Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are Leaf Scars For
Uploaded by
John Christian RubinoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are Leaf Scars For
Uploaded by
John Christian RubinoCopyright:
Available Formats
What are Leaf Scars for A leaf scar is the area left behind when a leaf breaks free
from a stem or a branch. When aleaf falls from a tree, the petiole softens and the leaf breaks free and falls. The petiole is the part of the leaf that connects it to the stem or branch of the plant. At the time the petiole breaks free, it severs all of the vessels through which food and water travel. After breaking free from the plant, the small area on the stem that is left open heals over and leaves a distinctive mark. This mark is easy to spot, as it is normally lighter than the stem. The mark is also speckled with dots which are located where the vessels used to be connected. These vessels are grouped together in clusters called bundle scars. Both the leaf scar and the bundle scars within are very useful for identifying plant species during the winter months. What are the small pores found in the leaf scars?
Buds
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of the stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots, or may have the potential for general shoot development. The term bud is also used in zoology, where it refers to an outgrowth from the body which can develop into a new individual.
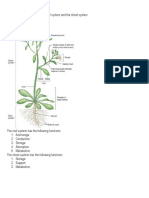
Lower part Petiole
Arrangement of vascular bundle
Stem vascular bundles in a ring Herb
An herb (US qualities.
[3]
/rb/ or UK /hb/)
[1][2]
is a plant that is valued for flavor, scent, medicinal or other
Herbs are used in cooking, as medicines, and for spiritual purposes.
Xylem and phloem as complex tissue
Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells and they work together as a unit. They transport water, salt and prepared food material to various parts of the plant body Aspect diff of woody and herbaceous
However, the amount of primary xylem, vascular cambium, and primary phloem is greater, and they form a complete cylinder
Twigs
first of all twigs are refered only for stems wich are just days old.after 2 years they form branches.after 2 years in a woody branch we can find both primary and secondary growth.
Tree killing Bark is the outermost layer of trees and other woody plants. It serves to protect the living tissues of the plant. Cutting the bark can damage these tissues. If damage is extensive, it may kill the tree monocots Have no vascular cambium Fleshy leaves
The fleshy leaves store food and water Function of underground stem
1) Perennation- to tied over unfavourable period. 2) Storage of food- food stored is edible. 3) Vegetative reproduction- new plants are being produced from underground stem herbaceous
2) Green Woody Woody,
You might also like
- Sample Chapter 1-3 - Quantitative StudyDocument18 pagesSample Chapter 1-3 - Quantitative StudySerc YablaNo ratings yet
- SiP ExeDocument8 pagesSiP ExeJomari Villadelrey100% (1)
- Pedroso - Edited FileDocument5 pagesPedroso - Edited FileHannah Jane Estorpe SibongaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Topic 4 STSDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Topic 4 STSRachell AvecillaNo ratings yet
- History Ilocos NorteDocument2 pagesHistory Ilocos NortepedroNo ratings yet
- Lagundi (Vitex Negundo, L) As Reviewed by The USA FDA in 2002Document39 pagesLagundi (Vitex Negundo, L) As Reviewed by The USA FDA in 2002BlogWatch50% (2)
- 1.1 History of Nursing TheoryDocument4 pages1.1 History of Nursing TheoryCharlette Mae Guadalupe (SHS)No ratings yet
- Nursing as an Academic DisciplineDocument20 pagesNursing as an Academic DisciplineJules Antonette RNNo ratings yet
- Applications - Denaturation PDFDocument2 pagesApplications - Denaturation PDFeleaphoebe16No ratings yet
- NCM 100Document11 pagesNCM 100rimeoznekNo ratings yet
- GE2 (RPH) Learning Module - WEEK 3 PDFDocument16 pagesGE2 (RPH) Learning Module - WEEK 3 PDFvia cubalNo ratings yet
- Health Education Module 1 YrDocument7 pagesHealth Education Module 1 YrKhloe Nicole AquinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Health EthicsDocument1 pageCase Study Health EthicsnellRQNANo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument71 pagesMetabolismBabylyn Austria100% (1)
- P.A. 1Document6 pagesP.A. 1SamSarah BongolanNo ratings yet
- Sas#16-Gen 005Document10 pagesSas#16-Gen 005Ave Gale Canada100% (1)
- TFN 1st NOTESDocument9 pagesTFN 1st NOTESPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- CU 11. Ethico Moral and Legal Foundations of Client EducationDocument5 pagesCU 11. Ethico Moral and Legal Foundations of Client Educationcloe blancaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice-Rle A. Environmental CleaningDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice-Rle A. Environmental CleaningViea Pacaco SivaNo ratings yet
- (Ha Lab) Sas#9Document9 pages(Ha Lab) Sas#9Erwin RomeroNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication: General Education DepartmentDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication: General Education DepartmentWhitney AcostaNo ratings yet
- Ex 8 Chem RepDocument17 pagesEx 8 Chem RepNicoleNo ratings yet
- Open Gloving With RationaleDocument2 pagesOpen Gloving With RationaleSean Rene DuayNo ratings yet
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- HEALTH ASSESSMENT OVERVIEWDocument72 pagesHEALTH ASSESSMENT OVERVIEWSM CervantesNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija Doctors Hospital PracticumDocument10 pagesNueva Ecija Doctors Hospital PracticumsoftenNo ratings yet
- Film AnalysisDocument1 pageFilm AnalysisNicoleFabrosNo ratings yet
- Script For TSB GRDDocument9 pagesScript For TSB GRDJuvel OrquinazaNo ratings yet
- Vasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1Document6 pagesVasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1PagodNo ratings yet
- Lydia HallDocument5 pagesLydia Hallbbasya eihyna100% (5)
- Exam - Philo 2Document15 pagesExam - Philo 2Jeffry VargasNo ratings yet
- CWTS - Livelihood Project PlanDocument2 pagesCWTS - Livelihood Project PlanKaye BaguilodNo ratings yet
- Sister Letty KuanDocument21 pagesSister Letty KuanMark Norriel CajandabNo ratings yet
- Aqua CinnamomiDocument1 pageAqua CinnamomiAndrea SantiaNo ratings yet
- Nicholas E Davies Award of Excellence Organizational)Document4 pagesNicholas E Davies Award of Excellence Organizational)Lohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNo ratings yet
- 7.) Review of Related LiteratureDocument7 pages7.) Review of Related LiteratureJayson BanalNo ratings yet
- Common Abbreviations Used in RXDocument3 pagesCommon Abbreviations Used in RXArrabellaNo ratings yet
- TFNDocument12 pagesTFNMardina A AbdulmaulaNo ratings yet
- A List of Protein Deficiency DiseasesDocument2 pagesA List of Protein Deficiency DiseasesJoseph Uday Kiran MekalaNo ratings yet
- Katie Ericksson's Metaparadigms of NursingDocument3 pagesKatie Ericksson's Metaparadigms of NursingAllyson Duy AngcosNo ratings yet
- 10 Helpful Ways To Get Away From AngerDocument2 pages10 Helpful Ways To Get Away From AngerMary Anne Rocafor NaelgasNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Assessment FindingsDocument4 pagesHead and Neck Assessment FindingsCiara Manguiat100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Effective Communication 2Document9 pagesLesson 1 Effective Communication 2ddddddaaaaeeeeNo ratings yet
- Health Education Plan For PTBDocument2 pagesHealth Education Plan For PTBSheena ClaireNo ratings yet
- 10 Herbal MedicineDocument5 pages10 Herbal MedicineJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- The Nurse As An EducatorDocument4 pagesThe Nurse As An EducatorAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Spanish Chapter 3Document3 pagesSpanish Chapter 3Gaelle CBNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document8 pagesExperiment 7Keo De LeonNo ratings yet
- Historical MethodDocument33 pagesHistorical MethodSharmaine BeranNo ratings yet
- Marilyn Ray Career History Theory of Bureaucratic Caring Powerpoint 2013 PDFDocument143 pagesMarilyn Ray Career History Theory of Bureaucratic Caring Powerpoint 2013 PDFVinz TombocNo ratings yet
- General Survey and Integumentary AssessmentDocument9 pagesGeneral Survey and Integumentary AssessmentAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- Initial ManuscriptDocument26 pagesInitial ManuscriptDennisse CastillonNo ratings yet
- Health Education Team 1 2Document14 pagesHealth Education Team 1 2Mark Justin Leal0% (1)
- Ass in RizalDocument2 pagesAss in Rizal6juztine9100% (3)
- 0 - Chapter II. Review of Related LiteratureDocument13 pages0 - Chapter II. Review of Related LiteratureJiyan LitohonNo ratings yet
- Long Green Chili ReportDocument12 pagesLong Green Chili ReportRoma Raquepo Ringor100% (1)
- Shoe Shine Startup FeasibilityDocument28 pagesShoe Shine Startup FeasibilityKaterina TagleNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab No. 3Document6 pagesAcs Lab No. 3Karyl GregorioNo ratings yet
- BoooplDocument2 pagesBoooplChristian Josh DinoyNo ratings yet
- Kerala Plus Two Botany Focus Area Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesKerala Plus Two Botany Focus Area Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsReshmaNo ratings yet
- FUNGI SOMATIC STRUCTURES AND ASEXUAL REPRODUCTIONDocument36 pagesFUNGI SOMATIC STRUCTURES AND ASEXUAL REPRODUCTIONDevesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.7extraction of Proteins From Plant TissuesDocument7 pages4.7extraction of Proteins From Plant Tissueskhmaj9792No ratings yet
- Growing Shrubs and Small Trees in Cold ClimateDocument449 pagesGrowing Shrubs and Small Trees in Cold ClimateBercea CostelNo ratings yet
- Flowers Meanings QuizDocument2 pagesFlowers Meanings QuizDiana RaduNo ratings yet
- Plants Specialized StructuresDocument38 pagesPlants Specialized StructuresKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- PLANTYDocument27 pagesPLANTYbry uyNo ratings yet
- CINCHONA BARK CHEMICAL PROPERTIESDocument17 pagesCINCHONA BARK CHEMICAL PROPERTIESManisha SawantNo ratings yet
- Xamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument31 pagesXamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
- A9 Dualling Programme Appendix A12.1: Scientific Plant and Animal NamesDocument8 pagesA9 Dualling Programme Appendix A12.1: Scientific Plant and Animal NamesAslam PaktiawalNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Plant Species: Tsinjoarivo, Madagascar Growth Form Family Scientific NameDocument8 pagesInventory of Plant Species: Tsinjoarivo, Madagascar Growth Form Family Scientific NameHarryNo ratings yet
- Promalin 6P BrochureDocument6 pagesPromalin 6P Brochurepratiksha24No ratings yet
- NEET-2020 Model Paper-1: BiologyDocument17 pagesNEET-2020 Model Paper-1: BiologyKavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Fibrinolytic Activity of Some Nigerian Medicinal PlantsDocument8 pagesFibrinolytic Activity of Some Nigerian Medicinal PlantsSabrina JonesNo ratings yet
- Science X MS Set BDocument6 pagesScience X MS Set BSUCHITRA HOSMANINo ratings yet
- Borzicactus HoxleyiDocument2 pagesBorzicactus HoxleyiMiguelProNo ratings yet
- Biology One Mark QuestionDocument12 pagesBiology One Mark Questionvishali GNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Annuals Under Open ConditionDocument8 pagesProduction Technology of Annuals Under Open ConditionABHISHEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal Kingdom TestDocument3 pagesPlant & Animal Kingdom Test10 Harsheeta RoyNo ratings yet
- Green Algae: A Diverse Group of Photosynthetic EukaryotesDocument3 pagesGreen Algae: A Diverse Group of Photosynthetic EukaryotesGladys CardonaNo ratings yet
- FitoterapiaDocument107 pagesFitoterapiaJunior Calderon100% (1)
- An Overview of Nitella in Australia (Characeae, Charophyta) : Australian Systematic Botany January 2009Document27 pagesAn Overview of Nitella in Australia (Characeae, Charophyta) : Australian Systematic Botany January 2009Atika AuliaNo ratings yet
- Stott FloralFemininityPictorial 1992Document19 pagesStott FloralFemininityPictorial 1992grossmann.anna93No ratings yet
- Synopsis Fungorum 35: FungifloraDocument61 pagesSynopsis Fungorum 35: FungifloraDomenico Fitofago ValenzanoNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Amoeba and Plant Cell StructureDocument5 pagesExercise: Amoeba and Plant Cell StructureNnmarziana NickNo ratings yet
- Homologous and Analogous Organs Class Xii PracticalDocument4 pagesHomologous and Analogous Organs Class Xii PracticalAnushree100% (3)
- Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022-1Document3 pagesBiology Paper 2 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022-1balozi training InstituteNo ratings yet
- BOTANICAL NAMES OF SHRUBS, TREES AND PLANTSDocument18 pagesBOTANICAL NAMES OF SHRUBS, TREES AND PLANTSAKASH DAYALNo ratings yet
- Jenis dan Struktur BuahDocument11 pagesJenis dan Struktur BuahBenna DaurinNo ratings yet
- 20220721.102006 Botany PET Syllabus PDFDocument35 pages20220721.102006 Botany PET Syllabus PDFPadmini SahuNo ratings yet