf("\n\n"); }
Control Loop programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating the loop construction. Program using char data type and simple for loop:
#include <stdio.h> /* library header */ main() { char ch; for (ch = 'A' ; ch <= 'z' ; ch++) printf("%c\n" , ch); }
This program demonstrates the while loop .
#include <stdio.h> main() { int lower , upper , step; float fahr , celsius; lower = 0 ; upper = 300; step = 20 ; fahr = lower; while ( fahr <= upper ) { celsius = (5.0 / 9.0) * (fahr - 32.0); printf("%4.0f %6.1f\n" , fahr , celsius); fahr = fahr + step; } }
This program uses do-while and for loop constructions and standard library mathematical functions.
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> main() { int i , j , k; double a=10.0 , b=.0; do { printf("%f\n" , pow(a,b)); /* standard function */ b++; } while (b<100); i = 2;
2 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
for (j=2 ; j<100 ; j=j+2) { i=i*j ; printf("%d\n" , i); } }
Conditional Execution programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating if else and select statements (also break and continue statements). This program demonstrates the if else statement.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int a , b; printf("Enter two numbers: "); scanf("%d%d" , &a , &b); if (b) printf("%d\n" , a/b); else printf("... cannot divide by zero\n"); }
Another example of if else statement.
#include <stdio> #include <conio> main() { int a,b; char ch; printf("Do you want to: \n"); printf"Add, subtract, Multiply, or Divide?\n"); /* force user to enter valid response */ do { printf("Enter first letter: "); ch=getchar(); printf("\n"); } while (ch!='A' && ch!='S' && ch!='M' printf("Enter first number: "); scanf("%d", &a); printf("Enter second number: "); scanf("%d", &b); if (ch=='A') printf("%d", a+b); else if (ch=='S') printf("%d", a-b); else if (ch=='M') printf("%d", a*b); else if (ch=='D' && b!=0) printf("%d", a/b); }
&& ch!='D');
The switch statement is often used to process menu commands.
#include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h>
3 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
main() { int a,b; char ch; printf("Do you want to:\n"); printf("Add, Subtract, Multipy, or Divide\n"); /* force user to enter valid response */ do ( printf("Enter first letter: "); ch =getchar(); printf("\n"); } while (ch!='A' && ch!='S' && ch!='M' && ch!='D'); printf("Enter first number: "); scanf("%d", &a); printf("Enter second number: "); scanf("%d", &b); switch (ch) { case 'A' : printf("%d", a+b); break; case 'S' : printf("%d", a-b); break; case 'M' : printf("%d", a*b); break; case 'D' : if (b!=0) printf("%d", a/b); break; } }
The statement sequence associated with a case may be empty allowing two or more cases to share a common statement sequence.
#include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> main() { char ch; printf("Enter the letter: "); ch=getchar(); switch(ch) { case 'a' : case 'e' : case 'i' : case 'o' : case 'u' : printf(" is a vowel \n"); break; default: printf(" is a consonant"); } }
A simple program to show the use of the continue statement.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int x ;
4 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
for ( x=0 ; x<=100 ; x++) { if (x%2) continue; /* using modulus operation */ printf("%d\n" , x); }
This program jumps out of an infinite loop using the break statement.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int t ; for ( ; ; ) { scanf("%d" , &t) ; if ( t==10 ) break ; } printf("End of an infinite loop...\n"); }
Structure and Nesting programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating nested block structures. This program uses nested for loop construction.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int i , j; for (i=2 ; i<1000 ; i++) { for (j=2 ; j<= i/2 ; j++) if (!(i%j)) break; if (j>i/2) printf("%d is a prime\n" , i); } }
This example program uses a do-while and nested if else construction.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int a , b; do { printf("Enter first number: "); scanf("%d" , &a); printf("Enter second number: "); scanf("%d" , &b); if (a<b) printf("First number is less than second\n\n"); if (b<a) printf("Second number is less than first\n\n");
5 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
} while (a < 999); }
This program uses nested for loop and if else construction.
#include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> main() { int answer, count, chances, right; for (count=1; count<11; count++) { printf("What is %d + %d?", count, count); scanf("%d", &answer); if (answer == count+count) printf("Right!\n"); else { printf("Sorry, you're wrong \n"); printf("Try again\n"); right = 0; /* nested for *? for (chances=0; chances<3 && ! right; chances++){ printf("\nWhat is %d + %d?",count, count); scanf("%d", &answer); if (answer == count+count){ printf("Right!\n"); right=1; } } /* if answer still wrong, tell user */ if (!right) printf("the answer is %d.\n", count+count); } /* end of else part */ } /* end of outter for loop */ }
Functions and Prototype programs
This section contains example programs to demonstrate the use of functions. This is a program to demonstrate the use of functions 1. with no parameters 2. with parameters
#include <stdio.h> main() { int number; prompt(); /*function call no parameters */ scanf( "%d" , &number ); factor(number); /* function call with parameters */ } prompt() /* function */ { printf("Input a number... "); }
6 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
factor(int t) /* function */ { int sum = 1; int i ; for (i = 1 ; i <= t ; i++) sum = sum*i; printf("Factorial %d is %d\n" , t , sum); }
Here is a volume computing program using a function prototype.
#include <stdio.h> /* this is volume()'s prototype */ double volume(double s1, double s2, double s3); void main() { double vol; vol = volume(12.2, 5.67. 9.03); printf("Volume: %f", vol); } /* compute the volume of a cube. */ double volume(double s1, doublbe s2, double s3) { return s1*s2*s3; }
Recursion when applied to a computer language means that a function can call itself. An example follows:
#include <stdio.h> void recurse(int i); void main(void) { recurse(0); } void recurse(int i) { if (i<10) { recurse(i+1); printf("%d ",i); } }
This program prints
9876543210
on the screen.
Array programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating the use of arrays. A simple program to demonstrate the definition and use of an array.
7 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
#include <stdio.h> main() { int i[10],j; for ( j=0 ; j<10 ; j++) i[j] = j ; for ( j=0 ; j<10 ; j++) printf("%d\n" , i[j]) ; }
A program to demonstrate the use of an array.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> main() { int i , min_value , max_value ; int list[10] ; for ( i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) list[i] = rand() ; /* Find the minimum value */ min_value = 32767 ; for ( i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) if (list[i]<min_value) min_value=list[i] ; printf("Minimum value generated is %d\n" , min_value) ; /* Find the maximum value */ max_value = 0 ; for ( i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) if (list[i]>max_value) max_value=list[i]; printf("Maximum value generated is %d\n" , max_value) ; }
This program uses a bubble sort.
#include <stdio.h> include <stdlib.h> main() { int item[100]; int a,b,t; int count; /* read in numbers */ printf("How many numbers ?"); scanf("%d", &count); for (a=0;a<count;a++) scanf("%d", &item[a]); /* now sort using bubble sort */
8 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
for (a=1; a<count; a++) for (b=count-1; b>=a; --b) { /* compare adjacent elements */ if (item[b-1] > item[b]) { /* exchange elements */ t= item[b-1]; item[b-1] - item[b]; item[b] = t; } } /* display sorted list */ for (t=0; t<count; t++) printf("%d ", item[t]); }
An example program using a two-dimensional array now follows.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int twod[4][5]; int i,j; for(i=0; i<4; i++) for(j=0; j<5; j++) twod[i][j] = i*j; for (i=0; i<4; i++) { for (j=0; j<5; j++) printf("%d !, twod[i][j]); printf("\n"); } }
The program output looks like this:
00000 01234 02468 036912
Pointer programs
This section contains example programs demonstrating the use of pointers. An example program using simple pointers.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int balance; int *address; int value; balance = 5000; address = &balance; value = *address; printf("Balance is : %d\n" , value); }
9 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
Another example using pointers.
#include <stdio.h> main() { int *p , num; p = # *p = 100; printf("%d\n" , num); (*p)++; printf("%d\n" , num); (*p)--; printf("%d\n" , num); }
An example program demonstrating pointer Arithmetic.
#include <stdio.h> main() { char *c , ch[10]; int *i , j[10]; float *f , g[10]; int x; c = ch; i = j; f = g; for ( x=0 ; x<10 ; x++ ) printf("%p %p %p\n" , c+x , i+x , f+x); }
An example program using pointers and arrays.
#include <stdio.h> main() { char str[80]; char token[10]; char *p , *q; printf("Enter a sentence: "); gets(str); p = str; while (*p) { q = token; while (*p != ' ' && *p) { *q = *p; q++ ; p++; } if (*p) p++; *q = '\0';
10 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
printf("%s\n" , token); } }
String programs
This section contains example programs to demonstrate the use of strings. A simple string example.
#include <stdio.h> main() { char str[80] ; printf("Enter a string: ") ; gets(str) ; printf("%s" , str); printf("\n"); }
The follow program requests the input of two strings, then demonstrates the four string functions with them.
#include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> main() { char str1[80], str2[80]; int i; printf("Enter the first string: "); getstr(str1); printf("Enter the second string: "); getstr(str2); /* see how long the strings are */ printf("%s is %d chars long\n", str1, strlen(str1)); printf("%s is %d chars long\n", str2, strlen(str2)); /* compare the strings */ i= strcmp(str1, str2); if (!i) printf("The strings are equal.\n"); else if (i<0) printf ("%s is less than %s\n", str1,str2); else printf("%s is greater than %s\n", str1, str2); /* concatenate str2 to end of str1 if there is enough room*/ if (strlen(str1)+ strlen(str2) < 80) { strcat(str1, str2); printf("%s\n", str1); } /* copy str2 to str1 */ strcpy(str1, str1); printf("%s %s\n", str1, str2); }
Structure programs
11 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
This section contains example programs to demonstrate the use of structures. This program stores data in a structure and displays the values.
#include <stdio.h> void main(void) { struct s_type { int i; int j; } s; int i; i=10; s.i=100; s.j=101; printf("%d %d %d", i, s.i, s.j); }
The variable i and the structure element i have no relationship to each other. A function may return a structure to the calling procedure.
#include <stdio.h> struct s_type { int i; double d; } var1; struct s-type f(void); void main(void) { var1=f(); printf("%d %1f", var1.i, var1.d); } struct s_type f(void) { struct s_type temp; temp.i=100; temp.d = 123.23; return temp; }
This program passes a structure to a function.
#include <stdio.h> struct s_type { int i; double d; } var1; void f(struct s_type temp);
12 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
void main(void) { var1.i=99; var1.d = 98.6; f(var1); } void f(struct s_type temp) { printf("%d %1f", temp.i, temp.d); }
The following program illustrates how to use a pointer to a structure.
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> strct s_type { int i; char str[80]; } s, *p; void main(void) { p= &s; s.i = 10; /* this is functionally the same */ p ->i=10; /* as this */ strcpy(p->str, "I like structures"); printf("%d %d %s", s.i, p->1, p->str); }
File Handling programs
This section contains programs demonstrating file handling and command line arguments. The following program reads a text file and counts how many times each letter from 'A' to 'Z' occurs and displays the results.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib> #include <ctype.h> int count[26]; void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { FILE *fp; char ch; int i; /* see if file name is specified */ if (argc!=2) { printf("File name missing"); exit(1); } if ((fp= fopen(agv[1], "r")) == NULL) { printf("cannot open file"); exit(1);
13 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
} while ((ch=fgetchar(fp)) !=EOF) { ch = toupper(ch); if (ch>='A' && ch<='Z') count[ch-'A']++; } for (i=0; i<26; i++) printf("%c occurred %d times\n", i+'A', count[i]); fclose(fp); }
This program uses command line arguments to read and display the contents of a file supplied as an argument.
#include <stdio.h> #define CLEARS 12 /* constant */ main(int argc , char *argv[]) { FILE *fp , *fopen(); int c; putchar(CLEARS); while ( --argc > 0 ) if ((fp=fopen(argv[1], "r"))==NULL) { printf("I can't open %s\n", argv[1]); break; } else { while ((c= getc(fp)) !=EOF) putc(c,stdout); /* display to the screen */ fclose(fp); } }
This program gives a further example of the use of argc & argv
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> main(int argc , char *argv[]) { double a , b; if (argc != 3) { printf("Usage: add number number ...\n"); exit(1); } a = atof(argv[1]); b = atof(argv[2]); printf("%lf\n" , a + b); }
Complex programs combining sections
14 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
This example program creates and accesses a simple database.
/**********************************************************/ /* A simple Data Base Program */ /**********************************************************/ # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <string.h> # define MAX 100 /* constant*/ struct addr { /*struct called list*/ char name[30] ; char street[40] ; char town[20] ; char county[20] ; char code[10] ; } list[MAX]; /* 100 records*/ main() { int choice; init_list(); /* initialze the list */
for(;;) { choice = menu_select(); /* get user's selection*/ case 1: enter(); /* enter a new entry */ break; case 2: del(); /* delete an entry */ break; case 3: show_list(); /* display the list */ break; case 4: search(); /* find an entry */ break; case 5: save(); /* save to disk */ break; case 6: load(); /* read from disk */ break; case 7: exit(0); } } } /*********************************************************/ /* Function del */ /*********************************************************/ del() { int i; char str[255]; inputs("enter name: " , str , 30); i = find(str); if (i>=0) *list[i].name = '\0' ; else printf("not found\n") ; }
switch(choice) {
/**********************************************************/ /* Function display */ /**********************************************************/ display(int i) {
15 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
printf("%s\n" , list[i].name); printf("%s\n" , list[i].street); printf("%s\n" , list[i].town); printf("%s\n" , list[i].county); printf("%s\n" , list[i].code); } /**********************************************************/ /* Function enter */ /**********************************************************/ enter() { int i; for(;;) { i = find_free(); /* find a free structure */ if(i<0) { printf("list full\n"); return; } inputs("enter name: ", list[i].name,30); if(!*list[i].name) break; inputs("enter street: ", list[i].street, 40); inputs("enter town: ", list[i].town, 20); inputs("enter county: ", list[i].county, 20); inputs("enter Postal code: ", list[i].code, 10); } } /**********************************************************/ /* Function find */ /**********************************************************/ find(char *name) { int i; for(i=0 ; i<MAX ; i++) if(!strcmp(name ,list[i].name)) break; if(i==MAX) return else return i; } /**********************************************************/ /* Function find_free */ /**********************************************************/ find_free() { register int i; for(i=0; i<MAX; i++) if(!*list[i].name) return i; return } /**********************************************************/ /* Function init_list */ /**********************************************************/ init_list() { register int i; for (i=0 ; i<MAX ; i++) *list[i].name = '\0' } /**********************************************************/ /* Function inputs */ /**********************************************************/ inputs( char *prompt , char *s , int count) {
/* stop entering */
16 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
char str[255]; do { printf(prompt); gets(str); if(strlen(str) 1; 1; ;>=count) printf("\ntoo long\n"); } while(strlen(str)>=count); strcpy(s , str); } /**********************************************************/ /* Function load */ /**********************************************************/ load() { FILE *fp; if ( (fp=fopen("mlist" , "rb")) == NULL) { printf("cannot open file\n"); return; } printf("\nloading file\n"); fread(list , sizeof list , 1 , fp); if (ferror(fp)) printf("An error occurred while reading file.\n"); fclose(fp); } /**********************************************************/ /* Function menu_select */ /**********************************************************/ menu_select() { char s[80]; int c; printf("1. Enter a name\n") ; printf("2. Delete a name\n") ; printf("3. List the File \n"); printf("4. Search\n") ; printf("5. Save the file\n") ; printf("6. Load the file\n") ; printf("7. Quit\n") ; do { printf("\nEnter your choice: "); gets(s); c = atoi(s); } while(c<0 || c>7); return c; } /**********************************************************/ /* Function save */ /**********************************************************/ save() { FILE *fp; if ( (fp=fopen("mlist" , "wb")) == NULL) { printf("cannot open file\n"); return; } printf("\nsaving file\n");
17 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
fwrite(list , sizeof list , 1 , fp); if (ferror(fp)) printf("An error occurred while writing file.\n"); fclose(fp); } /**********************************************************/ /* Function search */ /**********************************************************/ search() { int i; char name[30]; inputs("enter name to find: " , name , 30); if ((i=find(name))<0) printf("not found\n"); else display(i); } /**********************************************************/ /* Function show_list */ /**********************************************************/ show_list() { int i; for(i=0 ; i<MAX ; i++) { if(*list[i].name) { display(i); printf("\n\n"); } } printf("\n\n"); }
[program] The second example program uses functions to play a simple game of tic tac toe.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> char matrix[3][3]; main() { char done; printf("This is the game of tic tac toe...\n"); printf("You will be playing against the computer.\n") ; done = ' '; init_matrix(); do { disp_matrix(); get_player_move(); done = check(); if (done != ' ') break; get_computer_move(); done = check();
18 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
} while (done == ' '); if (done == 'X') printf("\n\nYou won!!!\n"); else printf("I won!!!\n"); disp_matrix(); } /**********************************************************/ /* fuction to initialise matrix */ /**********************************************************/ init_matrix() { int i , j ; for (i=0 ; i<3 ; i++) for (j=0 ; j<3 ; j++) matrix[i][j] = ' '; } /**********************************************************/ /* fuction to get players move */ /**********************************************************/ get_player_move() { int x , y ; printf("Enter coordinates of your X: "); scanf("%d%d" , &x , &y); x--; y--; if (matrix[x][y] != ' ') { printf("Invalid move, try again...\n"); get_player_move(); } else matrix[x][y] = 'X'; } /**********************************************************/ /* fuction to get computer move */ /**********************************************************/ get_computer_move() { int i , j ; for (i=0 ; i<3 ; i++) { for (j=0 ; j<3 ; j++) if(matrix[i][j]==' ') break; if (matrix[i][j] == ' ') break; } if (i*j == 9) { printf("draw....\n"); exit(0); } else matrix[i][j] = 'O'; } /**********************************************************/ /* fuction to display matrix */ /**********************************************************/ disp_matrix() { int t ; printf(" 1 2 3\n");
19 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
Introduction to C Programming: Computer Centre: University of Leicester
file:///C:/Documents%20and%20Settings/Alberto/Mis%20documentos/...
for (t=0 ; t<3 ; t++) { printf(" %c | %c | %c %d" , matrix[t][0], matrix[t][1], matrix[t][2] , t+1); if (t!=2) printf("\n---|---|---\n"); } printf("\n"); } /**********************************************************/ /* fuction to check matrix */ /**********************************************************/ check() { int i ; for (i=0 ; i<3 ; i++) if(matrix[i][0] == matrix[i][1] && matrix[i][0] == return matrix[i][0]; for (i=0 ; i<3 ; i++) if(matrix[0][i] == matrix[1][i] && matrix[0][i] == return matrix[0][i]; if(matrix[0][0] == matrix[1][1] && matrix[1][1] == return matrix[0][0]; if(matrix[0][2] == matrix[1][1] && matrix[1][1] == return matrix[0][2]; return ' '; } [program]
matrix[i][2])
matrix[2][i])
matrix[2][2])
matrix[2][0])
Back
Continue
Information Suppliers: Richard Mobbs, Head of Learning Technology, University of Leicester, Computer Centre
Marina Carter, Postgraduate Student, Loughborough University.
Last updated: 09 July 2001 09:59 Document owner: University CWIS Maintainer Computer Centre Web maintainer
20 de 20
16/03/2006 12:53 p.m.
You might also like
- C Programming Solution For Class 12 PDFDocument29 pagesC Programming Solution For Class 12 PDFdipeshc04574% (23)
- C CodesDocument130 pagesC CodesDevi SinghNo ratings yet
- RATS - Rough Auditing Tool For SecurityDocument9 pagesRATS - Rough Auditing Tool For SecuritySuPY87No ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument12 pagesC ProgrammingAshraf Bin AlamNo ratings yet
- C Programming NoteDocument8 pagesC Programming NoteAshraf Bin AlamNo ratings yet
- Simple ProgramDocument14 pagesSimple ProgramshwetaNo ratings yet
- 15-BISE Lahore - C Language Practicals-StudentNotesDocument6 pages15-BISE Lahore - C Language Practicals-StudentNotesadilNo ratings yet
- CC 02 PythonDocument23 pagesCC 02 PythonayoubNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: A Tutorial Introduction Chapter 1: A Tutorial IntroductionDocument17 pagesChapter 1: A Tutorial Introduction Chapter 1: A Tutorial Introductionswh601No ratings yet
- C Programming Lab ProgramsDocument39 pagesC Programming Lab Programsans_h2003No ratings yet
- C Programs ExampleDocument7 pagesC Programs ExampleEunice CameroNo ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument27 pagesHello WorldSwadesh KumarNo ratings yet
- C Programming Logics1Document109 pagesC Programming Logics1sam_003No ratings yet
- PPS Unit 2 LaqsDocument20 pagesPPS Unit 2 Laqssanju83285No ratings yet
- CP Manual PDFDocument79 pagesCP Manual PDFsatyam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Rdinaz PDFDocument18 pagesRdinaz PDFvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- 2 SequenceDocument14 pages2 SequencelaltejaNo ratings yet
- C Example Programs: Input and Output ProgramsDocument21 pagesC Example Programs: Input and Output Programsbsr987No ratings yet
- Swap Number Using Third Variable: 1. Write A Program That Swaps Two Numbers With and Without Using Third VariableDocument95 pagesSwap Number Using Third Variable: 1. Write A Program That Swaps Two Numbers With and Without Using Third VariablevaishaliNo ratings yet
- All C ProgrammingTutorialsDocument26 pagesAll C ProgrammingTutorialsRislan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Practical Programs 1. Write A Program To Find The Largest of Three Numbers Using If and Conditional OperatorDocument16 pagesPractical Programs 1. Write A Program To Find The Largest of Three Numbers Using If and Conditional OperatorComputer DepartmentNo ratings yet
- C RecordDocument28 pagesC RecordDragu StelianNo ratings yet
- Programming AssignmentDocument27 pagesProgramming Assignments.mohaiminmahinNo ratings yet
- MABRAS - TechM216 - MIDTERM - TAUTHODocument4 pagesMABRAS - TechM216 - MIDTERM - TAUTHOEdy Halen L. TauthoNo ratings yet
- C Language Lab ManualDocument35 pagesC Language Lab ManualSiddhartha KancharlaNo ratings yet
- 50 C ProgramDocument12 pages50 C ProgramSasi PlacementsNo ratings yet
- C Programs 2016Document24 pagesC Programs 2016Fresh EpicNo ratings yet
- CS AbstractDocument61 pagesCS AbstractSudip BiswasNo ratings yet
- C Second SemDocument73 pagesC Second SemAshwin JagtapNo ratings yet
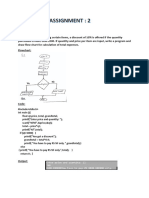
- Write An Algorithm and Draw Corresponding Flowchart To Calculate The Factorial of A Given NumberDocument33 pagesWrite An Algorithm and Draw Corresponding Flowchart To Calculate The Factorial of A Given NumberjitheshpimsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CPDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 CPlokeshjoshimjNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument45 pagesC ProgramsNEERNo ratings yet
- C ProgramDocument16 pagesC ProgramMunavalli Matt K SNo ratings yet
- 5th ChapterDocument4 pages5th ChapterFahim AhammedNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument10 pagesC ProgramsBrensa Rumao100% (1)
- Homework Loops 3Document6 pagesHomework Loops 3Avishek RauniyarNo ratings yet
- #Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DDocument22 pages#Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DChinnaraoNo ratings yet
- Program 1: Te A Program To Implement BisecDocument24 pagesProgram 1: Te A Program To Implement BisecAnshumanSrivastavNo ratings yet
- two-Dimensional Arays in CDocument4 pagestwo-Dimensional Arays in CV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- List of Small ProgrammesDocument17 pagesList of Small ProgrammesSwapnil BorseNo ratings yet
- Eee 152Document35 pagesEee 152rushoeeeNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming or C ProgrammingDocument8 pagesComputer Programming or C ProgrammingDoinik DorkarNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise For C ProgrammingDocument51 pagesLab Exercise For C ProgrammingAhmed NUR HUSIEN100% (1)
- 24) Explain About Strings With Program?: 1 G Viswanath, M.Tech, (PH.D), Associate Professor, Vemu Institute of TechnologyDocument5 pages24) Explain About Strings With Program?: 1 G Viswanath, M.Tech, (PH.D), Associate Professor, Vemu Institute of TechnologyMusic TweetsNo ratings yet
- Rohini 66913029385Document7 pagesRohini 66913029385r10797335No ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Docx Prog FundaDocument10 pagesLab Manual - Docx Prog FundaMemona LatifNo ratings yet
- Practical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Document15 pagesPractical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Vaibhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Write First Program: Compile F9 Execute or Press CRT+F9Document7 pagesWrite First Program: Compile F9 Execute or Press CRT+F9m.umair iftikharNo ratings yet
- 25 Programs of C-1Document31 pages25 Programs of C-1Azeem026No ratings yet
- Programs C Programming Engineering NotesDocument18 pagesPrograms C Programming Engineering NotesPurushotham DNo ratings yet
- Document From Ali ShahzadDocument6 pagesDocument From Ali ShahzadAli ShahzadNo ratings yet
- CS6212 PDS Lab Manual CSE 2013 RegulationsDocument52 pagesCS6212 PDS Lab Manual CSE 2013 RegulationsheyramzzNo ratings yet
- C Programming Lab ManualDocument9 pagesC Programming Lab Manualharshagowda0464No ratings yet
- C Program Practical FileDocument36 pagesC Program Practical FileSukhchain Singh100% (2)
- UNIX Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandUNIX Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- TCS NQT Model Programming/ Coding Questions PaperDocument7 pagesTCS NQT Model Programming/ Coding Questions PaperAnant SirsathNo ratings yet
- NINE Triangle Programs in C Language - SharadKguptaDocument12 pagesNINE Triangle Programs in C Language - SharadKguptasharadkumarguptaNo ratings yet
- Array and StringsDocument4 pagesArray and StringstovilasNo ratings yet
- Operator Quiz AnswersDocument21 pagesOperator Quiz AnswersWycliffe MwebiNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming MSWDocument5 pagesComputer Programming MSWanani samsonNo ratings yet
- FOP Practice FinalDocument155 pagesFOP Practice FinaljolieprincesseishimweNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 ArraysDocument26 pagesChapter7 Arrayshisham_eyesNo ratings yet
- 100 CodesDocument56 pages100 CodesWajiha TanveerNo ratings yet
- Zoho Based Basics Code QuestionsDocument20 pagesZoho Based Basics Code QuestionsPrathiksha SNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document19 pagesSet 1fffffNo ratings yet
- C, C++ Lab PracticalDocument27 pagesC, C++ Lab Practicalsantanu mahalaNo ratings yet
- C Mcq-Unit-IDocument91 pagesC Mcq-Unit-Igdeepthi100% (1)
- Theory About Data Input and Output in C ProgrammingDocument6 pagesTheory About Data Input and Output in C ProgrammingVinod DewaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - 221012 - 095918Document35 pagesLab 4 - 221012 - 095918Mihai LipcanNo ratings yet
- CCS - Embedded C Language For PICDocument44 pagesCCS - Embedded C Language For PICandrewssobral100% (2)
- Linux Objdump Command Examples (Disassemble A Binary File) : Home Free Ebook Start Here Contact AboutDocument17 pagesLinux Objdump Command Examples (Disassemble A Binary File) : Home Free Ebook Start Here Contact AboutttbaghNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Reference CardDocument2 pagesMATLAB Reference CardAkshar MeherNo ratings yet
- Samsung Interview ExpDocument18 pagesSamsung Interview ExpMohit SinghNo ratings yet
- CF Chap2 Engineering Fe Mcq'sDocument54 pagesCF Chap2 Engineering Fe Mcq'scutyverma100% (2)
- B.Tech. Mech. Practical File QuestionsDocument11 pagesB.Tech. Mech. Practical File QuestionskunalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2RjoNo ratings yet
- CS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Section NotesDocument9 pagesCS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Section NotesDevendra KumarNo ratings yet
- C Programming Assignment PDFDocument12 pagesC Programming Assignment PDFPritam Chatterjee0% (1)
- Origin CDocument110 pagesOrigin CmetalnonmetalNo ratings yet
- Learn C The Hard Way-1Document15 pagesLearn C The Hard Way-1ajith1990No ratings yet
- BCA T112C Language Question BankDocument5 pagesBCA T112C Language Question BankkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Technical 2Document46 pagesTechnical 2PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473No ratings yet
- SPDocument39 pagesSPKavita GohelNo ratings yet