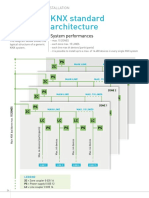
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Course UK
Uploaded by
Mubaraque MoosaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Course UK
Uploaded by
Mubaraque MoosaCopyright:
Available Formats
KNX System arguments
KNX Association
KNX BASIC COURSE
TableofContents
1
2
3
4
KNX Association: A Brief Outline ................................................................................. 3
Goals of the KNX Association ...................................................................................... 4
KNX: the Technology ................................................................................................... 5
KNX System specification ............................................................................................ 6
4.1
4.2
KNX Media ........................................................................................................... 6
Areas of application for the various media ........................................................... 7
4.2.1
5
6
7
8
9
Types of Configuration ..................................................................................... 7
ETS End user versions ................................................................................................ 8
KNX Interworking ......................................................................................................... 9
Success Rate ............................................................................................................. 10
The Advantages of KNX ............................................................................................ 10
Selling the benefits .................................................................................................... 12
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX System arguments
KNX Association
2
KNX BASIC COURSE
1 KNX Association: A Brief Outline
KNX Association has been set up in 1999 with headquarters in Brussels as the merger
between three former European associations promoting intelligent homes and buildings,
i.e.:
BCI (France) promoting the Batibus system;
EIB Association (Belgium) promoting the EIB system;
European Home Systems Association (Holland) promoting the EHS system.
KNX Association has the following goals:
definition of a new truly open standard KNX for intelligent homes and buildings;
establishing the KNX Trademark as a token for quality and multi-vendor interworking;
establishing KNX as the European and worldwide standard.
As long as needed, KNX Association also offers support for the legacy systems Batibus,
EIB and EHS, including certification according to these previous standards. As EIB is
backward compatible to KNX, most devices can be labelled both with the KNX as well as
the EIB logo.
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX System arguments
KNX Association
3
KNX BASIC COURSE
2 Goals of the KNX Association
z
Definition of testing and quality standards via working and expert groups
(KNX Specifications)
Technical Hotline for manufacturers developing KNX compatible devices
Issue of KNX Trademark on the basis of specifications through KNX
Certification
National and International Standardization Activities
Promotion of training measures by certification of training centers
Promotional activities (web site, trade fairs, brochures, )
Encouraging forming of national groups
Scientific Partnership for Technical institutes
Rest specification work/promotion/certification of legacy systems
Figure 1: Goals of the KNX Association
KNX Association consisted of 9 members when it was founded: this number has
meanwhile increased to more than 125 (until June 2008), including companies that were
before not a member in any of the legacy associations. These companies represent more
than 80% of the European market for installation devices and white goods. The current
membership list is available at any time under www.knx.org.
As far as the legacy associations is concerned,
the Batibus Club was transformed into the national group KNX France;
the KNX Association has taken over the development and sale of the KNX software
packages from EIBA Brussels. This amongst others includes the ETS (Engineering
Tool Software) (see later);
EHSA will be integrated in the KNX structures.
At the end of 2003, the KNX Standard was approved by CENELEC (European Committee
of Electrotechnical Standardisation) as the European Standard for Home and Building
Electronic Systems as part of the EN 50090 Series. The KNX Standard was also
approved by CEN (EN 13321-1 for media and protocol and EN 13321-2 for KNXnet/IP). At
the end of 2006, KNX was also approved as a world standard (ISO/IEC 14543-3).
In 2007, the Chinese translation of the international standard achieved GB/Z status as
GB/Z 20965.
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX System arguments
KNX Association
4
KNX TP1 Topology
KNX Association
KNX BASIC COURSE
TableofContents
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Topology .................................................................................................................... 40
Topology: Area .......................................................................................................... 41
Topology: Several Areas............................................................................................ 42
Individual Address ..................................................................................................... 43
Coupling Unit: Gate Function ..................................................................................... 44
Coupler: Block Diagram ............................................................................................. 45
Coupling Unit: Types and Functions .......................................................................... 46
Coupling Unit: Fields of Application ........................................................................... 47
Connecting Several Lines .......................................................................................... 48
Practical Example for explanation of functionality...................................................... 49
Internal Line Telegram ............................................................................................... 50
Line-crossing Telegram ............................................................................................. 51
Area-crossing Telegram............................................................................................. 52
Coupling Unit: Routing Counter ................................................................................. 53
KNX Internal and External Interfaces...................................................................... 54
Topology Structure in building ................................................................................ 55
Taking into account higher telegram rates: IP Network ............................................. 57
Limits to the use of IP routers .................................................................................... 59
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX TP1 Topology
KNX Association
39
KNX BASIC COURSE
Figure 1: Topology - Line
1 Topology
Each bus device (DVC) can exchange information with any other device by means of
telegrams.
One line consists of a maximum of 4 line segments, each with a maximum of 64 bus
devices. Each segment requires an appropriate power supply. 1
The actual number of devices is dependent on the power supply selected and the power
input of the individual devices.
This chapter assumes the use of central power supply units only. For distributed power supply
units, consult chapter TP1 installation.
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX TP1 Topology
KNX Association
40
KNX BASIC COURSE
Figure 2: Topology - Area
2 Topology: Area
If more than 1 line is to be used or if a different structure is to be selected, then up to 15
lines can be connected to a main line via a line coupler (LC). This is called an area.
It is also possible to have up to 64 bus devices on the main line. The maximum number of
bus devices on the main line decreases by the number of line couplers in use.
Each line, including the main line, must have its own power supply unit.
Line repeaters may not be used on backbone or main lines.
Home and Building Management Systems
KNX TP1 Topology
KNX Association
41
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
KNX BASIC COURSE
TableofContents
1
THE ETS 3 PROFESSIONAL SOFTWARE: GENERAL ASPECTS........................ 127
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
General aspects ............................................................................................... 127
Concept of ETS 3 Professional ........................................................................ 127
System requirements ....................................................................................... 128
Installation of ETS 3 Professional .................................................................... 129
Licensing .......................................................................................................... 130
Project design with ETS 3 Professional - Principles ........................................ 131
Starting ETS 3 Professional ............................................................................. 132
Working with ETS 3 Professional ..................................................................... 133
ETS 3 Professional settings and options ......................................................... 134
1.9.1
1.9.2
1.9.3
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
2
Converting ETS 2 databases ........................................................................... 139
Product data ..................................................................................................... 140
Import ............................................................................................................... 141
Product catalog ................................................................................................ 142
Exporting product databases ........................................................................... 143
OPENING A PROJECT WITH ETS 3 PROFESSIONAL ......................................... 144
2.1
2.2
2.3
Creating a new project ..................................................................................... 144
Opening existing projects ................................................................................. 145
Project properties ............................................................................................. 146
2.3.1
2.3.2
2.3.3
2.3.4
2.3.5
2.4
Tab page Common ...................................................................................... 146
Tab page History Overview .......................................................................... 146
Tab page Security ........................................................................................ 146
Tab page Comment ..................................................................................... 147
Tab page Backbone Line ............................................................................. 147
Views in Project Design ................................................................................... 148
2.4.1
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.4
3
Tab page Presentation ................................................................................. 135
Databases .................................................................................................... 137
Working with multiple databases.................................................................. 138
Building view ................................................................................................ 149
Group Addresses view ................................................................................. 150
Topology view .............................................................................................. 151
Device view .................................................................................................. 152
QUICK PROJECT DESIGN WITH ETS 3 PROFESSIONAL ................................... 153
3.1
3.2
3.3
Starting the project ........................................................................................... 153
Creating a building structure ............................................................................ 154
Product Finder ................................................................................................. 156
3.3.1
3.3.2
Finding products .......................................................................................... 156
Product information ...................................................................................... 157
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
125
KNX BASIC COURSE
3.3.3
3.4
Properties dialog of devices .......................................................................... 159
3.4.1
3.5
3.6
3.7
3.8
Inserting products ........................................................................................ 158
Device parameters ....................................................................................... 160
Editing objects .................................................................................................. 161
Setting the flags ............................................................................................... 162
Configuring the group addresses ..................................................................... 164
Allocation of group addresses .......................................................................... 165
3.8.1
3.8.2
Sending group address ................................................................................ 166
Acknowledge flag ......................................................................................... 167
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
126
KNX BASIC COURSE
1 THE ETS 3 PROFESSIONAL SOFTWARE: GENERAL ASPECTS
1.1 General aspects
KNX is a comprehensive, integrated system for home and building automation for the
implementation of upwardly compatible, flexible and cost-effective solutions. Due to its
functional versatility, its use is not confined to simple and limited installations but also
enables solutions for the complete building sector. KNX fulfils the requirements of
electrical installers during project design and installation, commissioning, operation of the
bus system through to maintenance. For planning, project design and commissioning of a
KNX installation, a software tool for planners and electrical installers is needed that is
both clearly structured and easy to use.
A comprehensive Online Help is also included in the tool. Via the F1 button, the user has
access to context-sensitive help, which is directly related to the current program section.
The planning and design of a building, in which one intends to use KNX is no different
than conventional electrical design. In the initial phase, the planner must consider the
following:
the type and use of the building
the building system components to be used and their functions,
the type and frequency of changes in usage,
any special requirements of the building contractor,
the cost implications.
The planning of the electrical installation is carried out as in conventional installations in
accordance with the general accepted rules for electrotechnical installations and the
conditions for connection as laid down by the electricity supply company. The standard
guidelines and rules for planning, execution and dimensioning must also be observed.
1.2 Concept of ETS 3 Professional
A software tool is made available to planners and electrical installers for the planning,
project design and commissioning of KNX systems. ETS stands for Engineering Tool
Software 1 . ETS TM is a registered trademark of the KNX Association in Brussels. Although
the ETS 3 Professional is a completely new developed software, great emphasis was laid
during its development on keeping the user interface as similar as possible to the previous
version, i.e. ETS 2.
The user interface of the ETS 3 was however completely revised as regards presentation
and operating philosophy. The presentation and operation of the software was adapted to
current standards, as known for instance from MS Windows Explorer. In this way
operation and orientation have been substantially simplified compared to ETS 2.
Formerly EIB-Tool-Software
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
127
KNX BASIC COURSE
1.3 System requirements
The following minimum system configuration is needed when using the ETS 3
Professional (recommended values are in brackets):
PC with 400 MHz (1 GHz) processor
128 MB (256 MB) RAM
MS Windows 98 / ME / 2000 / NT4 / XP
True colour VGA 800x600 (1024x768)
Hard disk with 3 GB of free memory
Interfaces: RS 232 or USB
These values apply for standard projects without so-called plug-in software. For more
complex projects or projects with products requiring a plug-in software, the following
higher system requirements apply:
PC with 1 GHz (2 GHz) processor
256 MB (512 MB) RAM
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
128
KNX BASIC COURSE
Figure 1: Installation of ETS 3 Professional
1.4 Installation of ETS 3 Professional
You will receive the ETS 3 Professional CD from KNX Association or you can download
the software from http://www.knx.org. If you have downloaded the software from internet,
you will have to start the installation of the software by extracting the downloaded file and
then by opening the installation program Ets3ProSetup.exe.
When installing, you have the option of choosing the desired installation type.
It is recommended that you run a complete installation.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
129
KNX BASIC COURSE
Figure 2: Licensing
1.5 Licensing
With the ETS 3 Professional, a new licensing procedure is introduced.
There are 4 versions of the ETS 3:
Demo: max. 1 project, max. 20 devices, no bus access,
Trainee: max. 1 project, max. 20 devices, no export, otherwise full functionality
Full version: with PC dependent key or with a PC independent dongle
Supplementary version. This version is intended as an extra license to a full version
for a second PC (Commissioning/Notebook). This version is also available with a PC
dependent key or with a PC independent dongle.
Regardless of which mode it will run in after installation, the ETS 3 Professional is fully
installed. The mode depends on the license key that is entered. After the installation, the
program will first run in Demo mode. You can access the license request and installation
window when starting ETS 3 Professional or via the menu item Extras/Licensing in the
menu bar.
The window offers the choice of licensing a full version, trainee version or a
supplementary version. Further dialogs for requesting the license key and for unlocking
the software will give you detailed information about how to proceed. You will also find a
detailed description of the licenses and the procedure on the ETS 3 CD.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
130
KNX BASIC COURSE
1.6 Project design with ETS 3 Professional - Principles
The following steps constitute a fundamental sequence when designing with ETS 3
Professional.
Make the necessary settings in ETS 3 Professional
Import or convert the product databases
Create the project and fill in the necessary data
Set up the project structure (building structure/bus topology)
Insert KNX devices (devices and their corresponding applications) into the building
structure
Set the parameters of the KNX products according to the requirements of your installation
Create group addresses
Link the group objects of the KNX products with the group addresses
Assign the inserted KNX products to the bus topology (final definition of the individual
address)
Assign the inserted KNX products to the created functions
Check the project design
Print out the documentation
Save your project
In special cases, it may be necessary to deviate from this sequence. For smaller projects,
some of these steps may be skipped in some cases, whereas more complex projects
(team projects) may require some additional design work.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Project Design: Basic
KNX Association
131
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
KNX BASIC COURSE
TableofContents
1
Commissioning ........................................................................................................ 217
1.1
1.2
Starting the commissioning ...................................................................................... 219
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.8
Bus access ....................................................................................................... 220
Configuring the interface .................................................................................. 221
Configuring local devices ................................................................................. 224
Opening the project .......................................................................................... 225
Selecting the view ............................................................................................ 225
Download ......................................................................................................... 227
Assigning individual addresses ........................................................................ 229
Downloading the application (application software) ......................................... 230
Reconfiguration ........................................................................................................ 231
3.1
3.2
3.3
4
5
6
7
8
Commissioning requirements .......................................................................... 217
Local or imported projects ................................................................................ 218
Carrying out project design changes ............................................................... 231
Reprogramming filter tables ............................................................................. 231
Commissioning devices ................................................................................... 231
Unloading bus devices ............................................................................................. 232
Resetting devices .................................................................................................... 233
Checking the local System ID (PL) .......................................................................... 234
Checking the System ID (PL)................................................................................... 235
Downloading the basic configuration (set PL repeater status)................................. 235
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
216
KNX BASIC COURSE
GENERAL NOTES
1 Commissioning
1.1 Commissioning requirements
It is not compulsory for the commissioning of a KNX installation to have a complete
installation of the bus system with all the bus devices. In larger projects (several building
sections), it is advisable e.g. to pre-program the bus couplers in the office or in the
workshop. As the complete data set does not necessarily need to be downloaded into the
bus coupler during commissioning, it is a good idea to first download the individual
addresses into the bus couplers and then the remaining relevant data once the bus
couplers are already installed in the system.
Regardless of whether the commissioning is carried out in the office, the workshop or on
the building site, the application modules of the flush-mounted devices should not yet be
installed so that the programming button and the programming LED are accessible. In
distribution boards, the covers should be removed so that the programming buttons and
LEDs of these KNX devices are also accessible. For built-in devices in suspended ceilings
or luminaries, it is a good idea to provide them at least with an individual address in the
workshop as these devices are generally difficult to access once they have been installed.
The stipulated checks during and after the installation must be completed successfully.
Commissioning can be done via:
A serial interface
A USB interface
Or a network connection
on the commissioning PC. The required settings will be explained in detail in the
paragraph Bus access and Configuring the interface.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
217
KNX BASIC COURSE
If the serial interface of the PC is a 9-pin plug, the contacts must connect the serial cable
to the KNX data interface (Pin1 on Pin1, Pin2 on Pin2 Pin9 on Pin9).
Since ETS 3, it is also possible to commission a KNX installation via USB. In both cases,
the corresponding settings must be carried out (see also setting the local individual
address or interface).
ETS 3 enables all functions to either be retrieved from the menu bar or via the context
menu (right mouse button). A large number of functions can also be started directly from
the toolbar via icons. The ETS 3 program thus behaves in the same way as the majority of
programs which run under the Windows TM operating system. All the following screenshots
only show examples. The functions must not necessarily be retrieved in the way that is
described here. Initially, it is worthwhile to use the right mouse button as often as possible
as it takes you directly to your required destination in most cases.
Figure 1: Local or imported projects
1.2 Local or imported projects
The project of the KNX installation must be contained in the database (e.g.eib.db) for
commissioning purposes. If the project has been configured on another PC, there are two
possibilities available:
The first option involves exporting the project with ETS 3 and importing it on the
commissioning PC. The necessary steps are described in the Project Design chapter. It
should however be ensured that all the additional installed programs e.g. for LC displays
are also installed on the commissioning PC.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
218
KNX BASIC COURSE
The second option involves copying the entire database (e.g. eib.db) from the first PC
onto the second PC. This process has the benefit that all the products are contained in the
database should an expansion be required at a later date. The disadvantage is that the
database can become very large under certain conditions (several 100 MB). The
database must either be burnt onto a CD or copied using a network connection or via
another data storage medium. It should moreover be noted whether the database
contains products which can only run with additional files (DLLs, parameter files etc.).
These must be copied with the correct paths. The recommendations of the manufacturer
must be observed!
Figure 2: Starting the commissioning
2 Starting the commissioning
The following menu icons are responsible for the commissioning or diagnostics:
Online
Prepares the PC for bus access
Download
opens the Download dialog for individual addresses and
programs
Device Info
opens the Device Info dialog
Bus Monitor
opens the bus monitor
Group Monitor
opens the group monitor
Furthermore you will find the following functions under the Commissioning resp.
Diagnostics menu:
Unload
A commissioned device will be set back to its original
state when selected
Reset Device
will send a restart command to a bus device
Individual Addresses
Compares the devices in the installation to the ones in
the project
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
219
KNX BASIC COURSE
Figure 3: Bus access
2.1 Bus access
Before the commissioning can be started, it is necessary to connect the interface for bus
communication with an appropriate cable connection to the commissioning PC and to
choose the correct setting on the commissioning PC. This can either be a serial interface
(RS232), a USB interface or a network connection. Irrespective of which interface has
been chosen, the communication settings in ETS should be checked before the initial
commissioning phase.
The submenu item Options is located under the Extras menu. The Communication
window contains the corresponding setting options.
Home and Building Management Systems
ETS 3 Commissioning
KNX Association
220
You might also like
- PySpark Data Frame Questions PDFDocument57 pagesPySpark Data Frame Questions PDFVarun Pathak100% (1)
- Product: ManualDocument20 pagesProduct: ManualSmartlife TechNo ratings yet
- 12.ETS5 Diagnostics E0115aDocument51 pages12.ETS5 Diagnostics E0115aIrina TiNo ratings yet
- KNX Cookbook v1Document108 pagesKNX Cookbook v1luis9000000% (1)
- KNX - Planner TrainingDocument41 pagesKNX - Planner TrainingMina AzmiNo ratings yet
- KNX PushbuttonsDocument126 pagesKNX PushbuttonsTaha Mallat100% (1)
- Lightmaster KNX Mmaster 16pp v3Document9 pagesLightmaster KNX Mmaster 16pp v3Tenchiu AndreeaNo ratings yet
- KNX Design Project Preparation enDocument32 pagesKNX Design Project Preparation enjfranbripi793335No ratings yet
- KNX InfoDocument26 pagesKNX Inforpandit075698No ratings yet
- KNX Project Design GuidelinesDocument16 pagesKNX Project Design GuidelinesmicaNo ratings yet
- KNX System Principles: Smart Home and Building Solutions. Global. Secure. ConnectedDocument16 pagesKNX System Principles: Smart Home and Building Solutions. Global. Secure. ConnectedMady Deka ApriliyaNo ratings yet
- DALI ManualDocument93 pagesDALI ManualtichvraNo ratings yet
- Presentation KPMG Industry 4 0 Digital SCM For Enabling Growt 2019Document43 pagesPresentation KPMG Industry 4 0 Digital SCM For Enabling Growt 2019JhonathaNo ratings yet
- ETS4 Planning Complex E0411bDocument59 pagesETS4 Planning Complex E0411benghassanain6486No ratings yet
- KNXDocument24 pagesKNXGabetsos KaraflidisNo ratings yet
- Schneider KNXDocument1 pageSchneider KNXRodrigo Pinetta100% (2)
- KNX Automation System ManualDocument59 pagesKNX Automation System ManualAnonymous zZWZsjWPNo ratings yet
- 01 Fail Safe PlanningDocument11 pages01 Fail Safe Planningbehrooz100% (1)
- How To Create KNX Design FragmentsDocument12 pagesHow To Create KNX Design FragmentsMessaoudi FaresNo ratings yet
- Catalog KNXDocument152 pagesCatalog KNXPopescu ConstantinNo ratings yet
- KNX Pro 2015Document93 pagesKNX Pro 2015Bobeică Iustin CătălinNo ratings yet
- KNX - 02 - 01 Cookbook Introduction v01.00.01Document4 pagesKNX - 02 - 01 Cookbook Introduction v01.00.01FabricioNo ratings yet
- 2 KNX Project Design GuidelinesDocument17 pages2 KNX Project Design GuidelinesEmil EremiaNo ratings yet
- KNX Home and Building ControlDocument92 pagesKNX Home and Building ControlMarius37No ratings yet
- KNX Solutions enDocument32 pagesKNX Solutions enalexwongks6118No ratings yet
- KNX System Principles enDocument16 pagesKNX System Principles en7esabat7033No ratings yet
- KNX Solutions EnglishDocument38 pagesKNX Solutions EnglishRobertoAraujoNo ratings yet
- KNX Checklist Project Start en ScreenDocument12 pagesKNX Checklist Project Start en ScreenMandy ThamNo ratings yet
- 2013 Descriere BMS ROMANA FinalDocument12 pages2013 Descriere BMS ROMANA FinalDumNo ratings yet
- KNX Eib eDocument24 pagesKNX Eib eAntonis BafatakisNo ratings yet
- Home AutomationDocument300 pagesHome AutomationRamomNo ratings yet
- KNX ArchitectureDocument1 pageKNX ArchitectureNoman KhalidNo ratings yet
- KNX IoTDocument16 pagesKNX IoTJUANJAUNNo ratings yet
- KNX Building Control SystemDocument11 pagesKNX Building Control SystemEnar PauNo ratings yet
- ABC's of DALI GuideDocument18 pagesABC's of DALI GuideZzzdddNo ratings yet
- KNX - CommunicationDocument25 pagesKNX - CommunicationEdouard BurnNo ratings yet
- KNX Vragen ExDocument5 pagesKNX Vragen ExkloesNo ratings yet
- KNX Planning SiemensDocument100 pagesKNX Planning SiemensTarik RachiahiNo ratings yet
- KNX System Design GuideDocument28 pagesKNX System Design GuideSameer C Musthafa100% (2)
- KNX Partner: Training CourseDocument14 pagesKNX Partner: Training CourseNawelNo ratings yet
- #01 KNX ArchitectureDocument35 pages#01 KNX ArchitectureMircea Remus AndoneNo ratings yet
- KNX Powerline PL110Document17 pagesKNX Powerline PL110Mircea Remus AndoneNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide KNX SensorsDocument39 pagesInstallation Guide KNX Sensorsmail87523No ratings yet
- Heating, Cooling, Ventilation With KNX: Solutions and ProductsDocument28 pagesHeating, Cooling, Ventilation With KNX: Solutions and ProductsDusko StefanovNo ratings yet
- Practical Guidance for Defining a Smart Grid Modernization Strategy: The Case of DistributionFrom EverandPractical Guidance for Defining a Smart Grid Modernization Strategy: The Case of DistributionNo ratings yet
- KNX Training. KNX Association VDocument65 pagesKNX Training. KNX Association VAIIOT SSSNo ratings yet
- KNX S Mode TutorialDocument40 pagesKNX S Mode Tutorialjcmendez506No ratings yet
- KNXDocument60 pagesKNXtrpac0% (1)
- 106 - KNX RFDocument17 pages106 - KNX RFMurali Varathan100% (1)
- KNX Planning Training: Time ScheduleDocument50 pagesKNX Planning Training: Time ScheduleGeorge TrisinaNo ratings yet
- The Worldwide STANDARD For Home and Building ControlDocument74 pagesThe Worldwide STANDARD For Home and Building ControlHoang Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- SIEMENS KNX ETS5-For-Beginners - en PDFDocument4 pagesSIEMENS KNX ETS5-For-Beginners - en PDFbbas6825No ratings yet
- Plan For Intelligent Future Safety: KNX CatalogueDocument182 pagesPlan For Intelligent Future Safety: KNX CatalogueMircea Constantin Gridan100% (1)
- KNX StandardDocument2 pagesKNX Standardrpandit075698No ratings yet
- KNX Projects: Electrical and Installation ConsiderationsDocument49 pagesKNX Projects: Electrical and Installation ConsiderationsTaty CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Read and Download Ebook KNX Advanced Course Documentation PDFDocument2 pagesRead and Download Ebook KNX Advanced Course Documentation PDFsina roshani payan0% (1)
- PRAESENSA Introduction 2018Document39 pagesPRAESENSA Introduction 2018Trần Văn BắcNo ratings yet
- KNX Pro OfficeDocument30 pagesKNX Pro OfficeBobeică Iustin CătălinNo ratings yet
- 01.system Arguments - EN0419aDocument14 pages01.system Arguments - EN0419aNicu PuscasNo ratings yet
- 101 - System ArgumentsDocument16 pages101 - System ArgumentsMurali VarathanNo ratings yet
- Cool KNX GuidelinesDocument12 pagesCool KNX Guidelineselan.ks786No ratings yet
- TS 2000Document4 pagesTS 2000Firdaus AriefatosaNo ratings yet
- OUTPUT - Technology PlanDocument6 pagesOUTPUT - Technology PlanEdward RaagasNo ratings yet
- Starrett Catalogue 32ΕDocument102 pagesStarrett Catalogue 32ΕChris ValNo ratings yet
- Copy Model in PdsDocument1 pageCopy Model in Pdsmoraima cameroNo ratings yet
- List of Dealers Who Did Not Login On GST Portal and Filled Nill ReturnDocument142 pagesList of Dealers Who Did Not Login On GST Portal and Filled Nill ReturnMayukh Singh0% (1)
- SOP For Automation Multiple GRN - HSD - ProcessDocument9 pagesSOP For Automation Multiple GRN - HSD - ProcessVibhor JainNo ratings yet
- Zyqad EquipmentDocument29 pagesZyqad EquipmentHardik AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide For Colubris/HP Gateways: 2008, Wifi-Soft Solutions All Rights ReservedDocument10 pagesQuick Start Guide For Colubris/HP Gateways: 2008, Wifi-Soft Solutions All Rights ReservedTùng LâmNo ratings yet
- Report :inventory Management SystemDocument61 pagesReport :inventory Management SystemShubham Saini0% (1)
- SPACE GASS Installation GuideDocument9 pagesSPACE GASS Installation GuideozbuildNo ratings yet
- Gs TTFDocument24 pagesGs TTFjonhinnoNo ratings yet
- 7 Standardisasi DataDocument37 pages7 Standardisasi DataRestina RitongaNo ratings yet
- FlexG DocUpdate Value Set SecurityDocument38 pagesFlexG DocUpdate Value Set Securitydsgandhi6006No ratings yet
- Sensors: Sensor and Sensor Fusion Technology in Autonomous Vehicles: A ReviewDocument37 pagesSensors: Sensor and Sensor Fusion Technology in Autonomous Vehicles: A ReviewRaka PratindyNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide For Windows: Section 1 - Create An Account at Udaan Translation Web InterfaceDocument15 pagesInstallation Guide For Windows: Section 1 - Create An Account at Udaan Translation Web Interfacekamarajme2006No ratings yet
- SDM Group AssignmentDocument41 pagesSDM Group AssignmentDaddy's PicksNo ratings yet
- Bulk SMS ProposalDocument5 pagesBulk SMS ProposalPrince JamesNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference For Sifmis Implementation Quality Assurance Consultant (Firm)Document8 pagesTerms of Reference For Sifmis Implementation Quality Assurance Consultant (Firm)Oshinfowokan OloladeNo ratings yet
- Ganister Documentation: How To Install and Run Ganister (Beta Version)Document13 pagesGanister Documentation: How To Install and Run Ganister (Beta Version)ymaingonNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Gecon: Grzegorz Klima, Karol Podemski, Kaja Retkiewicz-WijtiwiakDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Gecon: Grzegorz Klima, Karol Podemski, Kaja Retkiewicz-WijtiwiakVeljko BojovicNo ratings yet
- C2100UZ BasicManual EFGSpDocument146 pagesC2100UZ BasicManual EFGSpwlodekszNo ratings yet
- Systolic ArrayDocument42 pagesSystolic Arrayhimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- How To Integrate Google Drive With OdooDocument13 pagesHow To Integrate Google Drive With OdoorobogormanNo ratings yet
- 25355595Document26 pages25355595Essoff EssoffNo ratings yet
- Oop Exercises Java Programming TutorialDocument9 pagesOop Exercises Java Programming TutorialJoe TitanNo ratings yet
- (IN) SECURE Magazine Issue 14Document111 pages(IN) SECURE Magazine Issue 14insecuremag100% (3)
- Requirements Gathering Checklist: (Document Subtitle)Document4 pagesRequirements Gathering Checklist: (Document Subtitle)WeyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ns2Document239 pagesIntro To Ns2Umair Ali Soomro100% (1)