Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prednisolone
Uploaded by
Katie McPeek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
920 views2 pagesCommon side effects Much more common with high-dose long term therapy -- CNS: depression, euphoria, headache, personality changes, psychoses, restlessness. Monitor serum electrolytes and glucose, may cause hyperglycemia. May decrease serum potassium and calcium and increase serum sodium concentrations.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCommon side effects Much more common with high-dose long term therapy -- CNS: depression, euphoria, headache, personality changes, psychoses, restlessness. Monitor serum electrolytes and glucose, may cause hyperglycemia. May decrease serum potassium and calcium and increase serum sodium concentrations.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
920 views2 pagesPrednisolone
Uploaded by
Katie McPeekCommon side effects Much more common with high-dose long term therapy -- CNS: depression, euphoria, headache, personality changes, psychoses, restlessness. Monitor serum electrolytes and glucose, may cause hyperglycemia. May decrease serum potassium and calcium and increase serum sodium concentrations.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
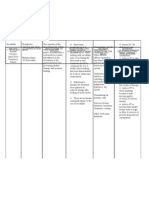
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Prednisolone Norpred Antiasthmatics, 50 mg IV Q Day
corticosteroids
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
1 hr Rapid Unknown 4-60 mg/day
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Used systemically and locally in a wide variet of chronic Do not use the acetate form of this drug for IV
diseases including: Inflammatory, allergic, hematologic, administration. May be added to D5W or 0.9% NaCl
neoplastic, autoimmune disorders, asthma. RATE: No more than 10 mg/min
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindicated in active untreated infections. Known
In pharmacologic doses, all agents suppress alcohol, bisulfite, or tartrazine hypersensitivity or
inflammation and the normal immune response. All intolerance. Use cautiously in chronic treatment; Stress;
agents have numerous intense metabolic effects. supplemental doses may be needed.
Suppress adrenal function at chronic doses of rednisolone Common side effects
5 mg/day. Prednisolone have minimal mineralocorticoid Much more common with high-dose long term therapy—
activity. Suppression of inflammation and modification CNS: Depression, euphoria, headache, personality changes,
of the normal immune response. Replacement therapy in psychoses, restlessness. EENT: Cataracts, increased
adrenal insufficiency. intraocular pressure. CV: hypertension. GI: Peptic ulceration,
anorexia, nausea, vomiting. DERM: acne, decreased wound
healing, ecchymosis, fragility, hirsutism, petechiae. ENDO:
adrenal suppression, hyperglycemia. F and E: fluid retention,
hypokalemia, hypokalemic alkalosis. HEMAT:
Thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis. METAB: Weight gain.
MS: muscle wasting, osteoporosis, aseptic necrosis of joints,
muscle pain. MISC: cushingoid appearance (moon face,
buffalo hump), increased susceptibility to infection.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) Monitor serum electrolytes and glucose, may cause
At chronic doses that suppress adrenal function, may hyperglycemia. Routine hematologic values, serum
decrease antibody response to and increase risk of electrolytes, and serum and urine glucose with long term
adverse reactions from live virus vaccines. May decrease treatment. May decrease WBCs. May decrease serum
salicylate levels and effectiveness. potassium and calcium and increase serum sodium
concentrations. May increase serum cholesterol and lipid
values. May decrease the uptake of thyroid. Periodic adenal
function tests should be ordered
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
Take as directed. Take missed doses as soon as remembered
unless almost time for the next dose. Do not abruptly stop
medication. Watch for signs of adrenal insufficiency.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Assess involved systems before and med? Decrease in presenting
periodically during therapy. Assess for signs Signs or symptoms of adrenal symptoms with minimal
of adrenal insufficiency (hypotension, weigh insufficiency systemic side effects.
loss, weakness, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, Supression of the inflammatory
lethargy, confusion, restlessness) before and immune responses.
administering. Monitor I & O and daily
weights. Observe for peripheral edema, steady
weight gain, rales/crackles, or dyspnea
You might also like
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Insulin As PartDocument3 pagesInsulin As PartRezaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- CloxacillinDocument3 pagesCloxacillinRoberto Manuel IINo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Pioglitazone Dosage, Uses, Side Effects and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesPioglitazone Dosage, Uses, Side Effects and Nursing ResponsibilitiesNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Cloxacillin Classification, Mechanism, IndicationsDocument3 pagesCloxacillin Classification, Mechanism, IndicationsKrizzia CarlosNo ratings yet
- Drug Action, Contraindications, Adverse Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Action, Contraindications, Adverse Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- CetirizineDocument2 pagesCetirizineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyw dNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CHDCDocument1 pageDrug Study CHDCIannBlancoNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Document1 pageMagnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Danielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDocument2 pagesDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Treatment/ Infusion d5lrDocument1 pageTreatment/ Infusion d5lrjbespirituNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument14 pagesTB DrugsLexy CadigalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 pagesDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Insulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesInsulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone and MgSO4Document2 pagesDexamethasone and MgSO4Nasriah MacadatoNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy OrsdDocument10 pagesDrugstudy OrsdRafmar A. SalundaguitNo ratings yet
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument1 pagePrednisoneCassieNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument2 pagesNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheetsm_r0se_k0hNo ratings yet
- Predacot PrednisoneDocument1 pagePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Predacot PrednisoneDocument1 pagePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Methylprednisolone (Solu Medrol)Document3 pagesMethylprednisolone (Solu Medrol)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- PulmicortDocument2 pagesPulmicortKatie McPeek100% (2)
- HaldolDocument2 pagesHaldolKatie McPeek100% (2)
- NarcanDocument1 pageNarcanKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ValiumDocument1 pageValiumKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- SynthroidDocument3 pagesSynthroidKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- ZocorDocument2 pagesZocorKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- VigamoxDocument1 pageVigamoxKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- XopenexDocument1 pageXopenexKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- WellbutrinDocument1 pageWellbutrinKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Tag A MetDocument1 pageTag A MetKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Toprol XLDocument2 pagesToprol XLKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Pro To NixDocument2 pagesPro To NixKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Re QuipDocument1 pageRe QuipKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- SenokotDocument1 pageSenokotKatie McPeek100% (1)
- NorvascDocument1 pageNorvascKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- RestorilDocument1 pageRestorilKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Re Me RonDocument2 pagesRe Me RonKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Pep CidDocument1 pagePep CidKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ProzacDocument1 pageProzacKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument2 pagesPrednisoneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ReglanDocument1 pageReglanKatie McPeek100% (1)
- PrazosinDocument1 pagePrazosinKatie McPeek0% (1)
- PaxilDocument1 pagePaxilKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- NarcanDocument1 pageNarcanKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- MorphineDocument2 pagesMorphineKatie McPeek100% (2)
- DOC-20240110-WA0016.Document176 pagesDOC-20240110-WA0016.Sreeja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris STR Bid Suci Rahma Damayanti - 1aDocument5 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris STR Bid Suci Rahma Damayanti - 1aSucirahma100% (1)
- Emilok 2011 MKT Plan TOTAL2Document19 pagesEmilok 2011 MKT Plan TOTAL2maawi2002yahoocomNo ratings yet
- APCA Beating - Pain 2nd EdDocument110 pagesAPCA Beating - Pain 2nd EdMichaelNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi BPHDocument31 pagesPatofisiologi BPHHendry Cleodora RomeoNo ratings yet
- Vol18no8 PDF Version Emerging InfectionsDocument183 pagesVol18no8 PDF Version Emerging InfectionsrehanaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Evaluation of Stroke - UpToDateDocument57 pagesOverview of The Evaluation of Stroke - UpToDateclarissa suryaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SkoliosisDocument9 pagesJurnal SkoliosisLidya SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia and CopdDocument7 pagesAnaesthesia and CopdAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of heart failureDocument79 pagesPharmacotherapy of heart failureAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- CASE Study SampleDocument6 pagesCASE Study SampleMary Shane Aragon MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Adime Note Allison 2Document3 pagesAdime Note Allison 2api-457873289No ratings yet
- 3.4 Balroga - Kaumarbhritya (Ayurvedic Pediatrics)Document4 pages3.4 Balroga - Kaumarbhritya (Ayurvedic Pediatrics)Dr Thushar T.SNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury and AdaptationDocument18 pagesCell Injury and AdaptationNazneen ShawarNo ratings yet
- SMLLDocument8 pagesSMLLArifa Al HusnahNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin 500mg Tab (Zithromax)Document6 pagesAzithromycin 500mg Tab (Zithromax)Mayownski TejeroNo ratings yet
- HIV Transmission, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentDocument4 pagesHIV Transmission, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentBatch V Med 2 SY 21-22No ratings yet
- Ice Berg Phenomenon of DiseaseDocument50 pagesIce Berg Phenomenon of DiseaseMan BoruahNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: DR Tariq Masood TMO Radiology Department, HMCDocument82 pagesCase Presentation: DR Tariq Masood TMO Radiology Department, HMCg1381821No ratings yet
- Patient Referral FormDocument2 pagesPatient Referral Formbasel samNo ratings yet
- Female Genital TuberculosisDocument6 pagesFemale Genital TuberculosisallauddinbarackzaiNo ratings yet
- PED2 6.04 Evaluation of The Child With A LimpDocument15 pagesPED2 6.04 Evaluation of The Child With A LimprachelNo ratings yet
- Reference DataDocument7 pagesReference DataDicky D HutapeaNo ratings yet
- Adjustment DisorderDocument7 pagesAdjustment DisorderRif'aNo ratings yet
- A Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterDocument10 pagesA Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterRazonable Morales RommelNo ratings yet
- National Diabetes Registry Report Vol 1 2009 2012 PDFDocument54 pagesNational Diabetes Registry Report Vol 1 2009 2012 PDFkhairul azlanNo ratings yet
- Water SolutionDocument4 pagesWater Solutionagustiani ari wahyu utamiNo ratings yet
- Older People - Patterns of IllnessDocument4 pagesOlder People - Patterns of IllnessTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- A Single-Arm Study of Sublobar Resection For Ground-Glass Opacity Dominant Peripheral Lung CancerDocument15 pagesA Single-Arm Study of Sublobar Resection For Ground-Glass Opacity Dominant Peripheral Lung CancerYTM LoongNo ratings yet
- Relapsing Polychondritis Morphology, Etiology, Pathogenesis and TreatmentDocument1 pageRelapsing Polychondritis Morphology, Etiology, Pathogenesis and TreatmentRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaNo ratings yet