0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesIV Cannulation Clinical Learning Guide
1. The document outlines the steps for intravenous cannulation, including collecting necessary equipment, selecting an appropriate vein site, preparing the patient and cannula, performing the cannulation procedure safely, and disposing of used equipment properly.
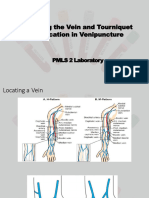
2. Key steps include selecting a vein in the forearm or hand that is palpable, straight, and away from joints; preparing the site with a tourniquet and swab; inserting the cannula at a 30 degree angle and watching for flashback; securing the cannula and disposing of the needle.
3. Post-procedure tasks involve disposing of sharps properly and cleaning any blood.
Uploaded by
mzainal_18Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesIV Cannulation Clinical Learning Guide
1. The document outlines the steps for intravenous cannulation, including collecting necessary equipment, selecting an appropriate vein site, preparing the patient and cannula, performing the cannulation procedure safely, and disposing of used equipment properly.
2. Key steps include selecting a vein in the forearm or hand that is palpable, straight, and away from joints; preparing the site with a tourniquet and swab; inserting the cannula at a 30 degree angle and watching for flashback; securing the cannula and disposing of the needle.
3. Post-procedure tasks involve disposing of sharps properly and cleaning any blood.
Uploaded by
mzainal_18Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd