Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.10. Elements: GUI-Inaccessible Elements New Elements Modified Elements Undocumented Elements Archived Elements
Uploaded by
ILAYAPERUMAL KOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.10. Elements: GUI-Inaccessible Elements New Elements Modified Elements Undocumented Elements Archived Elements
Uploaded by
ILAYAPERUMAL KCopyright:
Available Formats
ANSYS, Inc.
Release Notes Page: 1
3.10. Elements
This section describes changes to elements at Release 13.0. Some elements are not available from within the GUI. For a list of those elements, see GUI-Inaccessible Elements in the Element Reference . New Elements Modified Elements Undocumented Elements Archived Elements
3.10.1. New Elements
The following new elements are available in this release: SURF159 -- This element models axisymmetric solid surface loads acting on general axisymmetric solid (SOLID272 or SOLID273) elements. The element has quadratic displacement behavior on the master plane and is well suited to modeling irregular meshes on the master plane. It is defined by two or three nodes on the master plane, and nodes created automatically in the circumferential direction (based on the master plane nodes). FLUID220 -- This 3-D 20-node acoustic fluid element models the fluid medium and the interface in fluid/structure interaction problems. This element is well suited for modeling sound wave propagation and submerged structure dynamics. FLUID221 -- This 3-D 10-node acoustic fluid element models the fluid medium and the interface in fluid/structure interaction problems. This
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 2
element is well suited for modeling sound wave propagation and submerged structure dynamics. HSFLD241 -- This 2-D hydrostatic fluid element models fluids that are fully enclosed by 2-D planar and axisymmetric solids. This element is well suited for modeling fluid-solid interaction with incompressible or compressible fluids under uniform pressure. It can be used in geometrically linear as well as nonlinear static and transient dynamic analyses. HSFLD242 -- This 3-D hydrostatic fluid element models fluids that are fully enclosed by 3-D solids or shells. This element is well suited for modeling fluid-solid interaction with incompressible or compressible fluids under uniform pressure. It can be used in geometrically linear as well as nonlinear static and transient dynamic analyses. REINF263 -- This 2-D reinforcing element is used with a standard 2-D solid or shell element (referred to as the base element) to provide extra reinforcing to that element. It uses a smeared approach and is suitable for modeling evenly spaced reinforcing fibers that appear in layered form. SOLID278 -- This 3-D 8-node thermal solid element is applicable to steady state and transient analyses. The element has two forms: homogeneous thermal solid and layered thermal solid. It is designed to be a companion element for structural solid element SOLID185. SOLID279 -- This 3-D 20-node thermal solid element is applicable to steady state and transient analyses. The element has two forms: homogeneous thermal solid and layered thermal solid. It is designed to be a companion element for structural solid element SOLID186.
3.10.2. Modified Elements
The following elements have been enhanced in this release: PLANE77 -- This element now has a plane thickness option (KEYOPT(3)). FLUID116 -- This coupled thermal-fluid pipe element has a new KEYOPT(1) = 3 option to specify the PRES degree of freedom when it is
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 3
KEYOPT(1) = 3 option to specify the PRES degree of freedom when it is connected to a hydrostatic fluid element (HSFLD241 or HSFLD242). This option converts the fluid element mass flow rate to volume change for compatibility with the new hydrostatic fluid elements. SURF151 -- For improved accuracy in convection analyses, this 2-D surface effect element has a new option for adding two extra nodes from FLUID116 elements. For the one-extra-node option (KEYOPT(5) = 1), film effectiveness and free stream temperatures may now be input for convection surface loads. SURF152 -- For the one-extra-node option (KEYOPT(5) = 1), film effectiveness and free stream temperatures may now be input for convection surface loads. TARGE170, CONTA173, and CONTA174 -- These 3-D surface-to-surface contact and target elements now support a geometry correction feature that can be applied to spherical and revolute contact and target surfaces to reduce discretization errors associated with faceted surfaces. CONTA173 and CONTA174 -- These 3-D surface-to-surface contact elements support the new projection-based method specified by setting KEYOPT(4) = 3 for the contact detection option. CONTA171 through CONTA177 -- The following improvements are available for these contact elements: KEYOPT(10), which controls the contact stiffness update method, has been simplified in these elements. Several of the options have been removed from this KEYOPT; KEYOPT(10) = 0 and 2 are still available. A new real constant, STRM, allows you to specify the load step number in which the ramping option for initial contact penetration will take place. Used in conjunction with KEYOPT(9) = 2 or 4, this feature is useful for modeling multiple interference fits that take place sequentially over several load steps. The following new contact output quantities are available: VREL -- slip rate; GGAP -- true geometric gap/penetration at current converged substep; FSTART -- fluid penetration starting time. (FSTART is available only for surface-to-surface contact elements.)
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 4
CONTA171 through CONTA178 -- You can now input a coefficient of restitution via the new contact element real constant COR. When using impact constraints to model impact between rigid bodies, the coefficient of restitution can be used to model loss of energy during impact. SHELL181 -- KEYOPT(4) has been removed from this four-node structural shell element. The element now uses the constitutive algorithm exclusively for nonlinear shell-thickness updates. Real constant support has been undocumented. SHELL208, SHELL209 -- KEYOPT(4) has been removed from these shell elements. The elements now use the constitutive algorithm exclusively for nonlinear shell-thickness updates. PLANE223, SOLID226, and SOLID227 -- These coupled field elements have been enhanced with new nonlinear material capabilities. Plasticity, viscoelasticity, and viscoplasticity/creep material properties can now be specified via the TB command. PLANE233, SOLID236, SOLID237 -- These current-technology elements now support stranded coil analyses via the new KEYOPT(1) = 2 option. The stranded coil analysis option is suitable for modeling a stranded winding with a prescribed current flow direction vector. The stranded coil may be voltage- or current-driven, as well as circuit-fed. SHELL281 -- KEYOPT(2) and KEYOPT(4) have been removed from this eight-node structural shell element. The element now uses an advanced shell formulation that accurately incorporates initial curvature effects. The new formulation generally offers improved accuracy in curved shell structure simulations, especially when thickness strain is significant or the material anisotropy in the thickness direction cannot be ignored. Real constant support has been undocumented.
3.10.3. Undocumented Elements
The following legacy elements have been undocumented at this release, as follows:
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 5
follows: Suggested Undocumented Current-Technology Legacy Element Element BEAM3 Recommendations Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Constrain UZ, ROTX, and ROTY to simulate 2-D behavior. Issue a SECTYPE,,BEAM command. Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Constrain UZ, ROTX, and ROTY to simulate 2-D behavior. Issue a SECTYPE,,BEAM command. Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Issue a SECTYPE,,BEAM command. BEAM188 or BEAM189 Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Issue a SECTYPE,,BEAM or possibly a SECTYPE,,TAPER command. A SECOFFSET command may be necessary. Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Constrain UZ, ROTX, and ROTY to simulate 2-D behavior. Issue a SECTYPE,,TAPER command. A SECOFFSET command may be necessary.
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
BEAM23
BEAM24 BEAM44
BEAM54
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 6
COMBIN7 LINK1 LINK8 LINK10
MPC184
Set KEYOPT(1) = 6. ---
LINK180
To simulate LINK10 functionality, set the LINK180 tension/compression option (real constant TENSKEY). ----
LINK32 PIPE17 PIPE20 PIPE60 PLANE67 SHELL57 SOLID69 p-elements: SOLID127 SOLID128 PLANE145 PLANE146 SOLID147 SOLID148 SHELL150
LINK33 PIPE288 ELBOW290 PLANE223 SHELL131 SOLID226
-Set KEYOPT(1) = 110. Set KEYOPT(3) = 2. Issue SECTYPE,,SHELL. Set KEYOPT(1) = 110.
NA
The p-method has been undocumented.
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 7
For information about other elements that have been undocumented in prior releases, see the archived release notes on the ANSYS Customer Portal.
3.10.4. Archived Elements
The following legacy elements have been moved to the Feature Archive: Archived Legacy Element BEAM4 CONTAC12 CONTA178 Suggested Current-Technology Element BEAM188 or BEAM189 Recommendations Set KEYOPT(3) = 3. Issue a SECTYPE,,BEAM command. Constrain the UZ degree of freedom to simulate 2-D behavior. CONTA178 does not support the circular gap option of CONTAC12. --Set KEYOPT(1) = 3. Set KEYOPT(2) = 3. -Issue SOCEAN and ocean (OCxxxxxx) commands to apply ocean loading. Set KEYOPT(3) = 2. May require
PIPE16 PIPE18 PLANE42 SOLID45 CONTAC52 PIPE59
PIPE288 ELBOW290 PLANE182 SOLID185 CONTA178 PIPE288
SHELL63
SHELL181
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
ANSYS, Inc. Release Notes Page: 8
a finer mesh. PLANE82 SOLID92 SOLID95 PLANE183 SOLID187 SOLID186 (Homogenous Structural Solid) --Set KEYOPT(2) = 1. For nonlinear analysis, set KEYOPT(2) = 0 (default).
Release 13.0 - 2010 SAS IP, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contains proprietary and confidential information of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates
You might also like
- SiLENSe 5.1 ReleaseNotesDocument10 pagesSiLENSe 5.1 ReleaseNotesPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNotes PDFDocument21 pagesReleaseNotes PDFFrancisco Jose Arista QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Utomatic Ynamic Ncremental Onlinear Nalysis: ADINA System 8.7 Release NotesDocument25 pagesUtomatic Ynamic Ncremental Onlinear Nalysis: ADINA System 8.7 Release NotesCarlos Gustavo MéndezNo ratings yet
- Implicit GuideDocument18 pagesImplicit Guide蕭宇程No ratings yet
- PIPE59Document28 pagesPIPE59ODG_290473No ratings yet
- LS-Dyna Impact Analysis TutorialDocument29 pagesLS-Dyna Impact Analysis Tutorialsravis69100% (1)
- Using Sliding Mesh AnsysDocument38 pagesUsing Sliding Mesh AnsysChien Manh NguyenNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The LS-DYNA Hourglass Formulations Via The 3D Patch TestDocument9 pagesAn Assessment of The LS-DYNA Hourglass Formulations Via The 3D Patch Testmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURAL - Chapter 14 - Explicit Dynamics Analysis (UP19980818)Document26 pagesSTRUCTURAL - Chapter 14 - Explicit Dynamics Analysis (UP19980818)Rory Cristian Cordero RojoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12. Using Sliding MeshesDocument36 pagesTutorial 12. Using Sliding MeshesAndre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Automated Spot Weld ModelingDocument7 pagesAutomated Spot Weld Modelingnunoaguiar8No ratings yet
- Fatfree User ManualDocument33 pagesFatfree User ManualLit Phen TuNo ratings yet
- Input Parameters For Springback Simulation Using LS-DYNADocument11 pagesInput Parameters For Springback Simulation Using LS-DYNAseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- Airbag Simulation With Ls-DynaDocument25 pagesAirbag Simulation With Ls-Dynasaketh ReddyNo ratings yet
- PI31xx-xx-EVAL1 ZVS Isolated DC-DC Converter Evaluation BoardDocument16 pagesPI31xx-xx-EVAL1 ZVS Isolated DC-DC Converter Evaluation BoardallallaNo ratings yet
- ADINA System 9.0Document56 pagesADINA System 9.0hamidNo ratings yet
- Release Notes LS-DYNA 971 r7.1.0 Rev4Document42 pagesRelease Notes LS-DYNA 971 r7.1.0 Rev4sdyyds2004No ratings yet
- XFOIL 6 Guia de UsuarioDocument34 pagesXFOIL 6 Guia de Usuariotorups99No ratings yet
- Quick Start TutorialDocument9 pagesQuick Start Tutorialbramo96No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Using The Mixing Plane ModelDocument36 pagesChapter 13: Using The Mixing Plane ModelramgopaljhaNo ratings yet
- Logg 4000Document7 pagesLogg 4000Stjepan FrljicNo ratings yet
- CAEfatigue VIBRATION Installation and User Guide ExamplesDocument13 pagesCAEfatigue VIBRATION Installation and User Guide ExamplesHarsha KolarNo ratings yet
- FLO-2D Porting Document (PRO Model)Document5 pagesFLO-2D Porting Document (PRO Model)Jason ChupicaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Version 10Document6 pagesANSYS Version 10pankaj0983No ratings yet
- Ansys LS-DynaDocument213 pagesAnsys LS-DynaUmesh Vishwakarma50% (4)
- Tutorial 8. Using Multiple Rotating Reference FramesDocument22 pagesTutorial 8. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frameswaleed yehiaNo ratings yet
- Rel Notes v161Document5 pagesRel Notes v161zebra00No ratings yet
- Release Notes Sap 2000 V 2110Document11 pagesRelease Notes Sap 2000 V 2110thekrauser96No ratings yet
- Vilanova - Pid Tuning For Cascade Control System DesignDocument4 pagesVilanova - Pid Tuning For Cascade Control System DesignCarlos BellatinNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Symmetry TopicsDocument73 pagesCyclic Symmetry TopicsMoisés MachadoNo ratings yet
- EnergySupply A1 A3 HN 202 069Document11 pagesEnergySupply A1 A3 HN 202 069cabecavilNo ratings yet
- Guida A Xfoil (Guide To Xfoil)Document28 pagesGuida A Xfoil (Guide To Xfoil)Giovanni ViciconteNo ratings yet
- Paper Gotheburg 2007 Airbags FinalDocument26 pagesPaper Gotheburg 2007 Airbags FinaleefbfbfkbjkdkkdnsNo ratings yet
- FEA Information Co.: For The LS-DYNA Global CommunityDocument0 pagesFEA Information Co.: For The LS-DYNA Global CommunityleawoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Flow Simulation Using Star CCM+Document9 pagesNumerical Flow Simulation Using Star CCM+Alexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- BASIC ReportDocument4 pagesBASIC ReportvalfleiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFD Anasisly: (Fluent & Gambit)Document20 pagesIntroduction To CFD Anasisly: (Fluent & Gambit)Avinash VasudeoNo ratings yet
- Guide to Using CAESAR II Software for Stress AnalysisDocument83 pagesGuide to Using CAESAR II Software for Stress AnalysisSaúl Mendoza100% (5)
- Ls DynaDocument33 pagesLs DynaRajNo ratings yet
- Example 10Document3 pagesExample 10Anitha Hassan KabeerNo ratings yet
- Framecad-Bs En1991-13-2006Document11 pagesFramecad-Bs En1991-13-2006Aie BantuganNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet: G L Cae/PDocument14 pagesRevision Sheet: G L Cae/PErico Antonio TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Altistart 48 Installation Guide1Document84 pagesSchneider Electric Altistart 48 Installation Guide1Victor HaraujoNo ratings yet
- Pipe 288Document22 pagesPipe 288rezajun2820No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3. Introduction: Modeling External Compressible FlowDocument32 pagesTutorial 3. Introduction: Modeling External Compressible Flowİbrahim MercanNo ratings yet
- Impact Analysis Using LS-Dyna TutorialDocument29 pagesImpact Analysis Using LS-Dyna TutorialSumit SehgalNo ratings yet
- Cadfem Advanced Sealings PDFDocument12 pagesCadfem Advanced Sealings PDFsvk_ntNo ratings yet
- The 2008 Revision of IEEE C37.2 Standard Electrical Power System Device Function Numbers, Acronyms and Contact DesignationsDocument12 pagesThe 2008 Revision of IEEE C37.2 Standard Electrical Power System Device Function Numbers, Acronyms and Contact DesignationsAdil AbdoNo ratings yet
- Addendum To UmatDocument3 pagesAddendum To UmatGokul MuthupandiNo ratings yet
- Ls Dyna PaperDocument10 pagesLs Dyna PaperSaw RexNo ratings yet
- W7619en DS7 ProductInfoDocument6 pagesW7619en DS7 ProductInfore marNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Modeling Aeroacoustics For A Helmholtz ResonatorDocument19 pagesTutorial Modeling Aeroacoustics For A Helmholtz ResonatorgokulpawarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of a Rubber Oil Pan Gasket RTV Pad Using ABAQUS ExplicitDocument11 pagesAnalysis of a Rubber Oil Pan Gasket RTV Pad Using ABAQUS Explicitklomps_jrNo ratings yet
- ReleasenotesDocument35 pagesReleasenotesdenise_rosales_1No ratings yet
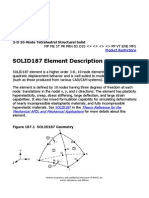
- Solid 187Document9 pagesSolid 187niteen_mulmule485No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Modern Borehole Analytics: Annular Flow, Hole Cleaning, and Pressure ControlFrom EverandModern Borehole Analytics: Annular Flow, Hole Cleaning, and Pressure ControlNo ratings yet
- QB114462Document8 pagesQB114462ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Private Car Policy WordingDocument9 pagesPrivate Car Policy WordingILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument4 pagesManualILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- 2-Critical Speed of ShaftDocument5 pages2-Critical Speed of ShaftRidani Faulika Amma100% (3)
- ExercisesDocument1 pageExercisesILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- ME6503 Design of Machine Elements Question BankDocument9 pagesME6503 Design of Machine Elements Question BankILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Merit Vol II Issue IV - April 2015 (LO)Document13 pagesMerit Vol II Issue IV - April 2015 (LO)ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- GATE 2017 Exam Pattern: Section No. No. of Questions Marks Per Total MarksDocument1 pageGATE 2017 Exam Pattern: Section No. No. of Questions Marks Per Total MarksILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- 2016 Digital Trends Survey ResultsDocument47 pages2016 Digital Trends Survey ResultsILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Publication 10 5968 1369Document2 pagesPublication 10 5968 1369ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Madeeasy List IitDocument1 pageMadeeasy List IitILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery (Nov, Dec2012)Document3 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery (Nov, Dec2012)Vijaya Prabhu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture (1) Properties of Fluids: LecturerDocument28 pagesLecture (1) Properties of Fluids: LecturerILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and MachineryNovDec2014R2013Document3 pagesFluid Mechanics and MachineryNovDec2014R2013ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- 5th SemesterDocument8 pages5th SemesterILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Madeeasy List NitDocument1 pageMadeeasy List NitILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- GKP List PsuDocument2 pagesGKP List PsuILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Vision Based Mobile Robot For Pipe Line Inspection and CleaningDocument5 pagesIntelligent Vision Based Mobile Robot For Pipe Line Inspection and CleaningILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- GKP All About GateDocument7 pagesGKP All About GateILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Gate Cut Off MarksDocument1 pageGate Cut Off MarksVikas SurarapuNo ratings yet
- DME Question BankDocument4 pagesDME Question BankILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Pearson Gate 2016 Detailed Analysis MeDocument4 pagesPearson Gate 2016 Detailed Analysis MeILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular Bars and FormulasDocument25 pagesTorsion of Circular Bars and FormulasAjoy Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pagesKinematics of MachineryILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery ME6401Document2 pagesKinematics of Machinery ME6401Thiru Moorthy100% (1)
- ME 6603 Finite Element Analysis - Assignment 2Document2 pagesME 6603 Finite Element Analysis - Assignment 2ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Finite (Mayjune2013)Document4 pagesFinite (Mayjune2013)ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Rajalakshmi Institute of Technology OverviewDocument2 pagesRajalakshmi Institute of Technology OverviewILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Academic Performance of Affiliated Colleges 042014Document19 pagesAcademic Performance of Affiliated Colleges 042014ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Presentation - Anish Kumar DakshDocument23 pagesMid Term Presentation - Anish Kumar DakshShubhadeep MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Science Test - 1 QuarterDocument3 pagesScience Test - 1 QuarterCeeKay0% (1)
- Activity 2.2 Atomic Orbitals - S2-2015Document10 pagesActivity 2.2 Atomic Orbitals - S2-2015Devandra Eko RadityoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 2 Solutions PDFDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 2 Solutions PDFUmesh S Rathore100% (2)
- ProblemsDocument2 pagesProblemsJoisy Sarco CondoriNo ratings yet
- Price 1998Document11 pagesPrice 1998LỢI NGUYỄN CÔNGNo ratings yet
- OIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoDocument8 pagesOIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoMario Vazquez BNo ratings yet
- RC Corbel Design (ACI318-05)Document2 pagesRC Corbel Design (ACI318-05)Mohammed Z. AlSaqqa100% (1)
- Conductimetric Analysis of Water Soluble Ionic Contamination of Blasting AbrasivesDocument3 pagesConductimetric Analysis of Water Soluble Ionic Contamination of Blasting AbrasivesCristhian CoariteNo ratings yet
- BOSCH Bio DecontaminationH2O2Document25 pagesBOSCH Bio DecontaminationH2O2Davide GrioniNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and InstallationsDocument36 pagesCorrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and Installationsdamnamyte100% (1)
- Aluminum Conditioner DX 503Document7 pagesAluminum Conditioner DX 503Mark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Third Order Elastic ConstantsDocument3 pagesThird Order Elastic ConstantsElango PaulchamyNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test and Oil Test of Distribution TransformerDocument6 pagesInsulation Resistance Test and Oil Test of Distribution TransformerBash MatNo ratings yet
- 9 InsulatorDocument39 pages9 InsulatorLeo KhkNo ratings yet
- The TBV AdvantageDocument24 pagesThe TBV AdvantageRaushNo ratings yet
- The WATERMARK CODEX MentalismDocument10 pagesThe WATERMARK CODEX Mentalismtrixter11793100% (1)
- Oxygen MSDS Safety GuideDocument4 pagesOxygen MSDS Safety Guidelutfi_thalib3175No ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Semiconductor NanocrystalsDocument259 pagesOptical Properties of Semiconductor Nanocrystalsanhthigl25No ratings yet
- What Is The Major Function of The Coating On An Arc Welding ElectrodeDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Major Function of The Coating On An Arc Welding ElectrodeElham Jaraine Garcia Lpt100% (4)
- Processing of The Pyrite Concentrates To Generate Sulfurous Anhydride For Sulfuric Acid ProductionDocument6 pagesProcessing of The Pyrite Concentrates To Generate Sulfurous Anhydride For Sulfuric Acid ProductionLuis La TorreNo ratings yet
- ZR53 MSDSDocument5 pagesZR53 MSDSAnonymous PinM7iNo ratings yet
- Investigating Osmolarity in Plant TissuesDocument2 pagesInvestigating Osmolarity in Plant TissuessofiaNo ratings yet
- Ampere Weber Electrodynamics HistoryDocument59 pagesAmpere Weber Electrodynamics Historyhanon90% (1)
- 02 - STRUCTURE - 01 - European Fitness For Service Network (FITNET) Fatigue Module DevelopmentDocument10 pages02 - STRUCTURE - 01 - European Fitness For Service Network (FITNET) Fatigue Module DevelopmentnotsofarNo ratings yet
- BMW Fault Codes OBDDocument15 pagesBMW Fault Codes OBDtitibacsiNo ratings yet
- PCCDocument12 pagesPCCAjit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Calibration Sheet Ultrasonic Test EquipmentDocument1 pageCalibration Sheet Ultrasonic Test EquipmentjohnNo ratings yet
- Aiats PDFDocument2 pagesAiats PDFAbhishek Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- TPO Product CatalogDocument210 pagesTPO Product CatalogMiguel BrionesNo ratings yet