Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calibration SI Units
Uploaded by
api-37070940 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views17 pagesTom tat cau chuyen ve viec lua chon don vi chuan cho he do luong SI. Trich trong 1 bai giang o truong TU Delft, Ha Lan.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTom tat cau chuyen ve viec lua chon don vi chuan cho he do luong SI. Trich trong 1 bai giang o truong TU Delft, Ha Lan.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views17 pagesCalibration SI Units
Uploaded by
api-3707094Tom tat cau chuyen ve viec lua chon don vi chuan cho he do luong SI. Trich trong 1 bai giang o truong TU Delft, Ha Lan.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Official calibration SI units
• Time (s)
• Length (m)
• Mass (kg)
• Current (A)
• Temperature (K)
• Amount of substance (mol)
• Luminous intensity (cd)
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 24
Riddle
• It’s money but it can be killed
• It flies and heals all wounds
• We can be ahead of it, over it, on it or out of it.
• We can win it, save it or lose it.
TIME!
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 25
Measurement of Time
• Day, night, moon cycle, position of the sun
• Angular measurement
• Babylonia subdivision 12:60:60, 360:60:60
• Hourglass
• Resonator, pendulum (Galileo, based on
gravity) and mass spring system:
• Mechanical movement (Q~10)
• Tuning fork (Q~30)
• Quarz cristal (Q >100)
• Atom vibrations (Q>>1000)
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 26
Time standard
• The absolute time was first related to the highest point of the
position of the sun but now the astronomic position of the earth
is taken as reference.
• The relative time is referred to:
At the start of the 20th century:
• 1 second is 1/31,556,925.974,74 of the tropical sun year on
december 31st 1899 at 12 AM. GMT.
In 1968
• 1 second is 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation caused by the
transition between two electron spin energy levels at the ground
state of Caesium 133
• It is accurate up to 1 second in 300,000 years (1:1013)
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 27
Length is one of the oldest measures
and often based on human references
• 1 mile is 1000 double steps of an average Roman
soldier
• Foot, thumb, yard
A living length standard
For the yard
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 28
Length
• 1 mile is 1000 double steps of an average Roman soldier
• Foot, thumb, yard, el
• Inch = 3 barley corns
• Huygens (1664):
• Length of a pendulum with 1 second period. Link with time!
• In 1799 the standard was based by Jean Henri van Swinden on
1/10,000,000 of the distance from the pole to the equator
• In 1875 the standard was based on a Pt-Ir bar
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 29
The present length standard is based
on the wavelength of light.
• 1 meter = path travelled by light
in 1/299,792,458 s.
• Older standards shouldn’t change!
• Dutch standard today is HeNe
laser with Iodine absorption cell.
• The laser is tuned to the absorption
spectre of the Iodine gas giving a
reproduceability of better then
1: 100,000,000,000 (1011)
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 30
Mass started with weight.
• Measured and compared with a
balance
• Standards were items assumed to
be of constant weight:
• Seeds of a tree (Egypt) Quirat (Carat!)
• Shekel, Talent, Unciae (Ounce! Inch!)
• Libra, pound (lb, £)
• A pound is no pound (pond). Its
mass became a political issue but
trade forced the politicians to an
international standard.
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 31
The Swiss mr. Trallès came with a
mass standard (~1800)
• 1kg 1/1,000 of a cubic meter water
• With a derived mass of 1 kilogram in Platina
• Many derived standard kilograms were made over the
years and all differ a bit in the order of tens of a
milligram (1:10,000,000 = 1: 107)
• Influence of air, pollution, contamination etc.
• No better way of standardisation of mass exists today
• A silicon ball with perfect surface is considered as
alternative.
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 32
The standard of current (A)
• Originally it was the current that caused a certain
amount of silver to precipitate from AgNO3.
• Now the Amp is based on the Ayrton-Jones current
balance.
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 33
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 34
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 35
This is not manageable so other standards
are chosen:
• Farad based on the laws of capacity
(surface, distance dielectrical
constant)
8.8541878176 × 10í12 F/m (C2/Jm),
• Volt based on the AC Josephson
effect in superconductivity which
translates a voltage into a frequency
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 36
Josephson junction
A DC Voltage over a Josephson Junction results in an AC current with frequency:
For 1 uV this means:
The standard volt is now defined as the voltage required
to produce a frequency of 483,597.9 GHz.
This can be done with an accuracy of 1010
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 37
Now Amp relates to voltage and
Farad
• The charge in a capacitor equals
Q = CV
• Current through a capacitor gives
a voltage change
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 38
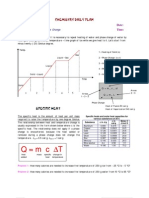
And last but not least temperature
Always related to specific assumed fixed temperatures in
Nature:
• Fahrenheit (one of the stories) took the coldest temp he
could create as 0 0F and his own body temperature as 100 0F.
He found the freezing point of water (32 0F) and boiling point
(212 0F) being a nice 180 0F apart. Measurement errors made
it necessary to correct this later
• Celcius took the water characteristics
• Kelvin took the same division as Celcius but started at the
absolute zero.
• Ideal Gas law: PV = nRLJ
• Extrapolation from known fixed points
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 39
Primary fixed points for temperature
calibration
WB2303 measurement theory and praxis (2006-2007) 40
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Pre Board EsasDocument112 pagesPre Board EsasJohn Lloyd SantosNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Semi-Conductor Physics SyllabusDocument2 pagesSemi-Conductor Physics SyllabusAnkit kumarNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Conduction 3Document120 pagesConduction 3VINEET VYASNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Magnetism SC L4-5Document12 pagesMagnetism SC L4-5Abhishek tiwariNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- G204Document5 pagesG204Gul Hassan Akhunzada100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Measurement of RLC &Q Using LCR-Q MeterDocument6 pagesMeasurement of RLC &Q Using LCR-Q MeterKshitiz Panwar50% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Equilibrium Worksheet 2Document9 pagesEquilibrium Worksheet 2haileyNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Science 7 Third Quarter ExamDocument7 pagesScience 7 Third Quarter ExamKenny Ann Grace Batiancila100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 3 2Document26 pages3 2Naidu SairajNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Panel Design and Calculate Bus Bar SizeDocument14 pagesPanel Design and Calculate Bus Bar SizeThirumal100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document19 pagesChapter 2TearlëşşSufíåñNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Introduction To Planar Laser-Induced FlourescenceDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Planar Laser-Induced FlourescencegaccioNo ratings yet
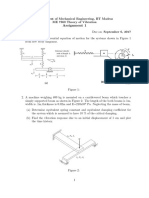
- ME7360 Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesME7360 Assignment 1 PDFVivek V ShetNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- NumecDocument14 pagesNumecDinie Abdullah ZamawiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- LAS SHS PhySci MELC 7 Q2 Week-3Document10 pagesLAS SHS PhySci MELC 7 Q2 Week-3Nini VillezaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- GBD26KS La26r71b GBD32KS La32r71b GBD40KS La40r71b GBD32KS La32r71wDocument177 pagesGBD26KS La26r71b GBD32KS La32r71b GBD40KS La40r71b GBD32KS La32r71wARTMehr Eng. GroupNo ratings yet
- SIM Metrology SchoolDocument56 pagesSIM Metrology SchoolDaniNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiDocument7 pagesA New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiAlberto JimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Stage Compressor With IntercoolerDocument5 pages2 Stage Compressor With IntercoolerKatrina Charles100% (1)
- Section 1.3 Hydraulic System Power RequirementDocument4 pagesSection 1.3 Hydraulic System Power Requirementaerogem618No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Crystal Defects PDFDocument1 pageCrystal Defects PDFJohan Steven Rivera RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Particle Size and Size Distribution of Superabrasive PowdersDocument12 pagesParticle Size and Size Distribution of Superabrasive PowdersjhscribdaccNo ratings yet
- CH 101Document2 pagesCH 101nagravNo ratings yet
- 3.1-3.2 Laplace - S EquationDocument15 pages3.1-3.2 Laplace - S EquationCargo86No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Consolidation of Boron Carbide - A ReviewDocument37 pagesSynthesis and Consolidation of Boron Carbide - A ReviewEvandro SilvaNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkDocument6 pagesStudent Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkEngwarwickNo ratings yet
- Formation Evaluation: Pulsed Neutron Capture LogsDocument16 pagesFormation Evaluation: Pulsed Neutron Capture LogsAG YNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Drop Weight CrusherDocument2 pagesDrop Weight CrushermuralidharanNo ratings yet
- SPE 16959 Material Balance Calculations For Solution-Gas-Drive Reservoirs With Gravity SegregationDocument12 pagesSPE 16959 Material Balance Calculations For Solution-Gas-Drive Reservoirs With Gravity SegregationMuhammed Al-BajriNo ratings yet
- Geophysics) Seismic Vibrator Control and The Downgoing P-WaveDocument9 pagesGeophysics) Seismic Vibrator Control and The Downgoing P-WavebrcountryNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)