Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obgyn Mnemonics
Uploaded by
api-3700579Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Obgyn Mnemonics
Uploaded by
api-3700579Copyright:
Available Formats
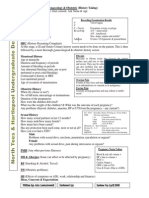
OBSTETRICS/ GYNECOLOGY ASHERMAN:
Acquired Anomaly
MNEMONICS Secondary to Surgery
Hysterosalpingography confirms diagnosis
Endometrial damage/ Eugonadotropic
Post-partum examination simplified checklist
Repeated uterine trauma
Missed Menses
BUBBLES:
Adhesions
Breast
Normal estrogen and progesterone
Uterus
Bowel
Bladder
Lochia
Episotomy
Surgical site (for Cesarean section) CVS and amniocentesis: when performed
"Chorionic" has 9 letters and Chorionic villus sampling performed at 9
weeks gestation.
Miscarriage: recurrent miscarriage causes "AlphaFetoProtein" has 16 letters and it's measured at 16 weeks gestation.
RIBCAGE:
Radiation
Immune reaction Shoulder dystocia: management
Bugs (infection)
Cervical incompetence HELPER:
Anatomical anomaly (uterine septum etc.) Call for Help
Genetic (aneuploidy, balanced translocation etc.) Episiotomy
Endocrine Legs up [McRoberts position]
Pressure subrapubically [not on fundus]
Enter vagina for shoulder rotation
Reach for posterior shoulder and deliver posterior shoulder/ Return head
Forceps: indications for use into vagina [Zavanelli maneuver] for C-section/ Rupture clavicle or pubic
symphisis
FORCEPS:
Fully dilated cervix
0 ["Zero"] CPD
Ruptured membranes Oral contraceptive complications: warning signs
Cephalic or at least deliverable presentation/ Contracting uterus
Episiotomy done/ Epidural done ACHES:
P!ss and S#!t (bladder and bowel empty) Abdominal pain
Chest pain
Headache (severe)
Eye (blurred vision)
Oral contraceptives: side effects Sharp leg pain
CONTRACEPTIVES:
Cholestatic jaundice
Oedema (corneal) Alpha-fetoprotein: causes for increased maternal serum AFP during
Nasal congestion pregnancy
Thyroid dysfunction
Raised BP "Increased Maternal Serum Alpha Feto Protein":
Acne/ Alopecia/ Anaemia Intestinal obstruction
Cerebrovascular disease Multiple gestation/ Miscalculation of gestational age/ Myeloschisis
Elevated blood sugar Spina bifida cystica
Porphyria/ Pigmentation/ Pancreatitis Anencephaly/ Abdominal wall defect
Thromboembolism Fetal death
Intracranial hypertension Placental abruption
Vomiting (progesterone only)
Erythema nodosum/ Extrapyramidal effects
Sensitivity to light Early cord clamping: indications
RAPID CS:
Post-partum haemorrhage (PPH): causes Rh incompatibility
Asphyxia
4 'T's: Premature delivery
Tissue (retained placenta) Infections
Tone (uterine atony) Diabetic mother
Trauma (traumatic delivery, episiotomy) CS (caesarian section) previously, so the funda is RAPID CS
Thrombin (coagulation disorders, DIC)
Gestation period, oocytes, vaginal pH, menstrual cycle: normal
Asherman syndrome features numbers
4 is the normal pH of the vagina.
40 weeks is the normal gestation period.
400 oocytes released between menarche and menopause.
400,000 oocytes present at puberty.
28 days in a normal menstrual cycle.
280 days (from last normal menstrual period) in a normal gestation period.
Multiple pregnancy complications Secondary amenorrhea: causes
HI, PAPA: SOAP:
Hydramnios (Poly) Stress
IUGR OCP
Preterm labour Anorexia
Antepartum haemorrhage Pregnancy
Pre-eclampsia
Abortion
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): complications
I FACE PID:
Infertility
Fitz-Hugh-Curitis syndrome
Abscesses
Chronic pelvic pain
Ectopic pregnancy
Peritonitis
Intestinal obstruction
Postpartum collapse: causes Disseminated: sepsis, endocarditis, arthritis, meninigitis
HEPARINS:
Hemorrhage
Eclampsia
Pulmonary embolism
Amniotic fluid embolism
Regional anaethetic complications APGAR score components
Infarction (MI)
Neurogenic shock SHIRT:
Septic shock Skin color: blue or pink
Heart rate: below 100 or over 100
Irritability (response to stimulation): none, grimace or cry
Prenatal care questions Respirations: irregular or good
Tone (muscle): some flexion or active
ABCDE:
Amniotic fluid leakage?
Bleeding vaginally? Fetus: cardinal movements of fetus
Contractions?
Dysuria? "Don't Forget I Enjoy Really Expensive Equipment":
Edema? Descent
Fetal movement? Flexion
Interal rotation
Extension
Abdominal pain: causes during pregnancy Restitution
External rotation
LARA CROFT: Expulsion
Labour
Abruption of placenta
Rupture (eg. ectopic/ uterus) IUGR: causes
Abortion
Cholestasis IUGR:
Rectus sheath haematoma Inherited: chromosomal and genetic disorders
Ovarian tumour Uterus: placental insufficency
Fibroids General: maternal malnutrition, smoking
Torsion of uterus Rubella and other congenital infecton
Preeclampsia: classic triad Vaginal pH
PREeclampsia: Vagina has 4 labia and normal pH of vagina is about 4.
Proteinuria
Rising blood pressure
Edema
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): causes, effects
"PID CAN be EPIC":
Forceps: indications for delivery · Causes:
Chlamydia trachomatis
FORCEPS: Actinomycetes
Foetus alive Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Os dilated · Effects:
Ruptured membrane Ectopic
Cervix taken up Pregnancy
Engagement of head Infertility
Presentation suitable Chronic pain
Sagittal suture in AP diameter of inlet
Delivery: instrumental delivery prerequisites PAINS:
Period that is late
AABBCCDDEE: Abdominal cramps
Analgesia Increase in body temperature
Antisepsis Noticeable vaginal discharge
Bowel empty Spotting
Bladder empty
Cephalic presentation
Consent
Alpha-fetoprotein: some major causes for increased maternal serum
Dilated cervix
AFP during pregnancy
Disproportion (no CPD)
Engaged
TOLD:
Episiotomy
Testicular tumours
Obituary (fetal death)
Liver: hepatomas
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB): 3 major causes Defects (neural tube defects)
DUB:
Don't ovulate (anovulation: 90% of cases)
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): first line treatment
Unusual corpus leuteum activity (prolonged or insufficient)
Birth control pills (since increases progesterone-estrogen ratio)
Treat PCOS with OCP's (oral contraceptive pills).
Spontaneous abortion: definition
Female pelvis: shapes
"Spontaneous abortion" has less than 20 letters [it's exactly 19 letters].
GAP:
Spontaneous abortion is defined as delivery or loss of products of
· In order from most to least common:
conception at less than 20 weeks gestation.
Gynecoid
Android /Anthropoid
Platypelloid
B-agonist tocolytic (C/I or warning)
RLQ pain: brief female differential
ABCDE:
AEIOU: Angina (Heart disease)
Appendicitis/ Abscess BP high
Ectopic pregnancy/ Endometriosis Chorioamnionitis
Inflammatory disease (pelvic)/ IBD Diabetes
Ovarian cyst (rupture, torsion) Excessive bleeding
Uteric colic/ Urinary stones
Post-partum haemmorrage (PPH): risk factors
PARTUM: Sexual response cycle
Polyhydroamnios/ Prolonged labour/ Previous cesarian
APH/ ANTH EXPLORE:
Recent bleeding history EXcitement
Twins PLateau
Uterine fibroids Orgasmic
Multiparity REsolution
Omental caking: likeliest cause Labour: preterm labor causes
Omental CAking = Ovarian CA DISEASE:
· "Omental caking" is term for ascities, plus a fixed upper abdominal and Dehydration
pelvic mass. Almost always signifies ovarian cancer. Infection
Sex
Exercise (strenuous)
Activities
Parity abbreviations (ie: G 3, P 2012) Stress
Environmental factor (job, etc)
"To Peace And Love":
T: of Term pregnancies
P: of Premature births
A: of Abortions (spontaneous or elective) Ovarian cancer: risk factors
L: of Live births
· Describes the outcomes of the total number of pregnancies (Gravida). "Blue FILM":
Breast cancer
Family history
Infertility
IUD: side effects Low parity
Mumps
Antepartum hemorrhage (APH): major differential
APH:
Abruptio placentae
Placenta previa
Hemorrhage from the GU tract
Labour: factors which determine rate and outcome of labour
3 P's:
Power: stength of uterine contractions
Passage: size of the pelvic inlet and outlet
Passenger: the fetus--is it big, small, have anomalies, alive or dead
You might also like
- OBGYN Student Study GuideDocument39 pagesOBGYN Student Study GuideGoffo13100% (4)
- TRP OB-GYN Study GuideDocument28 pagesTRP OB-GYN Study Guideemmaaziz100% (9)
- ObyGyn - OSCE (FG2)Document23 pagesObyGyn - OSCE (FG2)roorian100% (1)
- ObGyn - OutlineDocument85 pagesObGyn - OutlineMatt McGlothlin100% (2)
- OB/GYN Student Study Guide Abbreviations and DefinitionsDocument38 pagesOB/GYN Student Study Guide Abbreviations and DefinitionsMin-Joo Esther Park100% (1)
- Ob-Gyn OsceDocument2 pagesOb-Gyn Oscechristietwong100% (1)
- ObsGyn OSCE NotesDocument52 pagesObsGyn OSCE Notesmysorewala100% (11)
- Ob Gyn Notes - UWorld 2018Document17 pagesOb Gyn Notes - UWorld 2018Fake person0% (1)
- ObGyn Case FilesDocument27 pagesObGyn Case Filesyanks1120100% (3)
- OB-GYN - Shelf Review NotesDocument47 pagesOB-GYN - Shelf Review NotesJackJoseph95% (19)
- Obstetrics PDFDocument14 pagesObstetrics PDFKatheryn100% (1)
- Pre-pregnancy counseling for epilepsy patientDocument73 pagesPre-pregnancy counseling for epilepsy patientAwais Awais100% (6)
- Clinical Pearls for Reproductive HealthDocument4 pagesClinical Pearls for Reproductive HealthD50% (4)
- Normal Menstrual Cycle and Reproductive PhysiologyDocument18 pagesNormal Menstrual Cycle and Reproductive PhysiologyKatheryn100% (2)
- Study Notes Obstetrics GynecologyDocument55 pagesStudy Notes Obstetrics GynecologyMedShare82% (17)
- Gynecology History TakingDocument1 pageGynecology History TakingSulabh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- OSCE GynecologyDocument55 pagesOSCE GynecologySyahmi Yahya88% (8)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology - 2009Document45 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology - 2009CCGMP100% (1)
- C. Anovulation: C. Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument18 pagesC. Anovulation: C. Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingJan Mikhail Frasco100% (1)
- Case Report: Pregnant Patient with VomitingDocument8 pagesCase Report: Pregnant Patient with VomitingAbdullah Matar86% (7)
- Study Guide For OBGYNDocument34 pagesStudy Guide For OBGYNFiorellaBeatriz100% (1)
- Obs and Gynae Data Interpretation Past PaperDocument21 pagesObs and Gynae Data Interpretation Past PaperShaheera Shamsudin100% (2)
- Obstetrics NotesDocument28 pagesObstetrics NotesMariam A. Karim100% (1)
- Neonate ExaminationDocument11 pagesNeonate ExaminationJana AldourNo ratings yet
- University of Shendi Faculty of Medicine and Surgery OSCE GuideDocument35 pagesUniversity of Shendi Faculty of Medicine and Surgery OSCE GuideYassin Jamal67% (3)
- Obgyn NotesDocument2 pagesObgyn NotesBillie AllenNo ratings yet
- History Taking in ObgynDocument17 pagesHistory Taking in Obgynselvie87100% (1)
- Mks Notes in Obgyn eDocument134 pagesMks Notes in Obgyn eإسراء محمود100% (3)
- Obgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONDocument94 pagesObgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONvalentinemusa218100% (1)
- OBGYN NotesDocument29 pagesOBGYN NotesavavNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument46 pagesObstetricsanaskabaha100% (3)
- PEDIATRICS NOTES LEGAL ISSUES PHYSICAL EXAMDocument64 pagesPEDIATRICS NOTES LEGAL ISSUES PHYSICAL EXAMrvar839100% (2)
- Ob OsceDocument13 pagesOb OsceMark Lopez100% (3)
- Essay Q's Obs and Gyn 2Document2 pagesEssay Q's Obs and Gyn 2whoosh200886% (7)
- All Obgyn Osce (2) Good Book For OsceDocument75 pagesAll Obgyn Osce (2) Good Book For OsceMohamed Hassan91% (47)
- First Aid For The Obstetrics & Gynecology ClerkshipDocument253 pagesFirst Aid For The Obstetrics & Gynecology ClerkshipSimona Prodanoiu100% (17)
- Comprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdFrom EverandComprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dewhurst's Textbook of Obstetrics & GynaecologyFrom EverandDewhurst's Textbook of Obstetrics & GynaecologyChristoph LeesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Unofficial Guide to Obstetrics and Gynaecology: Core O&G Curriculum Covered: 300 Multiple Choice Questions with Detailed Explanations and Key Subject SummariesFrom EverandThe Unofficial Guide to Obstetrics and Gynaecology: Core O&G Curriculum Covered: 300 Multiple Choice Questions with Detailed Explanations and Key Subject SummariesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- MnemonicsDocument3 pagesMnemonicsXyzhie McCrudenNo ratings yet
- Obstetric MnemonicDocument6 pagesObstetric Mnemonicadwait marhattaNo ratings yet
- L5 - Bleeding in Early Pregnancy (Miscarriage, Ectopic, Molar Pregnancy)Document3 pagesL5 - Bleeding in Early Pregnancy (Miscarriage, Ectopic, Molar Pregnancy)BrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: Prepared By: Nurul Syazwani Binti RamliDocument26 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage: Prepared By: Nurul Syazwani Binti RamliNurul Syazwani RamliNo ratings yet
- WH Buzzwords Compilation 2020Document3 pagesWH Buzzwords Compilation 2020hexagridledsNo ratings yet
- Uwise HYDocument3 pagesUwise HYJack GuccioneNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument38 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationsAzim Syahmi Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- Emed - OB Part 1Document6 pagesEmed - OB Part 1Princess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahDocument33 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Gynecology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesGynecology MnemonicsJared Khoo Er HauNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument158 pagesGynaecologySyahrul ShaaraniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Reluctant Obstetrician': Early Pregnancy Late PregnancyDocument1 pageSyllabus For The Reluctant Obstetrician': Early Pregnancy Late Pregnancysakshi yadavNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics MnemonicsDocument17 pagesObstetrics MnemonicsNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Signs and Stages of PregnancyDocument4 pagesSigns and Stages of PregnancyIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuDocument44 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuLiangkiuwiliuNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesMagnesium SulfateArabela TumbadoNo ratings yet
- Obs-Gynae CP Final (2nd Batch)Document89 pagesObs-Gynae CP Final (2nd Batch)Dipesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Document55 pagesMenorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Aizi DwimeilaNo ratings yet
- ABNORMALDocument33 pagesABNORMALJc Mae CuadrilleroNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsDocument19 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALDocument56 pagesApproach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - PINCIPLES, GRAFTS & FLAPSDocument47 pagesLecture 1 - PINCIPLES, GRAFTS & FLAPSapi-3700579100% (1)
- RDocument15 pagesRapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Pediatric IssuesDocument21 pagesPediatric Issuesapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Ethics GifttotDocument15 pagesEthics Gifttotapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Maternal Fetal ConflictsDocument25 pagesMaternal Fetal Conflictsapi-3700579100% (4)
- Infertility and New Reproductive Technologies 2Document27 pagesInfertility and New Reproductive Technologies 2api-3700579100% (1)
- Surrogate MotherhoodDocument19 pagesSurrogate Motherhoodapi-370057975% (4)
- Proxy ConsentDocument19 pagesProxy Consentapi-3700579100% (2)
- Neonatal Issues - FINALDocument9 pagesNeonatal Issues - FINALapi-3700579No ratings yet
- HB 3773Document9 pagesHB 3773api-3700579No ratings yet
- EthicsDocument33 pagesEthicsapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Med EthicsDocument8 pagesMed Ethicsapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Infertility and New Reproductive TechniquesDocument16 pagesInfertility and New Reproductive Techniquesapi-3700579100% (1)
- Ivf EtDocument6 pagesIvf Etapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Early Induction of LaborDocument26 pagesEarly Induction of Laborapi-3700579100% (1)
- Chromosomal AnomaliesDocument12 pagesChromosomal Anomaliesapi-3700579100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument17 pagesEctopic Pregnancyapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Direct Vs IndirectDocument16 pagesDirect Vs Indirectapi-3700579100% (1)
- Dyspnea 2007Document68 pagesDyspnea 2007api-3700579100% (1)
- Christian Principles of EthicsDocument27 pagesChristian Principles of Ethicsapi-3700579100% (1)
- AbortionDocument31 pagesAbortionapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Skin Case An A 12706Document17 pagesSkin Case An A 12706api-3700579No ratings yet
- 17-Year Old CaseDocument12 pages17-Year Old Caseapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Endocrine Pa Tho LectureDocument105 pagesEndocrine Pa Tho Lectureapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PathologyDocument79 pagesGastrointestinal Pathologyapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Hepatic PathologyDocument50 pagesHepatic Pathologyapi-3700579100% (1)
- GIT Pathology Lecture 2005Document161 pagesGIT Pathology Lecture 2005api-3700579100% (5)
- Breast SituationalDocument19 pagesBreast Situationalapi-3700579No ratings yet
- He Ma To PathologyDocument30 pagesHe Ma To Pathologyapi-3722051No ratings yet
- MCQs First YearDocument2 pagesMCQs First YearF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Prelim ExamDocument27 pagesPharmacology Prelim ExamKate Onniel RimandoNo ratings yet
- As Biology AnswersDocument303 pagesAs Biology AnswersWael TareqNo ratings yet
- FP TCLDocument2 pagesFP TCLlaliejhessNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Glucose Tolerance TestDocument10 pagesUnit 2 Glucose Tolerance TestMs.V. Mahesha Asst. Prof.No ratings yet
- Pengendalian Persediaan Tablet Tambah DarahDocument8 pagesPengendalian Persediaan Tablet Tambah DarahadnanNo ratings yet
- Vietnamese-English Medical TerminologyDocument12 pagesVietnamese-English Medical Terminologyvietboi61275% (4)
- Nutrition Final Exam Study GuideDocument3 pagesNutrition Final Exam Study GuideSasha CohenNo ratings yet
- Layette Preparation Handout-1Document2 pagesLayette Preparation Handout-1alainea100% (1)
- NFDN 2004 Assignment 1 Teaching Plan 2019Document5 pagesNFDN 2004 Assignment 1 Teaching Plan 2019Jasmine NyottaNo ratings yet
- Uts 1-2. Pregnancy Diagnosis English Version PDFDocument71 pagesUts 1-2. Pregnancy Diagnosis English Version PDFRafiq SamtoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Anemia Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesNutritional Anemia Lesson PlanDarren Cariño100% (1)
- Instructional Design Project Identification Template 281 29Document2 pagesInstructional Design Project Identification Template 281 29api-627764163No ratings yet
- ÓbitoDocument111 pagesÓbitoDamián López RangelNo ratings yet
- Chinese Gender Calendar: Calculator, 2017 Predictor Chart for Baby GenderDocument6 pagesChinese Gender Calendar: Calculator, 2017 Predictor Chart for Baby GenderAnonymous uDuusWmdtNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument33 pagesPlacenta PreviamidoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology GCSE: Topic 7: Animal Coordination, Control and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesEdexcel Biology GCSE: Topic 7: Animal Coordination, Control and HomeostasissamNo ratings yet
- A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study of Sublingual, Vaginal, and Rectal Misoprostol For The Management of First Trimester Missed AbortionsDocument7 pagesA Randomized Controlled Clinical Study of Sublingual, Vaginal, and Rectal Misoprostol For The Management of First Trimester Missed AbortionsasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Nutrients Intake and Risk of Preeclampsia in Pregnant WomenDocument8 pagesNutrients Intake and Risk of Preeclampsia in Pregnant WomenewanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Document98 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Miraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Female 2021Document51 pagesInfertility - Female 2021Nikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Aphrodisiac Mother & Aunty: XyshivaDocument13 pagesAphrodisiac Mother & Aunty: XyshivaAnonymous pmVnncYJ60% (5)
- 2017 FhsisDocument480 pages2017 FhsisFidel Mar SebastianNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Cytology Assessment of Feto-Placental FunctionDocument3 pagesHormonal Cytology Assessment of Feto-Placental FunctionElina G100% (1)
- Acusera 2111EC 2112EC 2113C Mindray CL Series - Update 09 2022Document3 pagesAcusera 2111EC 2112EC 2113C Mindray CL Series - Update 09 2022Ulises Saldias RoaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Identifying and Describing The Parts of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument82 pagesLesson 1: Identifying and Describing The Parts of The Female Reproductive SystemLendel Mariz O. CepilloNo ratings yet
- Dystocia Diagnosis and Management in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesDystocia Diagnosis and Management in 40 CharactersShia LevyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Background To The StudyDocument69 pagesChapter One: Background To The Studythesaintsintservice100% (1)
- Embracing The Cross of InfertilityDocument20 pagesEmbracing The Cross of InfertilityLeopoldo Varela Acosta100% (2)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument13 pagesPre EclampsiaEniamrahs DnalonNo ratings yet