Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan - Kyphosis
Uploaded by
Green MarlCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan - Kyphosis
Uploaded by
Green MarlCopyright:
Available Formats
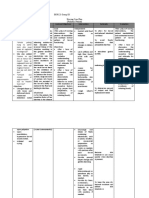
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE: Nanghihina ako, pakiramdam ko hindi ko kayang gumalaw (I feel
weak, I cant move)
DIAGNOSIS
Impaired physical mobility related to neuromascular impairment.
INFERENCE
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
INDEPENDENT: Continually assess motor function by requesting patient to perform certain actions like shrugging shoulders, spreading fingers. Assist with full range of motion exercises in all extremities and joints using slow, smooth movements. Position arms at 90-degree angle at regular intervals. Elevate lower extremities at intervals when in chair or raise foot or bed when permitted in individual situation.
RATIONALE
Evaluates status of individual situation, affecting type and choice of interventions.
EVALUATION
After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate techniques or behaviors that enable resumption of activity.
as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Paralysis. Muscle atrophy. V/S taken as follows: T: 37.1 P: 89 R: 20 BP: 110/90
After 8 hours Kyphosis of nursing (Greek interventions, kyphos, a the patient hump), in will general terms, demonstrate is a curvature of techniques or the upper behaviors that spine. It can be enable either the result resumption of of bad posture activity. or a structural anomaly in the spine. In the sense of a deformity, it is the pathological curving of the spine, where parts of the spinal column lose some or all of their lordotic profile. This causes a bowing of the back, seen as a slouching posture. Symptoms of kyphosis, that may be present or not, depending on the type and extent of the deformity,
Enhances circulation, restores muscle tone and joint mobility.
Prevents frozen shoulder contractures. Loss of vascular tone and muscle action results in pooling of blood and venous stasis in the lower abdomen and lower extremities, with increased risk of hypotension and thrombus formation.
include mild back pain, fatigue, appearance of round back and breathing difficulties. Severe cases can cause great discomfort and even lead to death.
Prevents fatigue, Plan activities to allowing provide opportunity for uninterrupted rest maximal efforts periods. or participation Encourage by the patient. involvement within individual tolerance or ability. Encourage use of relaxation techniques. Inspect skin daily. Observe for pressure areas and provide meticulous care. Reduces muscle tension, may limit pain of muscle spasm. Altered circulation, loss of sensation, and paralysis potentiate pressure sore formation.
COLLABORATIVE: Consult with physical therapist. Helpful in planning and implementing individualized exercise program and identifying assistive devices to maintain function, enhance mobility and independence.
You might also like
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultDocument11 pagesSepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultShrests SinhaNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Nursing SkillDocument1 pageNursing SkillMarina Wasem NetzlaffNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- How to treat and prevent breast engorgementDocument1 pageHow to treat and prevent breast engorgementkurniaNo ratings yet
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 pagesNusing Careplanardec_143No ratings yet
- Bowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsDocument9 pagesBowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsners_gun100% (1)
- EvistaDocument18 pagesEvistaBrankoPopovićNo ratings yet
- NCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisDocument2 pagesNCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- Ix. List of Priority ProblemDocument10 pagesIx. List of Priority ProblemshinloNo ratings yet
- Amoeboid ProtozoaDocument33 pagesAmoeboid ProtozoaGangadharKasinathSastryNo ratings yet
- Malaria PosterDocument1 pageMalaria PosterTommaso ForzaNo ratings yet
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 NCPDocument1 pageCase Study 2 NCPJayson SamonteNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Fetal Well BeingDocument22 pagesEvaluation of Fetal Well BeingJoanah Mae AsuncionNo ratings yet
- NCP BPHDocument1 pageNCP BPHyasiraNo ratings yet
- Panhypopituitarism: Causes, Signs, and TreatmentDocument22 pagesPanhypopituitarism: Causes, Signs, and TreatmentRocel Devilles100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCDocument4 pagesPhenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCkeitacNo ratings yet
- Share DRUGSTUDYDocument4 pagesShare DRUGSTUDYTyronne JingcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Stroke PtDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans for Stroke PtJuls Flares SycaycoNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations For Nursing StudentsDocument7 pagesAbbreviations For Nursing StudentssodiwoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- NCM104b BSN220 Mobility NursingDocument9 pagesNCM104b BSN220 Mobility NursingChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- PROM Guide - Written RequirementsDocument22 pagesPROM Guide - Written RequirementsDarla Janyll RegañonNo ratings yet
- NCP GeDocument14 pagesNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Irrigation Clinical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesVaginal Irrigation Clinical GuidelinesAnonymous 0C4OZmRNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Document2 pagesDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNo ratings yet
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementKhalid KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- MastitisDocument13 pagesMastitisapi-232713902No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaBinita Shakya100% (1)
- MicrocephalyDocument4 pagesMicrocephalykurei_bluflamedNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobiltyDocument4 pagesNCP ImmobiltyAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Premenstrual Dysphoric DisorderDocument11 pagesPremenstrual Dysphoric Disorderapi-3764215No ratings yet
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 pagesConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorders in ChildrenDocument22 pagesSeizure Disorders in ChildrenBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyGAYOL BREEN IRAH A.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health and Environmental Sanitation PDFDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Community Health and Environmental Sanitation PDFKaty SanchezNo ratings yet
- Augmentin drug classification, dosage, indications, contraindications and nursing interventionsDocument2 pagesAugmentin drug classification, dosage, indications, contraindications and nursing interventionsCherubim Lei DC FloresNo ratings yet
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 pagesTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- Hyperkalemia Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesHyperkalemia Discharge PlanDe Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk FactorsmkhoNo ratings yet
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Child - Major Burn PDFDocument3 pagesChild - Major Burn PDFAldith GrahamNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke NCPDocument11 pagesIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanCatherine Joy VillapandoNo ratings yet