Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Telecommunicatie
Uploaded by
njirtak92Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Telecommunicatie
Uploaded by
njirtak92Copyright:
Available Formats
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 1/12
Telecommunicatie
Introduction
Different certificates
Certificates o VHF: restricted operator o SRC: Short Range Certificate o ROC: Restricted Operator Certificate o LRC: Long Range Certificate o GOC: General Operator Certificate VHF & SRC => pleasure craft ROC & GOC => merchant marine Valid for 5 years
VHF equipment
Non-portable Portable (obligatory in lifeboat)
General
International regulations
Convention of ITU (International Telecommunication Union) Radio regulation Genve SOLAS European Regulations BIPT (Belgisch Instituut voor Postdiensten en Telecommunicatie)
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 2/12
Telecommunicatie
VHF range
Limited to line of sight direct path Used for o Intraship o Ship to ship o Ship to shore
Authority
Master of ship responsible for use of equipment Equipment must be licensed Operators must have appropriate certificate
Radio equipment
Certificate o Ships name registration o Call sign o MMSI o List all equipment o Used channels Legislation o Original certificate must be available o Sanctions according to national law o Secrecy of communication
Equipment
Power
Fixed VHF: 6 25 W Reduced power: 0,5 1 W o Can be demanded o Not on distress urgency security channels Portable VHF: 0,1 1 W
Dual watch
Listening watch on two channels with one radio Changes every 2,5 s for very short time to channel 16 Transmission found on 16, stays Triple watch & multiple watch also possible
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 3/12
Telecommunicatie
GSM phones
Global System for Mobile communications Increased use worldwide Not instead of VHF o Insufficient coverage o Line in use / network saturated => emergency calls not privileged o Call only between 2 o Direct contact with approaching help not possible o Positioning & localisation is difficult o Network saturated => can be blocked o Connection can be impossible o Battery can be dead
Portable radios
Walkie talkie Emergency => channel 16 Normal use => channel 15 & 17 According to national laws
Conformity
If conform => certificate On board SOLAS vessels
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 4/12
Telecommunicatie
Frequencies
Between 156 162 MHz Power 15 25 W => range 30 Power 1 W => range 6 7 Range depends on numerous factors Use of electromagnetic waves defined by o Frequency Grouped in 8 bands
o Wave length o Speed Duplex o Channel with 2 frequencies o Possible simultaneously listen & speak o Requires 2 frequencies Semi-duplex o For ship no difference with simplex o Requires 2 frequencies Simplex o Changing from sending to receiving with OVER o Requires 1 frequency
VHF-DSC
Digital Selective Call Easily sending of distress alert Information easily transmitted GMDSS certificated required
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 5/12
Telecommunicatie
Channels VHF-band
Channel 06
First international ship-to-ship channel Belgium: used by pilots
Channel 08
First Belgian ship-to-ship channel
Channel 13
Used worldwide as navigation safety communication channel Normally monitored by commercial vessels if danger of collision exists Watch on channel 13 when underway English communication
Channel 16
Emergency channel Priority on other messages May be used to call coastal stations Watch on channel 16 when underway Preferably in English Distress & urgency messages after alert via DSC channel 70
Channel 15 & 17
Intra-ship communication
Channel 23
Communication with yachting ports
Channel 27
Oostende radio
Channel 67
SAR Can also be used for anti-pollution purposes
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 6/12
Telecommunicatie
Channel 70
DSC channel Listening watch on channel 70 After alert, communication on channel 16 VHF radios without DSC => channel 70 blocked
Channel 73
Anti-pollution
Channel 75 & 76
Protection channel 16 Limited communication Reduced power
Channel 77
Social & familial communication Reduced power
Channel 82
Bunkering operations
Channel 87H & 88H
AIS
Use of VHF
Procedures
Messages regarding safety, navigation or traffic information Listen before transmitting
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 7/12
Telecommunicatie
Discipline
Absolute minimum of communication Procedures followed Short sentences, speaking clearly & slowly Professional calls Channel 77 for private calls PTT used to absolute minimum Transmission kept at minimum No music broadcasted
Instructions from a shore station
Construction must be followed o Request radio silence o Reduce power output o Listening watch on specific channel In emergency instructions disregarded => notice after emergency
Reception confirmation
On request, reception of message should be confirmed
Identification
Name Call sign Name & call sign
Language
Ship shore: language of country of shore station / English Ship ship: language of country of receiving vessel / English
Spelling
NATO phonetic alphabet
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 8/12
Telecommunicatie
Priority
Sequence o Distress MAYDAY By captains orders Serious risk & immediate response required Not participating stations radio silence Reception confirmed MAYDAY RELAY Station in distress leads communication o Urgency PAN PAN No imminent risk Preferably sent on channel for shipping information o Security SECURITE Danger regarding safety of navigation / meteorology o Routine Each call start with announcement of type of call Test calls o No other communication transmitted / received o Reduced to minimum o Maximum of 10s o TEST o Test all radios o Self test
Specific communication at sea
Watch
For all ships with radio equipment Listening watch on channel 16
Public radio communication
Telephone call on public channels Also telegrams & faxes Accounting Authority Identification Code Service offered by fewer stations Oostende Radio still offers that service
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 9/12
Telecommunicatie
AIS
Automatic Identification System Automatic exchange navigational data between ships / ship shore Max power 25 W Radio positioning system Plotting on ECDIS &/or radar Equipment o Antenna o VHF transmitter o 2 VHF receivers o DSC channel 70 receiver o Internal GPS receiver Static data o MMSI o IMO number o Identity (name & call sign) o Length & beam o Type of ship o Location positioning fixing antenna Dynamic data o Position o UTC o COG o SOG o Heading o Navigation status Voyage-related data o Draught o Hazardous cargo o Destination & ETA Type of messages o Short safety-related o Free o CPA & TCPA alarm Modes o Autonomous (= continuous operation in all areas) o Assigned (= data transmission interval remotely controlled) o Polled (= in response top interrogation) Channels 87B & 88B Can be switched off Advantages with radar o Information provided in near real-time o Instant presentation of target course alternations o Not subject to target swap, loss in clutter, loss due to fast maneuvers o Detect ships within VHF coverage
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 10/12
Telecommunicatie
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 11/12
Telecommunicatie
ALRS
General
Admiralty List of Radio Signals By UKHO 6 volumes Yearly publications Covering all aspects of maritime communication Updated via Notices to Mariners
Volume 1
Coast radio stations NP 281 Contents o GMDSS o Maritime stations listing o Ship reporting systems o Piracy & robbery reporting procedures o Shore based MMSI numbers
Volume 2
Radio aids to navigation, satellite navigation systems, radio time signals & electronic position fixing systems NP 282 Contents o Radar beacons o DGPS stations o International times o Electronic positioning fixing systems o
Volume 3
Maritime Safety Information services NP 283 Contents o Maritime weather services o Listing NAVTEX stations o MSI broadcasts o
3de Bach NW
Samenvatting p. 12/12
Telecommunicatie
Volume 4
Meteorological observation stations NP 284 Contents o All MET observation stations listed o Worldwide coverage o Revised every 18 months
Volume 5
GMDSS NP 285 Contents o Worldwide communication for distress & SAR o GMDSS information for students o Only SOLAS compliant for GMDSS in English o
Volume 6
Pilot services, VTS & port operations NP 286 Contents o Detailed pilot information o Global VTS information o Harbour communications o
You might also like
- REGULATIONS AND PROCEDURES FOR SHIP RADIO COMMUNICATIONDocument26 pagesREGULATIONS AND PROCEDURES FOR SHIP RADIO COMMUNICATIONmendesNo ratings yet
- Marcom Report UpdatedDocument42 pagesMarcom Report UpdatedDenmark SinayNo ratings yet
- Marine radio essential for safety at seaDocument2 pagesMarine radio essential for safety at seaRaymond Warta Kurnia100% (1)
- Maritime Radio CommunicationDocument50 pagesMaritime Radio CommunicationMeghali BorleNo ratings yet
- Marine VHF Radio Sample PagesDocument24 pagesMarine VHF Radio Sample PagesSyed HussainNo ratings yet
- Marine CommunicationsDocument32 pagesMarine CommunicationsMahami M Prosper100% (1)
- Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS)Document39 pagesGlobal Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS)jeanpaul CAYTANNo ratings yet
- Communication On Water: Sail More SafelyDocument6 pagesCommunication On Water: Sail More SafelyЯeaderNo ratings yet
- SOLAS Safety Convention GuideDocument45 pagesSOLAS Safety Convention GuideOjok JodNo ratings yet
- Marine Communications: Safety at Sea SeminarDocument62 pagesMarine Communications: Safety at Sea SeminarWendel SalemNo ratings yet
- 06 Emergency CommunicationsDocument4 pages06 Emergency CommunicationsNgaire Taylor100% (1)
- Branches of NTC: Type of Message Appropriate Channel(s)Document6 pagesBranches of NTC: Type of Message Appropriate Channel(s)-Annette Dizon-No ratings yet
- Gmdss Goc c1 FinalDocument154 pagesGmdss Goc c1 FinalmarcpadsNo ratings yet
- Maritime Electronics and Communications: Safety at SeaDocument50 pagesMaritime Electronics and Communications: Safety at Seawaleed yehiaNo ratings yet
- Marine VHF RadiosDocument10 pagesMarine VHF RadiosAbby DominguezNo ratings yet
- SRC VHF HandoutDocument28 pagesSRC VHF HandoutWing Wing100% (1)
- GMDSS: Global Maritime Distress and Safety SystemDocument110 pagesGMDSS: Global Maritime Distress and Safety SystemAmin Al Qawasmeh100% (1)
- Marine Communications: Safety at Sea SeminarDocument62 pagesMarine Communications: Safety at Sea SeminardogcanterburyNo ratings yet
- VHF HF/SSB AisDocument56 pagesVHF HF/SSB AisErsin BliojuNo ratings yet
- Slagen Refinery Harbor Procedure (Exxon Mobil)Document28 pagesSlagen Refinery Harbor Procedure (Exxon Mobil)kanakarao1No ratings yet
- 5 GMDSS PDFDocument9 pages5 GMDSS PDFTaufiq JahanNo ratings yet
- AnDocument13 pagesAnVasileNo ratings yet
- GMDSSDocument22 pagesGMDSSAngjuang Adi Panji Pratama100% (5)
- Soal Latihan GMDSSDocument69 pagesSoal Latihan GMDSSRudi Anton SinagaNo ratings yet
- Passage Plan - Amsterdam - TuxpanDocument11 pagesPassage Plan - Amsterdam - TuxpanAdrian Cretu100% (1)
- ESATtrueDocument1,111 pagesESATtruevon kervy onradeNo ratings yet
- Article 50 ExplanationDocument4 pagesArticle 50 Explanationphyton lostNo ratings yet
- Maritime Communications in The Philippines: National Telecommunications Commission September 9, 2013Document21 pagesMaritime Communications in The Philippines: National Telecommunications Commission September 9, 2013Tina ChanNo ratings yet
- Module1 QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule1 Questionsnirala6100% (1)
- Manajemen Frekuensi Radio MaritimDocument47 pagesManajemen Frekuensi Radio MaritimMulyadiNo ratings yet
- GMDSSDocument32 pagesGMDSSLucian Encutu100% (2)
- Chapter 4-DISTRESS SIGNALSDocument22 pagesChapter 4-DISTRESS SIGNALSmendes100% (1)
- Radio HandbookDocument72 pagesRadio Handbookringbolt100% (4)
- Coastguard Boating Education Marine Radio Operator Manual v2.05Document65 pagesCoastguard Boating Education Marine Radio Operator Manual v2.05recutuNo ratings yet
- Types of Communication in The Maritime Mobile ServiceDocument18 pagesTypes of Communication in The Maritime Mobile ServiceEydri YanNo ratings yet
- Proiect Ciuclea Alin Petrica GMDSS IFR FE41Document30 pagesProiect Ciuclea Alin Petrica GMDSS IFR FE41Alin PetricaNo ratings yet
- Day1 1Document81 pagesDay1 1Christine Joy RozanoNo ratings yet
- Gmdss - Function 1 - Gmdss (1 - 446)Document76 pagesGmdss - Function 1 - Gmdss (1 - 446)AnkunNo ratings yet
- Student: Pavel Mircea Grupa: TA 31 Profesor: Pricop CodrutaDocument51 pagesStudent: Pavel Mircea Grupa: TA 31 Profesor: Pricop CodrutaMircea PavelNo ratings yet
- Radio Telegram Charges CalculatorDocument101 pagesRadio Telegram Charges CalculatorLemon SweaterNo ratings yet
- Gmdss GuideDocument12 pagesGmdss GuideAbdel Nasser Al-sheikh Yousef67% (3)
- Marcomm Week 1Document26 pagesMarcomm Week 1jandrielayba3No ratings yet
- lectionDocument12 pageslectionGeorge KandelakiNo ratings yet
- DS GMDSS LB General Questions 13p 110qDocument13 pagesDS GMDSS LB General Questions 13p 110qJe AnnNo ratings yet
- Gmdss Sea AreasDocument2 pagesGmdss Sea AreasChristos Anthoulakis100% (1)
- GMDSS Guide: Global Maritime Distress and Safety System ExplainedDocument52 pagesGMDSS Guide: Global Maritime Distress and Safety System Explainedtualpu100% (3)
- Soal Tryout GMDSSDocument30 pagesSoal Tryout GMDSSToni DeckNo ratings yet
- Vadinar Essar TerminalDocument4 pagesVadinar Essar TerminalHittesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Radio Handbook 2012Document72 pagesRadio Handbook 2012Trinity ParoreNo ratings yet
- No.10 GMDSSDocument32 pagesNo.10 GMDSSBernard MamoraNo ratings yet
- Digital Selective CallingDocument7 pagesDigital Selective CallingDicky KusdyNo ratings yet
- ZRXZR 01 PDocument6 pagesZRXZR 01 Pasdqwe123dsaNo ratings yet
- PORT Info BOOK 2022Document18 pagesPORT Info BOOK 2022Vader ManNo ratings yet
- Digital Selective Calling in VHF and MF Bands.: Shore Distress AlertDocument4 pagesDigital Selective Calling in VHF and MF Bands.: Shore Distress AlertKhasy Jeans P. TamposNo ratings yet
- GMDSS Lection Week 3Document17 pagesGMDSS Lection Week 3George KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Port Safety Regulations for Oil Terminals in AalborgDocument31 pagesPort Safety Regulations for Oil Terminals in AalborgMohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- GMDSS General Operators Certificate Course Notes PDFDocument52 pagesGMDSS General Operators Certificate Course Notes PDFNikita Bushtian100% (1)
- Marine Radio Operator Permit Manual: Pass Your Marine Operator Permit ExamFrom EverandMarine Radio Operator Permit Manual: Pass Your Marine Operator Permit ExamNo ratings yet
- ZeevaartkundeDocument18 pagesZeevaartkundenjirtak92No ratings yet
- Maritieme EconomieDocument25 pagesMaritieme Economienjirtak92No ratings yet
- RoDocument18 pagesRonjirtak92100% (1)
- VeiligheidDocument39 pagesVeiligheidnjirtak92No ratings yet
- KaartpassenDocument25 pagesKaartpassennjirtak92No ratings yet
- Basic Design of ShipDocument4 pagesBasic Design of Shipnjirtak92No ratings yet
- ZeevaartkundeDocument14 pagesZeevaartkundenjirtak92No ratings yet
- KaartpassenDocument9 pagesKaartpassennjirtak92No ratings yet
- 5 Categories of Solution: PreventionDocument53 pages5 Categories of Solution: Preventionnjirtak92No ratings yet
- Basistechnieken Maritiem VervoerDocument19 pagesBasistechnieken Maritiem Vervoernjirtak92No ratings yet
- OffshoreDocument23 pagesOffshorenjirtak92No ratings yet
- ECDISDocument27 pagesECDISnjirtak92100% (8)
- Container Stowage Plans ExplainedDocument24 pagesContainer Stowage Plans ExplainedMohd akifNo ratings yet
- Development Approach PlanDocument15 pagesDevelopment Approach PlanGaurav UpretiNo ratings yet
- Planning For Good AcousticsDocument1 pagePlanning For Good Acousticsa_j_sanyal259No ratings yet
- Vim 101 - A Beginner's Guide To VimDocument5 pagesVim 101 - A Beginner's Guide To VimHuy TranNo ratings yet
- MAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1Document24 pagesMAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1K ULAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Mission Statement Template 05Document3 pagesMission Statement Template 05Sead ZejnilovicNo ratings yet
- GT2-71D Amplifier Unit Data SheetDocument3 pagesGT2-71D Amplifier Unit Data SheetKenan HebibovicNo ratings yet
- MT6771 Android ScatterDocument27 pagesMT6771 Android ScatterСенильга МакароваNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber LecturesDocument161 pagesOptical Fiber LecturesZakareya FathallaNo ratings yet
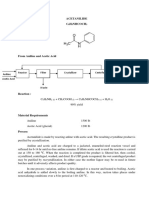
- Acetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerDocument4 pagesAcetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerAnonymous 4hx84J3No ratings yet
- Forty Studies That Changed Psychology 5th Edition PDFDocument2 pagesForty Studies That Changed Psychology 5th Edition PDFsaid hassan0% (1)
- BS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Document46 pagesBS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Shaiful ShazwanNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 Combined Graphs Line Graph and Table 1Document6 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 Combined Graphs Line Graph and Table 1Sugeng RiadiNo ratings yet
- Azubuko v. Motor Vehicles, 95 F.3d 1146, 1st Cir. (1996)Document2 pagesAzubuko v. Motor Vehicles, 95 F.3d 1146, 1st Cir. (1996)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document28 pagesChapter 10ahmedNo ratings yet
- RPG One 1.5 2.5Document2 pagesRPG One 1.5 2.5YJ JangNo ratings yet
- Portarlington Parish NewsletterDocument2 pagesPortarlington Parish NewsletterJohn HayesNo ratings yet
- Grade6 Integers Multiple Additions Subtractions PDFDocument9 pagesGrade6 Integers Multiple Additions Subtractions PDFEduGainNo ratings yet
- Using the TreeView Control in Visual FoxProDocument5 pagesUsing the TreeView Control in Visual FoxProJulio RojasNo ratings yet
- DesertationDocument145 pagesDesertationhishamromi760% (1)
- Saurabh Pandey - Management Trainee - Recruitment - 5 Yrs 10 MonthsDocument2 pagesSaurabh Pandey - Management Trainee - Recruitment - 5 Yrs 10 MonthsDevraj GurjjarNo ratings yet
- Company Profile 2016 PDFDocument81 pagesCompany Profile 2016 PDFabioduncityNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Khaled CVDocument2 pagesMohamed Khaled CVMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument6 pagesProject Proposalapi-386094460No ratings yet
- Emulsifier Solutions: Targeted Applications. Established SuccessDocument32 pagesEmulsifier Solutions: Targeted Applications. Established SuccessSen D' Favian100% (1)
- 280Document6 pages280Alex CostaNo ratings yet
- AirROC T35 D45 D50 Tech SpecDocument4 pagesAirROC T35 D45 D50 Tech SpecmdelvallevNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiDocument4 pages(IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- TOT Calendar Oct Dec. 2018 1Document7 pagesTOT Calendar Oct Dec. 2018 1Annamneedi PrasadNo ratings yet
- We BradDocument528 pagesWe BradBudi SutomoNo ratings yet